Lecture 1 -- Central Nervous System (CNS) Overview
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What does the Central Nervous System (CNS) consist of?
Brain and spinal cord
What protects the brain and spinal cord?
Bony structures and meninges
What structures belong to the forebrain?
Cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, limbic system and olfactory bulb
What structures belong to the hindbrain?
Pos, Medulla oblongata and cerebellum
What does the CNS form from?
From Rostral neural tube → Vesicles
What structures are derived from the forebrain?
Prosencephalon → Telencephalon → Cerebrum
Prosencephalon → Diencephalon → Thalamus, hypothalamus
What structures are derived from the mesencephalon?
Mesencephalon → Mesencephalon → Midbrain
What structures are derived from the rhombencephalon?
Rhombencephalon → Metencephalon → Pons, cerebellum
Rhombencephalon → Myelencephalon → Medulla oblongata
Where does the closure of the neural tube begin?
Closure begins in the cervical region
Rostral end of the neural tube that form the brain has to fold up in a certain way in order to fit into the skull → Three main flexure form. What are they?
Cephalic flexure
Pontine flexure
Cervical flexure
What separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres?
Longitudinal fissure
What separate the cerebrum from the midbrain and cerebellum
Transverse fissure
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Nourishment, waste removal, protects the brain
What is the condition when the neural tube doesn't close?
Encephalocele
Spinal bifida = Vertebrae has not fully formed
Meningocele = Dura on the outside the spinal cord has not fully formed ? Cause the CSF in arachnoid bulge outwards
Meningomyelocele = More sever condition of meningocele → Spinal cord tissue is prolapsed out
