Chapter 2 Microbiology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:27 PM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Atom
smallest unit of matter
contains a nucleus and an electron cloud
composed of subatomic particles
join together to form molecules
contains a nucleus and an electron cloud
composed of subatomic particles
join together to form molecules
2
New cards
Ionic Bonds
attractions between cations (electron donor) and anions (electron acceptor)
3
New cards
Cation
positively charged ion
4
New cards
anion
negatively charged ion
5
New cards
covalent bonds
involves sharing electrons
6
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
weak polar bonds based on partial electrical attractions
7
New cards
Decomposition reactions
breaks down chemical bonds
AB→ A + B
AB→ A + B
8
New cards
Hydrolysis
“water loosening or breaking”
ABCDE + H2O→ABC -- H + HO -- DE
ABCDE + H2O→ABC -- H + HO -- DE
9
New cards
Catabolism
breakdown of complex molecules withing body cells that produces energy
\--CD → C + D + energy
\--CD → C + D + energy
10
New cards
Synthesis Reaction
Forms chemical bonds
A + B → AB
A + B → AB
11
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis (condensation)
* formations of a water molecule
* ABC-- H + OH -- DE → ABCDE + H20
* ABC-- H + OH -- DE → ABCDE + H20
12
New cards
Anabolism
synthesis of new molecules within body cells that uses energy
\-- C + D + energy → CD
\-- C + D + energy → CD
13
New cards
Exchange Reaction
involves decomposition of first, then synthesis
\-- AB + CD → AD + CB
\-- AB + CD → AD + CB
14
New cards
Reversible Reaction
occurs simultaneously in both directions
* AB
* AB
15
New cards
Enzymes
protein catalysts that lower the activation energy of reactions
not changed or used up in a reaction
not changed or used up in a reaction
16
New cards
Activation energy
amount of energy needed to get a reaction started
chemical reactions in cells cannot start without help
chemical reactions in cells cannot start without help
17
New cards
Exergonic (exothermic) reactions
produce more energy than they use
generates body heat
generates body heat
18
New cards
Endergonic (endothermic) reactions
use more energy than they produce
uses body heat
uses body heat
19
New cards
solution
mixture of 2 or more substances
20
New cards
solvent
medium (liquid, air)
21
New cards
solute
atoms, ions, or molecules which are dispersed (or dissolved) in solvent
22
New cards
solubility
water’s ability to dissolve a solute in a solvent to make a solution
23
New cards
ionization (dissociation)
ionic bonds broken in water due to polarity of water
24
New cards
hydration sphere
sheath of water molecules around an ion in solution
25
New cards
hydrophilic
water loving
molecules that interact readily with water molecules
ions, polar molecules
molecules that interact readily with water molecules
ions, polar molecules
26
New cards
H+
extremely reactive in solution
27
New cards
pH
concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution
28
New cards
concentration
the amount of solute in a solvent (mg/mL)
29
New cards
Neutral pH
balance of H+ and OH-
\-pH of human blood -- from 7.35 to 7.45
\-pH of human blood -- from 7.35 to 7.45
30
New cards
Acidic
pH lower than 7.0
high H+ concentration
high H+ concentration
31
New cards
Basic (alkaline)
pH higher than 7.0
low H+ concentration
low H+ concentration
32
New cards
pH scale
inverse relationship with \[H+\]
ranged from 0-14
ranged from 0-14
33
New cards
acid
a solute that dissociates in solution & releases H+
proton donor
strong acids dissociates completely in solution (HCI)
HCI → H+ Cl-
proton donor
strong acids dissociates completely in solution (HCI)
HCI → H+ Cl-
34
New cards
Base
a solute that removes hydrogen ions from a solution
proton acceptor
strong bases dissociate completely in solution (NaOH)
NaOH → Na+ OH-
proton acceptor
strong bases dissociate completely in solution (NaOH)
NaOH → Na+ OH-
35
New cards
weak acids & weak bases
fail to dissociate completely (carbonic acid → bicarbonate)
