LS7A AOL #1 (Weeks 1-3)
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
H: 1
O: 2
N: 3
C: 4
How many covalent bonds can H, C, O and N form?
Single: 2
Double: 4
Triple: 6
In each type of bond, how many electrons are shared?
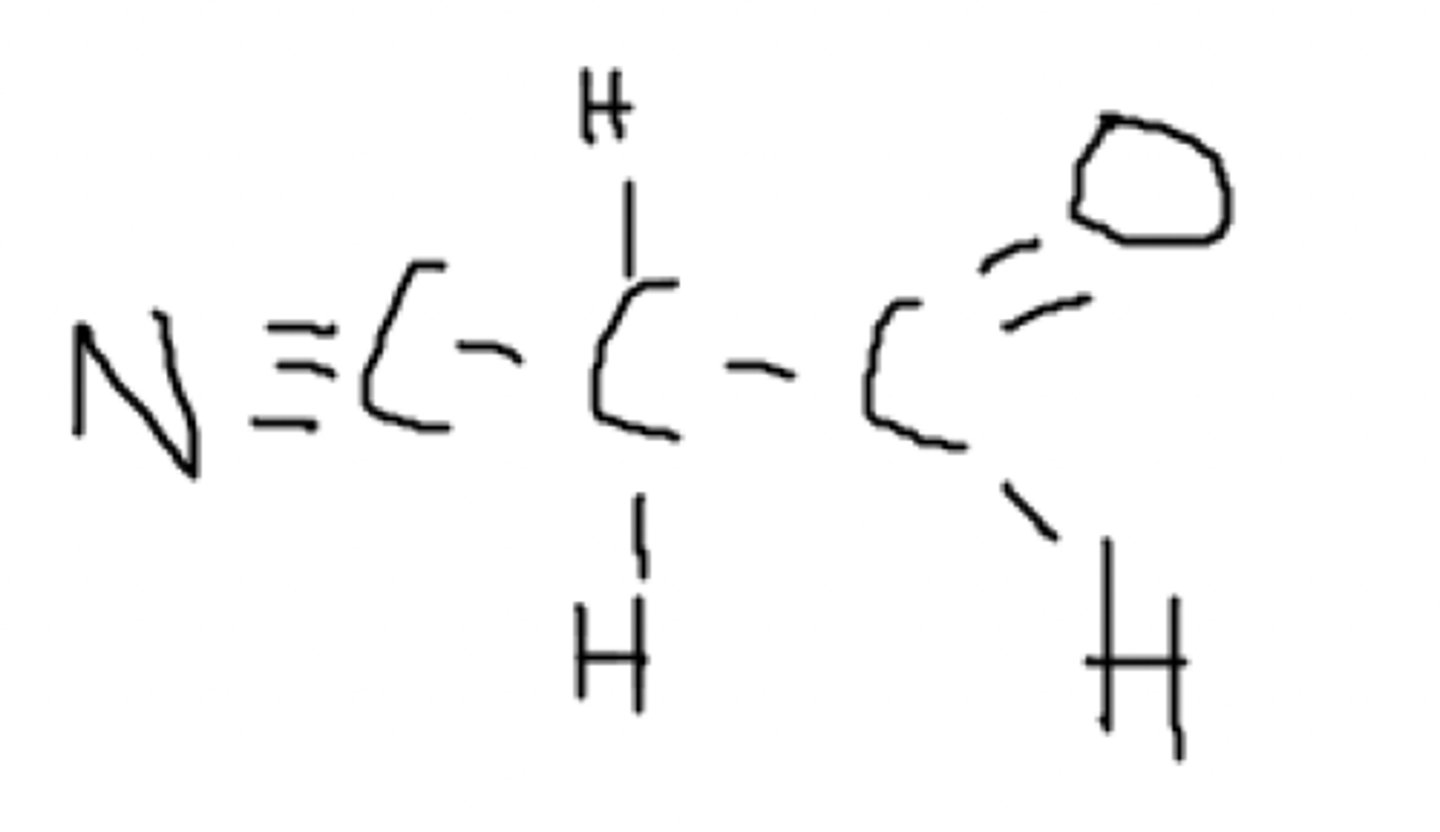
Yes, all of the bonds fulfill the bonding rules discussed in class
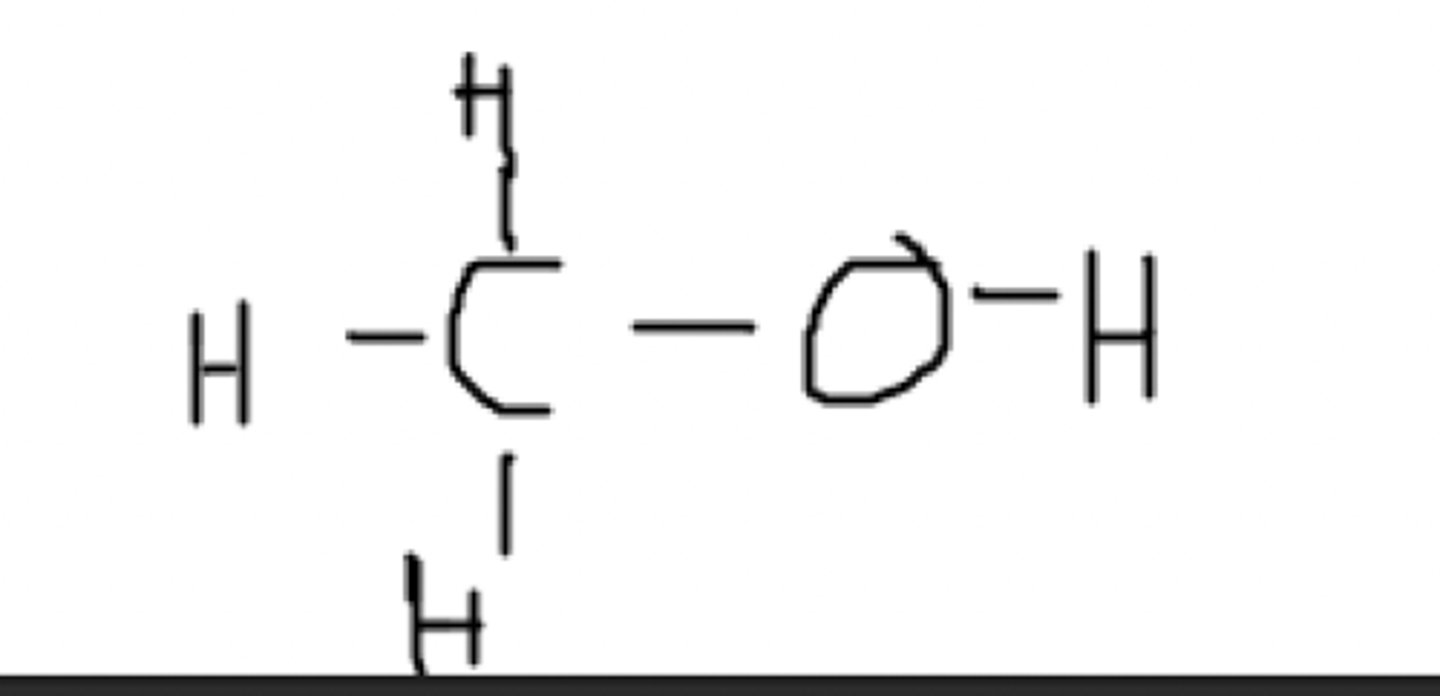
Can this molecule exist in nature?
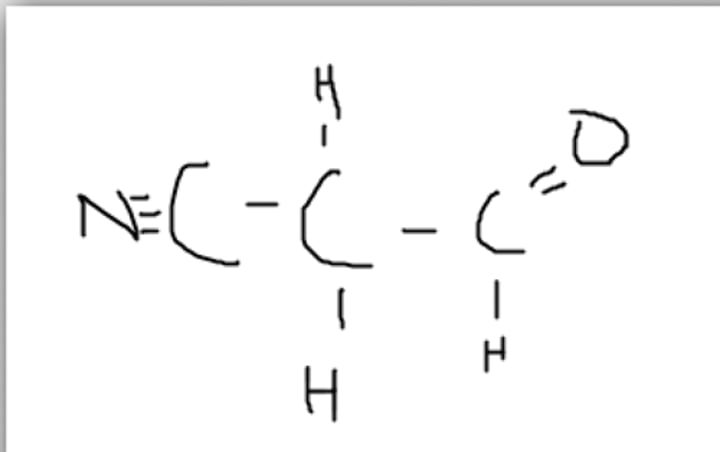
Yes, all of the bonds fulfill our bonding rules
Can this molecule exist in nature?
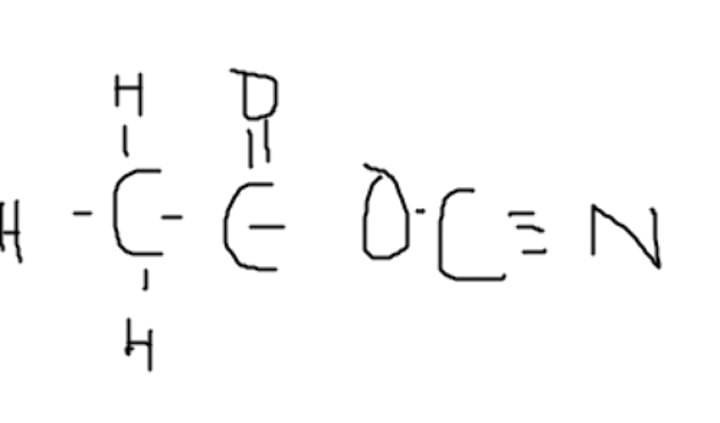
No, it can not. The nitrogen only has two bonds, and the second carbon only has three bonds
Can this molecule exist in nature?
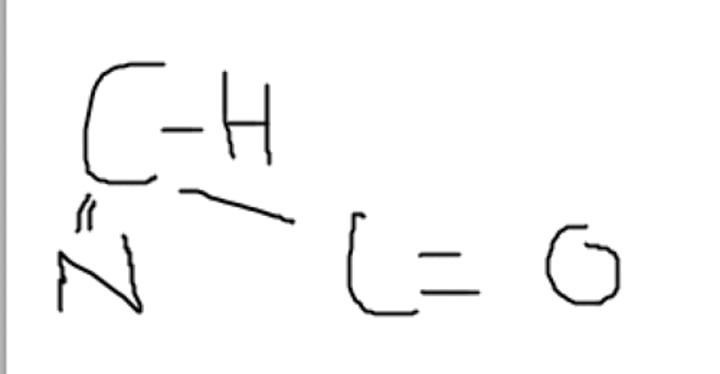
C = H < N = O
Compare the electronegativities of the four atoms fundamental to life.
Oxygen
In CO2 which atom is more likely to be electronegative?
If there is a difference in electronegativity between the atoms bonded
What makes a molecule polar?
Non-polar
Is the molecule C2H4 polar or non-polar?
Polar, it is polar due to the C and O bond and the C and N bond
Is this molecule polar or nonpolar? Where?
This is a non-polar molecule
Is this molecule polar or non-polar?
