Hydroelectric Power Plant Terms
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Forebay
Intake structure
Penstock
Surge chamber
Hydraulic turbines
Power house
Draft tube
Tailrace
The major components of a hydroelectric plant are as follows: DHIPPSTF
pelton, francis, kaplan.
Three main turbines names after their inventors
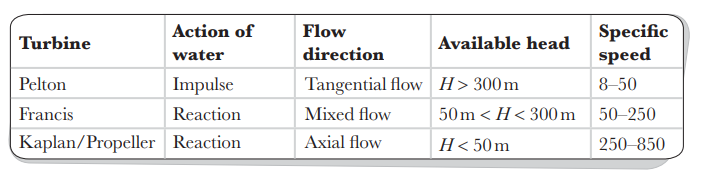
hydraulic turbines
Turbines that use water as the working fluid for the production of power are known as?
Impulse, Reaction
CLASSIFICATION OF HYDRAULIC TURBINES:
Action of water (Impulse or Reaction)
Direction of flow
Available Head
a. High Head (H>300m)
b. Medium Head (50m<H<300m)
c. Low Head (H<50m)
4. Specific Speed
The turbines can be classified under different headings:
head
indicates the energy in units of distance.
Hydraulic efficiency (𝑒ℎ)
- is defined as the ratio of power developed by the turbine runner to power available at turbine inlet
Turbine efficiency (𝑒𝑡)
- is defined as the ratio of turbine power output to the water power output
Mechanical efficiency (𝑒𝑚)
- is the ratio of power available at the shaft to the power
developed by the runner
Generator efficiency (𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑛)
- the ratio of the electrical power produced by the generator to mechanical power available at turbine–generator shaft
Overall efficiency (𝑒𝑜)
- is the efficiency of whole turbine-generator system which can
be obtained by dividing the power output of generator to the hydraulic power input to turbine
Volumetric efficiency (𝑒𝑣)
- is defined as the ratio of actual discharge to the total discharge
Pelton turbine or Pelton wheel
is a tangential flow impulse turbine. The water strikes the bucket along the tangent of the runner.
is a high head and low discharge impulse turbine.
works on the principle of conversion of available hydraulic energy first into kinetic energy of the jet and then into mechanical energy of the rotating wheel or runner, also known as Pelton wheel.
Adverse water conditions
- water conditions that limit the production of hydroelectric power, either because of low water supply or reduced gross head or both. Sometimes called critical water conditions
Appraisal study
- a preliminary feasibility study made to determine whether a detailed feasibility study is warranted. Also called a reconnaissance study.
Armature
- that part of an electric rotating machine that includes the main currentcarrying winding in which the electromotive force produced by magnetic flux rotation is induced; it may be rotating or stationary.
Availability
- the percentage of time a plant is available for power production.
Average availability (also hydrologic availability)
- the ratio of the average capacity of a hydroelectric plant in the peak demand months to its rated capacity. This ratio accounts for variations in streamflow and head.
Mechanical availability
- the ratio of the number of days in total period minus days out of service due to maintenance and forced outages, to the number of days in the total period.
Average annual flow
- the rate at which water flows through a conduit or channel, determined by averaging daily measurements of this rate over the course of a year; normally expressed in cubic feet per second or cubic meters per second.
Average load
- the hypothetical constant load over a specified period of time that would produce the same energy as the actual load would produce for the same period.
Average water conditions
- precipitation and runoff conditions which provide water for hydroelectric power development approximating the average amount and distribution available over a long time period, usually the period of record.
Axial hydraulic thrust
- in single-stage and multistage pumps, the summation of unbalanced impeller forces acting in the axial direction.
Backwater
- water level controlled by either a downstream reservoir, a channel restriction, or a stream confluence that affects the tailwater level of an upstream plant.
Black start
- the startup of a powerplant without an external electrical supply.
Block loading
- a generating plant is said to be block loaded when its output is increased or decreased in definite steps without regard to following a particular load shape.
A generating plant carries a block load when its output is maintained at a fixed level for an extended period of time.
Bulb turbine
- an axial flow turbine situated in a straight-through water
passage.
✓Bulkhead gate
- a gate installed at the entrance of a fluid passage and
used to dewater the passage for inspection and maintenance. Almost
always opened or closed under balanced pressure.
✓Equivalent thermal capacity
- the amount of thermal generating capacity
that would carry the same amount of system peak load as could be
carried by a given hydroelectric plant.