What does gray matter consist of?
Cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses
What does white matter consist of?
Axons
In brain, where do the grey matter and white matter located?
Grey matter: Outside cortex
White matter: Inside the brain
In spinal cord, where do the grey matter and white matter located?
Grey matter: Inside
White matter: Outside
What are clusters of cell bodies called in the CNS and in PNS?
CNS: Nuclei
PNS: Ganglia
What are bundles of axons called in the CNS and in PNS?
CNS: Tracts
PNS: Nerves
What are clusters of cell bodies called in the PNS?
Ganglia
What are gyri?
Ridges
What are sulci?
Furrows
What are folia?
Folds of the cerebellum → Grey matter is within it
What is the white matter branches in cerebellum?
Arbor Vitae/ Tree of life
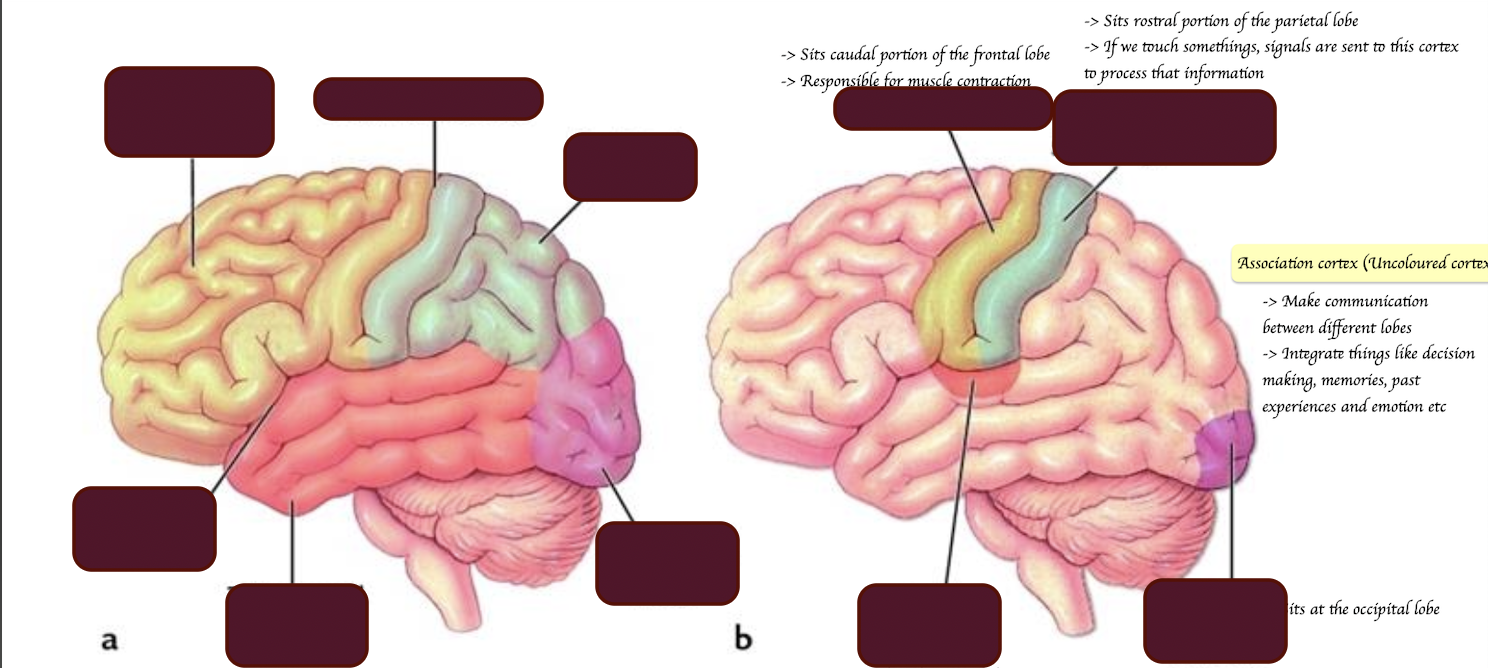
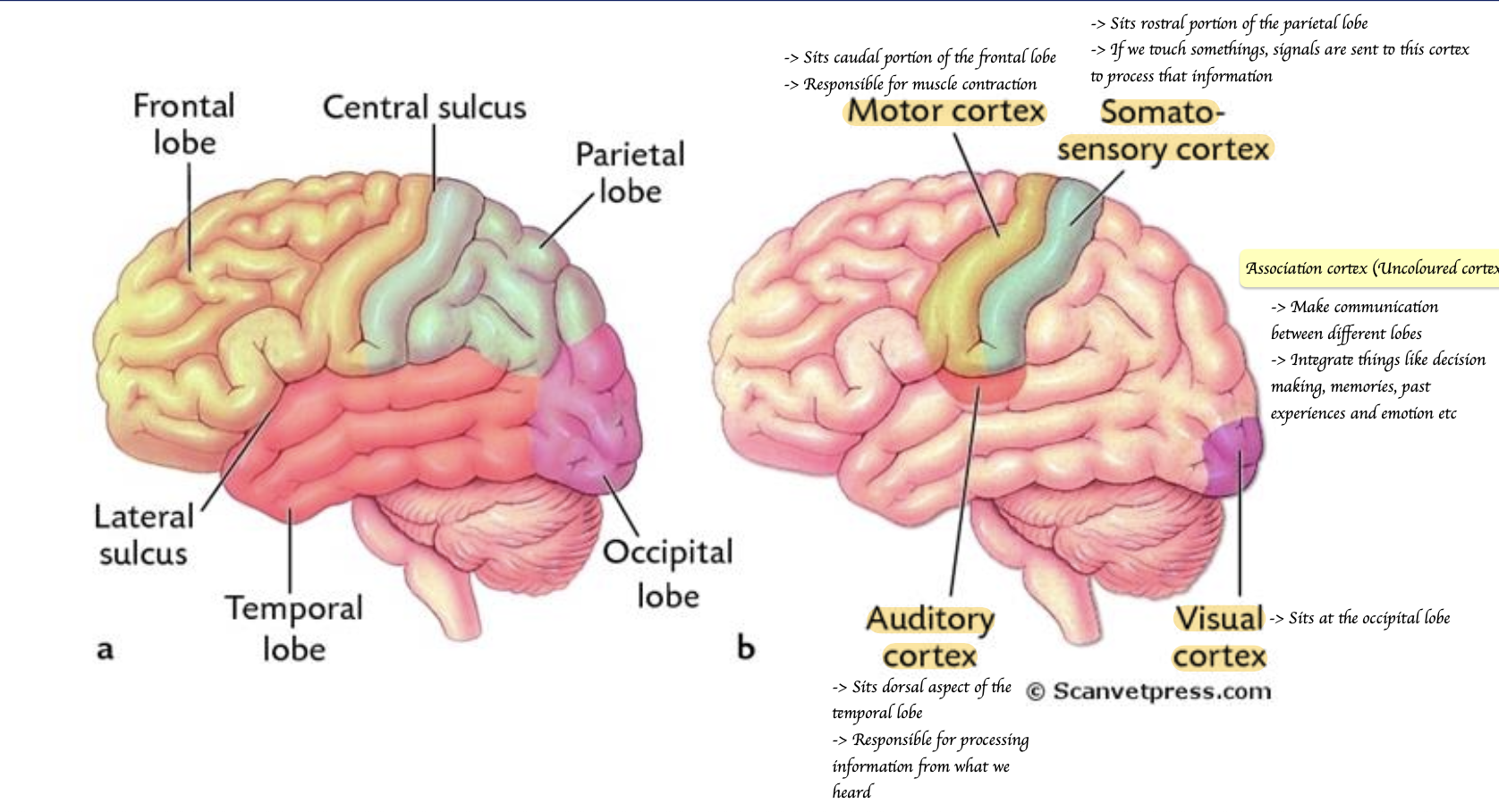
What are the lobes of the brain?
