Biology Final
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
Reproduction, growth, regeneration
Importance of Cell Division
Events for cell division to occur
Reproductive signal, DNA replication, segregation of DNA into new cells, cytokinesis (separation) of two new cells
G1 Phase
First phase of the cell cycle where cells grow and prepare for DNA replication. It is a crucial checkpoint for cell division.
S Phase
Phase of the cell cycle where DNA replication occurs
G2 Phase
The third phase of the cell cycle where the cell prepares for division. The cell duplicates its cytosol and organelles, cell grows again.
Cyclin-dependent kinases
Regulatory proteins that control cell cycle progression by phosphorylating target proteins. Activated by binding to cyclins, forming active kinase complexes. Protein and ATP bind to CDK and the protein substrate becomes phosphorylated which then regulates the cell cycle.
Cyclin
Protein that regulates the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Levels fluctuate throughout the cell cycle, peaking during specific phases to drive progression.
Histones
Proteins that package DNA into a compact structure called nucleosomes. They help regulate gene expression and provide stability to the DNA molecule.
Chromatin
The complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins found in the nucleus of a cell. It condenses to form chromosomes during cell division and controls gene expression.
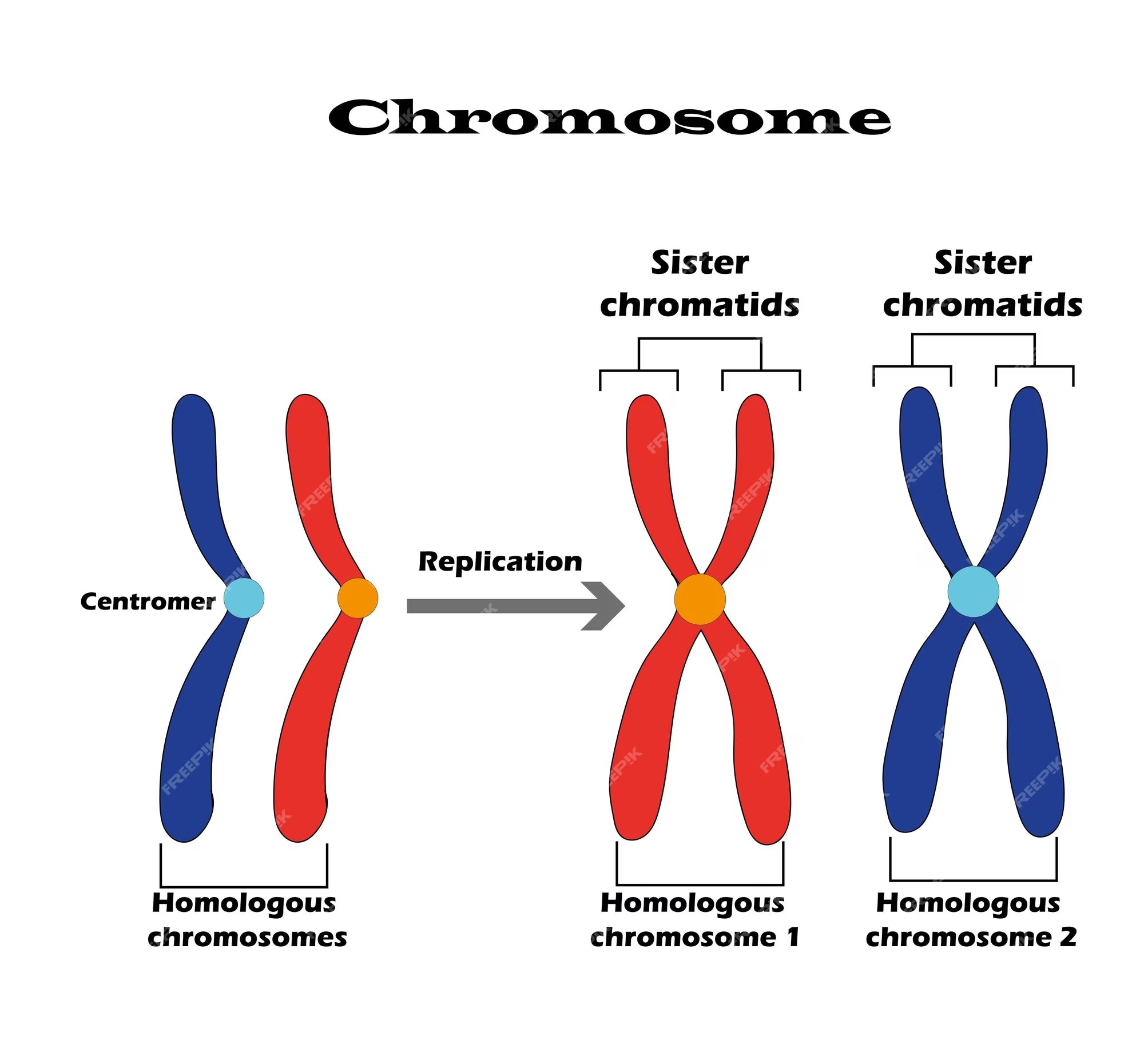
Sister Chromatids
The replicated copies of a chromosome that are held together by a structure called the centromere.
Prophase
First stage of mitosis, chromosomes condense and become visible, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibers form, and centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell.
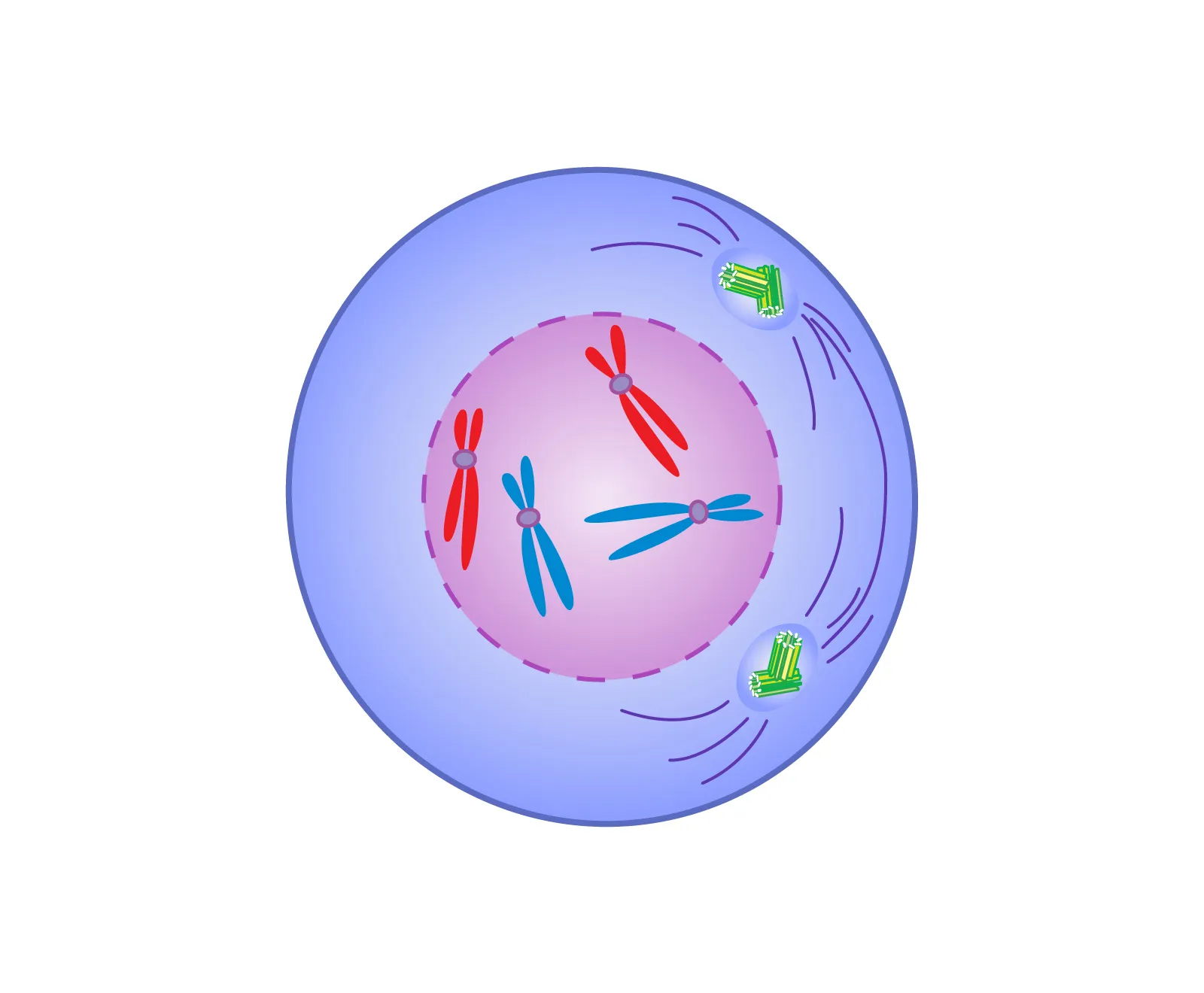
Prometaphase
