Amalgam Restorations- Biomedicine in Relation to Dentistry III BDS3
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Which 3 restorations are used for direct fillings?
Composites
GIC
Amalgams
What is special about mercury?
Mercury, Hg is the only metal which is liquid at normal temperature and atmospheric pressure and can dissolve other metals at room temperature
What is an amalgam?
A dental amalgam is any mixture, or blending, of mercury with another metal or alloy
Therefore, it's not possible to have a mercury-free amalgam
What system is dental amalgam based on?
Ag-Hg-Sn (silver, mercury, tin)
Other metals can be added to the system to modify its properties
Copper- increases its final strength
Zinc- reduces oxidation
What is the powder/liquid system in amalgams?
The liquid part is simply triple distilled Hg
The powder is an alloy based on the intermetallic compound Ag3Sn, known as the gamma phase
How do you manufacture the alloy needed for amalgams?
Melt components at high temperature in a reducing atmosphere to produce Ag3Sn but the problem is silver, copper and tin oxidise too easily
In what form does the final alloy need to be?
A powder form
What happens after the alloy is melted together as a homogenous liquid?
Lathe cut- cooled down/mechanically grinded
Spherical- atomisation in an inert atmosphere
How do you get the alloy lathe cut?

How do you get the alloy spherical?
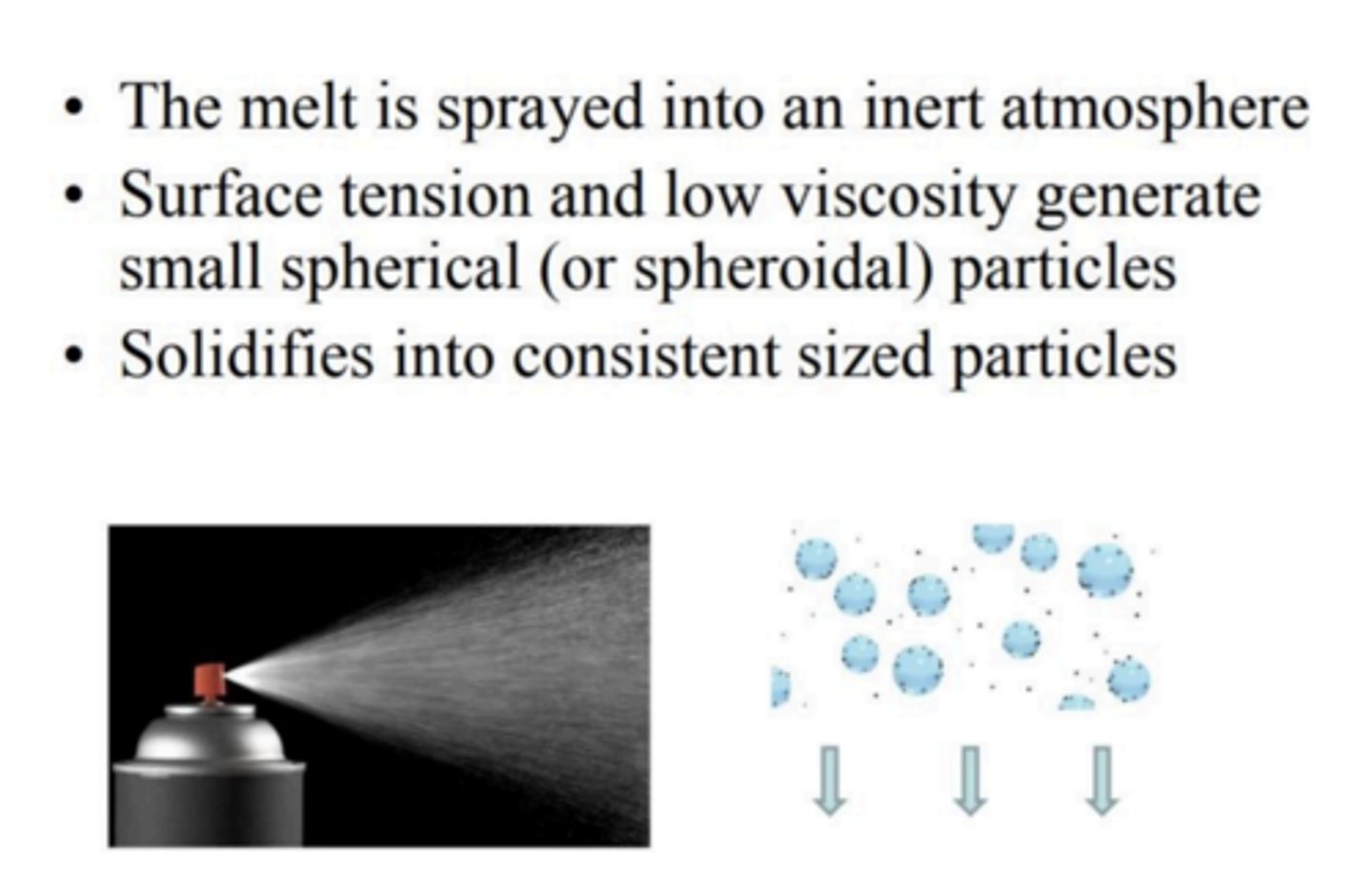
Why are many alloy powders formulated by mixing particles?
