Dinosaurs Midterm
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Sedimentary Rocks
Made of eroded pieces of rocks
Often buries organisms and creates fossils
Can tell the relative ages of these rocks
Collected in low-lying areas transported by wind, water, gravity, or ice
Igneous Rocks
Forms from melts that cool and solidify
Can tell the absolute ages
Rarely preserves fossils
Metamorphic Rocks
Form due to heat and pressure
Examples: Slate, Schist, Marble, Quartzite
Body Fossil
part of an organism
Trace Fossil
evidence of an organism’s activity
trackways/footprints, feces/coprolite, eggs, nests, burrows
Oldest definitive fossils
Stromalites in Western Australia ~ 3.5 billion years ago; bacterial body fossils
Isotope
Different variant of an element based upon number of neutrons
Carbon-12: 6 protons, 6 neutrons
Carbon-13: 6 p, 7 n
Carbon-14: 6 p, 8 n
*Two kinds of isotopes: stable and unstable (unstable parent changes into stable daughter)
Concept of deep time
Coined by James Hutton (18th century)
Idea that life has no record of beginning and no prospect to end
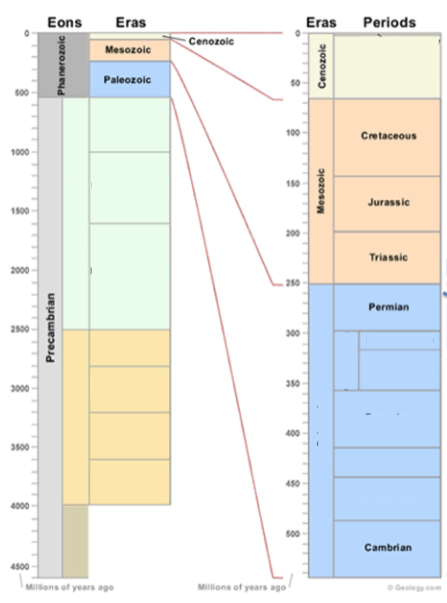
Geologic Time Scale
End-Permian extinction
Greatest mass extinction in history of life; ended around 80% of all species and 60% of genera (genuses)
Caused by the (1) formation of Pangaea and (2) volcanic eruptions
What specific influences during the formation of Pangaea caused the end-Permian extinction?
Severe decrease in shallow marine environments
new competition from invaders
low sea level
new ocean circulation and weather patterns
drier continents
What specific influences from volcanic eruptions caused the end-Permian extinction?
Presence of acid rain and pollution
CO2 released (global warming)
Acidification and anoxia in oceans
Ozone depletion
The Scientific Method
Observe
Hypothesize
Predict
Test Predictions
Be open to finding evidence to refute predictions
Darwin’s contributions to the theory of evolution
All organisms have a single common ancestor
Common Descent with Modification (over time)
Natural Selection
Artificial Selection (variation under domestication (like wolves turning to dogs))
Natural Selection
A mechanism that explains evolution
Others include sexual selection, genetic drift, historical contingency, group selection, etc.
Eukaryotes
Organism that has clearly defined nuclei and organelles surrounded by plasma membrane (specifically have mitochondria and chloroplasts)
Origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Added through the process of ENDOSYMBIOSIS for energy and protection
Transfer of function of gill arches
Used for filter feeding
Respiration
Function then made for jaws + respiration
** Human embryos also have gill arches
Sarcopterygii
Fleshy-limbed “fish”

Actinopterygii
Ray-finned “fish”
Gnathostome
Vertebrates with jaw mouths
Tetrapods
Vertebrates with four limbs and digits to walk on
Two types: Amphibians & Amniotes
Two types of Amniotes
Synapsides (and mammals) and reptiles (and birds)
Amniotes’ evolutionary novelties
Amniotic/self-contained eggs with membranes
Internal fertilization
“Waterproof skin”
Complex lungs
Tetrapods’ evolutionary novelties
Four limbs with digits
Vertebrae with struts
Robust hips attached to spine
Stapes (bone connecting eardrum to inner ear)
transfer of function from when it once was the upper jaw turned into the brain case
Diapsid
organisms that have two temporal fenestra
Synapsid
organisms that have one temporal fenestra