✓Hydraulic capacity
- the maximum flow which a hydroelectric plant can
utilize for energy.
✓Rated capacity
- the electrical load for which a generator, turbine,
transformer, transmission circuit, electrical apparatus, powerplant, or
power system is rated.
Capacity/Plant factor
- the ratio of the energy that a plant produces to the energy
that would be produced if it were operated at full capacity throughout a given period, usually a year.
✓Cavitation
- the formation of voids within a body of moving liquid (or around a
body moving in liquid) when the local pressure is lower than the vapor pressure, and the particles of liquid fail to adhere to the boundaries of the passageway. These voids fill with vapor and then collapse, causing pitting of metal on turbine blades.
✓Cogeneration
- the use of waste heat to drive turbine generators for electricity
generation. Also, the use of low-pressure exhaust steam from an electric
generating plant to heat an industrial process or a space.
✓Cold reserve
- reserve generating capacity available for service but not in
operation.
✓Critical speed
- the angular speed at which a rotating shaft becomes dynamically
unstable with large lateral amplitudes, due to resonance with natural frequencies of lateral vibration of the shaft.
Critical streamflow
- the amount of streamflow available for
hydroelectric power generation during the most adverse streamflow period.
✓Crossflow turbine
– a hydraulic machine that converts hydraulic
energy to mechanical energy by allowing water to flow in one side, then out the other side of a cylindrical turbine runner.
✓Cycling
- powerplant operation to meet the intermediate portion of
the load (9 to 14 hours per day).
✓Dead storage
- the portion of a storage basin or reservoir that
cannot be used for temporary water storage.
✓Dependable capacity
- the expected load-carrying ability of a
hydropower plant under specified conditions
✓Deriaz turbine
- a diagonal-flow turbine with a propeller runner whose
blades are adjustable and the axis of the blades is at an angle with the axis of the shaft.
✓Design head
- the head at which the runner of a turbine is designed to
provide the highest efficiency. Measured in feet or meters.
Draft
- the withdrawal of water from a reservoir.
✓Encroachment
- the reduction in generating head at a hydroelectric
project by a rise in tailwater elevation resulting from the backwater effects of a downstream reservoir.
✓Fuel displacement energy
- electric energy generated at a hydroelectric
plant as a substitute for energy which would otherwise have been
generated by a thermal-electric plant.
✓Firm energy
- the energy generating ability of a hydropower plant in a
specified time period and under adverse hydrologic conditions.
✓Forced vortex
- the rotation of a fluid, moving as a solid, about an
axis where every particle of the fluid has the same angular velocity.
✓Free vortex
- rotation of a fluid where each particle moves in a
circular path with a speed varying inversely as the distance from the center.
Governor
- the device which measures and regulates turbine
speed by controlling wicket gate angle to adjust water flow to the turbine.
Hydraulic loss
- the loss in energy due to flow (friction and form
loss)
✓Inflow
- the rate or volume of water that flows into a reservoir or
forebay during a specified period.
✓Leaf
- the elliptically shaped section of a wicket gate.
✓Low-head hydropower
- hydropower that operates with a head of 66 feet
(20 m) or less.
✓Manifold
– a section of steel pipeline that divides flow from a single
penstock into several smaller penstocks that feed multiple turbine
generator units.
✓Regimen/ Dynamic Equilibrium
- he major dimensions of the river
channels remain relatively constant or stable over an extended period of time under current flow characteristics.
✓Sequential Streamflow Routing (SSR)
- the chronological routing of
stream flows through a project or system of projects in order to define a project's firm yield, its energy or peaking power output, or its performance under specified operating criteria.
✓Sluice gate
- vertical-shaft slide gate often used for passing water
through a dam. Manual or motor-operated floor stands are used to raise and lower sluice gates.
✓Small hydropower
- hydropower installations that are 15,000 kW
{15 MW) or less in capacity.
✓Suspended load
- that part of the sediment load which is
suspended in the water column and is transported farther above the streambed by turbulent eddies and moves downstream in an irregular path.
✓Tailrace
- a channel for conducting water away from a powerplant
after it has passed through it. Sometimes called an afterbay.
✓Tailwater
- water surface downstream of the powerhouse.
✓Water hammer
- pressure changes in a pressure conduit or
penstock that are caused by the flow variation with time.
✓Vortex
– a flow with closed streamlines