Diversity and Selection
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What are gene mutations?
Involves a change in DNA base sequence
This can result in the formation of new alleles
What types of mutations can happen?
Substitution
Insertion
Deletion
What is a substitution mutation?
A mutation where one bases are substituted into DNA
For substitution mutations, why is it important that DNA is degenerate?
Since multiple triplets can code for the same amino acid, a substitution mutation will not always result in a mutation
What is the difference between harmful and beneficial mutations?
Harmful mutations could be a detriment to an organism, decreasing it’s likelihood of survival so the gene dies out quickly
Some mutations allow for organisms to be more adapted for survival purposes and so are beneficial and could increase in the population
What could be the effect of a substitution mutation?
No effect- a Silent mutation
Could cause a change in amino acid- hydrogen, ionic bonds and disulfide bridges formed in different places due to change in primary structure
Resulting protein is not functional or a different protein is made
Could be beneficial or harmful
A base in a triplet could code for a stop codon, making the polypeptide chain much shorter
Why are introns important for mutations?
Mutations in non-coding regions have no effect on protein synthesis
What is a deletion mutation?
A mutation where a base is completely removed from a DNA strand
What is an insertion mutation?
A mutation where a base is added into a gene
What is the effect of an insertion/deletion mutations?
They cause a frame shift after the point where the mutation occurs
Every amino acid downstream of the mutation will be effected
These mutations, especially earlier in the gene, are more likely to be harmful
What causes mutations?
They occur spontaneously all the time
Mutagenic agents increase the rate of mutations such as ionising radiation, chemicals and some viruses
How many chromosomes do normal body cells have?
Cells have the diploid number of chromosomes (2n) meaning each cell contains 2 of each chromosomes- 1 paternal, 1 maternal
How many chromosomes do gametes have?
The have a haploid number of chromosomes (n)
Why gametes being haploid important?
Because at fertilisation, the diploid number of chromosomes is restored
The new combination of alleles increases genetic diversity and the ability of a species to survive a changing environment
What are homologous chromosomes?
Chromosomes carrying the same genes, on the same loci but may have different alleles
What happens in interphase of meiosis?
Chromosomes replicate to form 2 sister chromatids joined at a centromere
Chromosomes remain long and thin
What happens in prophase 1?
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Homologous pairs of chromosomes form a bivalent and non-sister chromatids exchange genes (crossing over)
The spindle begins to form from the centrioles and the nuclear envelop breaks down
What happens in metaphase 1?
Bivalents/homologous pairs of chromosomes pair up at the equator of the cell
The position of homologous pairs is random which allows for independent segregation
What happens in anaphase 1?
Homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell as spindle fibres contract
What happens at telophase 1 and cytokinesis?
The chromosomes consisting of two chromatids joined at a centromere group together at opposite poles of the cell
The spindle fibres disappear and the nuclear envelope reforms
The cytoplasm divides producing two homologous haploid cells
What happens in prophase 2?
Spindle fibres form from centrioles in each cell
What happens in metaphase 2?
The chromosomes comprising of a pair of chromatids line up on the equator of the cell
What happens in anaphase 2?
Centromeres divide
Chromatids are pulled apart by spindle fibres to opposite poles of the cell
What happens in telophase 2/cytokinesis?
Spindle fibres break down
Nuclear envelope reforms around separated chromosomes
Cytoplasm of both cells divides to produce 4 haploid gametes that are genetically different
What happens during crossing over?
Occurs in prophase 1
Homologous pairs of chromosomes associate to form a bivalent
A chiasma forms where non-sister chromatids exchange alleles to from new allele combinations
What happens during independent segregation?
Occurs in metaphase 1
Random alignment of paternal and maternal chromosomes along the equator of the cell
Results in new combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the gametes formed
What is random fertilisation?
Any egg can be fertilised any sperm so there is a huge number of combinations of different alleles
This produces a zygote with different combinations of chromosomes and therefore different combinations of alleles
This further increases genetic diversity
Restores the diploid number of chromosomes
How can we find the different number of combinations of chromosomes in an organism?
No. of combinations to the power of the no. of pairs of chromosomes
What are plant lifecycles like?
