Unit 2 CNA Exam
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Medical Asepsis
A process or practice of reducing the number and transfer of pathogens from one place to another
Flexion
Bending a body part
Microorganisms
Tiny living things existing everywhere in the environment that are capable of developing into an illness —Also known as germs/microbes
Pathogens
Harmful germs or microorganisms that can cause infection
Infection
Condition or disease that happens when harmful germs enter the body and grow
Asepsis
Being free of disease-producing microorganisms, the absence of pathogens
Standard Precautions
Using specific infection control practices to prevent contact with body fluids of the person served. All human blood and certain human body fluids are treated as if known to be infectious.
Disinfection
To remove or kill most of pathogens from the object to clean the object.
Sterilization
All microorganisms or microbes and pathogens are destroyed
Autoclave
Machine that kills microorganisms, sterilizes by creating steam or a type of gas
Clean
An object is considered to have some germs on the surface but usually are devoid pathogens that could cause an infection
Dirty
An object is considered to have a number of germs and some may have the potential to be pathogens that could cause an infection
Microbes
Grow best in warm, dark, moist areas; with the presence of food like oxygen
Normal Flora
Microorganisms that normally live and no the body without causing harm to a healthy person
Bacteria
Staph, strep TB, Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycin resistant enterococcus (VRE), C-diff, etc.
Virus
AIDS, Hepatitis, etc.
Fungus
Yeast infections on skin, athlete's feet, or ringworm
Infection Control
The set of methods practiced in healthcare facilities to prevent and control the spread of disease
Localized Infection
An infection that is limited to a specific location in the body and has local symptoms
Systemic Infection
An infection that is in the bloodstream and is spread throughout the body, causing general symptoms
Healthcare Acquired Infection (HAI)
The spread of infection within the healthcare setting
Reinfection
Infection a second time around
Cross Infection
Spread by transferring mmicroorganisms from one resident to another
The CDC
A federal government agency that issues guidelines to protect the health of individuals and communities
Occupational Safety Health Administration (OSHA)
A federal government agency that is responsible for making rules to protect workers from hazards on the job --Creates guidelines to protect all staff, to assure safe and healthful working conditions
Potentially contaminated body fluids include..
Tears, saliva, vomit, urine, feces, pus, fluid from a wound, fluid coughed up, semen or vaginal secretions
Hand Washing
The most important thing a CNA can do to prevent the spread of disease
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Equipment that helps protect employees from serious injuries or illnesses resulting from contact with workplace hazards
Don
To put on
Doff
To take off
Airborne Transmission
Germs that are spread through the air --Eg. TB
Droplet Transmission
Germs spread through coughing, sneezing, laughing, or talking --Eg. Influenza
Contact Transmission
Germs spread through contact from one host to another
--Eg. Pink eye, C-diff, etc.
Isolation
A way to prevent the spread of microorganisms by limiting or avoiding exposure to infected persons
Biohazard Containers
Hard, leak proof containers that are usually red in color --Used for storing contaminated supplies or used sharps
Blood Borne Pathogens
Microorganisms found in human blood that can cause infection and disease
Hepatitis
An inflammation of the liver caused by viruses, alcohol abuse, some medications, and trauma
Hepatitis A
Transmitted person-to-person by the fecal-oral route or through consumption of contaminated food or water
Hepatitis B
Transmitted from mother to child during birth and delivery, as well as through contact with blood or other body fluids and improperly sterilized needles
Hepatitis C
Transmitted through contaminated blood
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
A disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) --Attack the body's immune system, gradually weakening and disabling it
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Antibiotic resistant infection often acquired in a healthcare facility --Almost always spread by direct physical contact with an infected person
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
Antibiotic resistance infection spread through direct contact as well as indirect contact
Clostridium Difficile (C-diff)
A spore forming bacteria which is part of the normal intestinal flora and when the flora is altered C-diff can grow and cause infection --Carried by direct and indirect contact
Tuberculosis (TB)
Highly contagious disease caused by bacteria carried on droplets suspended in the air
Latent TB
Person carries disease but does not show symptoms --Can not infect others
Active TB
Person is showing signs and symptoms --Can infect others
WHO
World Health Organization
How long does it take for a serious burn to occur?
5 seconds
What temp should bath water be?
