Chapter 14
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Infrared Spectrometry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Why do we need to be able to determine the structure of unknown compounds in organic chemistry?
To determine what lab reaction will occur as the outcome and to discover new compounds.
What is spectrometry?
The measure of mass
What is spectroscopy?
The study of the absorption of energy.
What does nulcear magneti resonance or NMR tell use?
The arrangement of specific atoms in a molecule.
What does 13C NMR tell us?
THe carbon skeleton
What does 1H NMR tell us?
The proton arrangement of an atom
What is the theory behind NMR?
Radio waves make nuclei resonate
What does Infrared spectroscopy (IR) tell us?
The functional groups present in a molecule.
i.e. C=C or C=O
What is the theory behind IR?
Infrared radiation makes bonds vibrate. The bond acts a a spring in the molecule with more or less energy depending on the molecule.
What does mass spectrometry (MS) tell us?
The molecular mass and structure of a molecule, allowing us to determine molecular formula and isotopes.
What is the theory behind MS?
Mass detection of ions; ionization by bombarding with electrons, chemicals, etc.
What is quantization?
The energy level at which a bond can vibrate.
Energy of a bond depends on the nature of the bond. What determines the nature of a bond?
Bond strength and Atomic MassThe types of atoms involved and their electronegativities.
When looking at an infrared spectrum of a molecule the y axis is marked as transistance. What is this?
How much light is transmitted though a sample. (A Percentage)
What is defined as the diagnostic region?
The range of wavelengths in an infrared spectrum that provides information about functional groups in a molecule. (Double bonds, Triple bonds, bonds to H, etc.) Occurs above 1500cm-1
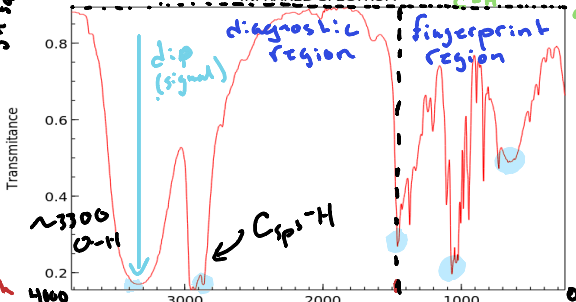
What is defined as the fingerprint region of an Infrared Spectrum?
The region of a spectrum that denotes single bonds such as C-C or C-O. Occurs below 1500 cm-1
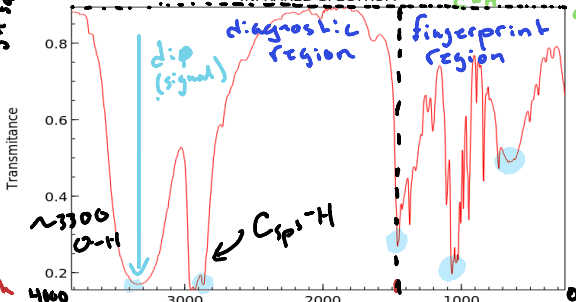
What does a dip (signal) denote in an infrared spectrum?
A specific type of bond located in the molecule.
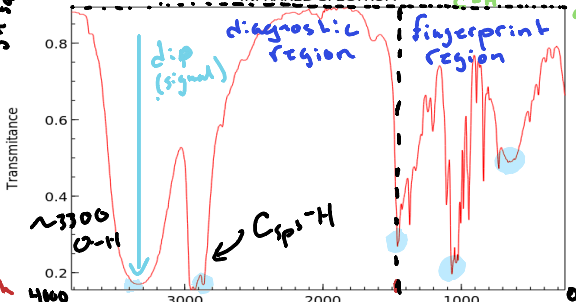
The wave number (ṽ) is proportional to what?
1 / 𝜆
What is bond energy proportional to?
Wavenumber or 1 / 𝝀
As atomic mass increases, …
Wavenumber decreases
As bondstrength increases, …
Wavenumber increases
What is the formula for wavenumber?
.