1. It increases packing efficiency
2. Reduces Hg needed
3. Increases performance
What are the differences between lathe-cut and spherical alloys?

What is the amalgamation reaction initiated by?
Vigorous mechanical mixing (trituration)
What is formed during the amalgamation reaction?
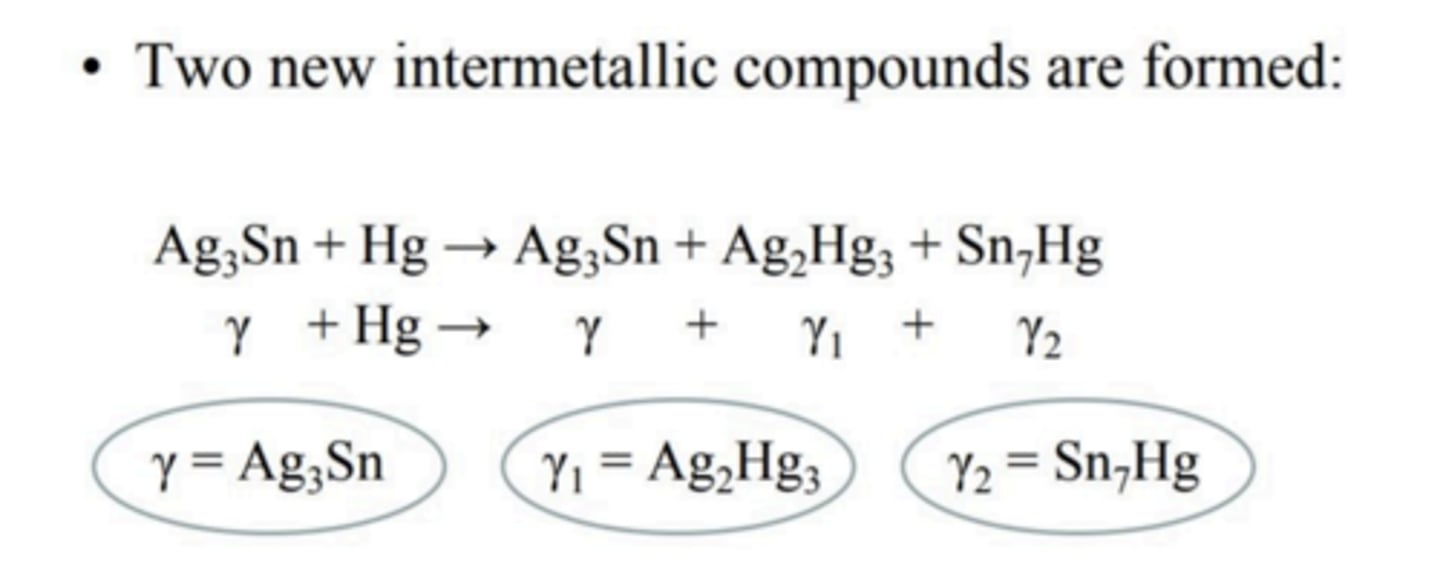
What happens in the initial setting reaction?
Initial dissolution: the outer surfaces of the silver/tin particles dissolve in the liquid mercury
Ag3Sn + Hg --> 3Ag + Sn + Hg
What happens after initial dissolution?
Formation of γ1: the silver reacts quickly to form Ag2Hg3 grains which stick preferentially along the alloy particles
2Ag + 3Hg --> Ag2Hg3
What happens after formation of γ1?
Formation of γ2: the tin reacts slowly to form γ2 which is randomly distributed inside the γ1 matrix
7Sn + Hg --> Sn7Hg
What happens after formation of γ2?