Stage in mitosis where nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing spindle fibers to attach to chromosomes. Chromosomes become highly condensed and start moving towards the center of the cell.
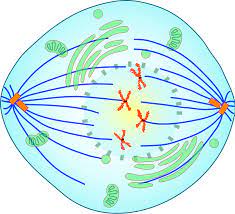
Metaphase
Stage of mitosis where chromosomes align in the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres, preparing for separation.
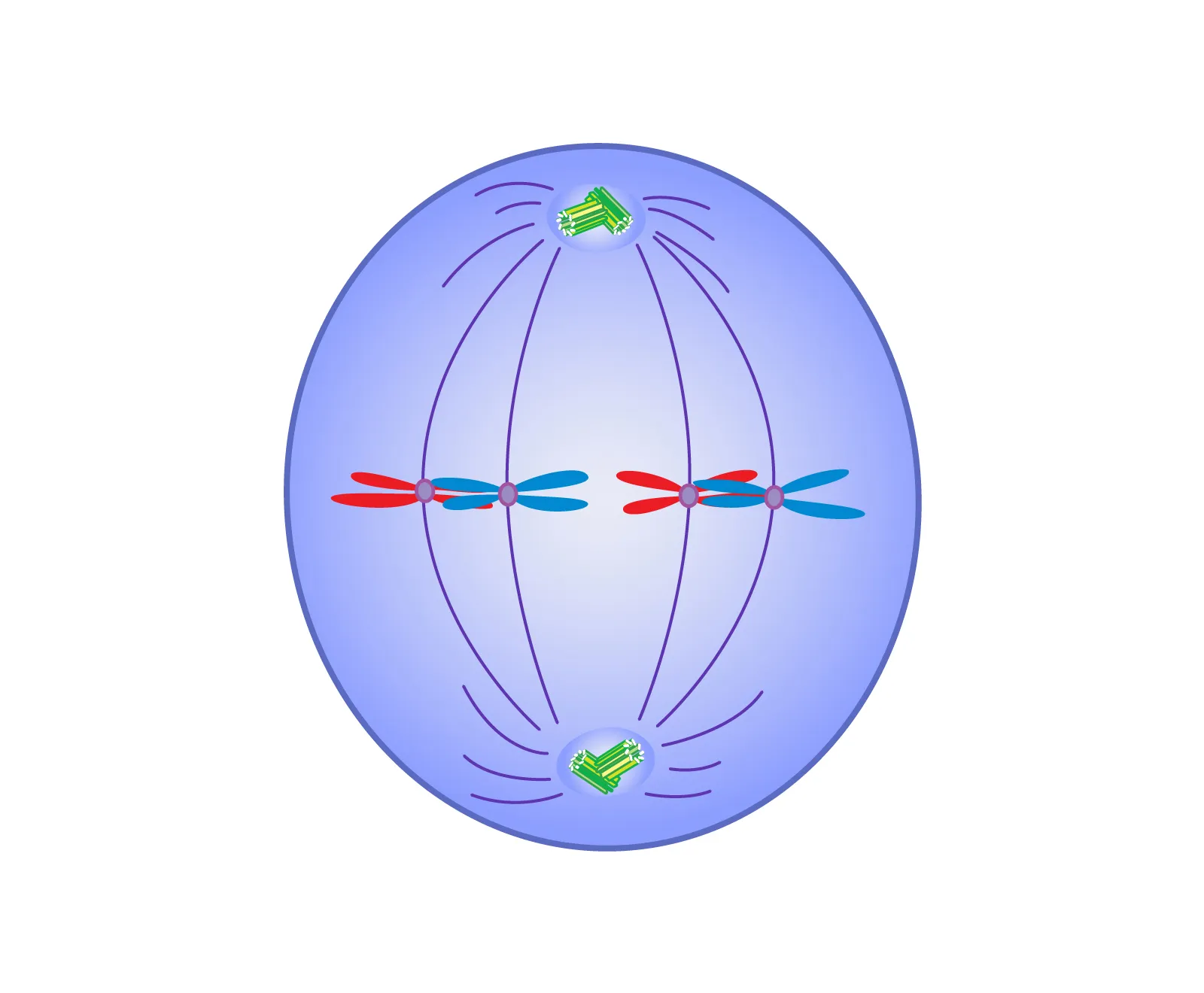
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
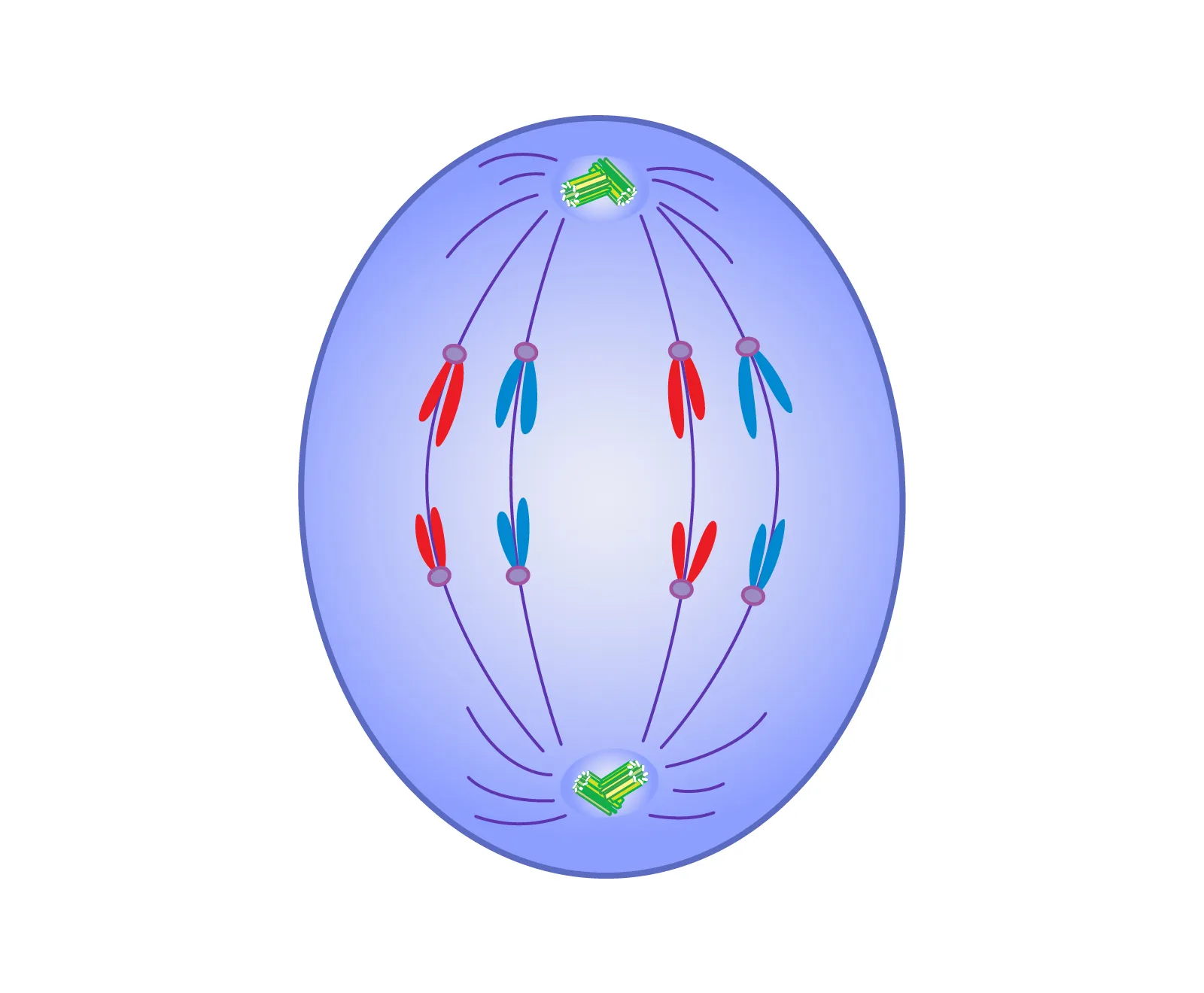
Telophase
The final stage of cell division where the chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, and two new nuclei are formed at opposite ends of the cell.