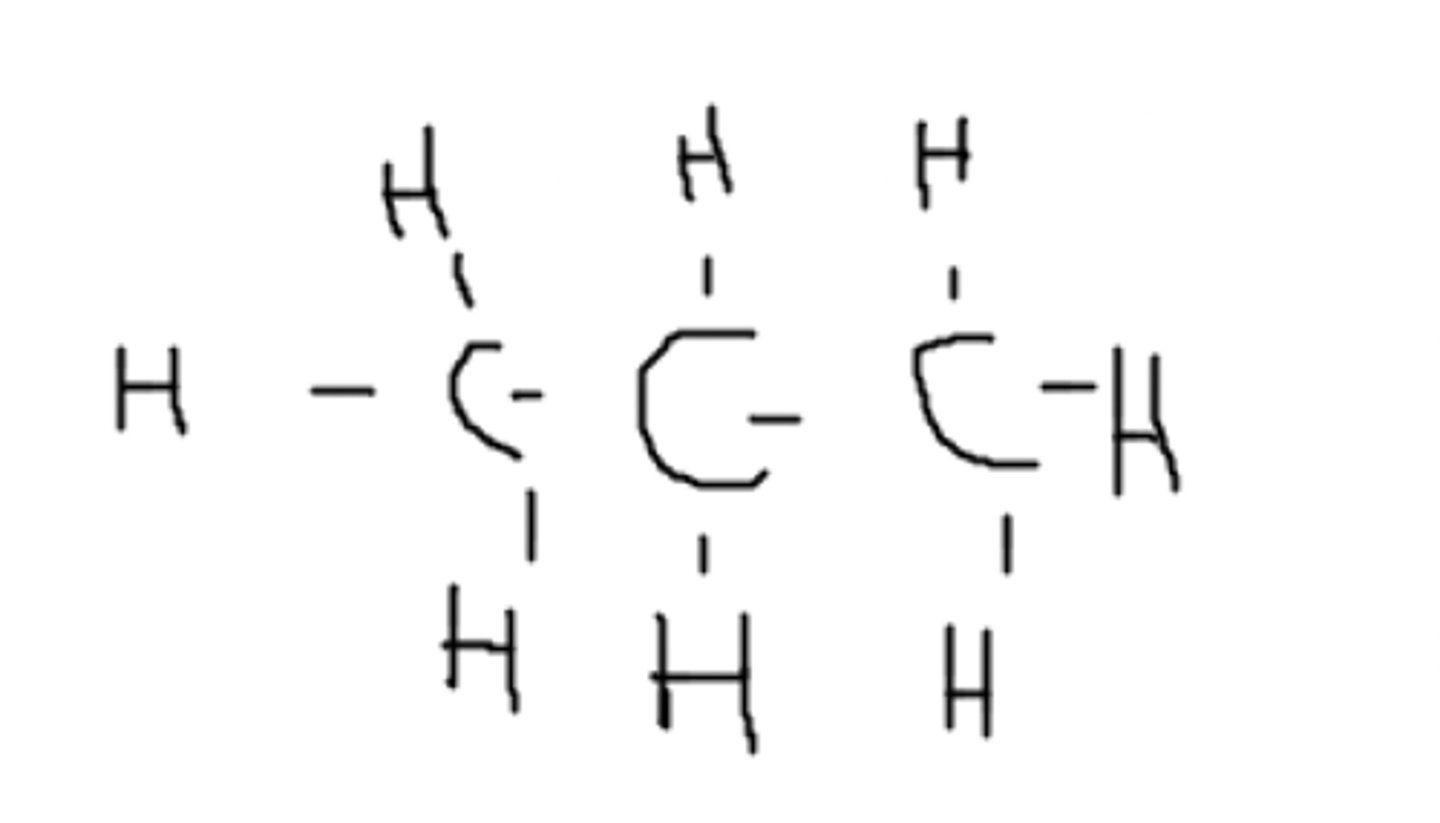
This is a polar molecule because of the X- C bond.
Consider X to be an imaginary molecule. Is this molecule polar or non-polar?
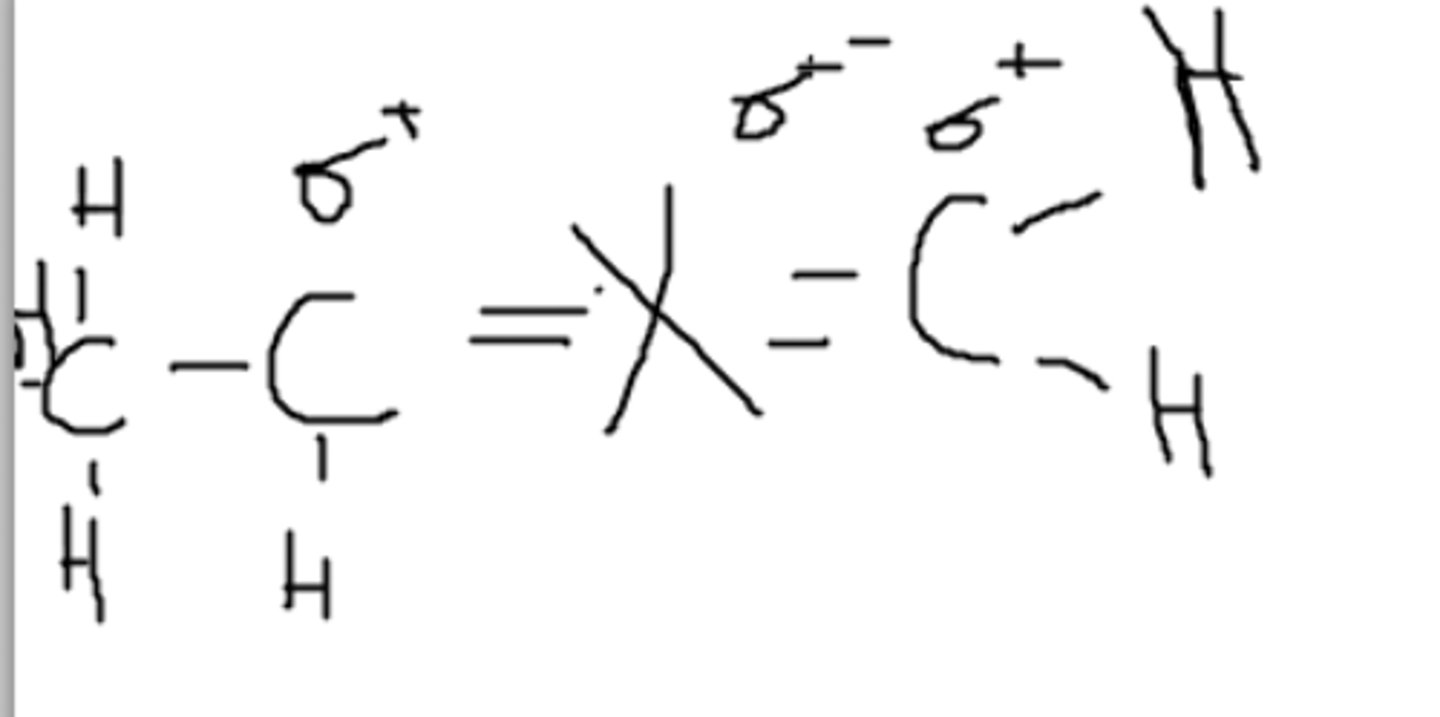
This is a polar molecule because of the X-C and X-O bond.
Consider X to be an imaginary atom. Is this molecule polar or non-polar?
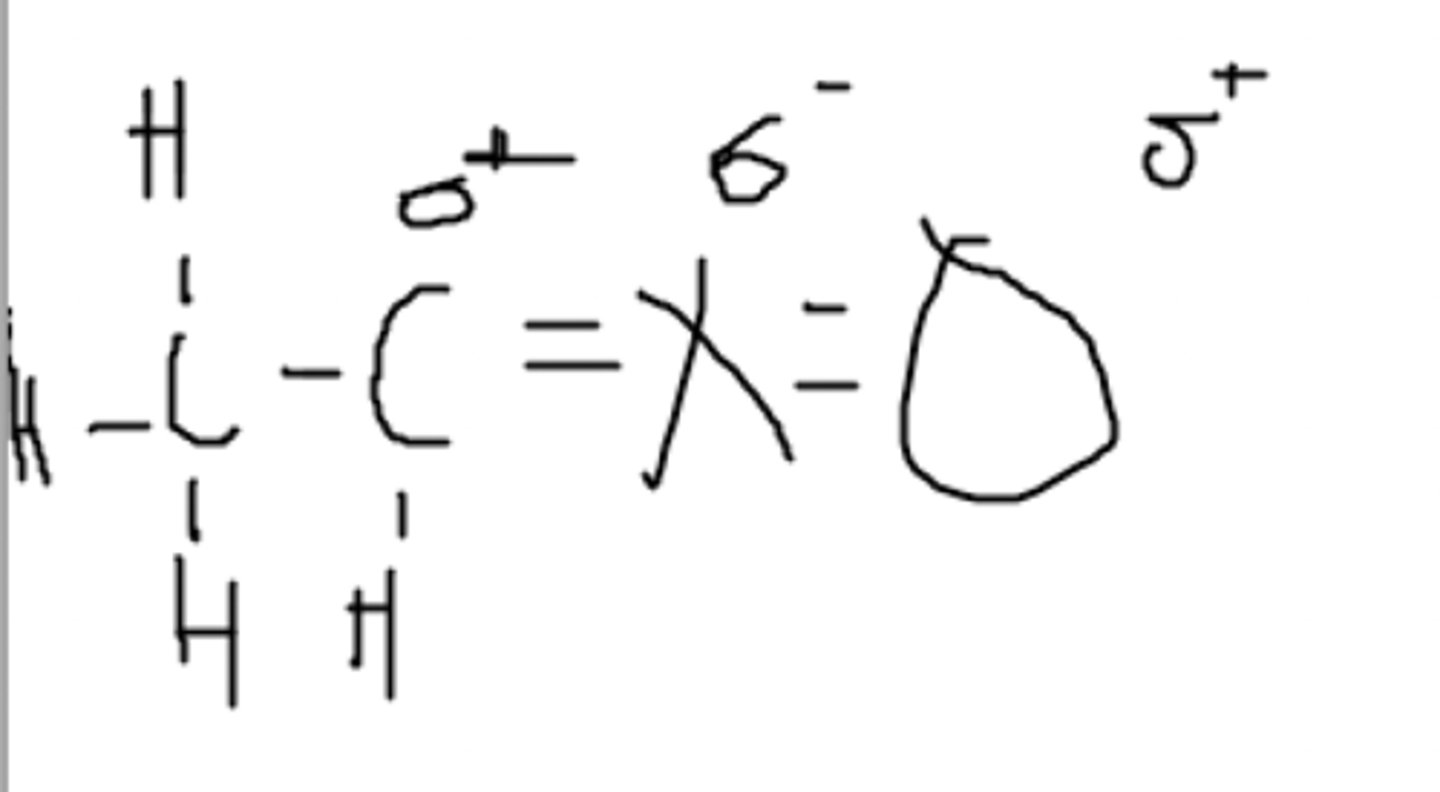
A nucleus that contains protons and neutrons, which is surrounded by shells of electrons
What is an atom made up of?
Bonds in which electrons are shared
What are covalent bonds?