You have a set amalgam: the reaction is completely set when the γ1 and γ2 phases have formed a solid matrix and no mercury is left to dissolve γ
What are the relative strengths of the different phases of the amalgam system?
Assuming that the amalgam has been correctly mixed, the tensile strength would be:
γ > amalgam > γ1 > γ2
γ2 is the weakest phase so reducing it will increase the strength of the restoration
How does the amalgam strengthen over time?
It takes up to 24 hours so it develops slowly and the amalgam remains weak at the time the patient leaves the surgery so it would be good practice to recall the patient after a week to refine the edges of the restoration and polish
Why is amalgam a relatively good replacement for the natural tooth substance?
The mechanical properties of an amalgam restoration are similar to those of natural tooth substance
How does the dimensions in an amalgam change over time?
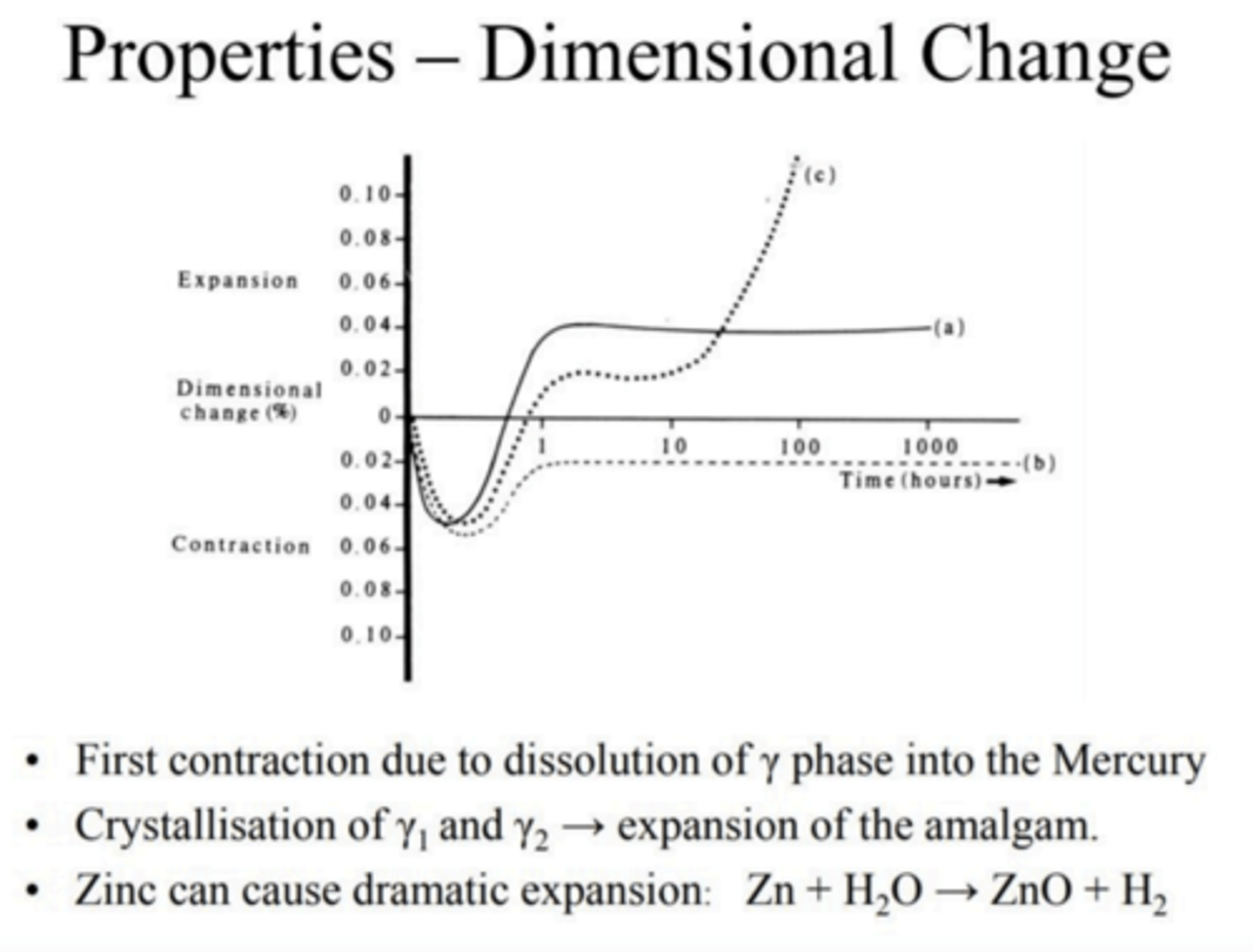
How do dimensional changes in an amalgam restoration concern us clinically?