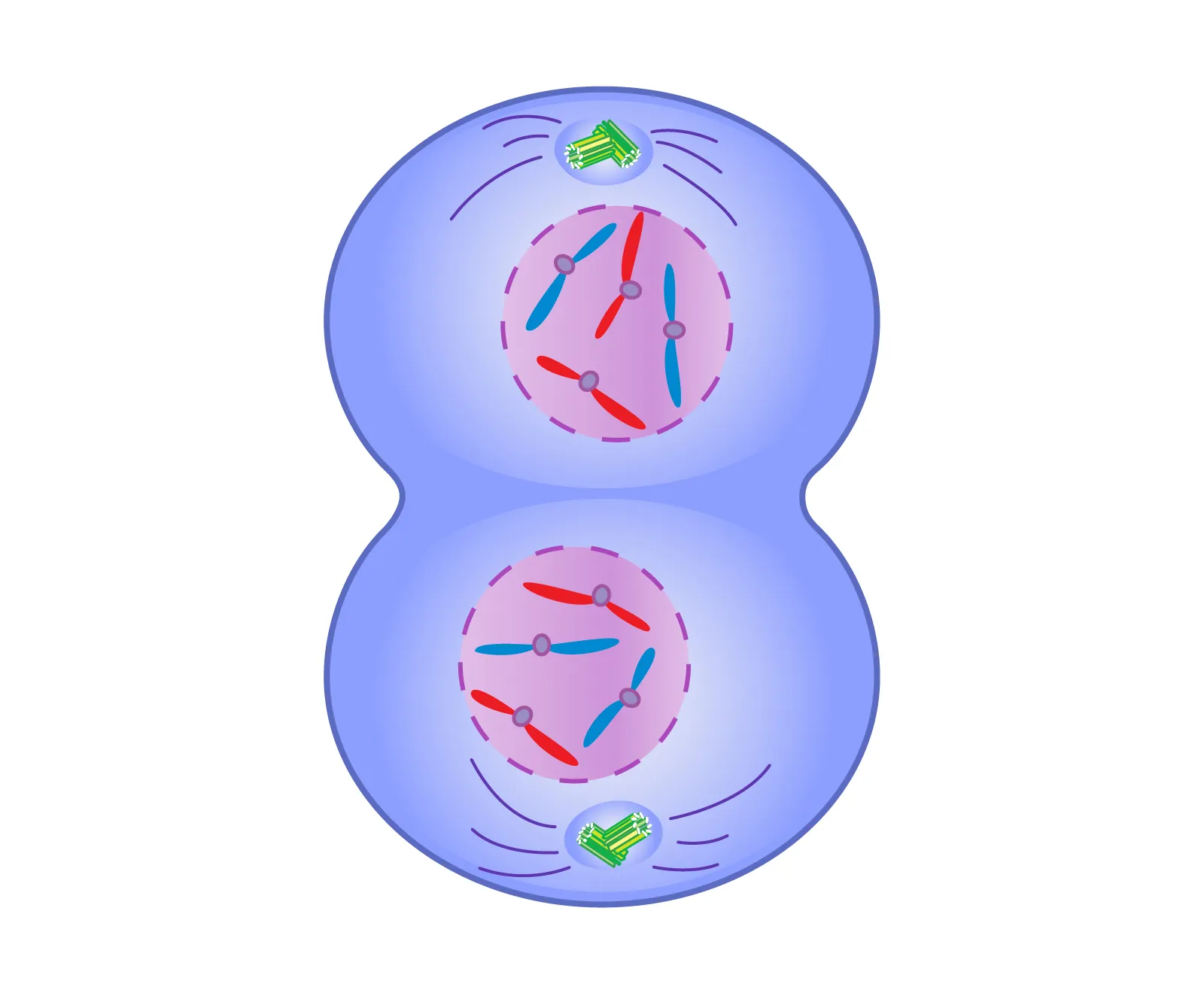
Spindle Fibers
Thread-like structures that form during cell division. They attach to chromosomes and help separate them into two new cells. Made of microtubules.
Cohesin
Protein complex that holds sister chromatids together after DNA replication until they separate during cell division. Essential for proper chromosome segregation.
Separase
Protein enzyme involved in cell division. Cleaves cohesin, allowing sister chromatids to separate during anaphase. Essential for proper chromosome segregation.
Cytokinesis