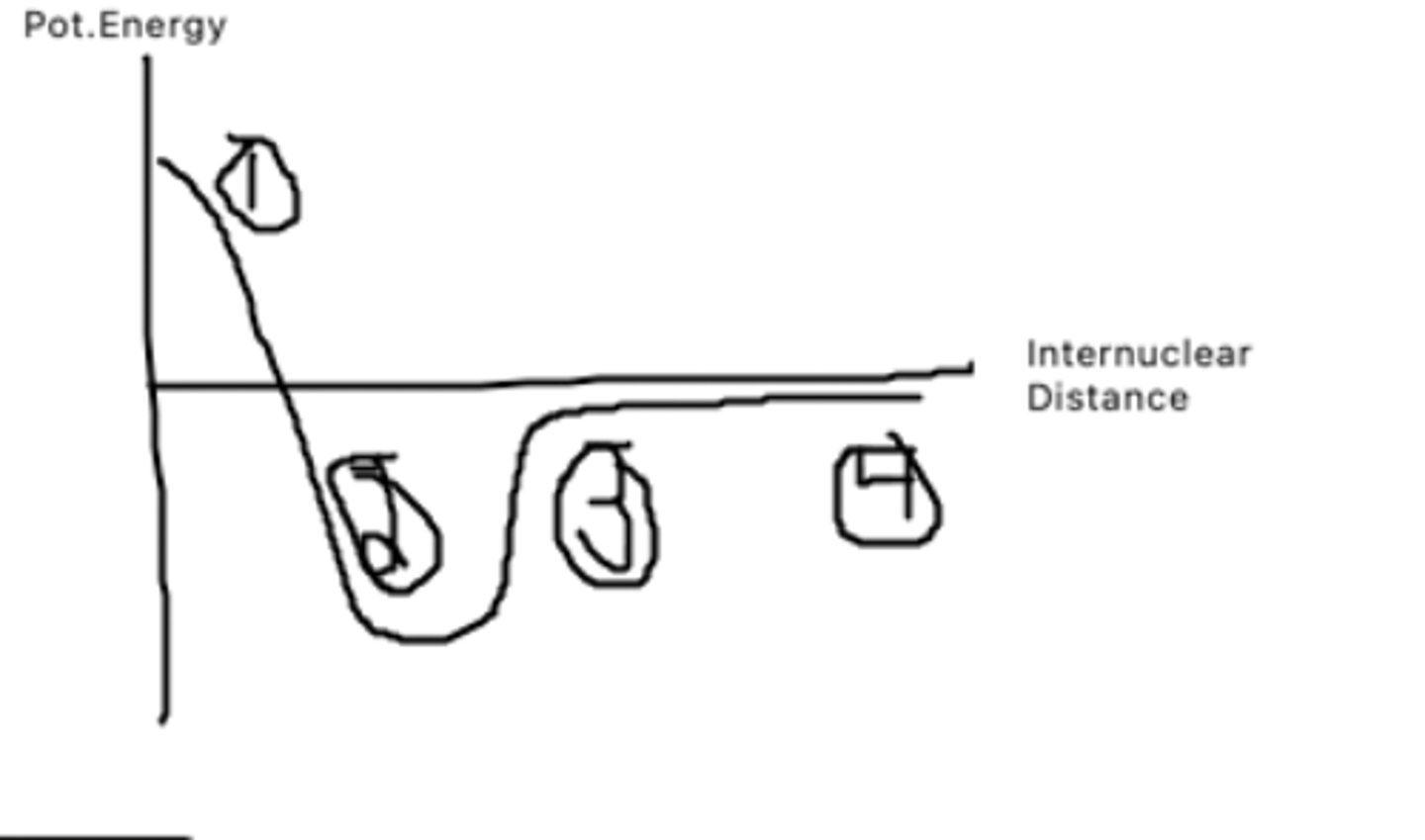
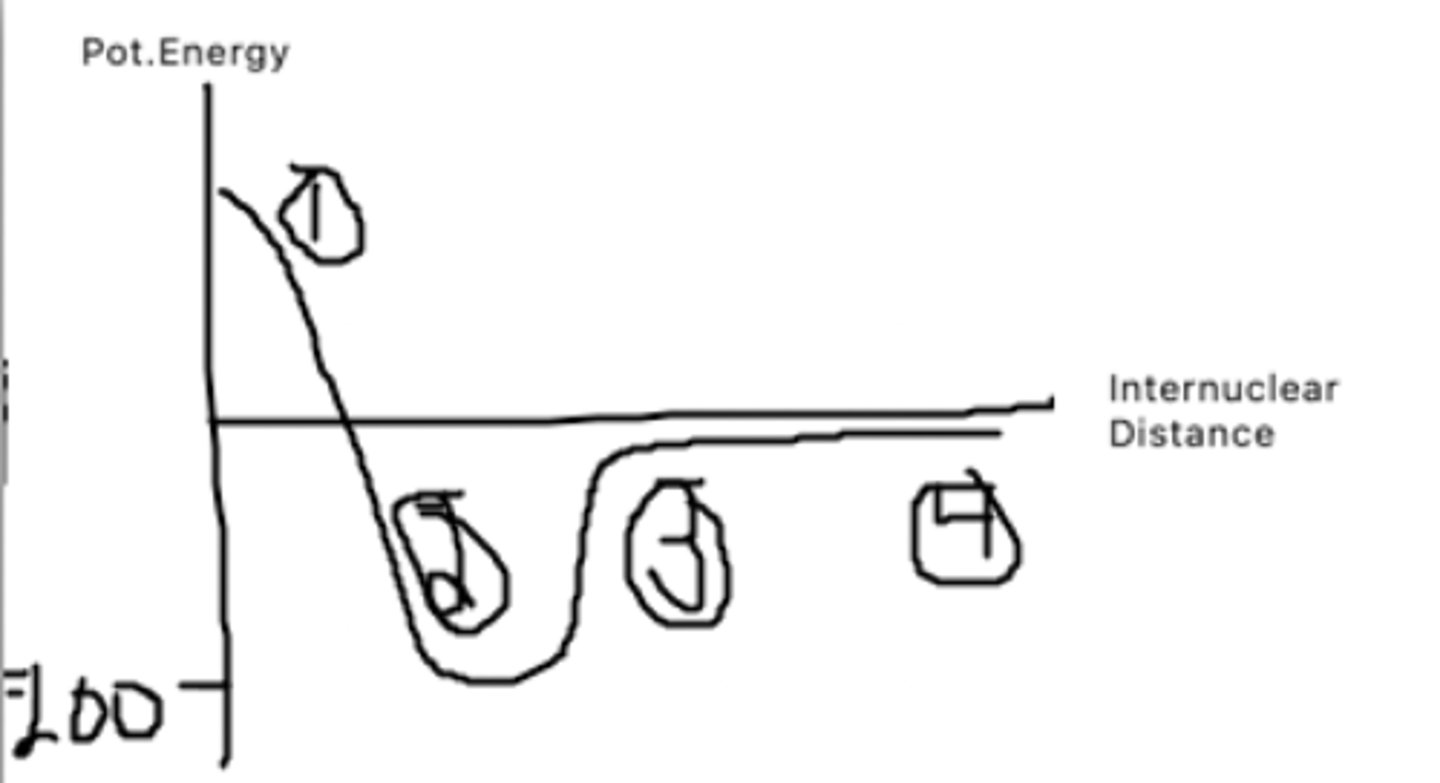
The atoms are too close to each other and thus have very high pot. energy as it takes a lot of energy to bring them that close together
What does point 1 represent?
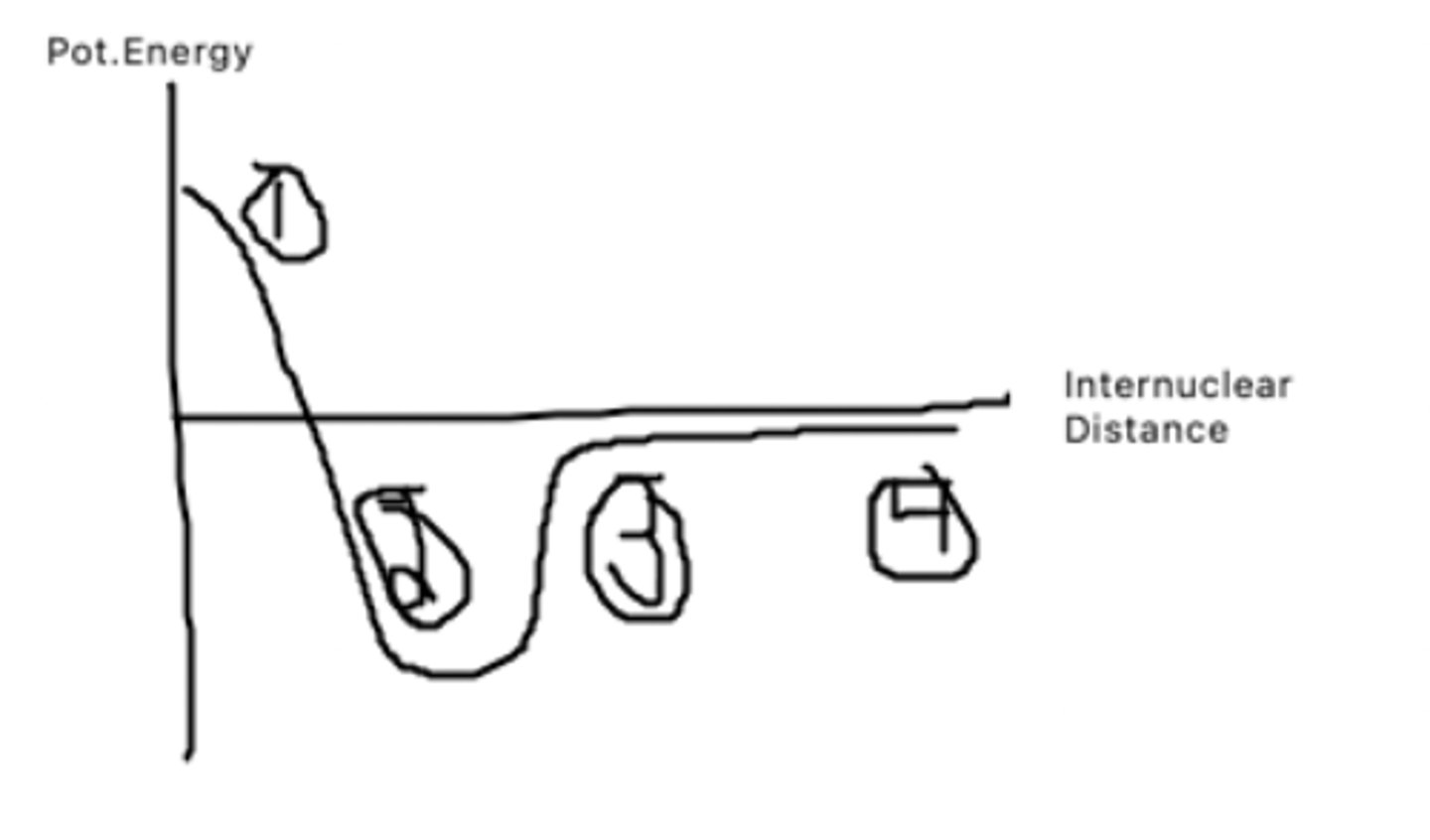
This is the bond distance, it is bond length at which pot. energy is minimized. The atoms want to be here as they have low pot to do other things
What does point 2 represent?
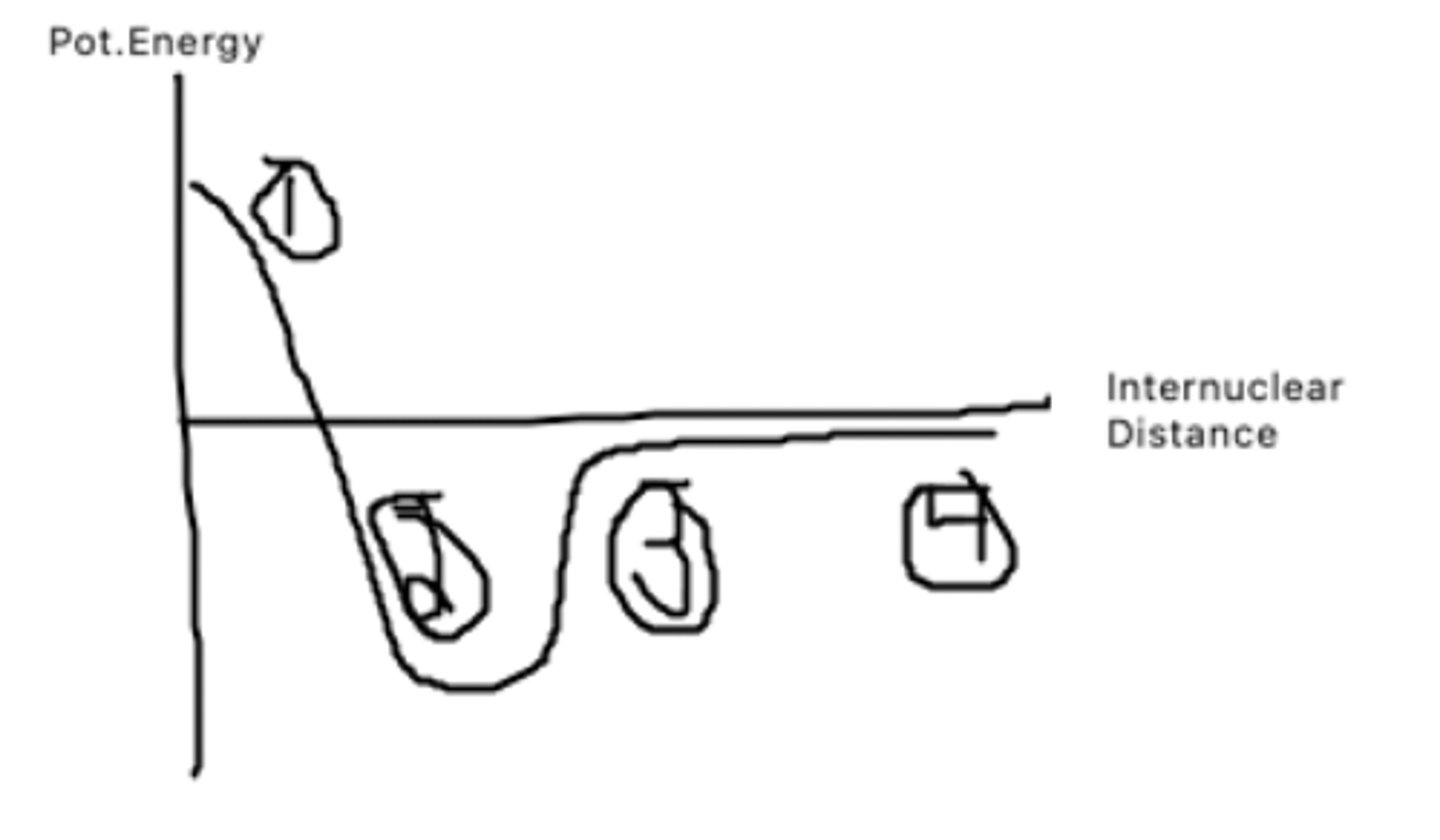
The atoms are getting farther apart, and pot energy is increasing as there is potential for the atoms to be doing other things.