Plants can reproduce sexually or asexually
A sexually reproducing plant will make a plant that reproduces asexually, then vice versa
Each reproductive event creates a new generation that alternate types of reproduction and this is called alternation of generations
What are sporophytes and gametophytes?
Sporophytes produced spores
Gametophytes produce gametes
What can happen during chromosomes mutation and what does it lead to?
There can be extra copies of a chromosomes or one copy missing
It leads to inherited conditions because errors are present in gametes (hereditary cells)
What happens during the chromosome mutation, non-disjunction and what is an example of this?
It is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during anaphase
An example of this is an extra copy of a 21 chromosome in humans leading to down syndrome
What does it mean for a species to have a high genetic diversity and how can this occur?
There are many different alleles in a population
This can happen by mutation or different alleles being introduced into a population when individuals from another population migrate into them- gene flow
What is a genetic bottleneck?
An event that causes a big reduction in the population and large number of organisms die before reproducing
It can also be an event where a small part of an original population becomes isolated for reasons such a geographical isolation or religion
This reduces the no. of different alleles
The survivors reproduce and a large population is creates from few individuals, and therefore the population has less alleles
What is the founder effect?
Happens when a few individuals from a population start a new colony and there are only a small number of different alleles in the initial gene pool
The frequency in each allele between the original population and the new colony may be very different
For example an allele that was rare may become very common, increasing chances of genetic disease
This can be a result of migration which causes geographical separation or can be because of something like religion
What happens during natural selection?
Mutations lead to different alleles in the population which increases genetic diversity
Individuals with beneficial alleles are more likely to survive against selection pressures such as an environment or predation and therefore reproduce
When the survivors reproduce, the next generation inherits the beneficial allele
The next generation are more likely to survive and reproduce so the frequency of the allele increases from generation to generation
Over time, the beneficial allele becomes increasingly common within the population
What is a selection pressure?
A factor that causes some organisms without beneficial characteristics to die off, and so individuals with beneficial characteristics are selected
What are the kinds of adaptations that can take place due to natural selection?
Behavioural- organism actions that increase chance of survival and reproduction
Physiological- processes inside an organisms body increasing it’s chances of survival
Anatomical- Structural features of an organism’s body increasing it’s chances of survival
What is directional selection?
Selection which favour one extreme of the population
For example, bacteria carrying alleles for antibiotic resistance will be favoured and then will survive, passing on the alleles to the next generation until that allele becomes abundant
What is stabilising selection?
Selection where the average characteristic is favoured
For example, the birth weight of babies shows that babies born of average size have a much lower mortality ratee then very light or very heavy babies
What is disruptive selection?
Selection where two extremes are favoured over the average
What are some aseptic techniques?
Regularly disinfect work surfaces
Use sterile equipment and discard appropriately after use- sterilisation can be done with flame and ethanol or an autoclave
Work near a Bunsen burner- hot air rises so microbes carried away from agar plate
Minimise the time spent with the lid open off of the agar
Flame neck of glass container of broth before and after use as this causes air to move out of the container, preventing unwanted organisms from falling in
What is phylogeny?
Study of evolutionary history of groups of organisms
How does selective breeding affect genetic diversity?
Decreases
Animals or plant bred for one or few specific desirable characteristics
What do phylogenetic trees show?
It shows the relationship between the members of different species
The point at which branches occur shows that two or more organisms share a common ancestor
The first branch shows the common ancestor for all of the different species
Closely related species will have diverge from one another from a recent common ancestor
What is taxonomy?
Science of classification
It involves naming some organisms and organising them into groups, making it easier to identify and study them
How are different groups of organisms classified?
The are 8 groups called taxa, each one is called a taxon
The order is domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
As we descend, the organisms sharing in the groups are more closely related
There are more groups at each level, but fewer organisms in each group
How are organisms grouped into a phylogenetic classification system?
Species grouped on evolutionary relationships
In a hierarchy with no overlap
What is a species?
A group of similar organisms able to produce and give fertile offspring
What is the binomial naming system?
All organisms are given one internationally accepted Latin name containing two parts
The first part is the genus with a capital letter
The second part in the name of the species in lower case
Name are always in italics are underlined
This avoids confusion with using common names
What is courtship behaviour?
