Structure of an Enzyme and Mechanism of Action
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
16. What is the monomer of a protein?
amino acid
17. Two of these bonds attach functional groups. Which functional groups are attached to this central carbon?
18. The third component bonded to that central carbon is a
19. The fourth component is what makes each monomer unique. This is called a/an BLANK group.
?
Hydrogen
R
20. The monomers of a protein are bonded together by a bond called a Blank bond. This bond is a blank covalent bond.
Peptide
Polar
21. When the monomers of a protein are bonded together to form a chain, this is called the BLANK structure of a protein.
Primary
22. There are two organelles (from lab 2) at which this structure (from the previous question) is produced in the cytoplasm of the cell. What are these two organelles?
free ribosome bound ribosome
23. Following the formation of the chain of monomers, a protein will fold to form the blank structure of the protein. This structure is the result of interactions between the functional groups listed above that form the backbone of the chain of monomers. Specifically what interaction is used to form this structure of the protein? blank
secondary
Hydrogen bond
24. Next, the three-dimensional shape of a protein is formed. This is called BLANK structure. Three-dimensional shape is formed by interactions among the BLANK groups of the monomer.
Tertiary
R
25. Name the four interactions that can occur between these parts of the monomer:
London forces
dipole-dipole
Hydrogen bond
Salt Bridge
26. Next, for some proteins, multiple subunits with 3-dimensional shape can interact to form the BLANK structure of the protein.
Quaternary
27. Considering your knowledge of the structure of a protein, what would all the small blue spheres represent in this figure of the macromolecule?
Amino acids
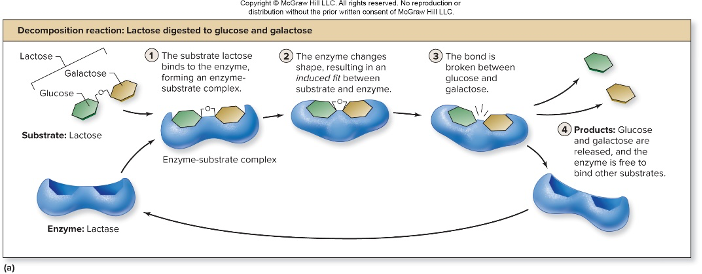
28. Review: Which kind of reaction is this (dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis)?
29. What is the enzyme?
30. What is the substrate?
31. What are the products?
Hydrolysis
Lactase
Lactose
Glucose and Galactose
32. Review: What macromolecule is lactose (which ends in the suffix –ose)?
carbohydrate
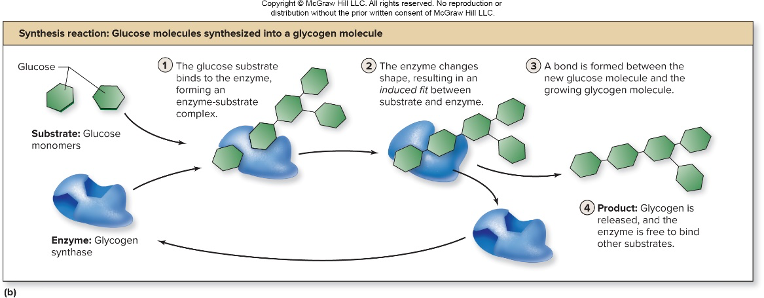
33. Review: What type of reaction is this (dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis)?
34. What is the enzyme?
35. What macromolecule is being built using this enzyme? Be specific!
Dehydration Synthesis
Glycogen Synthase
Glycogen