MBIO 3401 Exam 1 Study
1/207
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fall 2024 TTU Microbiology Exam 1 study guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
Koch’s Postulates
Microbe is in all cases of the diseased, but absent in healthy individuals
The microbe is isolated from the diseased host and grown in a culture
When the microbe is introduced to the healthy host, disease occurs
The same microbe strain is obtained from the newly diseased host
The criteria for establishing a causative link between an infectious agent and a disease
Koch’s Postulates
inoculated smallpox
Lady Mary Montagu
Made vaccination for smallpox from cowpox
Edward Jenner
Developed vaccines from weakened strains
Louis Pateur
Immunization
Stimulation of an immune response by deliberate inoculation with a reduced pathogen
Ignaz Semmelweis
ordered doctors to wash hands with chlorine and mortality rates decreased
Joseph Lister
Used carbolic acid to treat wounds and clean surgical tools
What are the principles for effective light microscopy?
Contrast, magnification, a wavelength smaller than the object, proper lighting, and focused lenses
Which methods in microscopy use interference?
Phase contrast microscopy (PCM) such as differential interference contrast microscopy (DIC)
Fluorescence Microscopy
specimen absorbs light of a defined wavelength and then emits lower light with longer wavelength so that specimen glows
Used to view marine and pathogenic bacteria
type of interference microscopy
Chemical Imaging Microscopy
uses mass spectrometry to see chemicals in cells