What does point 3 represent?
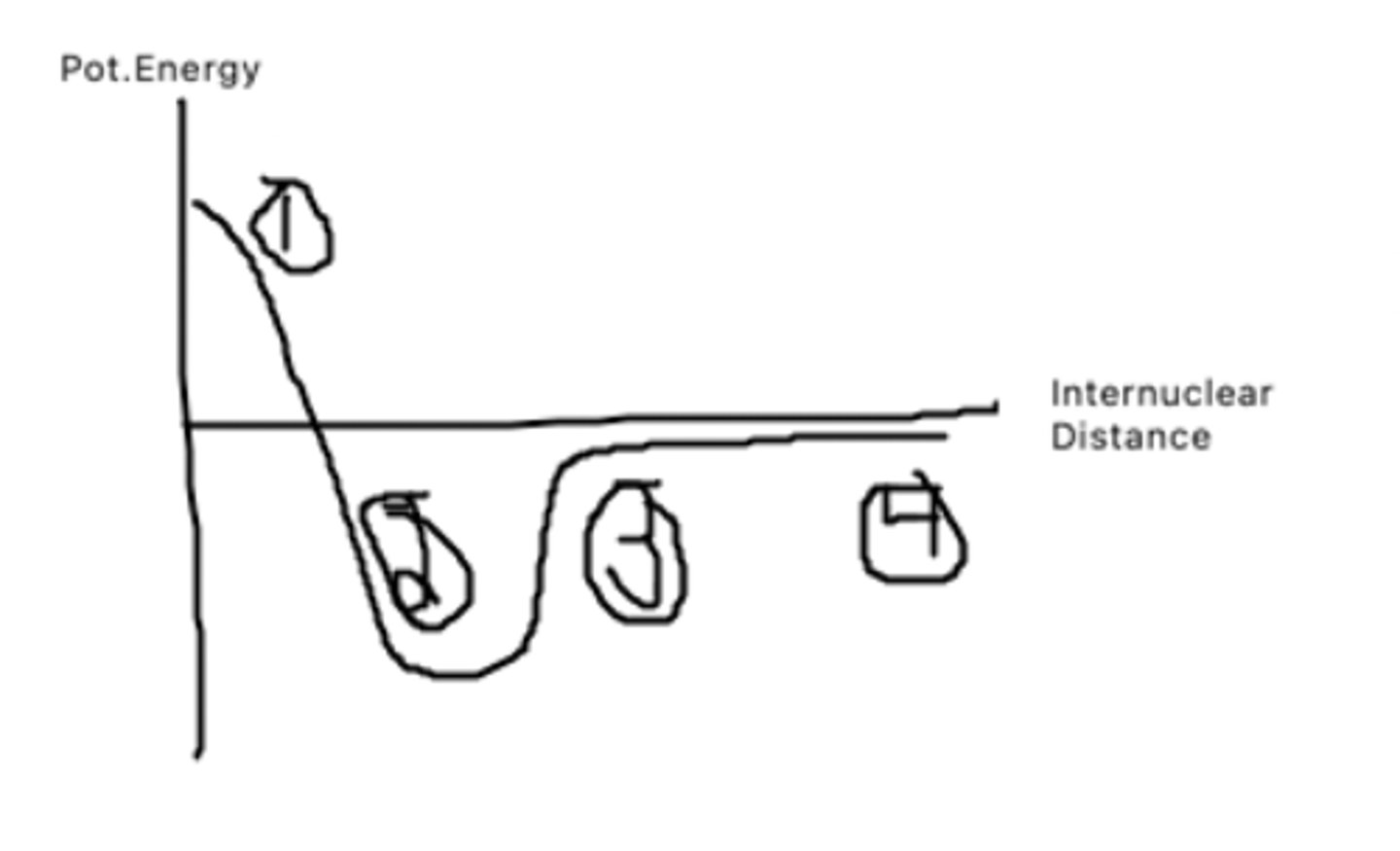
The atoms are very far apart and have barely any interaction with one another leading to a pot. energy of almost 0.
What does point 4 represent?
Breaking requires, forming releases
Does breaking a bond require or release energy? Forming?
200 kJ/mol
How much energy is required to break this bond?
#2
Which bond represents the strongest interaction?
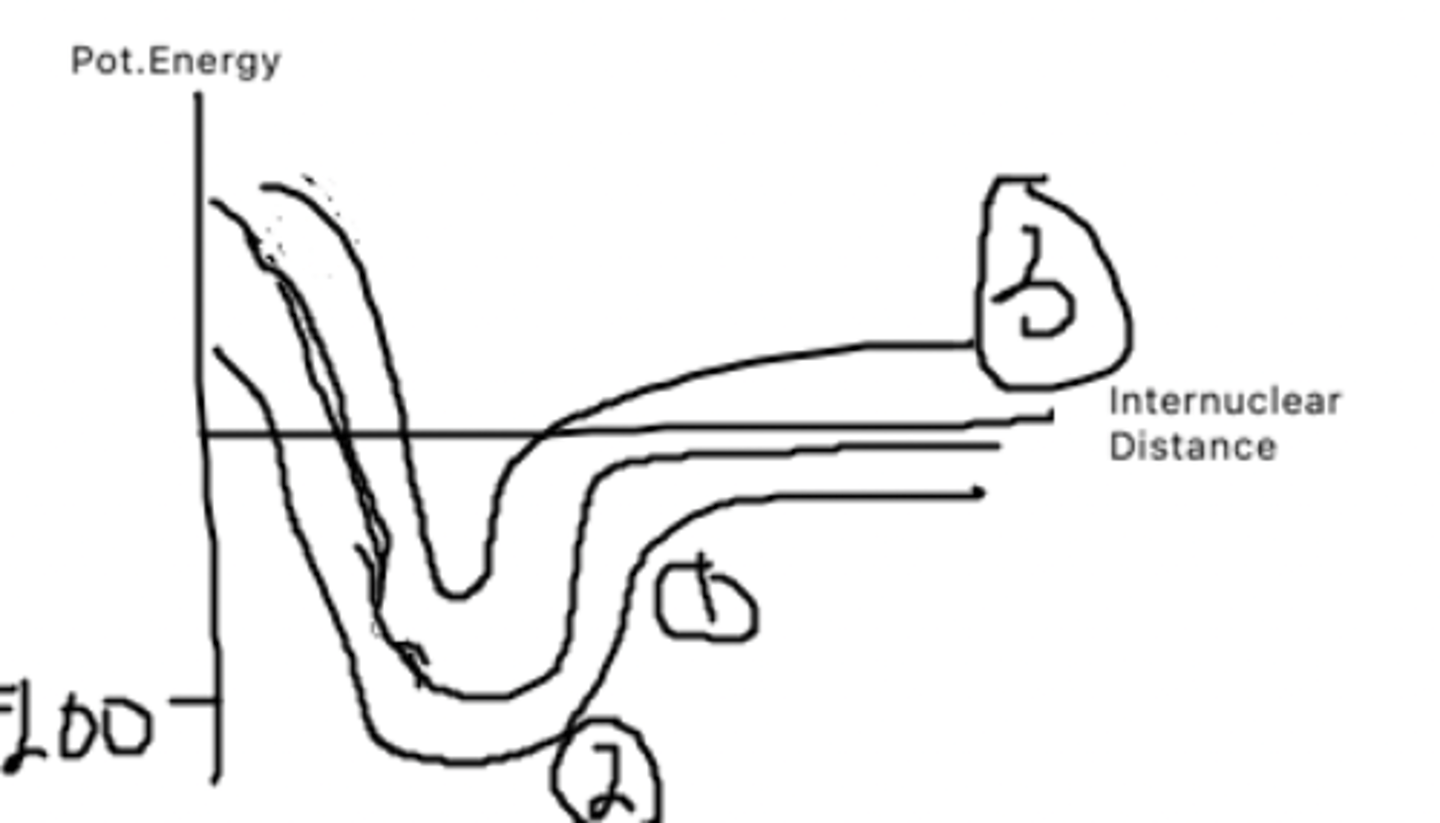
1. Covalent bonds
2. Ionic bonds
3. Ionic bonds in water
This graph represents: ionic bonds, ionic bonds in water, and covalent bonds. Which is which?
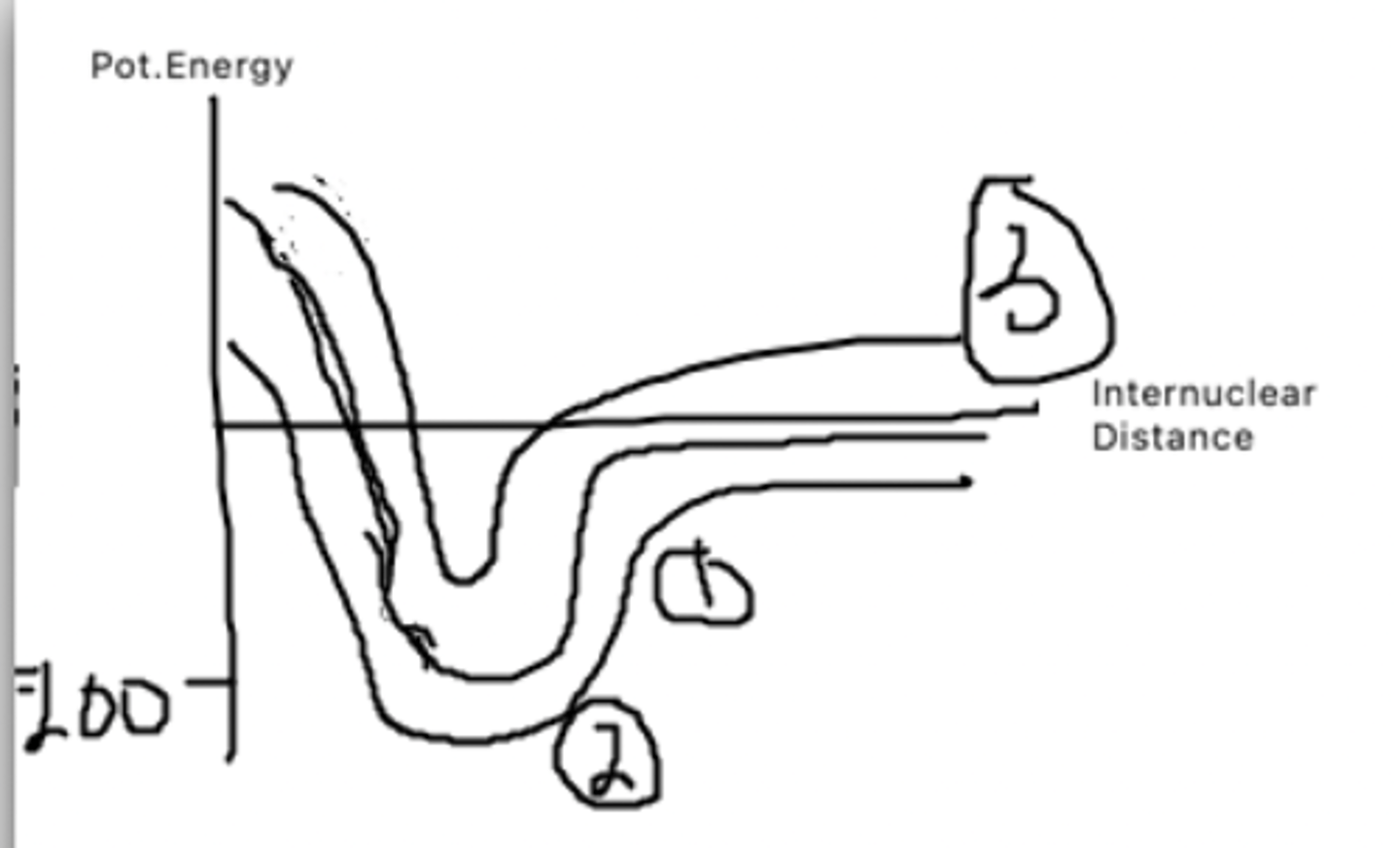
1. Hydrogen bonds
2. Polar covalent bond
3. Van der waals forces
This graph represnets hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and a polar covalent bond. Which is which?