As polarity increases, …
The intensity of a signal increases
As hydrogen bonding increases, …
The shape of the signal becomes broader
If overlapping peaks occur in an infrared spectrum that makes a portion of the graph appear broad what atom is likely involved?
carbon
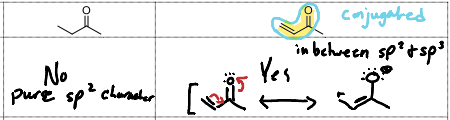
The effect of resonance is conjugation. What is Conjugation and what does it cause?>
The existence of alternating pi bonds (π-∂-π). This reduces the wavenumber by 30 points.
How doe we report information obtained from an IR spectrum?
Using the table to determine what functional groups are present and writing the observations in a clear format.
Report Wavenumber, Intensity, Shape, and Bond Stretch in that order with no decimals
i.e. 1735 cm-1 (strong, C=O of ester)
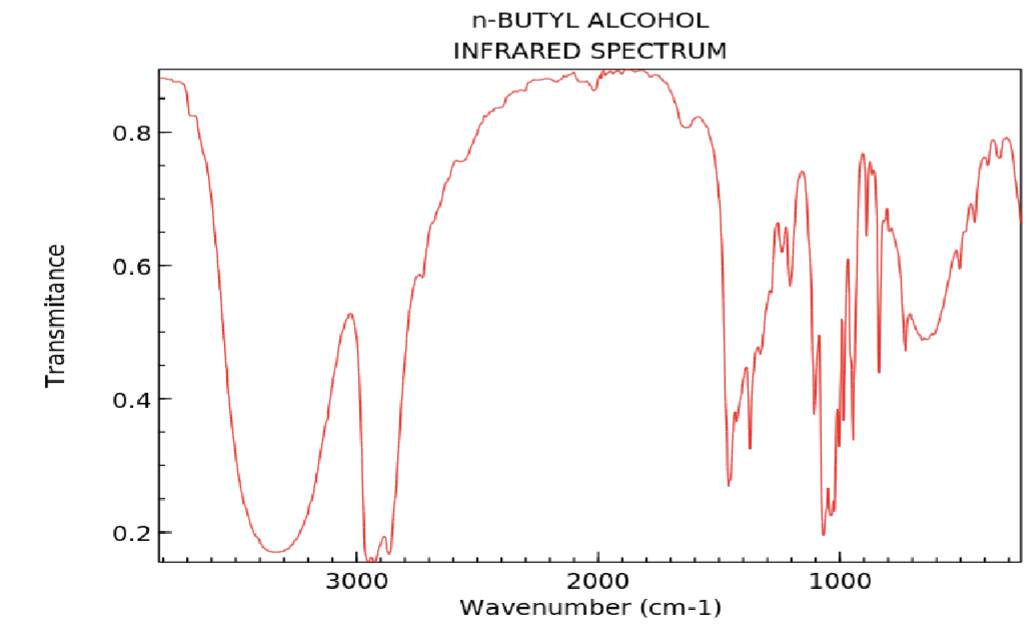
What can happen to the alcohol dip on an IR spectrum if in a dilute solution?
The dip can anrrow.
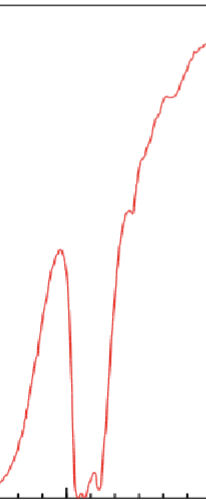
If a terminal alkyne is present where in the chart must you look after identifying the terminal alkyne?
The triple bond region around 2100-2260 cm-1
What value is C sp2 found above and C sp3?
3000 cm-1
Why does an aldehyde give two weak signals on an IR Spectrum?
Overtones due to Ferni resonance.
How do you distinquish an aldehyde from a ketone in an IR spectrum since the wave number for the carbonyl are nearly identical?