Dark-field optics
microbes appear as halos of bright light against darkness
detects of very narrow cells unresolved by bright-field microscopy
Phase-Contrast Microscopy (PCM)
uses differences in refractive index between the cytoplasm and the surrounding medium/organelles
Used to see live cells and organelles
Paramecium
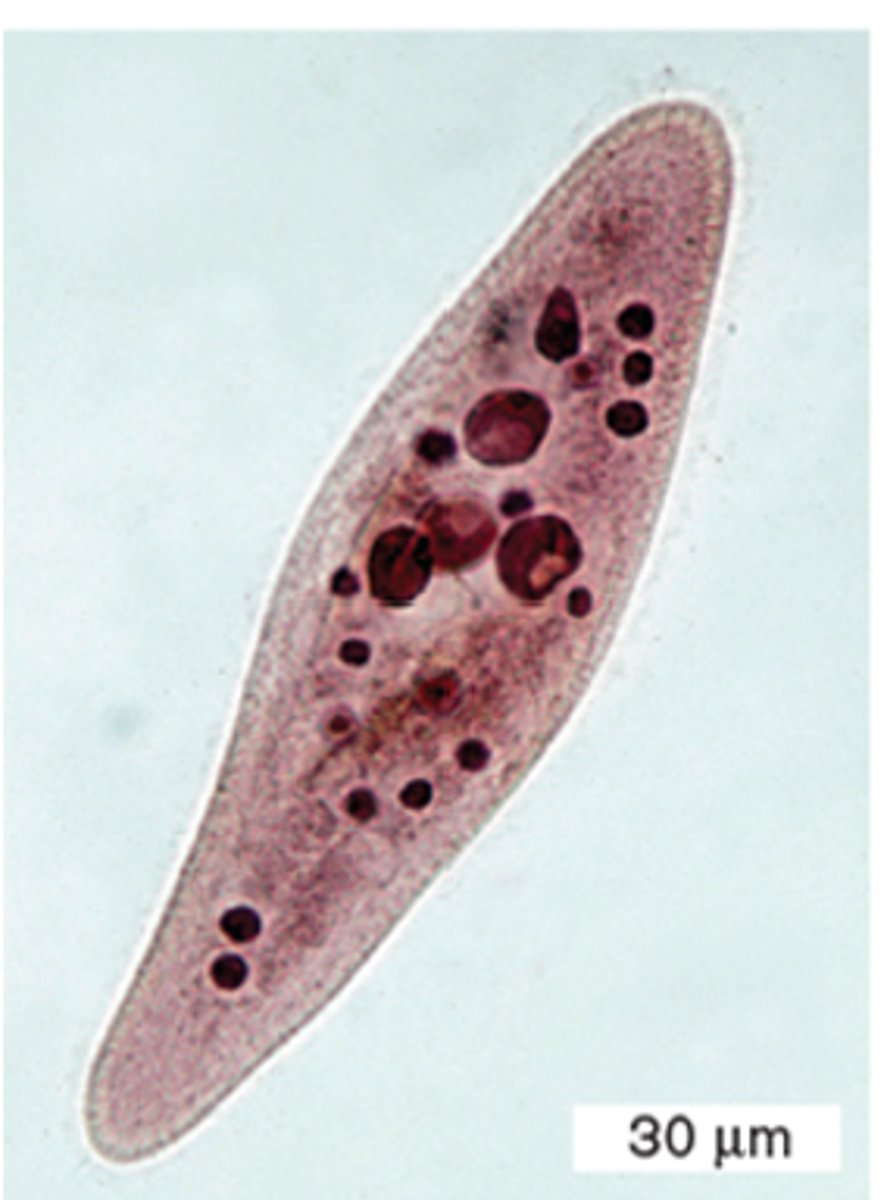
30 um; visible to human eye; stained light microscopy
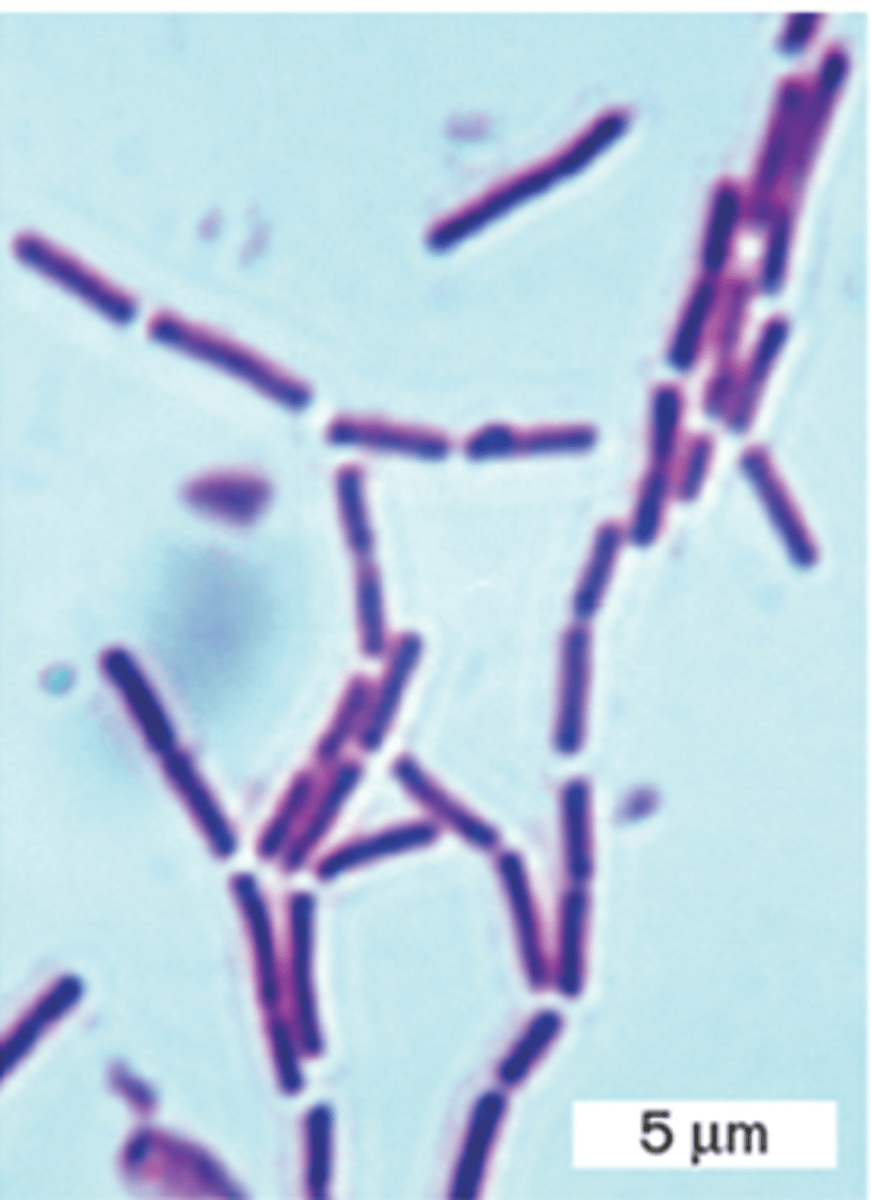
Pseudomonas
5 um; stained light microscopy
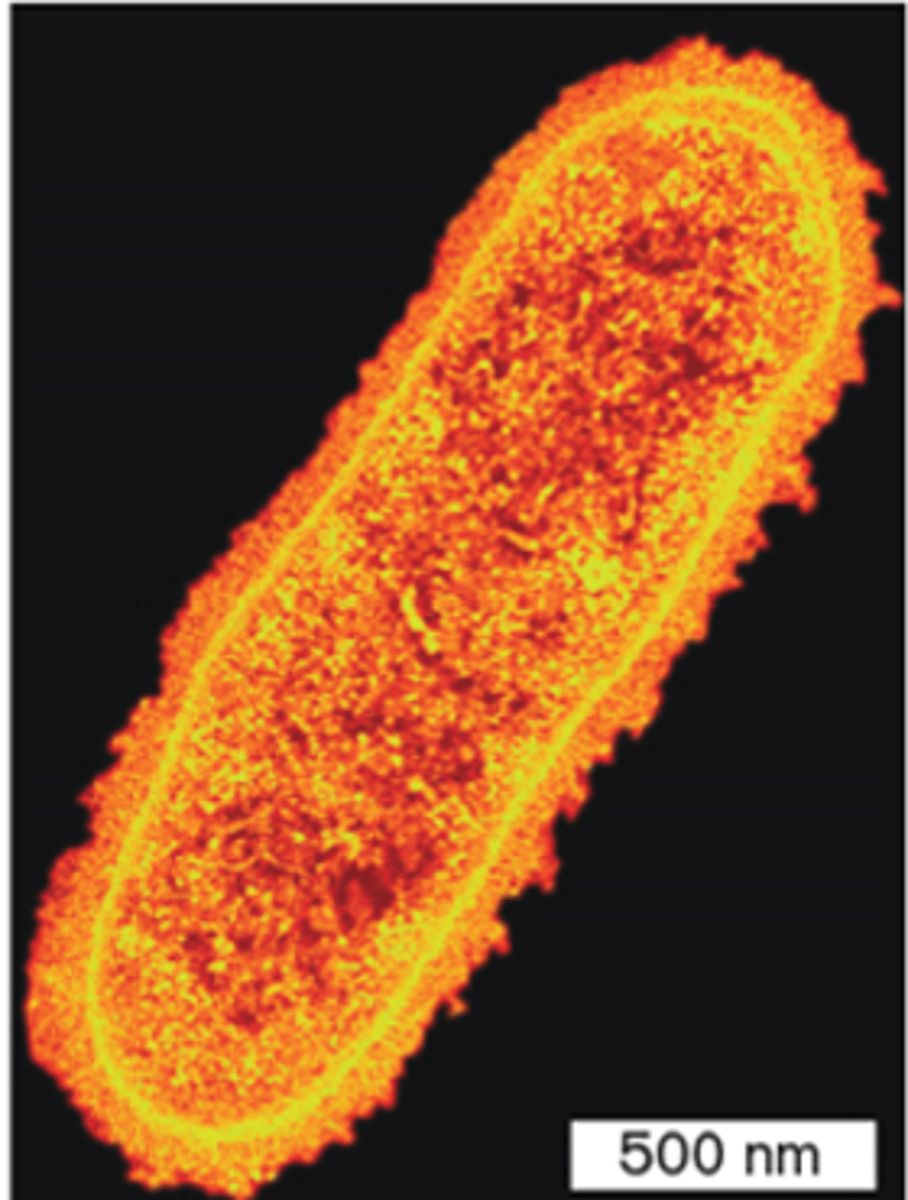
E. Coli
transmission electron microscopy
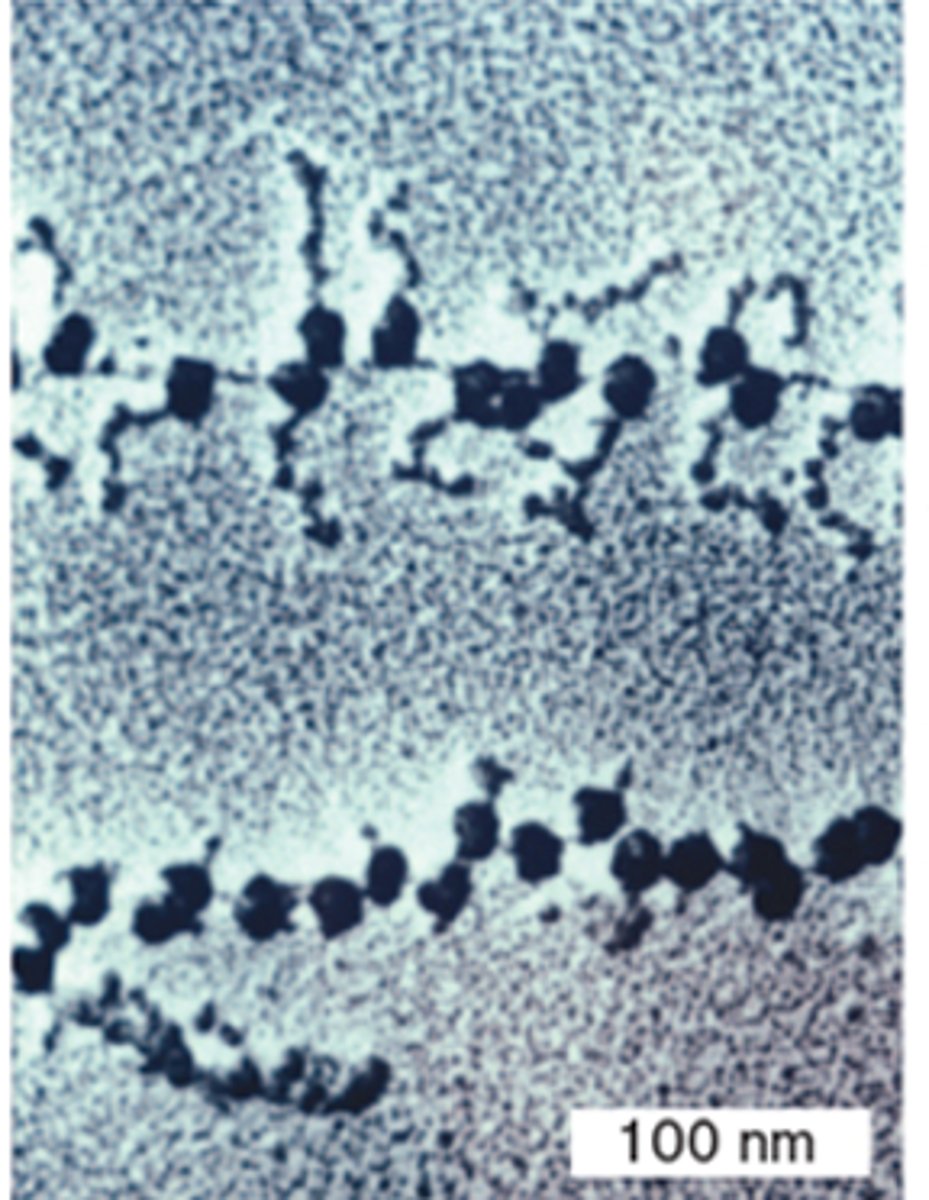
Ribosomes on mRNA
transmission electron microscopy
Autotrophs
gain energy from fixing CO2 and assemble into organic molecules
Heterotrophs
gain energy from organic molecules
Phototrophs
gain energy from chemical rxns triggered by light
Chemotrophs
gain energy from oxidation reduction rxns
Lithotrophs
gain electrons from inorganic molecules
Organotrophs
gain energy from organic molecules
Generation Time - time it takes for a population to double
(final cell number) = (original cell number) x (2^(n ~ number of generation)
Nt = N0 × 2^n
Extremophiles
organisms inhabiting any ecological niche outside normal conditions
Hyperthermophile
grows in temps >80 C
Alkaliphile
grows above 9 pH
Halophile
grows in high salt content
Barophile
growth at pressure >380 atm
Thermophile
grows in temps 50 C - 80 C
Mesophile
grows in temps 15 C - 40 C
Acidophile
grows below 3 pH
Psychrophile
grows at temp <15 C
Who developed the earliest immunizations? What diseases were they for?