When one atom completely steals an electron from another atom and they bind together
What is an ionic bond?
When a partially positive hydrogen atom binds with a partially negative oxygen or nitrogen
What is a hydrogen bond?
When its potential energy is the lowest
When is the bond most stable?
Due to random movement of electrons, tehre can be temporary dipoles in which there is a partial charge on one end of the molecule, which can induce a partial charge in another atom temporarily triggering a temporary attraction
What are van der Waals forces?
One that is generally polar and able to form hydrogen bonds with water
What is a hydrophilic molecule?
One that is generally non-polar and unable to form hydrogen bonds with water
What is a hydrophobic molecule?
1. Covalent bonds
2. Ionic bonds (in water)
3. Hydrogen bond
4. Van der Waals forces
Rank the bonds/electrostatic interactions in the amt of energy it would take to break them.
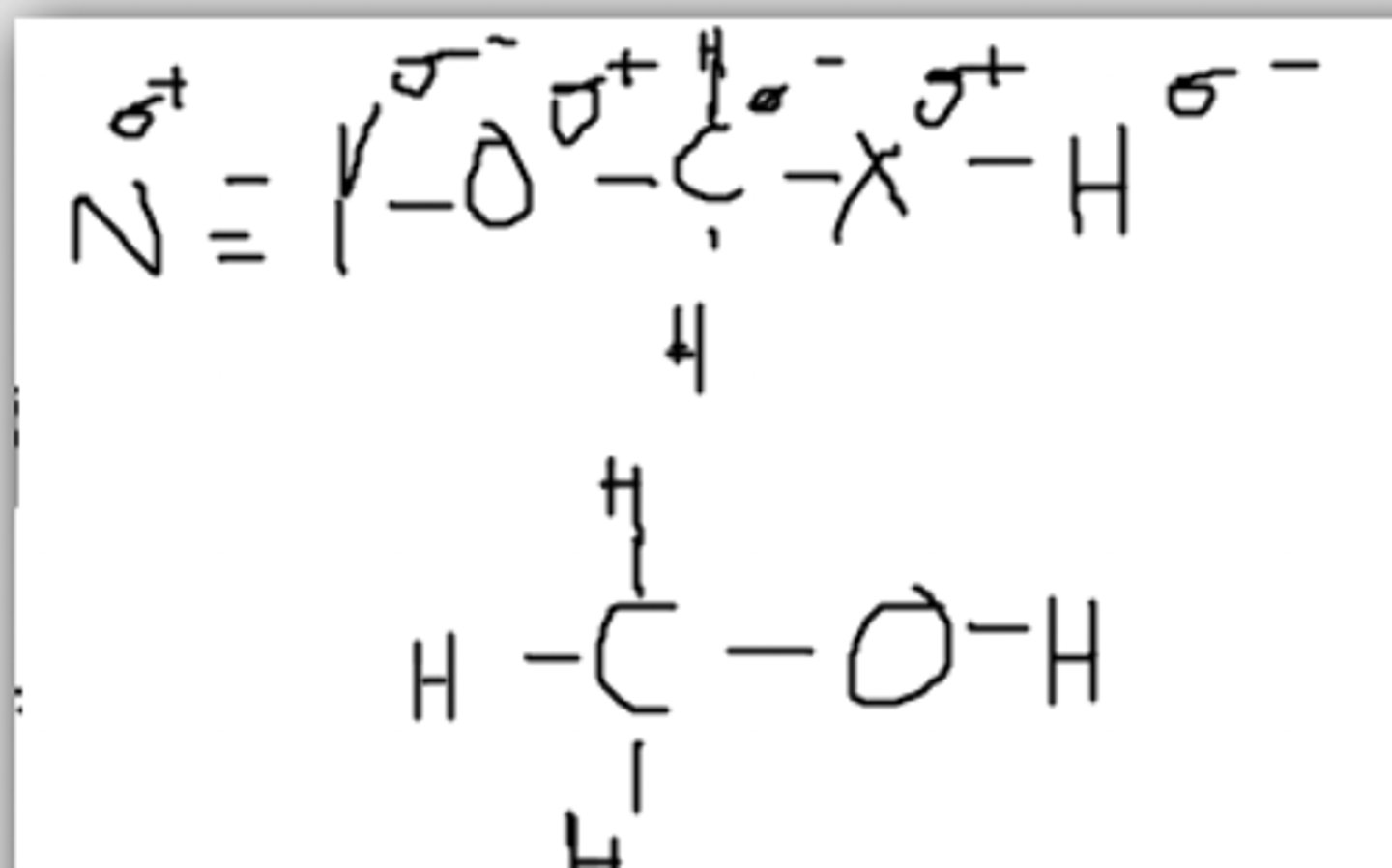
Yes, it can. The partially positive hydrogen can be attracted to a different partially negative Z.
Can this molecule hydrogen bond with itself? (Assume Z is an imaginary atom)
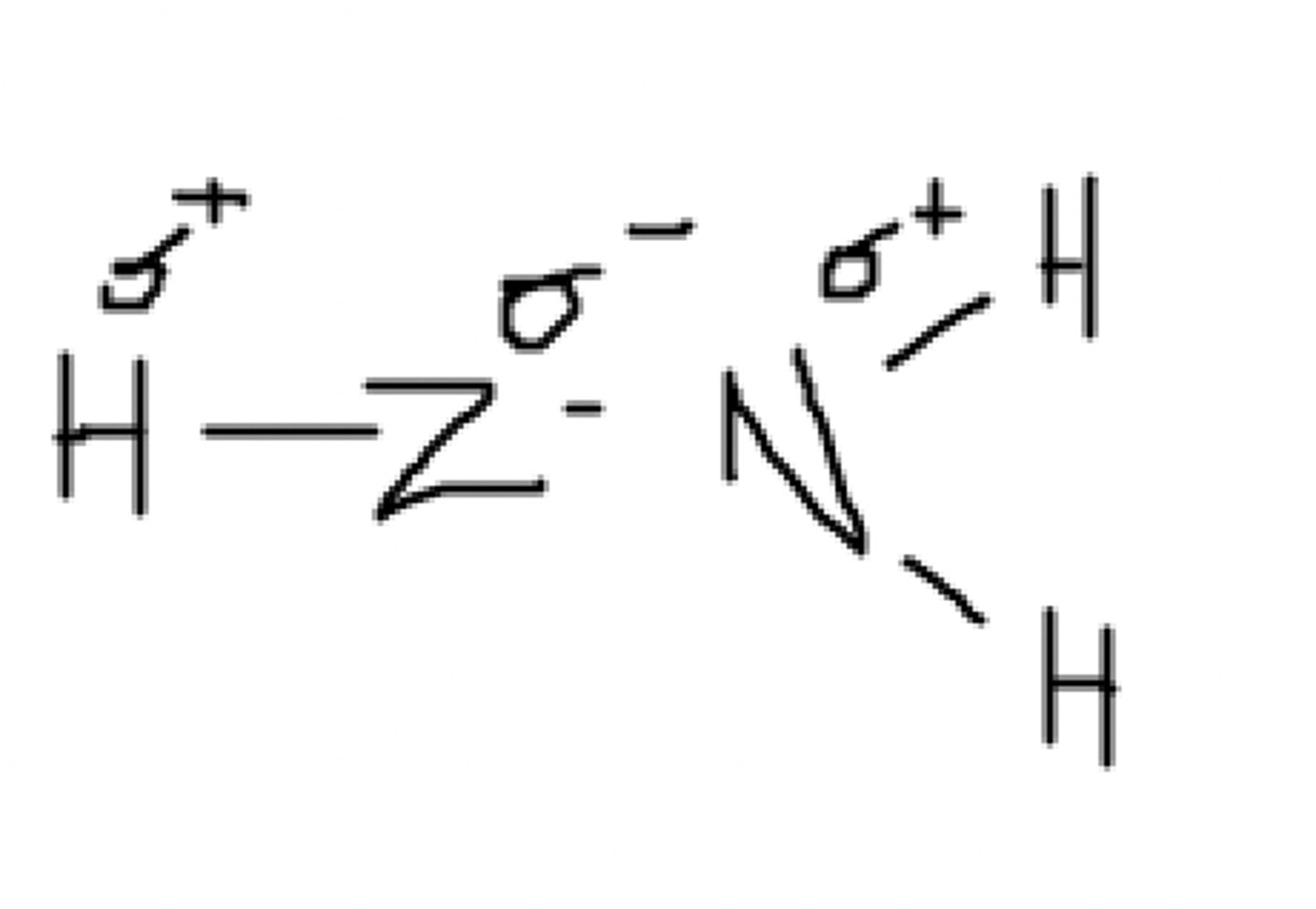
No, there is no partially negative molecule for the Hydrogen to be attracted to
Would there be hydrogen bonding between these two molecules?
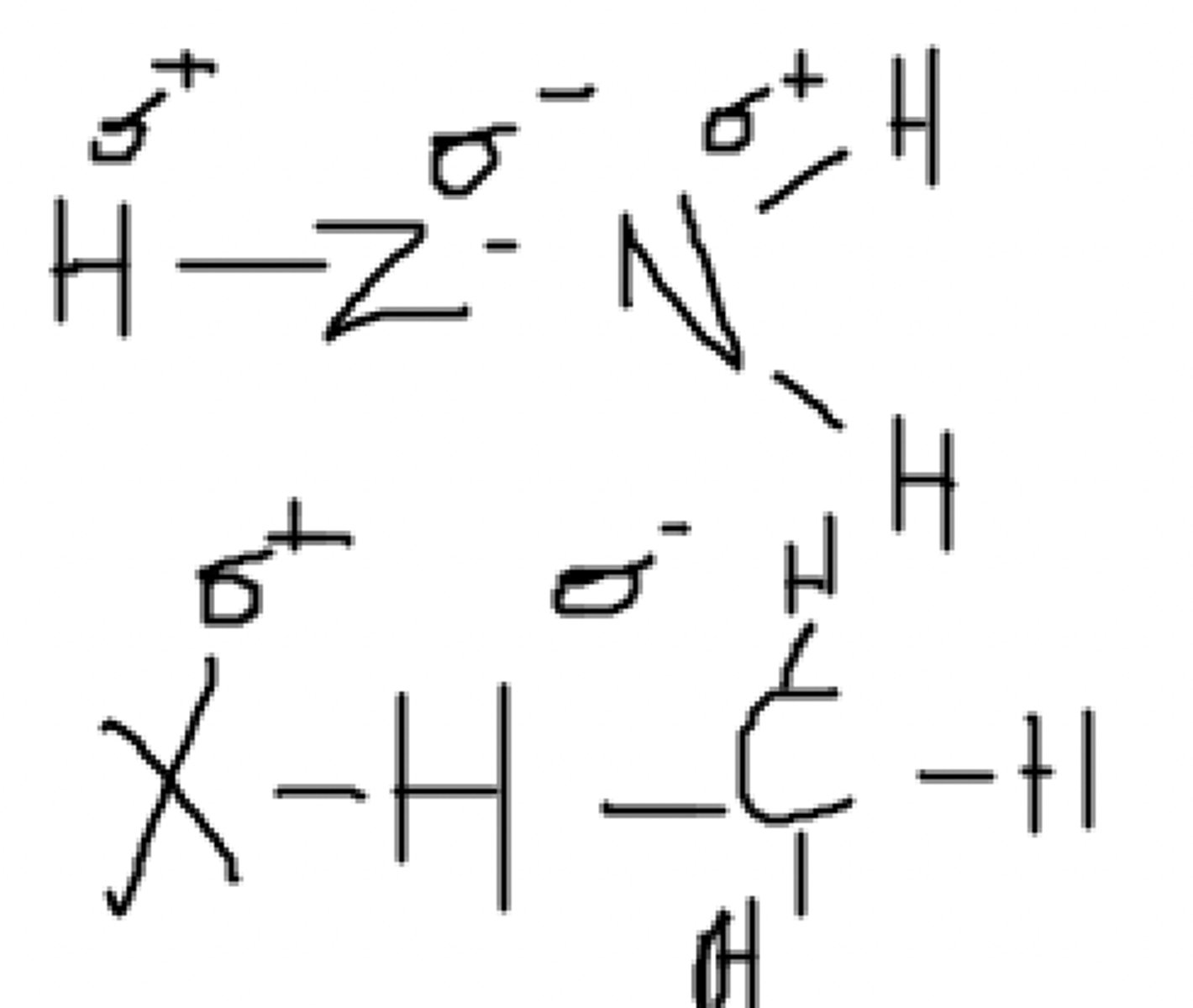
No, there is no partially positive hydrogen
Can this molecule hydrogen bond with itself?