Carried out to attract a mate of the right species
This can vary from releasing chemicals to a series of displays
This behaviour is species specific- only the individuals of the same species will recognise each other, making reproduction more successful and different species won’t produce fertile offspring
Because of this, courtship can be used to classify organisms
How can genome sequencing be used to classify organisms?
New technologies allow us to determine the base sequence of organism’s DNA
The DNA of two organisms can be compared to see similarity
The higher % similarity the DNA sequence orders share, the more closely related the species
Organisms of the same species may have slightly different base sequences as they have different alleles
How can amino acid sequence be used to compare organisms?
The sequence of amino acids is coded for by the sequence of bases in DNA
Related organisms will have similar amino acid sequences as they have similar DNA base sequences
How can we use immunological comparison to classify organisms?
Similar proteins will bind to the same antibodies
Human serum injected into an animal like a rabbit
The human antigens stimulate an immune response in the rabbit, so it produces anti-human antibodies
If the antibodies are added to isolated samples of other species, any protein like the human version will bind to the antibody- this causes a precipitate to form
The one that forms the least precipitate is the least related and vice versa
What happens during DNA hybridisation?
DNA from two a different species is separated by heating it, breaking weak H bonds between bases
The strands are mixed then cooled
When base sequences are complimentary, H bonds reform between the separated strands forming hybrid DNA- 1 strand form each species
DNA is the heated a second time to separate the hybrid strand again, and the temperature of complete separation is recorded
The higher the temperature, the more similar the two species as more energy was needed to break more hydrogen bonds
How has gene technology affected the way genetic diversity is assessed?
Before, genetic diversity would be measured by observable characteristics like eye colour
Now we can measure this directly as different alleles will have slightly different DNA bases sequences leasing to slightly different amino acid sequences
This is far more accurate than just observing different characteristics on the surface
What is biodiversity?
The variety of living organisms in an area/ecosystem/community
What is a community?
All the populations of different species in a habitat
What is species richness?
No. of different species in a community
What is the index of diversity and why is it used?
Species richness only relies on the number of species, not on the sizes of the populations of all of those species
Index of diversity takes both of these into account
What is variation and what is it caused by?
The differences between individuals
This can be caused by genetic or environmental factors
Most variation is caused by a combination of both of these
Why do we use samples and how do we do it?
Samples are used because they are far less time consuming to use than the whole population
These samples have to be random so you could make a gird on the area you want to sample
Then use a random number generator to pick a coordinate on the grid to sample
We then have to use a statistical text to ensure that our findings are not just due to chance
What is standard deviation and what is it used for?
The spread of data around the mean
A large standard deviation shows a large variation, while a small SD shows a small variation
You can use the SD to draw error bars on bar charts for example that extend above and below the maximum value
If the error bars overlap, it shows the difference between results is not significant
What is the equation for the index of diversity?
N=Total no. of organisms of all species
n=Total no. of organisms of one species
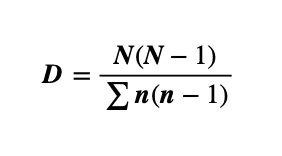
What do farmers do to increase farming space/yield that harms biodiversity?
Woodland clearance- destroys many trees and the species residing in them, destroys habitats
Hedgerow removal- turns lots of smaller fields into fewer large fields
Pesticides- kills pests that feed on crops- loss of food sources
Herbicides- kills unwanted plants (weeds), reduces the no, of organisms that feed on the weeds
Monoculture- only growing one type of plant, supports fewer organisms
How can biodiversity be conserved?
Legal protection to endangered species
Protected areas
Environmental stewardship schemes- encourage farmers to conserve biodiversity, like through growing more hedgerows
What are the biological advantages of hedgerows
Hedgerows have a lot of biodiversity
Birds can use them to nest
Important wild flowers in hedges that could be used for medicines for example
Animals use them for hunting and shelter
When collecting a sample, how should we know when to stop?
We could calculate a running mean
When this mean stays constant, we have enough values
What is the pentadactyl limb?
A limb with five digits (fingers or toes)
What are analogous characteristics?
Characteristics that have the same function but have originated in different ways
For example, wings on bats and birds
What are homologous characteristics?
A characteristic shared by organisms in different groups originating from a common ancestor
For example, the pentadactyl limb
What is horizontal gene transfer?
When bacteria share their genes with other bacteria
One bacteria share a plasmid through it’s pili