You must look for the C-H bond in an aldehyde, which is prsent in the region around 2720-2820 cm-1, indicating the presence of the aldehyde functional group.
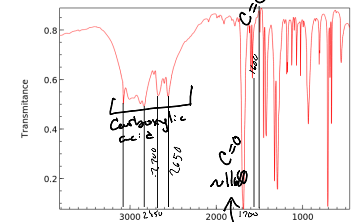
When identifying a Carboxylic acid what also must be account for and recorded other than the extremely wide dip?
An O-H bond
When recognizing an amide by the carbonyl group what also must be accounted for?
The N-H bond
What are the only fingerprint region C-O bonds to focus on?
Ester, Ether, and Alcohol Bonds

What does mass spectrometry do?
It detects exact mass of charged species
What does periodic table show in terms of atomic mass?
The average atomic mass of all kinds of isotopes.
What is the ratio of Chlorine isotopes?
The ratio of Chlorine isotopes is approximately 3:1, with about 75% being chlorine-35 and 25% chlorine-37.
What is the ratio of Bromine isotopes?
The ratio of Bromine isotopes is approximately 1:1, with about 50% being bromine-79 and 50% bromine-81.
What can mass spectrometry only detect?
Ions
What is the first step of mass spectrometry?
Inject and vaporize
Separate compounds using coupled instruments like GC-MS (Gas chromatography) and LC-MS (Liquid chromatography)
What is the second step of mass spectrometry?
Ionize the compound to create charged particles for analysis. Through either Electron-impact (EI) or Electrospray (ESI).
What is the result of ionization with electron impact (EI)?
It is a hard reaction that results in fragmentation.
What is the result of ionization with Electrospray (ESI)?
It is a softer reaction that is better for biomolecules such as proteins.
What is step three of mass spectrometry?
Separating ions using a mass analyzer that accelerates and deflects ions.
What is step four of mass spectrometry?
Detect the ions as a mass to charge ratio (m/z), If seen as a charge of +1 the ratio is the actual mass. This step involves measuring the abundance of ions at different m/z values to create a mass spectrum that represents the sample's composition.
In a mass spectrometry experiment was is detected?
The exact mass not the molecular weight.
What is the base peak in mass spectrometry?
The most intense peak in a mass spectrum, representing the most abundant ion.
What is the molecular ion peak in a mass spectrometry?
The peak that corresponds to the ions of the original molecule, indicating its molecular weight. It is typically the highest m/z value in the spectrum that reflects the intact molecule. Denoted as [M]+
A secondary peak that is a molecular ion peak denotes an isotope of the atom in question that is in lower abundance. How is it denotes?
[M+1]+
WHat is the fragment that you can view at the 77 mau point?
phenol group
What is the nitrogen rule of mass spectrometry?
A guideline stating that compounds with an odd number of nitrogen atoms have an odd molecular ion, while those with an even number have an even molecular ion. This rule helps in predicting the molecular formula based on the mass spectrum.
How do you determine the molecular formula of a compound continuing heteroatoms with mass spectrometry?
You have to look to IR or NMR.
What is the Hydrogen Definciecy Index state?
It is a measure of the degree of unsaturation in a compound, calculated as the difference between the number of hydrogen atoms in a fully saturated compound and the actual number of hydrogen atoms present. It helps in deducing the structure of organic compounds by telling you the number of π bonds and/or rings in a compound.
WHat does a Zero DUs mean?
The compound is saturated and there are no rings or π bonds.
How do yoou calculat eht number of carbon atoms in a molecule?
.
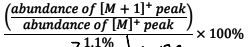
How do you determine the number of hydrogens in a molecular formula using mass spectrometry?
.
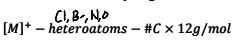
How do you determine if a molecular formula is resonable?