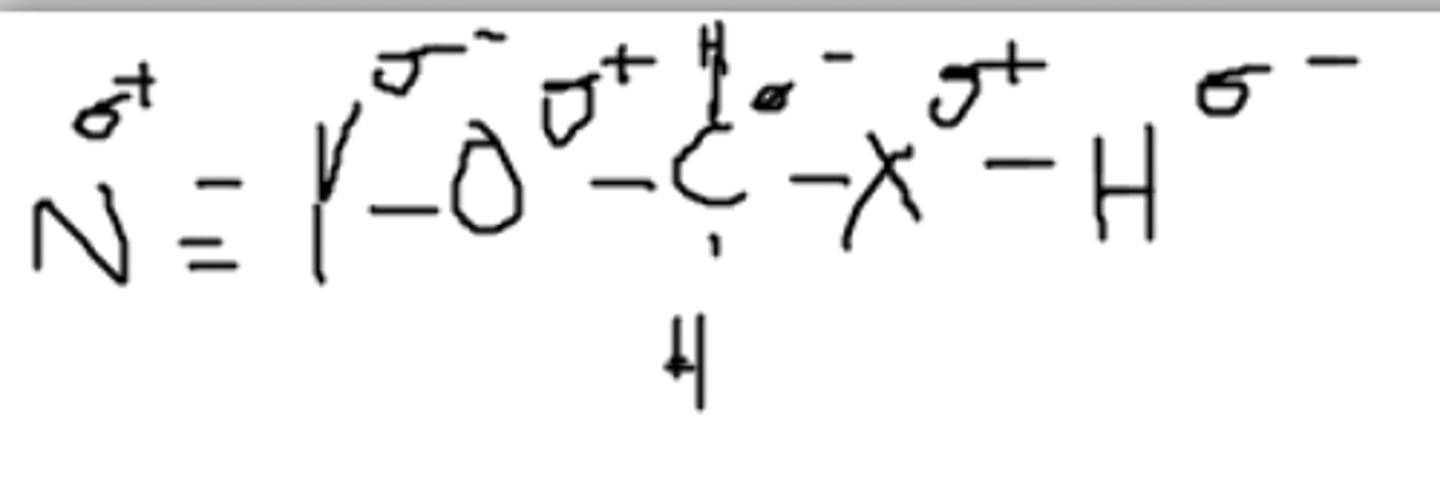
Yes, between the hydrogen on the second molecule and the Y on the first molecule (it is even more electronegative than oxygen!)
Can these two molecules hydrogen bond?
Yes, it can.
Can this molecule form hydrogen bonds with water?
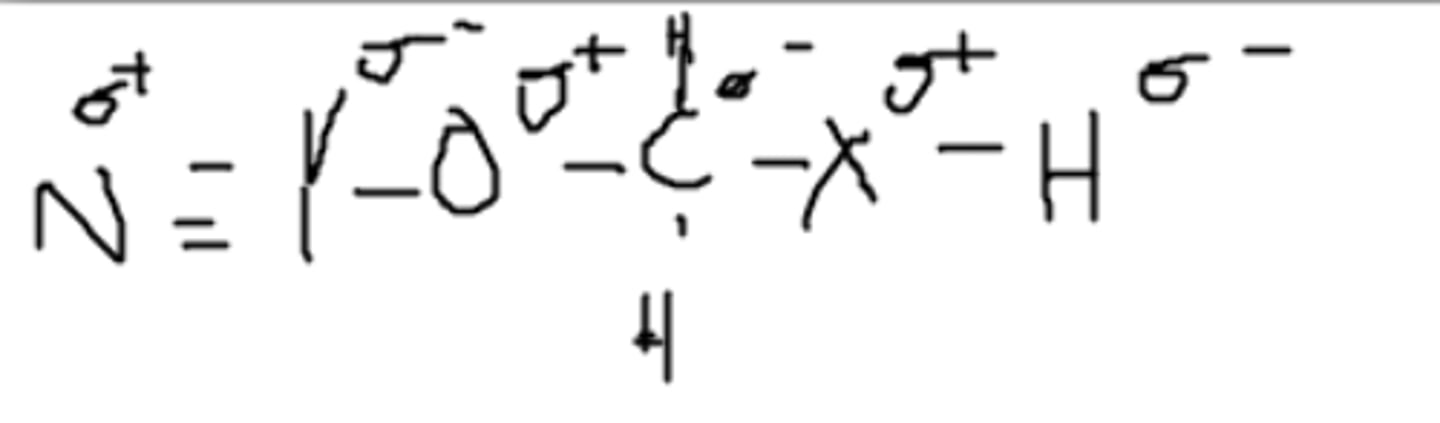
No, it is hydrophillic as it can form hydrogen bonds with water and thus would have a hard time passing through
Will this molecule be able to pass through the interior of the lipid bilayer?
Prokaryotic cells do not have organelles (lack internal compartments), prokaryotic cells have DNA in their nucleoid region and usually have plasmid, they are typically very small cells w/ a high surface area to volume ratio
What factors differentiate prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Plant cells have cell walls, chloroplast, vacuoles, and plasmodesmata
What factors differentiate plant and animal cells?
Cytoplasm is all the internal contents of a cell, while the cytosol is the gel-like substance that surrounds organelles in the cell
Differentiate between the cytoplasm and cytosol.
Prokaryote
You are studying cells in a lab and note a cell that seems to carry out all of its metabolic functions in the cytosol. What kind of cell is this likely?
Plant cell
You are studying cells in a lab and note a cell that when placed in a hypotonic solution does not burst. What kind of cell is this likely?
Prokaryote
You are studying cells in a lab and note a very small cell, yet one that is very efficient due to its surface area to volume ratio. What cell do you think this?
It produces a lot of the ATP the cell uses
What does a mitochondria do?
It is responsible for photosynthesis (production of sugars)
What does a chloroplast do?
It stores genetic information
What does the nucleus do?
Rough: protein production
Smooth: lipid production
What does the ER do?
Protein and lipid modification and helps package/sort molecules
What does the golgi apparatus do?
Breaks down molecules
What does the lysosome do?
Help contribute to structural rigidity of plants by contributing to turgor pressure
What does the vacuole do?
The cell is likely responsible for the production of many lipids
You are investigating a cell that has a very high concentration of smooth ER and vesicles. What is the function of the cell?
The cell is likely responsible for muscle contractons
You are investigating a cell that has a very high concentration of mitochondria and free-floating ribosomes. What is the function of the cell?
This cell is likely a part of an endocrine gland responsible for the production of non-stereoid hormones.
You discover a cell with a very high concentration of golgi apparatus and rough ER. What is the function of this cell?
Lysosomes
You are working with a cell responsible for breaking down antigens in the body. What would you expect to see a lot of in the cell?
Numerous ribosomes to produce protein channels to allow for ion transport
You are working with a cell responsible for communicating electrical signals. What would you expect to see a lot of in this cell?
Allows us to simplify a complex system and better communicate results with society
How can models of biological systems be useful?
It could cause you to make untrue assumptions and it fails to show function
What are the drawbacks of models of biological systems?
It involves a glycerol bonded to three fatty acids
Describe the structure of a triglyceride.
A chain of hydrocarbons
What is a fatty acid?
It is an amphipathic molecule with a polar phosphate head and two non-polar fatty acid tails
Describe the structure of a phospholipid.
Ring-like structure
Describe the structure of a cholesterol molecule.
Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen as they do not have a double bond in their hydrocarbon chain, while unsaturated fatty acids have less hydrogen and have a kink in their structure due to the presence of a double bond
Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
At room temp, saturated fatty acids are solids due to the fact that they are able to have more VDW interactions between them, while unsaturated fatty acids are liquid due to less VDW interactions
Describe the differnece in physical states between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
More saturated fatty acids = less fluid
More unsaturated fatty acids = more fluid
How do saturated/unsaturated fatty acids affect the fludiity of the plasma membrane?
The higher the temperature, the more fluid the membrane will be
How does temperature affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane?
Longer tails = more SA for VDW forces, less fluid
How does tail length affect the fludiity of the plasma membrane?
At low temperatures, cholesterol increases membrane fluidity by acting as a buffer stopping the phospholipids from getting too close, while at high temperatures, cholesterol decreases fluidity by holding the structure together
How does cholesterol affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane?
Smooth ER to produce cholesterol
A cell lives in a very cold enviornment. It wants to keep its membrane relatively fluid, what organelle should we expect to see a lot of in the cell?
This would mean crossing the hydrophobic portion of the membrane and they would usually like to avoid this
Why do the phospholipids rarely change sides?
Integral (embedded in the membrane), peripheral (attached to the membrane)
What are the two types of proteins found in the plasma membrane?
It will have polar sides that interact with the extracellular space/cytoplasm while having nonpolar interior to interact with the hydrophobic plasma interior
Explain the polarity of an integral protein.
This would happen in a hydrophobic/oily enviornment
Explain in which kind of enviornment this arrangment would happen.
In a hydrophillic/aqueuous enviornment
Explain in which kind of enviornment we would likely see a liposome.
The passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient
What is diffusion?
A saturated fatty acid is not an amphipathic molecule and therefore would not be able to be very selective in what gets in/out, while phospholipids are best fit to get this job done due to their amphipathic nature
Why couldn't a saturated fatty acid act as a semipermeable membrane while a phospholipid bilayer can?
Tonicity refers to the solute concentration in one solution compared ot another
What does tonicity mean?
Primary active transport is powered by the use of ATP, while secondary active transport is powered by an electrochemical gradient
Differentiate primary and secondary active transport
Carriers/channels
What are the two types of facilitated diffusion proteins?
A symport pumps molecules in the same direction, while an antiport pumps them in the opposite direction.
Explain the difference between an antiport and symport.
1. Small, non-polar molecules
2. Small, polar molecules
3. Large, polar molecules
4. Ions
Rank classes of the molecules based on how permeable they would be.
The C3H3NO
Which molecule is more likely to pass through the lipid membrane?
