DNA
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
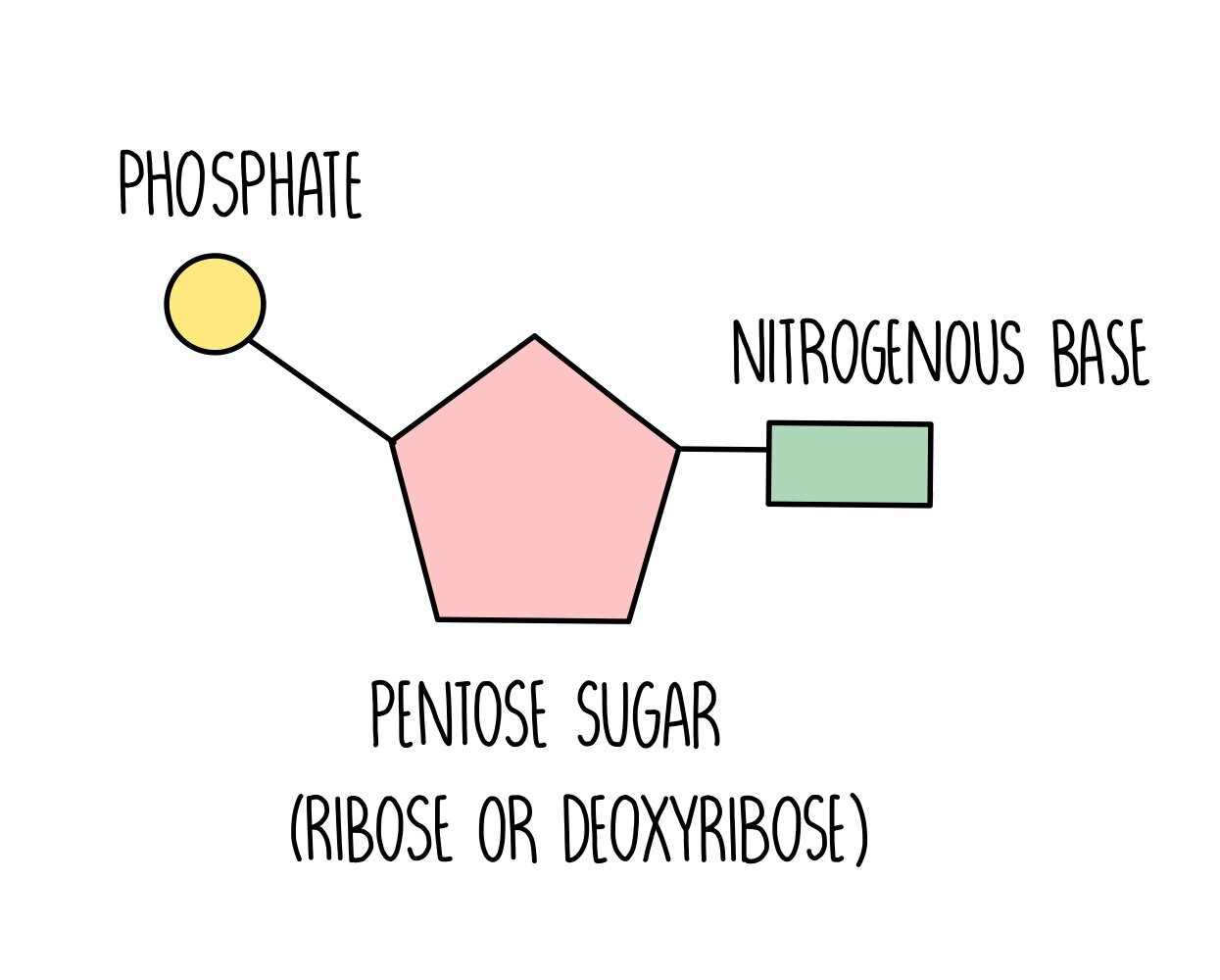
DNA structure
DNA is a double helix.
Made up of Nucleotides (monomers)
Contains a phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose), and molecular bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine).
Chargraff’s Rule
There are equal amounts of Adenine and Thymine and of Guanine as Cytosine.
A-T / G - C
Difference in percentages of nitrogenous bases can be caused by…
Mutations - A Change in the DNA sequence
Radiation such as X-rays and ultraviolet
Polymer and Monomer
Monomer - Nucleotides
Polymer - Nucleic Acid (DNA/RNA)
Rosalind Franklin
Used x-ray crystallography
Helped discover DNA structure by Wilkins
Watson and Crick
Created the first model of what DNA’s structure looked like.
DNA replication
DNA enters through the left side of the helicase.
The DNA is then spun as fast as a jet and unwinds the double helix into 2 strands.
One strand is copied continuously while the other side is copied backwards.
The strand being copied backwards is drawn out repeatedly in loops and copied one section at a time.
DNA replication structures
Origin - Where DNA replication starts.
Okazaki Fragments - Leading and Lagging Strands
Leading strand - The strand being copied continuously
Lagging Strand - The strand being copied backwards and in sections.
Helicase
“The Unzipping Enzymes”
Unzips the 2 DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides
DNA polymerase
“The Builder”
Enzyme that replicates DNA molecules to build a new strand of DNA
Primase
“The Initializer”
Makes the primer so that DNA polymerase so DNA can figure out where to go to start to work
Ligase
“The Gluer”
Helps glue the DNA fragments together
Anti-parallel
DNA polymerase builds the new strand in the 5’ → 3’ direction.
DNA vs. RNA
DNA:
Double-stranded
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Uses Thymine
RNA:
Single-stranded
Sugar: Ribose
Uses Uracil
Transcription
Occurs in Nucleus
DNA → mRNA
Use DNA as a template to make mRNA
Transcription Steps
Factors assemble at the start of the genes.
As it goes down the DNA strand, it unzips, copies hydrogen, and reads the genes for production.
RNA is released and matched with DNA.
Molecules go into the intake hole to create the RNA strand.
Translation
Occurs in ribosomes
mRNA → amino acids → proteins
Amino acids are building blocks of proteins.
mRNA is the template for the amino acids.
Translation Steps
After RNA is copied, it escapes into the outer part of the cell.
Forms a ribosome to translate genetic information into amino acids.
Bring the amino acid to the ribosome.
Each transfer molecule (tRNA) carries a 3-letter code matched with the RNA machine (ribosome).
RNA is pulled through, read off 3 letters at a time, and matched with 3 corresponding letters.
Amino acid is carried onto the chain and produces hemoglobin, which other organisms can receive.
Codons
3 bases within an mRNA molecule that code for an amino acid.
Anti-Codon
A 3-base code within a tRNA molecule that is complementary to a specific codon
Ex. If the codon is A U G, then the anti-codon is U A C.
Different kinds of DNA replication
Conservative - The original DNA remains, and a new one is created
Semi-conservative - means each new DNA has one old strand and one new strand.
Dispersive - means the new DNA strands are mixed pieces of old and new DNA all along the strand.
Hemoglobin
The molecule in red blood cells that ferries (carries) oxygen through the body.
Mutation
A change in DNA sequence
A genetic mutation can alter a person’s hemoglobin.
However, they are not harmful as long as you have one normal copy of the two genes.
Mutated genes are passed down from generation to generation
1 mutated gene
They were not harmed and were protected from malaria.
2 mutated genes
Can’t produce normal hemoglobin.
As a result, blood cells will take on a sickle shape and become defective → This led to clogged blood vessels.
This is called the sickle cell anemia
Leads to extreme pain, difficulty with breathing, kidney failure, and even strokes.