What happens in holoprosencephaly? What causes holoprosencephaly?
Forebrain fails to divide into two hemispheres = No longitudinal fiexure can be seen
Caused by corn lily ingestion
What are ventricles of the brain?
Spaces in the brain where CSF circulates
→ Spinal cord → Central canal → Fourth ventricle → Lateral ventricle → Third ventricle → Mesencephalic aquaduct → Fourth ventricle → Central canal
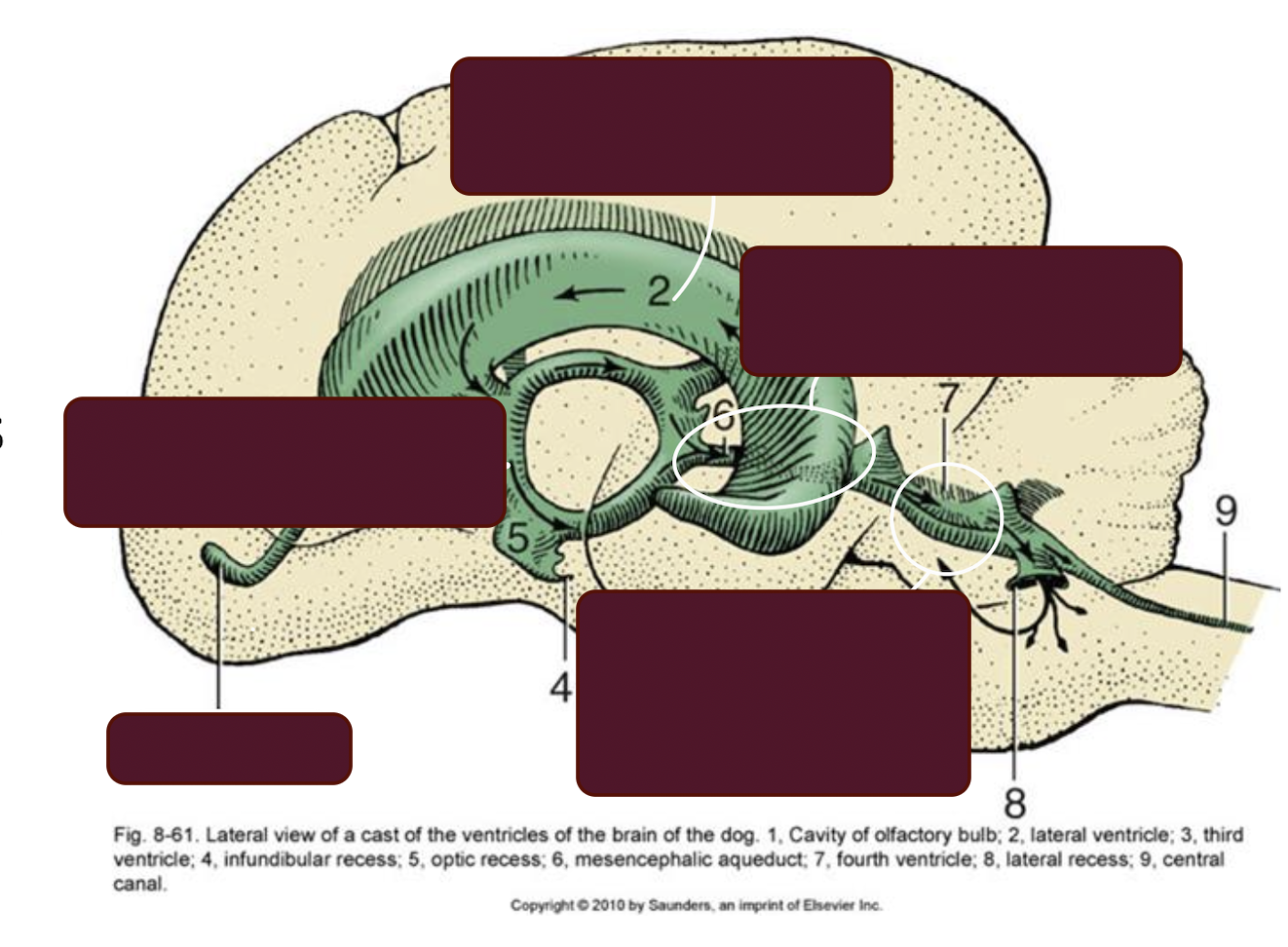
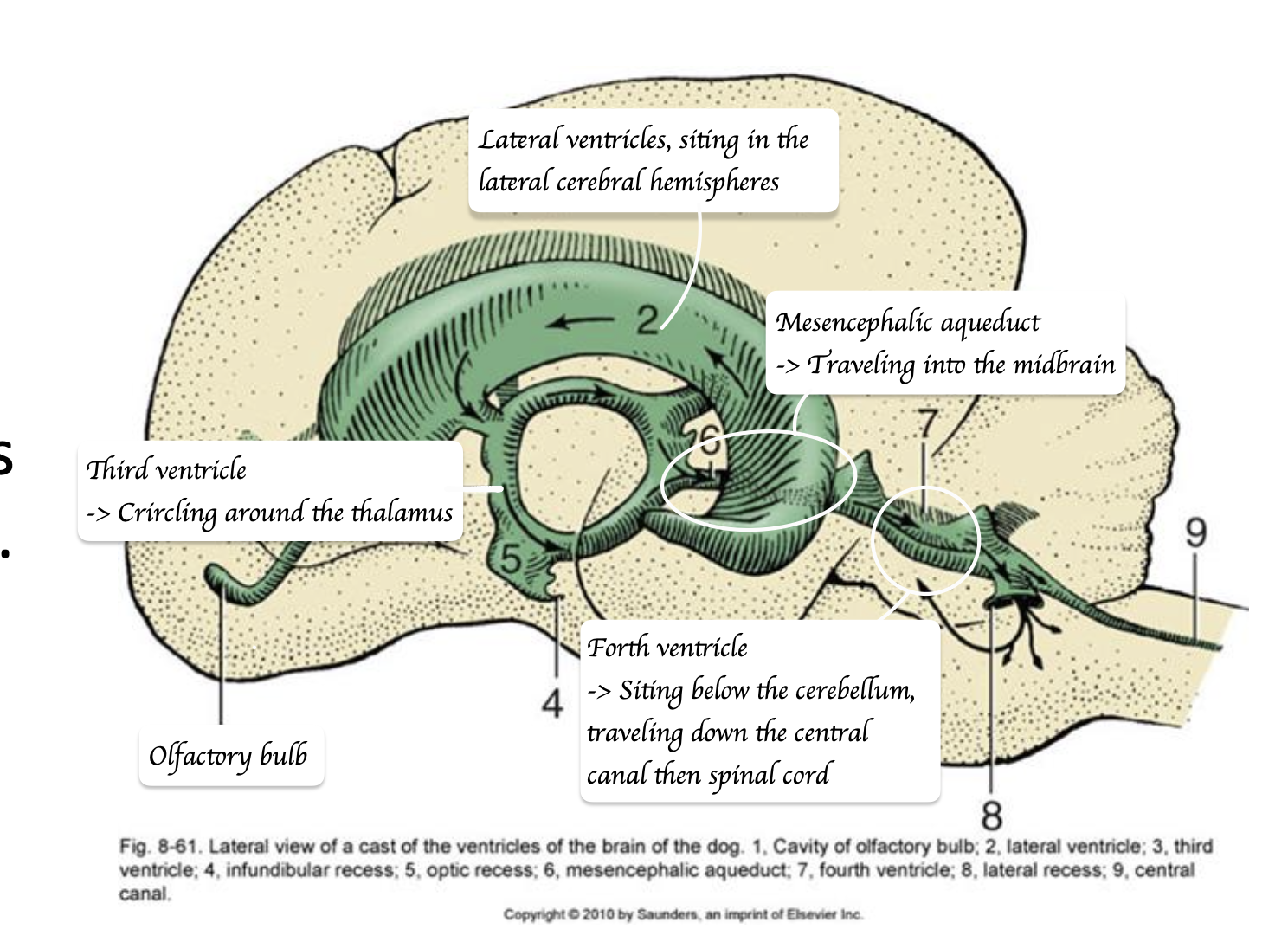
Which structure connects the third and fourth ventricles?
Mesencephalic aqueduct
What happens with hydrocephalus?
Increase pressure on the region of mesencephalic aqueduct → Block the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid → Build up of CSF in brain → Affect the pressure on the brain tissue + development
Where is the auditory cortex located?
Sits dorsal aspect of the temporal lobe
Where is the visual cortex located?
Sits at the occipital lobe
Where is the motor cortex located? What is it responsible for?
Sits at the caudal portion of the frontal lobe
Responsible for muscle contraction
Where is the somatosensory cortex located? What is it responsible for?
Rostral portion of the parietal lobe
If we touch somethings, signals are sent to this cortex to process that information
Apart from motor, auditory, visual and tomato-sensory cortex. What is the remaining part of the brain named? What is its function?
Association cortex
→ Integrates experiences with memories and emotion
What structures does rhinencephalon include?
Olfactory bulb, olfactory tracts, olfactory peduncle, piriform lobe, hippocampus and fornix
What is the function of rhinencephalon?
Sense of smell + Communicates with higher centre to affect emotion, behaviour and communication
Identify the key structure of rhinencephalon.