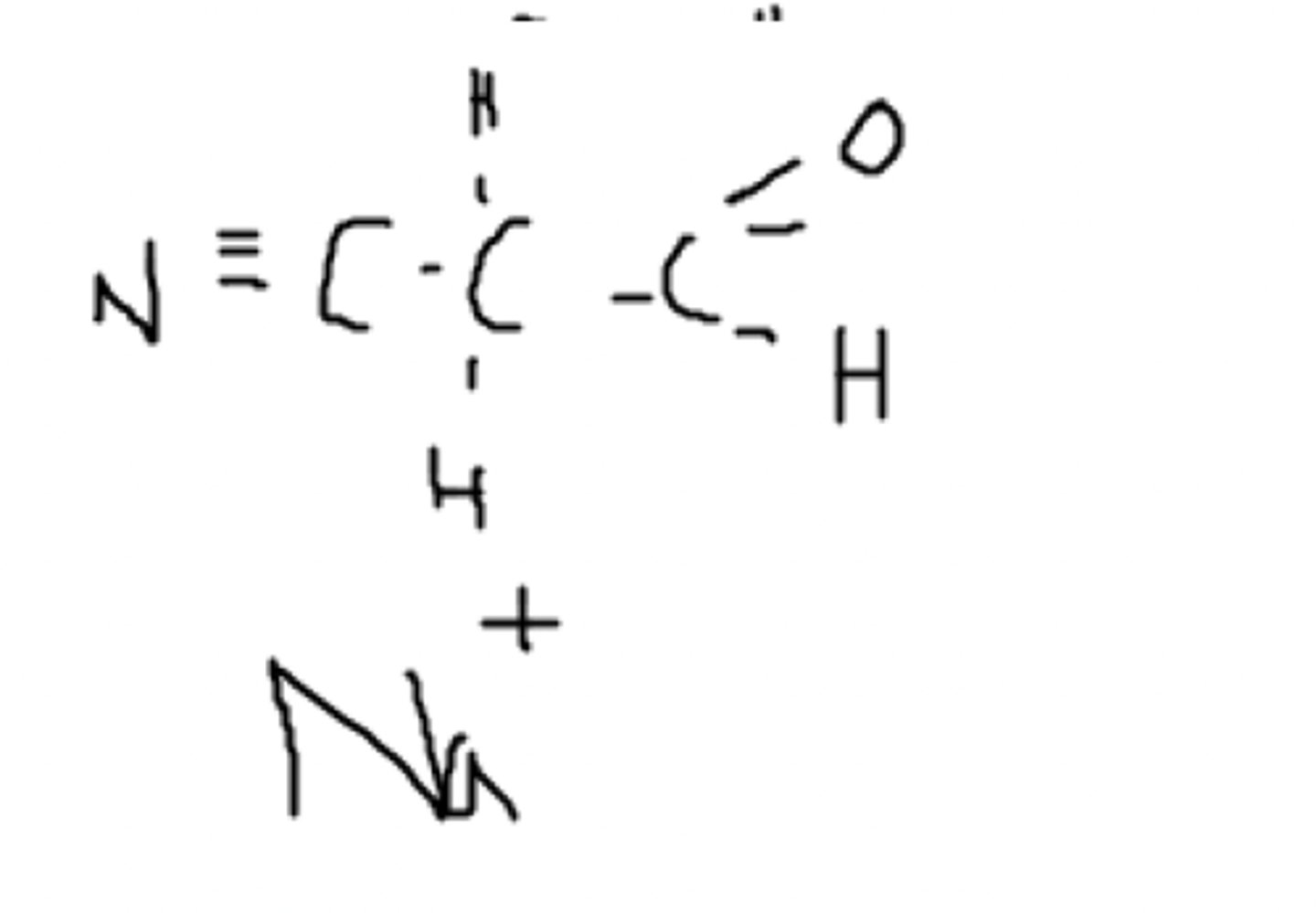
A large steroid
What molecule is more likely to pass through a lipid membrane: a large steroid or a large protein?
Water will flow out of the cell
A cell is placed in a hypertonic solution. Where will water flow?
Hypertonic
The right side of the beaker is ____ to the left side.
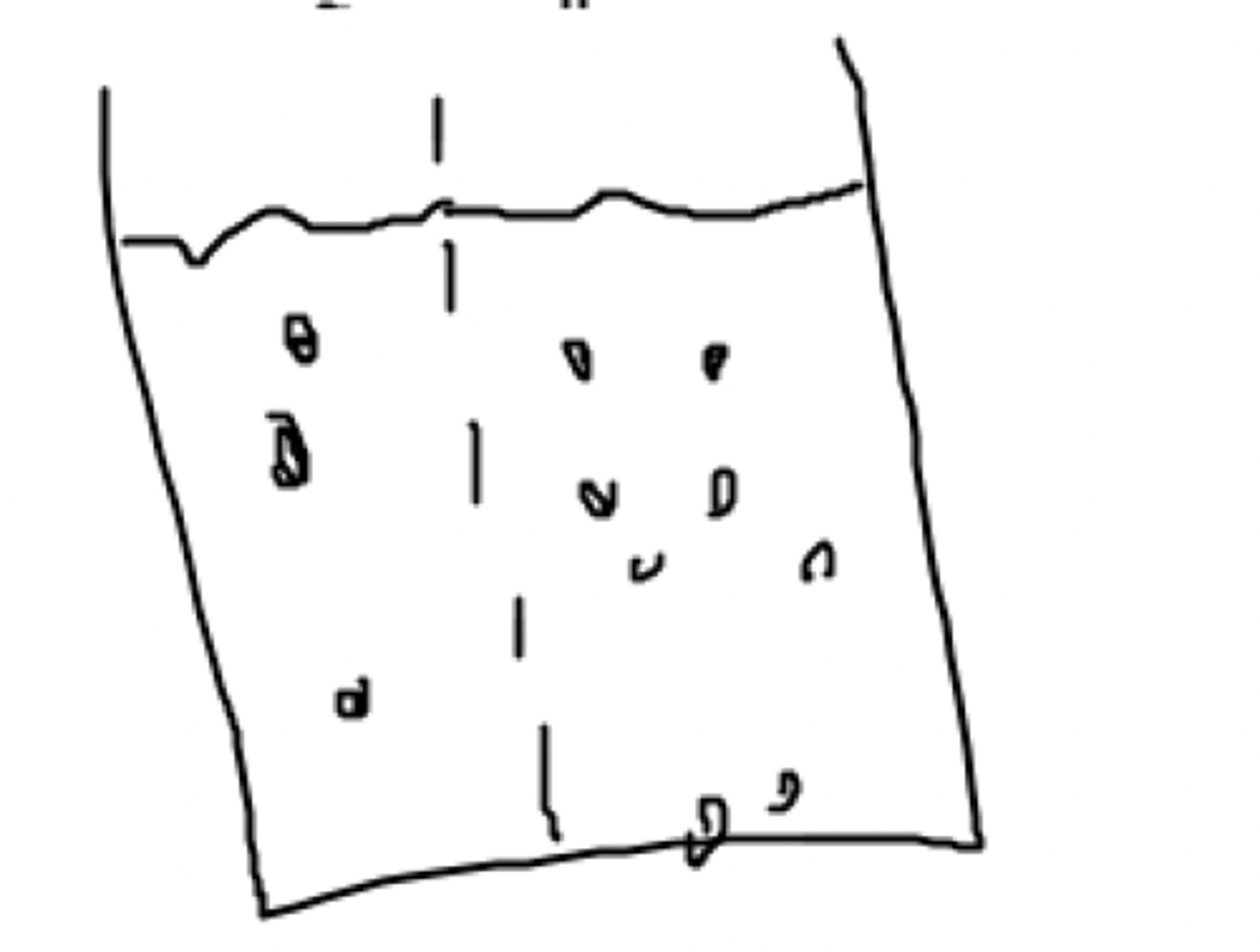
They will become isotonic to each other as water moves from the left side to right side
Assuming that the movemnet of water is allowed through the membrane, what willl happen to the comparative tonicity of the two solutions?
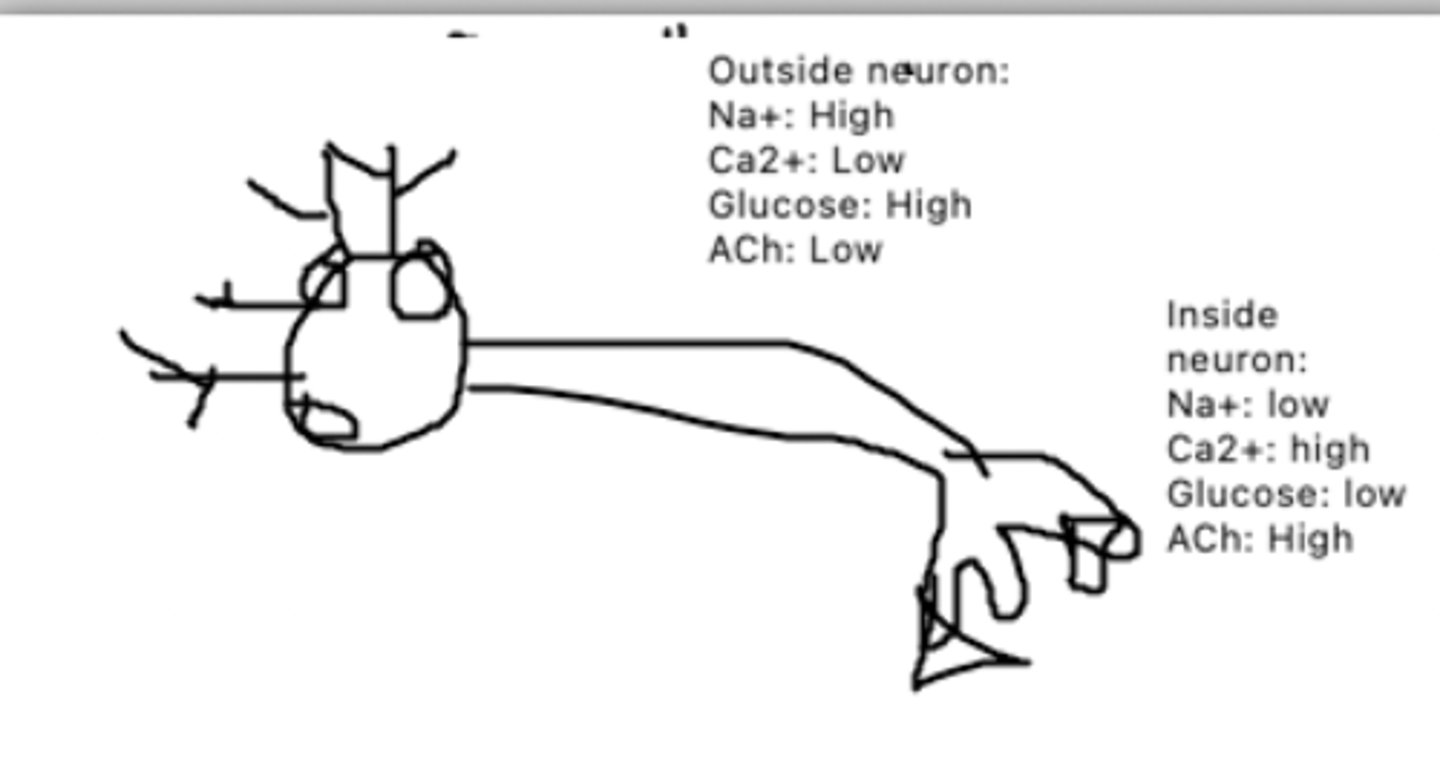
Na+/K+ pump: primary active transport
Glucose/Ca2+ co transporter: secondary active transporter
ACh channel: facilitated diffusion
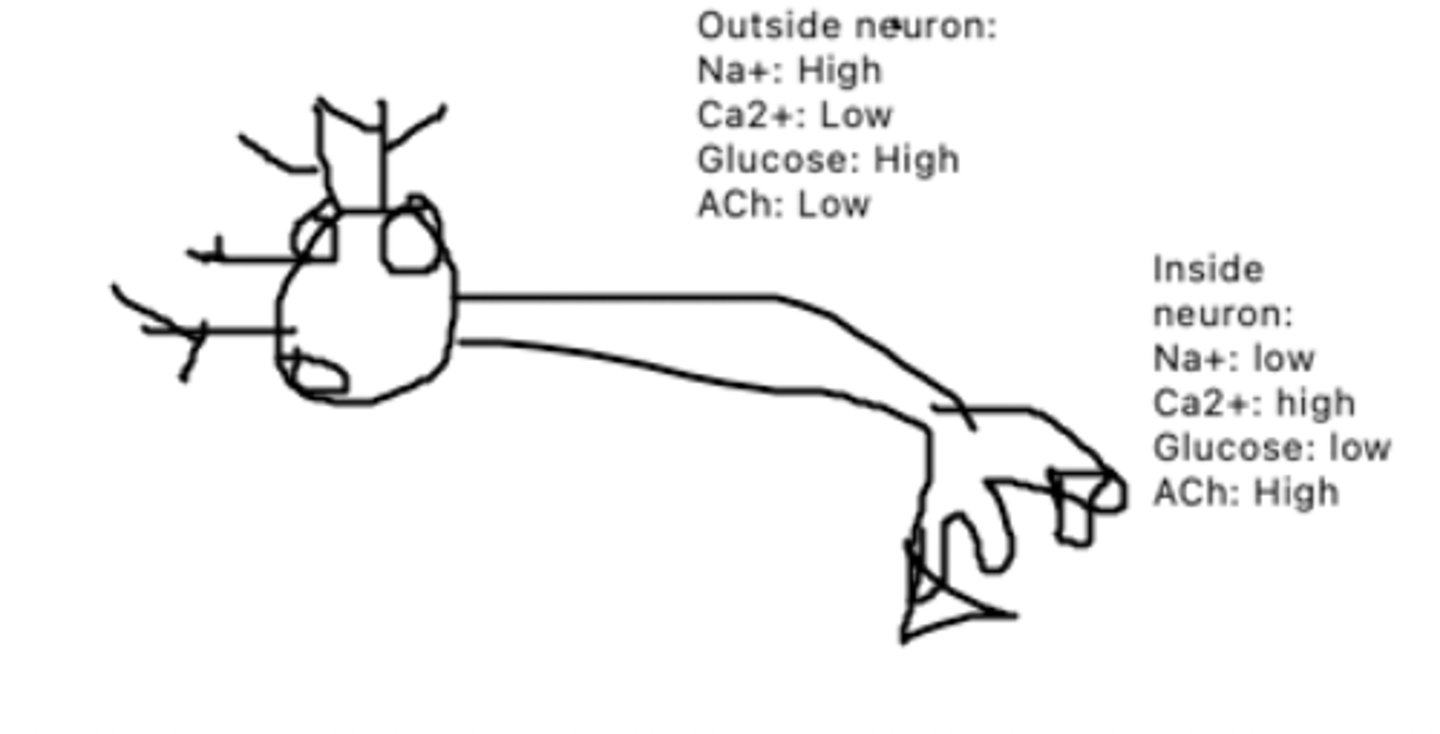
This is a diagram of a neuron. The circle proteins represent Na+/K+ pumps. The triangle proteins represent Glucose/Ca2+ cotransporters, while the square proteins represent ACh channels. What mechanism of transport is each channel?