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) developed the first vaccines based on attenuated (weakened) strains.
-Fowl cholera
-Rabies
Microbes live and grow just about everywhere on Earth, except:
A) Between your teeth after brushing and flossing.
B) On your cell phone.
C) In microscopic aerosols that we breathe.
D) Above 100°C or below minus 40°C.
E) None of the above.
E) None of the above
The first vaccination was performed by
and the first antibiotic was discovered
by
A) Lady Montagu; Louis Pasteur
B) Edward Jenner; Louis Pasteur
C) Edward Jenner; Alexander Fleming
D) Louis Pasteur; Alexander Fleming
E) Louis Pasteur; Edward Jenner
C) Edward Jenner; Alexander Fleming (penicillin)
Which of the following statements about the size of microbes is FALSE?
A) Eukaryotic microbes tend to be 2-20 nm.
B) Prokaryotic microbes tend to be less than 10 um.
C) A few bacterial species are large enough to be seen by the unaided eye.
D) None of the above statements is false.
C) Eukaryotic microbes tend to be 2-20 nm.
Which of the following transport mechanisms is unique to prokaryotes?
A) Simple diffusion
B) Facilitated diffusion
C) Coupled transport
D) Siderophores
E) Group translocation
E) Group translocation
All of the following statements about ABC transporters are true EXCEPT
A) They require energy
B) They are found only in prokaryotes
C) They can be used for import and export
D) They are the largest family of transporters
E) They are found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
B) They are found only in prokaryotes
What kind of culture transfer would most likely result in the shortest observed lag period?
A) From a complex medium to a fresh complex medium
B) From a complex medium to a minimal medium
C) to a medium at a different temperature
D) to a medium at a different pH
A) From a complex medium to a fresh complex medium
Bacterium Thi scourse has a generation time of 20 minutes. Starting with one cell in log phase, how many minutes does it take to produce about 1,000 cells? Assume all cells remain viable.
200
Why can't bacteria grow in solutions with very high concentrations of sugar?
A) Bacteria cannot digest pure sugar
B) Sugar contains toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS)
C) Sugar lowers the solution's osmolarity
D) Sugar raises the solution's osmolarity
E) Sugar raises the solution's pH
D) Sugar raises the solution's osmolarity
Which organism will grow most evenly throughout a tube of thioglycolate broth medium?
A) Strict aerobe
B) Microaerophile
C) Facultative aerobe
D) Aerotolerant anaerobe
E) Strict anaerobe
D) Aerotolerant anaerobe
Which of the following is NOT correctly defined?
A) Sanitation: killing of all living organisms
B) Disinfection: killing or removal of pathogens from inanimate objects
C) Sterilization: killing of all living organisms
D) Antisepsis: killing or removal of pathogens from the surface of living tissues
E) None of the above
A) Sanitation: killing of all living organisms
Laminar flow biosafety cabinets typically force air through HEPA filters which
-remove ~ 90% of airborne particulates 3 um or larger
-remove > 99.9% of airborne particulates 0.3 um or larger
-remove ~90% of airborne particulates
30 um or larger
-remove > 99.9% of airborne particulates 0.3 nm or larger mm or larger
-remove only airborne particulates 3
remove > 99.9% of airborne particulates 0.3 um or larger
What is the molecular basis of the antibiotic action of Penicillin?
-Penicillin inhibits protein synthesis
-Penicillin inhibits DNA replication
-Penicillin prevents peptidoglycan synthesis
-Penicillin prevents cell wall formation
-C and D
C and D
Which of the following statements about membrane lipids is true?
-Lipids of bacteria have ether linkages, while those of archaea have ester linkages.
-Lipids of bacteria have ester linkages, while those of archaea have ether linkages
-Lipids of bacteria and archaea have ester linkages.
-Lipids of bacteria and archaea have ether linkages.
Lipids of bacteria have ester linkages, while those of archaea have ether linkages
Which of the following is NOT a component of peptidoglycan?