Contraction results in marginal gaps
Expansion results in protrusions or even tooth cracks
New ISO standards require amalgam restoration material to not exceed contractions more than 0.1% and expansion by more than 0.2%
What are the thermal properties of amalgams?
High thermal diffusivity
This can result in thermal shock so you need to protect the base of the large cavity to avoid harmful effect on the pulp
Thermal expansion mismatch can cause microleakage which can increase occurrence of decay into dentine surrounding amalgam
What are the corrosion properties of amalgams?

What are the plastic deformation (creep) properties of amalgams?
Flow, or deformation, happens due to applied load over a long period of time and does not recover
The higher the content of γ2, the higher the creep
Creep causes protrusion --> weak unsupported edges--> fracture of the edges--> ditching
Why were high copper amalgams introduced in the 60s?
They were introduced in an attempt to eliminate the γ2 phase because a γ2-free amalgam shows increased strength with reduced corrosion and creep
There is a higher compressive strength and a faster achievement of final strength
What is the replacement phase in a high copper amalgam?
Dispersed phase

What is the clinical procedure of amalgam restorations?
1) Cavity preparation & pulp protection
2) Rubber dam, matrix and wedges application
3) Amalgam trituration
4) Amalgam application (small quantity)
5) Condensation
6) Repeat 4 & 5 until cavity is filled (in slight excess)
7) Carving and burnishing
8) Removing matrix
9) Refine carving in particular at the edges of restoration
10) Finishing & Polishing
How can you cavity prep well for an amalgam restoration?
Avoid leaving unsupported enamel
The lateral outer portion of the cavity can be used to create retentive structure which can help avoid creep and overhang
Create rounded shapes towards the centre of the cavity to avoid cracks from chewing forces
Consider support of residual enamel structure and proximity to pulp
What is the preferred delivery system of amalgam material?
It's to use capsules to ensure that the manufacturer's recommended ratio is used
Why is correct trituration essential?
To ensure both adequate amalgamation and the production of a plastic mix suitable for packing
What does the correct trituration time depend on and what are the consequences if this time is not observed?
It depends on both the alloy and the mixing system (between 5 and 20 seconds)
Under trituration does not allow adequate formation of γ1 and η phases and results in a crumbly mix
Over-trituration results in excessive contraction
What are the objectives of condensation for an amalgam restoration?
The objectives are to:
Remove excess Hg
Ensure that there are no voids in the restoration
Ensure marginal integrity
When must condensation be carried out and how?
Must be carried out immediately after mixing
Condense small increments
Overfill the cavity because the surface layers tend to be richer in Hg
Spherical amalgams require a lower condensation pressure than lathe cut
How do we carve and finish a restoration?
Carving of the restoration is possible for up to 2-3 minutes depending on the amalgam
Spherical restorations produce a better surface than lathe cut
Avoid too much pressure- friction heating can cause the release of Hg
A smooth surface minimises the possibility of corrosion
What are the limitations of dental amalgams?
No adhesion to tooth substance
Need retentive cavity design- loss of sound tooth substance
Poor aesthetics
Galvanic effects
High thermal diffusivity
What are the concerns about using mercury alloys?
Environmental:
1) Require adequate measures for disposal of excess amalgam material
2) Hg is a polluting agent
Health:
1) Mercury vapours are released in small amounts from dental amalgams
2) High levels of Hg vapours are associated with adverse effects in kidneys and brain
3) FDA has reviewed scientific evidences and determined that amalgam restorations are safe for adults and children 6>
4) Consider operator exposure
What does the Minimata Treaty of 2013 say?
The Minimata Treaty advocates a phase-down of the use of dental amalgam, in line with the domestic circumstances of each country and in tandem with recommendations for prevention programmes and increased research into alternative materials
The regulation does not ban the use of amalgam
What is important to consider about removal of dental amalgam restorations?
Hg levels during removal of amalgams exceed governments' safety limit
What safety measures can you take when removing amalgam restorations?
1. Avoid removing good congruous restorations
2. Use rubber dam on patient to avoid ingestion and inhalation of Hg microparticles
3. Use appropriate PPE and control aerosol
When is the use of amalgam strongly discouraged?
Treatment of deciduous teeth
Children under 15
Pregnant or breastfeeding women
(except when deemed unavoidable in view of clinical requirements)