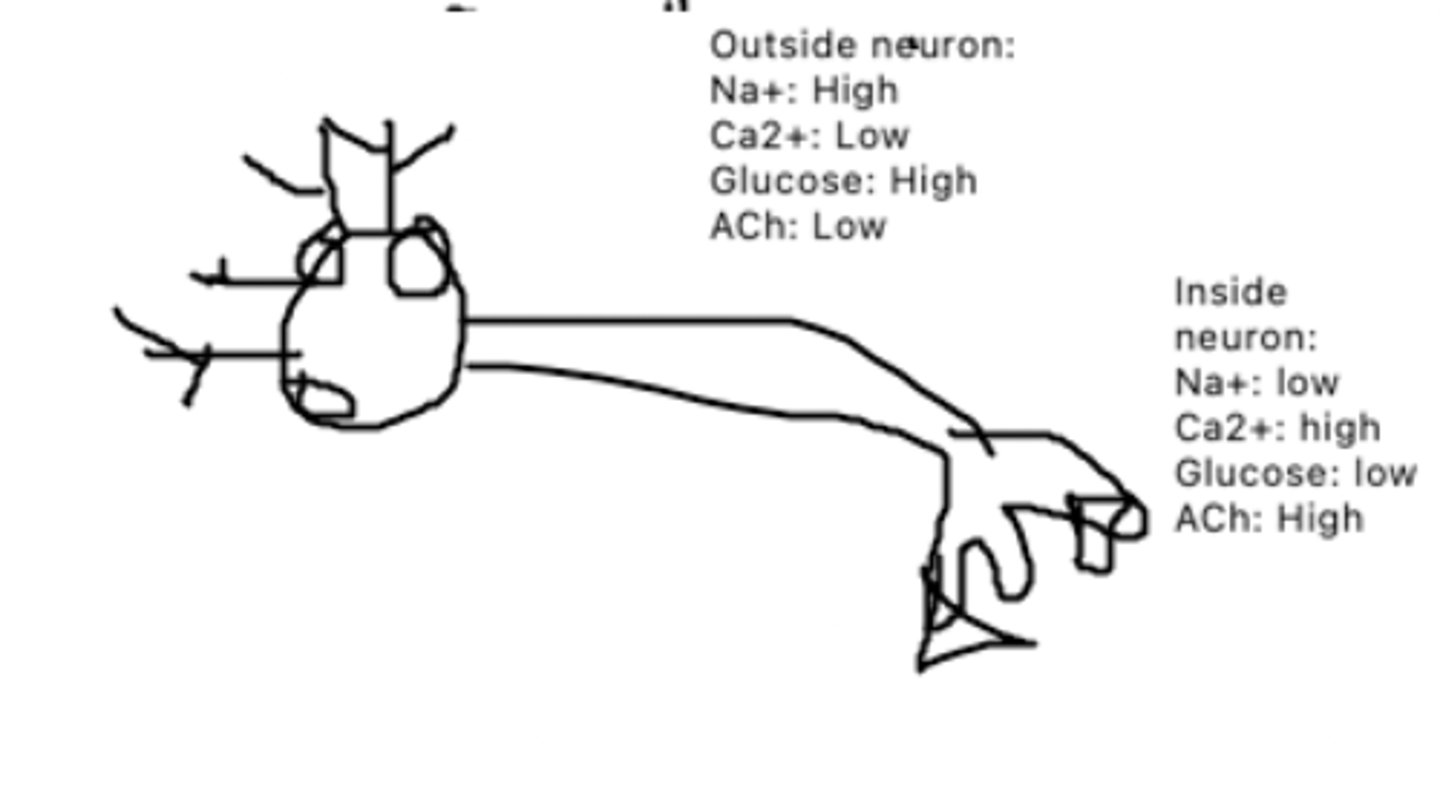
Na+: out, K+ in
Glucose: out of the cell
Ca2+ out of the cell
ACh: out of the cell
This is a diagram of a neuron. The circle proteins represent Na+/K+ pumps. The triangle proteins represent Glucose/Ca2+ cotransporters, while the square proteins represent ACh channels. How will each molecule be moving?
Oxygen can enter via simple diffusion, and water can enter via an aquaporin or facilitated diffusion
This is a diagram of a neuron. How could oxygen enter this neuron? Water?
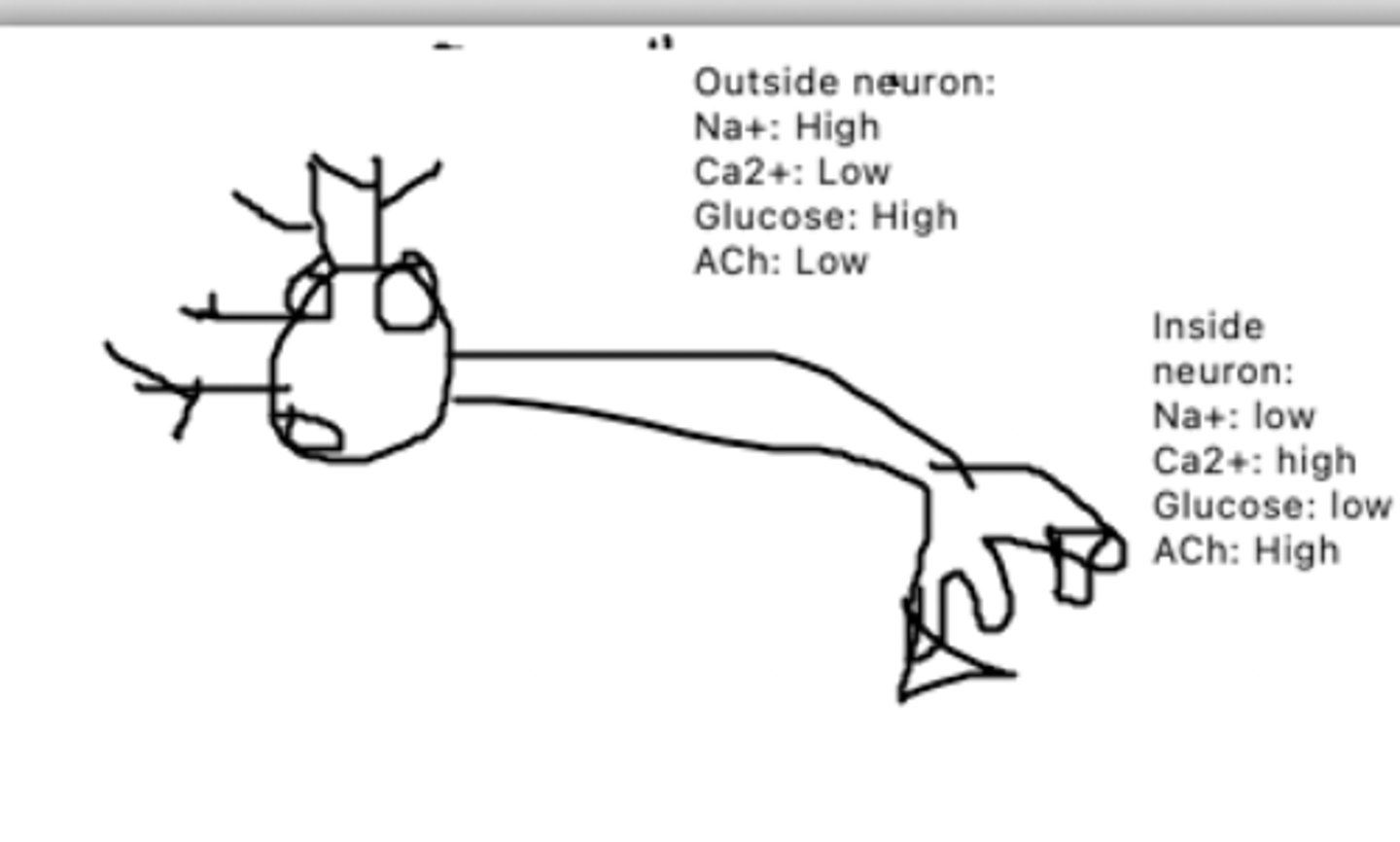
Ca2+ concentration inside the neuron would increase, while glucose concentration inside the neuron would increase
This is a diagram of a neuron. The circle proteins represent Na+/K+ pumps. The triangle proteins represent Glucose/Ca2+ cotransporters, while the square proteins represent ACh channels. How would transportation be affected if the Ca2+/glucose co transporter broke?
The entire set of chemical reactions in a cell
What is metabolism?
The breaking down of large molecules to simpler ones
What is catabolism?
The building up of more complex molecules from simple building blocks
What is anabolism?
Catabolism
In this chemical reaction, a large carbohydrate is broken down into its glucose monomers. What kind of chemical reaction would we consider this to be?
Kinetic energy: energy associated w/ movement
Pot. energy: energy that is stored (in chemical bonds)
What does kinetic energy refer to? Potential energy?
Release, require
Does making a bond require or release energy? Breaking a bond?
Anabolic pathways require us to both break and form bonds, and as a result, the net Gibbs free energy change for this pathway will be positive causing us to have put in energy
How can it be that making a bond releases energy, yet anabolic pathways require energy?
Energy is conserved, energy can be neither created nor destroyed
What does the first law of thermodynamics state?
More stable bonds have less chemical energy, while less stable bonds have more chemical energy
Explain the relationship between bond energy and the stability of the bond.
Transformations of energy always increases universal entropy
What does the second law of thermodynamics state?
The total energy in the system
What does enthlapy refer to?