-Peptide cross-links
-Amino acids
-Lipopolysaccharide
-N-acetylglucosamine
-N-acety|muramic acid
Lipopolysaccharide
All of the following are true about the prokaryotic outer membrane EXCEPT:
-It is composed of a simple phospholipid bilayer.
-It is found only in Gram-negative bacteria.
-It contains porins.
-It contains a toxic component.
-It contains a lipopolysaccharide layer.
It is composed of a simple phospholipid bilayer.
which of the following is a key tool used in cell fractionation?
-Autoclave
-DNA sequencer
-Thermocycler
-Ultracentrifuge
-Electron microscope
Ultracentrifuge
Prokaryotic chromosomes have:
-one origin of replication per chromosome and DNA is replicated unidirectionally
-one origin of replication which replicates and migrates as DNA is replicated bidirectionally multiple origins of replication per chromosome, with DNA replicated unidirectionally
-multiple origins of replication per chromosome, with DNA replicated bidirectionally
one origin of replication which replicates and migrates as DNA is replicated bidirectionally
All of these statements about prokaryotic flagella are correct EXCEPT:
-They are driven by the proton motive force.
-They are found in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
-Their motor is embedded in the cell envelope.
-They are used for chemotaxis.
-They move with a whiplike motion.
They move with a whiplike motion.
If the sequence of one strand of DNA is 5' TCGATC 3', what is the sequence of the complementary strand?
-5' CTAGCT 3'
-5' GCTAGC 3'
-5' AGCTAG 3'
-5' GATCGA 3'
5' GATCGA 3'
Which statement is correct about topoisomerases?
-Type I topoisomerases relieve
supercoiling by cleaving both strands of DNA
-Type Il topoisomerases introduce supercoiling by cleaving one strand of
DNA
-Type Il topoisomerases do not relieve supercoiling by cleaving both strands of DNA
-Type I topoisomerases relieve supercoiling by cleaving one strand of DNA§Replication ends at defined termination (ter) sites located opposite to the origin.
Type I topoisomerases relieve supercoiling by cleaving one strand of DNA
Which of these represents a correct order of proteins involved in bacterial DNA replication?
-DnaA → DNA pol Ill → primase → ligase
-Primase → DNA pol III → DnaA → ligase
-DnaA → primase → DNA pol llI → ligase
-Primase → DNA pol Ill → ligase → DnaA
DnaA → primase → DNA pol llI → ligase
Plasmids are usually transferred from one bacterium to another via the process of?
-transformation
-transduction
-transfection
-coinfection
-conjugation
conjugation
NGS stands for?
-Nick Generation Sealing
-Next Genomics Sanger
-Next Genome Sequencing
-Next Generation Sequencing
-Novel Genetic Sequencing
Next Generation Sequencing
Error-proof repair pathways include all the following EXCEPT
-photoreactivation
-base excision repair
-nucleotide excision repair
-nonhomologous end joining
nonhomologous end joining
The protein response_____is the activator of the SOS
-DNA pol Ill
-UvrD
-RecA
-LexA
-HisG
RecA
which list includes examples that are not examples of prokaryotic DNA transfer mechanism
-conjugation, transduction, and transformation
-vesicles nanotubules and phage-like gene transfer agents
-type IV pilus in transformation, and specialized transduction
-Hfr transfer of chromosomal genes via T4SS and conjugation
-recombinational repair and nucleotide excision repair of the conjugant pilus
recombinational repair and nucleotide excision repair of the conjugant pilus
which list includes examples that are NOT examples of prokaryotic DNA transfer mechanisms
-conjugation, transduction, and transformation
-vesicles, nanotubules, and phage-like gene transfer agents
-Hfr transfer of chromosomal genes via T4SS, and conjugation
-recombinational repair, and nucleotide excision repair of the conjugant pilus
recombinational repair, and nucleotide excision repair of the conjugant pilus
The sigma factor is directly required for
-transcription initiation
-Transcription elongation
-Translation initiation
-Translation elongation
transcription initiation
which of these represents a correct order of proteins involved in bacterial translation
A) EF-Tu -> IF2 -> RF3 -> EF-G
B) EF-Tu -> EF-G -> IF2 -> RF3
C) IF2 ->EF-Tu -> EF-G -> RF3
D) IF2 ->EF-G -> EF-Tu -> RF3
C) IF2 ->EF-Tu -> EF-G -> RF3
chaperones are the protein that
- initiate catalysis via chaperonin
-help guide or "chaperone" proteins to their substrates
-degrade misfolded proteins
-help proteins fold properly
help proteins fold properly
What historical person and intervention contributed most famously to modern day understanding of sanitation to reduce pathogenic bacterial transmission in clinical settings?