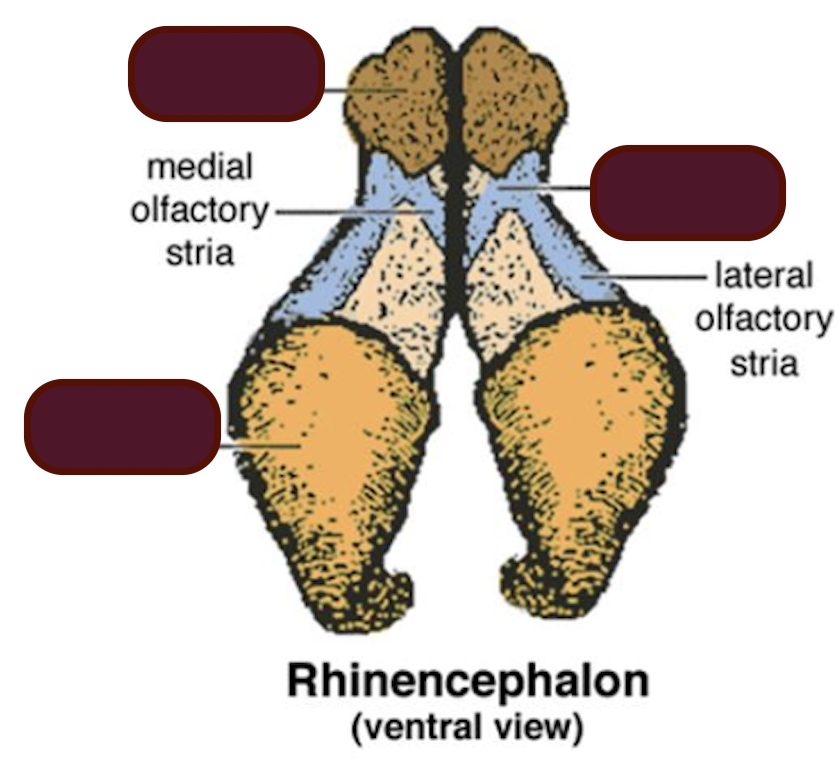
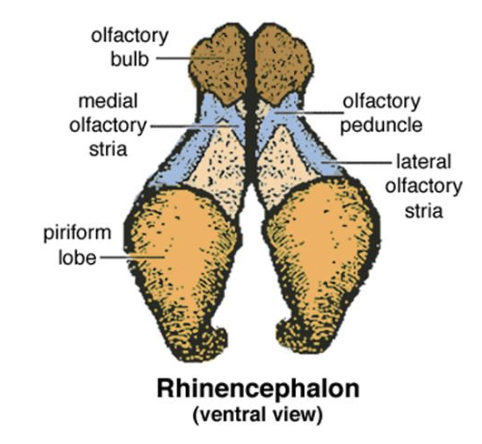
What is the function of frontal cortex?
Involved in decision making, planning, motivation, personality, memory
What are the function of temporal lobe?
Hearing, feeling, learning and fear
What are the functions of parietal Lobe?
Smell, touch, taste, language
What are the functions of the occipital lobe of cerebrum.
Vision
What is the function of limbic system?
Series of tracts and nuclei for emotion, learning and memory
What is the function of basal nuclei = Corpus striatum?
Planning and executing movement
What is the function of hypothalamus?
Endocrine and nervous system
What is the function of thalamus?
All sensory information except olfactory input + Sleep and wakefulness
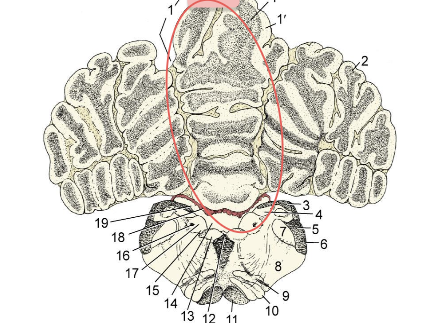
What structure is this in cerebellum?
Central cerebellar = Vermis
What are the functions of cerebellum?
Coordinates gait, maintains posture, controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity → Balance and coordination
NOT for muscle contraction
What are the functions of midbrain?
Include tectum → Orientate the head and body in response to sights and sounds
What are the function of brainstem?
Cardiovascular, respiratory and GI function
Why are the olfactory bulbs so much larger in dogs than in humans?
Important for survival