105-110 degrees
PASS
Pull
Aim
Squeeze
Sweep
RACE
Rescue
Alarm
Contain
Extinguish
Restraints
A physical or chemical way to restrict a person's voluntary movement
A restrained resident should be checked on every ____ minutes
15
A restrained person should be released every ___ hours
2
Ambulate
To walk
Where should a CNA stand when ambulating a resident
At the side or slightly behind the resident
Supine
A body position in which a person lies flat on their back
Lateral
A body position in which a person is lying on either side
Prone
A body position in which a person is lying on their stomach or the front side of their body
Folwer's
A semi-sitting body position in which a person's head and shoulders are elevated 45 to 60 degrees
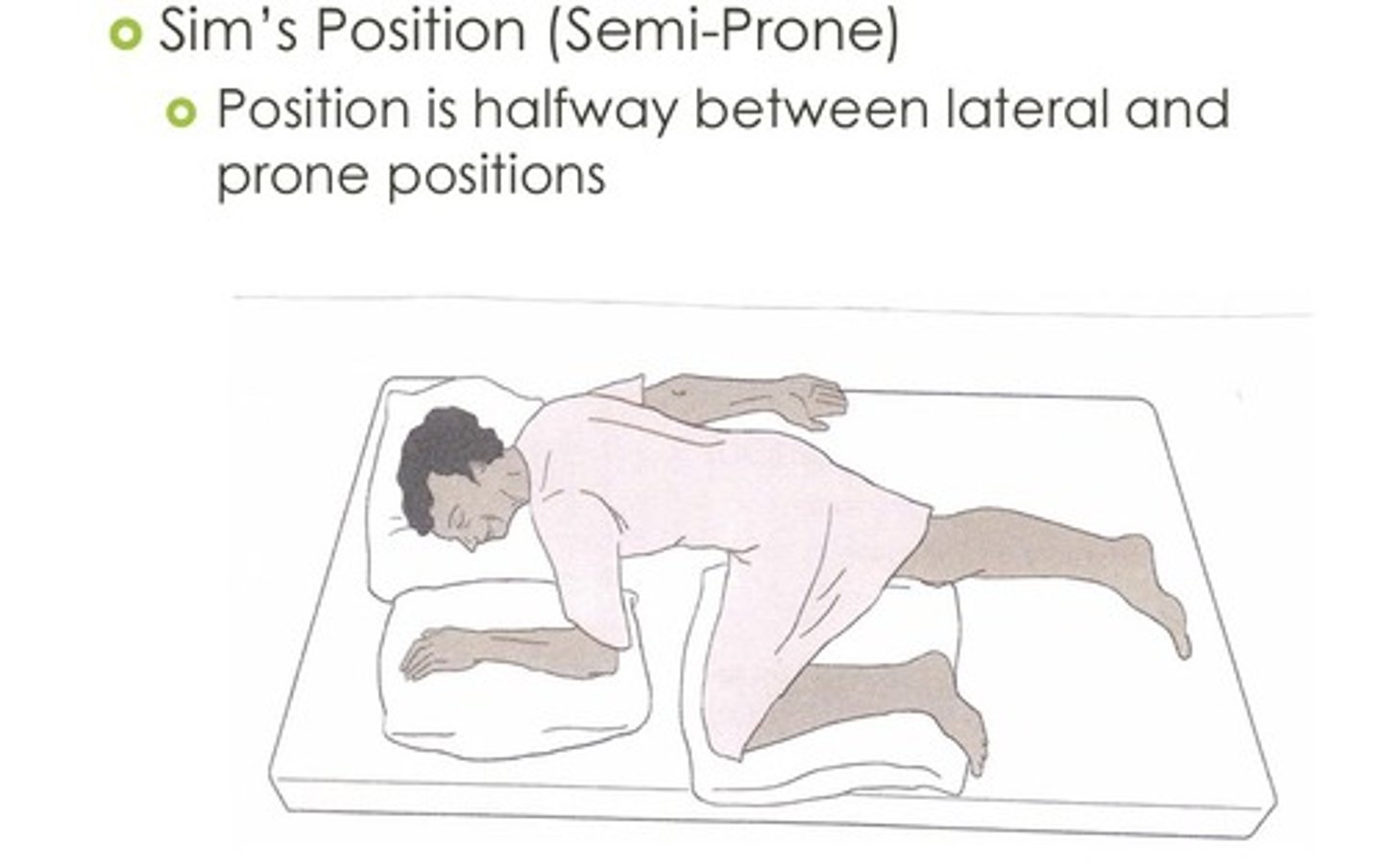
Sim's
A body position in which a person is lying on his left side with the upper knee flexed and raised toward the chest
Shearing
Rubbing or friction that results from the skin moving one way and the bone underneath it remaining fixed or moving inthe opposite direction
Friction
Rubbing of one surface against another
Arthritis
Inflammation or swelling in the joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune condition that causes joints to become red, swollen, and very painful
Osteoarthritis
Pain and stiffness in joints, especially weight-bearing joints, referred to as Degenerative joint Disease (DJD) or Degenerative Arthritis
Contractures
A permanent and often painful shortening of a muscle or tendon, usually due to lack of activity, that causes limited movement
Osteoporosis
A disease that causes bones to become porous and brittle
Foot Drop
A weakness of muscles in the feet and ankles that causes problems with the ability to flex the ankles and walk normally
Range of Motion
THe extent to which a joint is capable of being moved
Extension
Straightening a body part
Pronation
Turning downward
Supination
Turning upward
ABduction
Moving a body aprt away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Moving a body part toward the midline of the body
External/Internal Rotation
Turning a joint
Opposition
Touching the thumb to any other finger
Dorsiflexion
Bending backwards
Plantar Flexion
Bending the foot down