Anapsid
organisms that have no temporal fenestrae
Archosaur
Popular in most of the Mesozoic time period after the end-Permian extinction
Examples: crocodiles and relatives, Pterosaurs, Dinosaurs (including birds)
Traits of Archosaurs
Thecodonty
Antorbital fenestra
Mandibular fenestra
Parental care
Ornithodire
Two types: Pterosaurs & Dinosaurr
Evolutionary novelties of an ornithodire
Mesotarsal Ankle
ankle bone fused tibia and fibula together
limited range of motion in the ankle
Digitigrade foot posture
ankles off the ground when walking
organisms walk on digits/toes
longer limbs, making them more lithe and fast
Pterosaur
Winged reptile and archosaur
Dinosaur
Meaning “terrible lizard” as of 1842; coined by Richard Owen (1804-1892)
is a type of ornithodire and archosaur
extinct after the end-Cretaceous period
Temporal Fenestrae
Holes in the area behind the eyes in a skull
Antorbital fenestra
Holes in the area between the eyes and the nose of a skull
Mandibular fenestra
Holes in skulls near the mid-jaw
Monophyletic Groups
Ancestor + ALL descendants shown on a cladogram
is good because it shows complete branches on an evolutionary tree
no characters are cut out, some are just grouped together separately
Paraphyletic Groups
Ancestor + SOME descendants shown on a cladogram
is bad because it shows artificial, incomplete branches on an evolutionary tree
gives the false impression that non-groups exist
Polytomy
On a cladogram/phylogenetic tree where a single node branches into more descendant lineages
Convergent attributes
Attributes/characteristics not attained through biology, but through the function of that characteristic - is unrelated to the fact that another organism might have the same characteristics
Homologous attributes
Attributes/characteristics attained within an organism due to a common ancestor that also had that characteristic (biologically passed down, and therefore may be seen in other differing organisms)
Secondary loss
Evolutionary novelties in organisms lost over time/generations
Example: whales have a pelvic bone deep in their tissue, but its growth is stunted and not used
Sister group
Group most closely related to another shown on a cladogram
Mesotarsal ankle
Ankle bone fused with tibia and fibula found in ornithodires
promotes a limited range of motion in the ankle because of stiffness
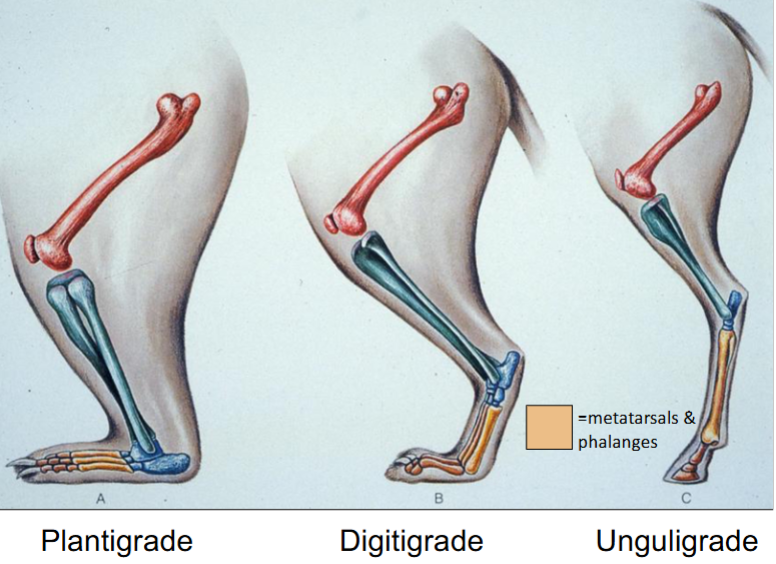
Various foot postures
Plantigrade
Digitigrade
Unguligrade
Dinosaur evolutionary novelties
Erect posture
Narrow tracked gait
Opening in hip socket bordered by a bony upper lip
Upright femur with inturned head
Relative Dating
age of rocks compared to other rocks
Relative dating principles
Original horizontality (Steno)
Lateral continuity (Steno)
Superposition (Steno)
Cross cutting relationships (Hutton)
Faunal Succession (Cuvier)
Absolute Dating
age of rocks in years; based upon radioactive decay of atoms within mineralsHal
Half life
Time required for ½ of the radioactive parent to decay into its daughter product
Radioactive decay
One element (parent) changes into another (daughter) with a more stable configuration
neutrons from the parent will leave through half-lives to create a daughter product, changing the atomic nuclei
Relative dating methods
Biostratigraphy
Use fossils to correlate rocks and determine their ages
Lithostratigraphy
Correlating rock types (sandstone with sandstone)
Often combined with biostratigraphy