H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3
help balance the pH
H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3
help balance the pH
36
New cards
salts
solution that dissociate into cations and anions (except hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions)
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
37
New cards
buffers
stabilize pH by removing or replacing H+
neutralizes either a strong acid or strong base
sodium bicarbonate is very important in humans
buffers carbonic acid
neutralizes either a strong acid or strong base
sodium bicarbonate is very important in humans
buffers carbonic acid
38
New cards
antacids
a basic compound that neutralizes acid and forms a salt
tums, rolaids
tums, rolaids
39
New cards
inorganic compounds
molecules not based on carbon or hydrogen
oxygen, water, inorganic acids, bases and salts, carbon dioxide
usually small and structurally simple
oxygen, water, inorganic acids, bases and salts, carbon dioxide
usually small and structurally simple
40
New cards
organic compounds
molecules based on carbon or hydrogen
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
41
New cards
functional group
an arrangement of atoms in an organic molecule that is responsible for most of the chemical properties of that molecule
42
New cards
organic molecules
contain H, C and usually O
covalently bonded
contain functional groups that determine chemistry
covalently bonded
contain functional groups that determine chemistry
43
New cards
macromolecules
polymers consisting of many small repeating molecules called monomers
monomers join by dehydration synthesis reactions
monomers join by dehydration synthesis reactions
44
New cards
carbohydrates
contain C, H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio
45
New cards
monosaccharides
simple sugars with 3 to 7 carbon atoms
46
New cards
disaccharides
two simple sugars condensed by dehydration synthesis
47
New cards
polysaccharides (starches)
many monosaccharides condensed by dehydration synthesis
hydrolysis breaks disaccharides → monosaccharides
hydrolysis breaks disaccharides → monosaccharides
48
New cards
structure of glucose
(picture)
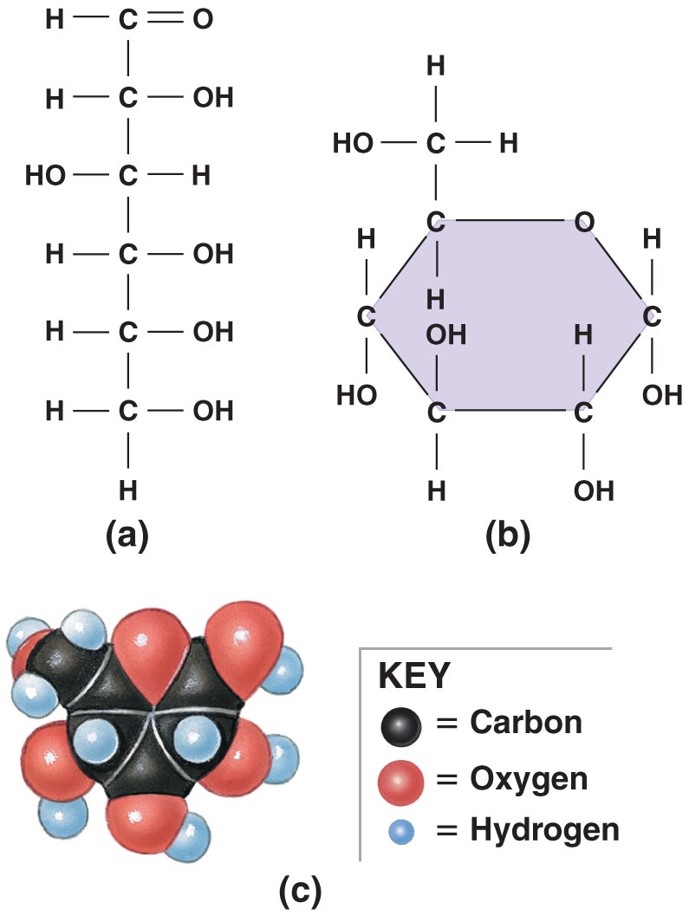
49
New cards
structure of polysaccharide glycogen
(picture)
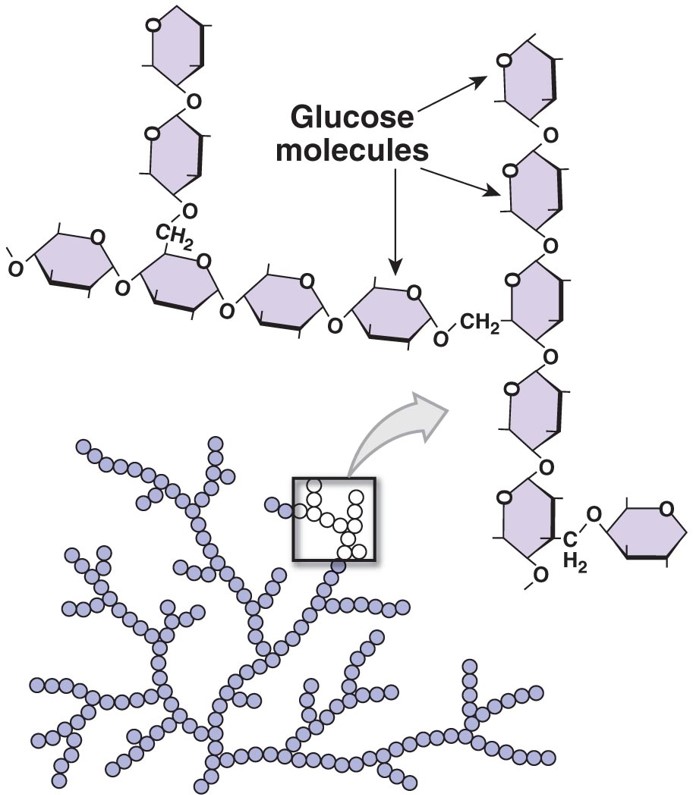
50
New cards
lipids
* carbon: hydrogen ration is 1:2
* contain much less O than carbs
* nonpolar & insoluble in water
* hydrophobic molecules: fats, oils, waxes
* need transporter in blood
* fatty acids, eicosanoids, glycerides, steroids, phospholipids, glycolipids
* primary components of cell membranes
* contain much less O than carbs
* nonpolar & insoluble in water
* hydrophobic molecules: fats, oils, waxes
* need transporter in blood
* fatty acids, eicosanoids, glycerides, steroids, phospholipids, glycolipids
* primary components of cell membranes
51
New cards
simple lipids
* fats or triglycerides
* contain glycerol and fatty acids
* formed by dehydration synthesis
* broken by hydrolysis
* chains of hydrocarbons
* contain glycerol and fatty acids
* formed by dehydration synthesis
* broken by hydrolysis
* chains of hydrocarbons
52
New cards
saturated
with hydrogen (no double bonds)
53
New cards
Unsaturated
( one or more double bonds between carbons)
54
New cards
complex lipids
contains C, H, and O & P, N, or S
phospholipids that make up membranes
phospholipids that make up membranes
55
New cards
hydrophilic
* water loving
* interacts with water
* ions and polar molecules
* interacts with water
* ions and polar molecules
56
New cards
hydrophobic
* water fearing
* does not interact with water
* nonpolar molecules, fats, oils
* does not interact with water
* nonpolar molecules, fats, oils
57
New cards
steroids
* four carbon rings with OH- group attached to one ring
* part of membranes; keeps membranes fluid
* part of membranes; keeps membranes fluid
58
New cards
proteins
* most abundant and important organic molecules
* contains C, H, O, N
* 20 amino acids - building blocks
* amino acid structure
* central carbon atom