1847, Ignaz Semmelweis ordered doctors to wash their hands with chlorine (antiseptic agent)
developed carbolic acid to treat wounds and clean surgical instruments.
Suddenly postpartum maternal death rates fell.
Joseph Lister
What do Koch's Postulates state? Why is each postulate important?
1. Microbe is always present in diseased host.
- absent in healthy
2. Microbe is grown in pure culture.
- no other microbes present
3. Pure microbe is introduced into healthy host.
- Individual becomes sick.
4. Same microbe is re-isolated from now-sick individual.
Criteria for establishing a causative link between an infectious agent and a disease
Koch's Postulates
What key principles make light microscopy effective? Which methods in microscopy use interference?
resolves images of individual bacteria by their absorption of light. (resolution, detection, and magnification) dark object against a light field.
Differential interference contrast microscopy
Phase-contrast microscopy (PCM)
Paramecium stained light microscopy
Pseudomonas light microscopy
C. Escherichia coli transmission electron microscopy, TEM
Ribosomes on messenger RNA transmission electron microscopy, TEM
Ribosome model (X-ray crystallography)
2 um – 20 cm
Protozoa, algae, fungi
-Structures can be seen under a light microscope.
-0.4 –10 mm
bacteria, archaea
-Subcellular structures too small to resolve by light microscopy
wave length of visible light
400-750 nm
Problem-solve a microscopy experiment: given cells with features you hypothesize to be present, but cannot see, choose an alternate microscopy approach.
bright field mircroscopy employs various stains
fluorescence employs fluorophores for labeling
Generates a dark image of an object over a light background
What are the terms for organismal classification based on biomass and carbon acquisition?
Autotrophs fix carbon dioxide and assemble into organic molecules (mainly sugars). (e.g. photoautotrophs, chemolithoautotrophs/lithotrophs)
Heterotrophs use preformed organic molecules. (e.g. photoheterotrophs, chemoheterotrophs/organotrophs)
use light energy or oxidation of minerals to capture CO2 and convert it to complex organic molecules.
autotrophs
degrade complex organic compounds (polysaccharides) through the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or fermentation.
heterotrophs
All life is based on carbon, acquired in different ways.
biomass
use preformed organic molecules. (e.g. photoheterotrophs, chemoheterotrophs/organotrophs)
some can be photosynthesized
Heterotrophs
obtain energy from chemical reactions triggered by light.
phototrophs
obtain energy from oxidation-reduction reactions.
chemotrophs
use inorganic molecules as a source of electrons.
lithotrophs
use organic molecules.
organotrophs
If a cell divides by binary fission, the
number of cells is proportional to 2n.
Final cell original number = cell number x 2^(number of generations)
Nt=N0x2^n
Imagine Bacillus cereus divides once every 30 minutes. If we begin a culture with 100 cells, how many bacteria will we have after 3 hours of logarithmic growth?
6400
What if you already know your Bacillus cereus culture has 6,400 cells and you began with 100 cells and incubated it at log growth for 3 hrs. How many generations of growth occurred? log Nt = log (N0) + nlog2
6 generations
What is the formula for log growth? How is this formula used to calculate the starting and final numbers of cells relative to the number of generations under log growth?
Nt = N0 x 2n
Where Nt is the final cell number,
N0 is the original cell number, and
n is the number of generations.
Any ecological niche outside this window is called "extreme," and organisms inhabiting them are called
Temperature > 100°C; pH 2
extremophiles
Sea level; Temperature 20oC-40oC; near-neutral pH; 0.9% salt; and ample nutrients
normal growth conditions
grow above 80 C
hyperthermophile
50 C-80 C
thermophile
15- 45 C
mesophile
grow below 15 C
psychrophile
grow above pH 9
alkaliphile
pH 5-8
neutrophile