By using teh DU and spectral data
If the peak of the molecule is found to be [M-H2O]+ what do you do to get [M]+
Add H2O
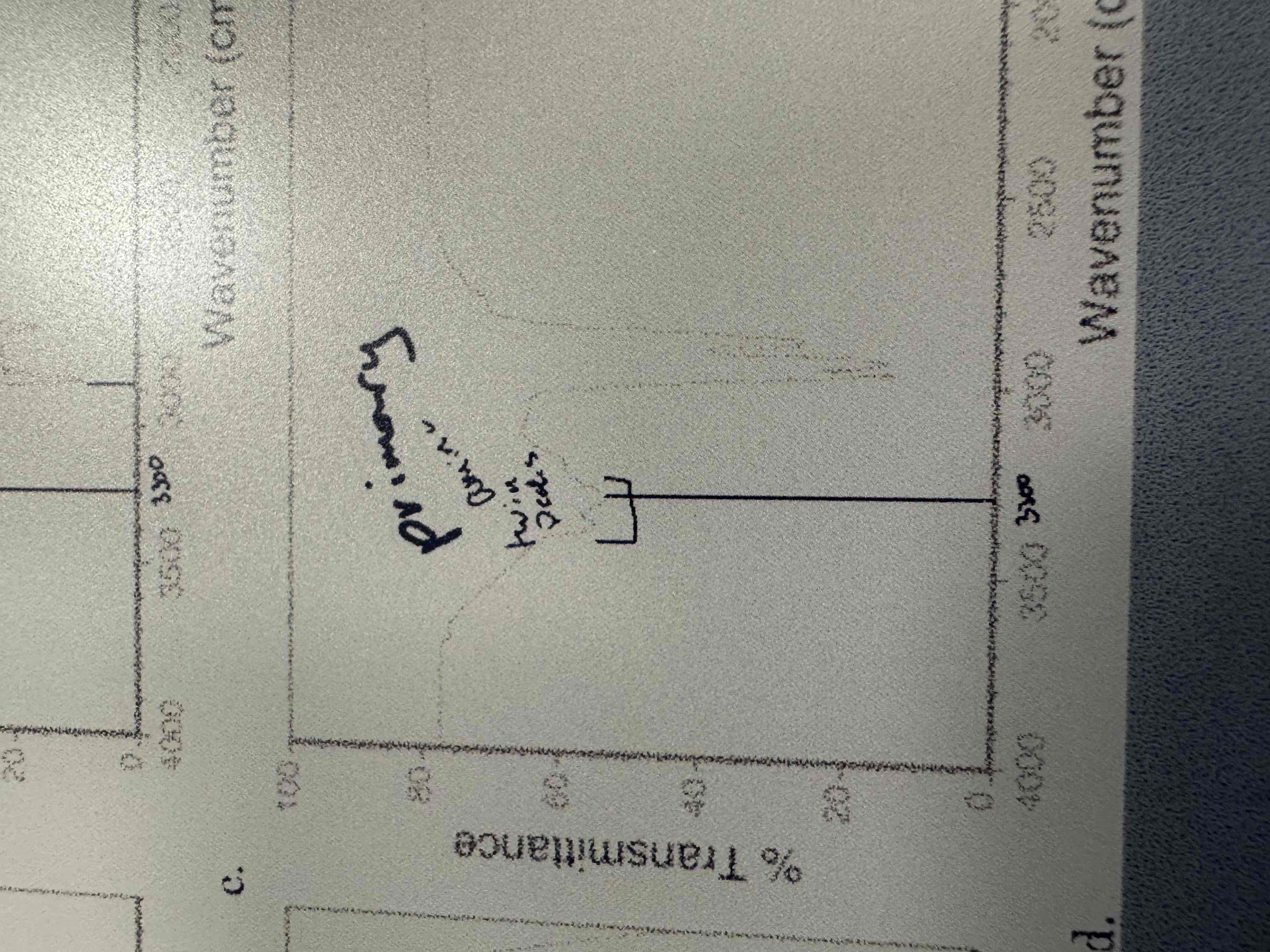
How do we differentiate between a primary and secondary amine on IR?
By looking for bumps in the signal. 2 bumps means a primary amine and 1 bump means a secondary amine