* hydrogen atom
* amino group (--NH2)
* carboxylic acid group (--COOH)
* variable side chain or R group
* contains C, H, O, N
* 20 amino acids - building blocks
* amino acid structure
* central carbon atom
* hydrogen atom
* amino group (--NH2)
* carboxylic acid group (--COOH)
* variable side chain or R group
59
New cards
amino acids
* exist in either of two stereoisomers: D or L
* L- forms are most often found in nature
* L- forms are most often found in nature
60
New cards
connecting amino acids
requires dehydration synthesis between amino group and carboxylic group producing a peptide bond
61
New cards
7 major protein functions
* support- structural proteins
* movement- contractile proteins
* transport- transport (carrier) proteins
* buffering- regulation of pH
* metabolic regulation- enzymes
* coordination and control- hormones
* defense- antibodies
* movement- contractile proteins
* transport- transport (carrier) proteins
* buffering- regulation of pH
* metabolic regulation- enzymes
* coordination and control- hormones
* defense- antibodies
62
New cards
protein structure
* conjugated proteins- consists of amino acids combined with other organic molecules
* glycoproteins
* nucleoproteins
* lipoproteins
* glycoproteins
* nucleoproteins
* lipoproteins
63
New cards
primary structure
the sequence of amino acids along a polypeptide
64
New cards
secondary structure
hydrogen bonds form spirals or pleats
65
New cards
tertiary structure
secondary structure folds into a unique shape
66
New cards
quaternary structure
final protein shape - several tertiary structures together
67
New cards
denaturation
change in structure
due to temp, pH changes
protein becomes nonfunctional
due to temp, pH changes
protein becomes nonfunctional
68
New cards
fibrous proteins
extended sheets or strands
69
New cards
globular proteins
soluble spheres with active functions
protein function based on shape
shape based on sequence of amino acids
protein function based on shape
shape based on sequence of amino acids
70
New cards
denaturation
proteins can undergo this
occurs when proteins encounter hostile environments such as temperature and pH
causes proteins to lose their shapes and functions
occurs when proteins encounter hostile environments such as temperature and pH
causes proteins to lose their shapes and functions
71
New cards
nucleic acids
* large organic molecules found in nucleus
* store & process information at molecular level
* store & process information at molecular level
72
New cards
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
* determines inherited characteristics
* directs protein synthesis
* controls enzyme production
* controls metabolism
* directs protein synthesis
* controls enzyme production
* controls metabolism
73
New cards
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
controls and performs intermediate steps in protein synthesis
74
New cards
nucleotides
building blocks of DNA, RNA
3 molecular parts:
1. sugar (deoxyribose or ribose)
2. phosphate groups
3. nitrogenous base
(A, G, T, C, or U)
3 molecular parts:
1. sugar (deoxyribose or ribose)
2. phosphate groups
3. nitrogenous base
(A, G, T, C, or U)
75
New cards
DNA
double stranded
* bases form hydrogen bonds to hold together
* twisting double- helix
* purines pair with pyrimidines
* adenine (A) to thymine (T)
* cytosine (C) to guanine (G)
* bases form hydrogen bonds to hold together
* twisting double- helix
* purines pair with pyrimidines
* adenine (A) to thymine (T)
* cytosine (C) to guanine (G)
76
New cards
RNA
usually single stranded
* uracil (U) replaces thymine; binds to adenine
* messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
* uracil (U) replaces thymine; binds to adenine
* messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
77
New cards
high energy compounds
nucleotides can be used to store energy
78
New cards
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
two phosphate groups; di- = 2
79
New cards
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
3 phosphate groups; tri- = 3