Process in cell division where the cytoplasm divides, forming two separate daughter cells. Occurs after the completion of mitosis or meiosis.
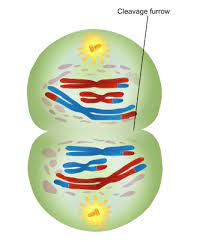
Cleavage Furrow
A temporary indentation that forms during cell division in animal cells. It marks the site where the cell will eventually separate into two daughter cells. ormed by the contraction of a ring of actin and myosin filaments, which gradually deepens until the cell is divided.
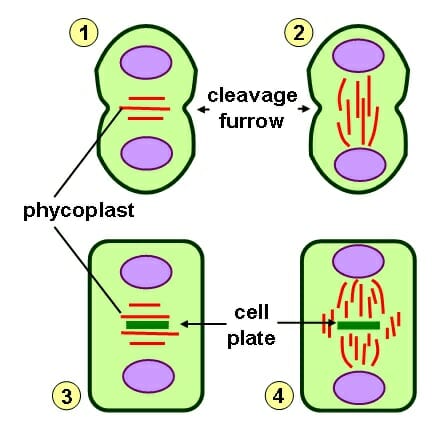
Cell Plate
Structure formed during cytokinesis in plant cells to separate the daughter cells. Consists of vesicles containing cell wall materials that fuse together to form a new cell wall.
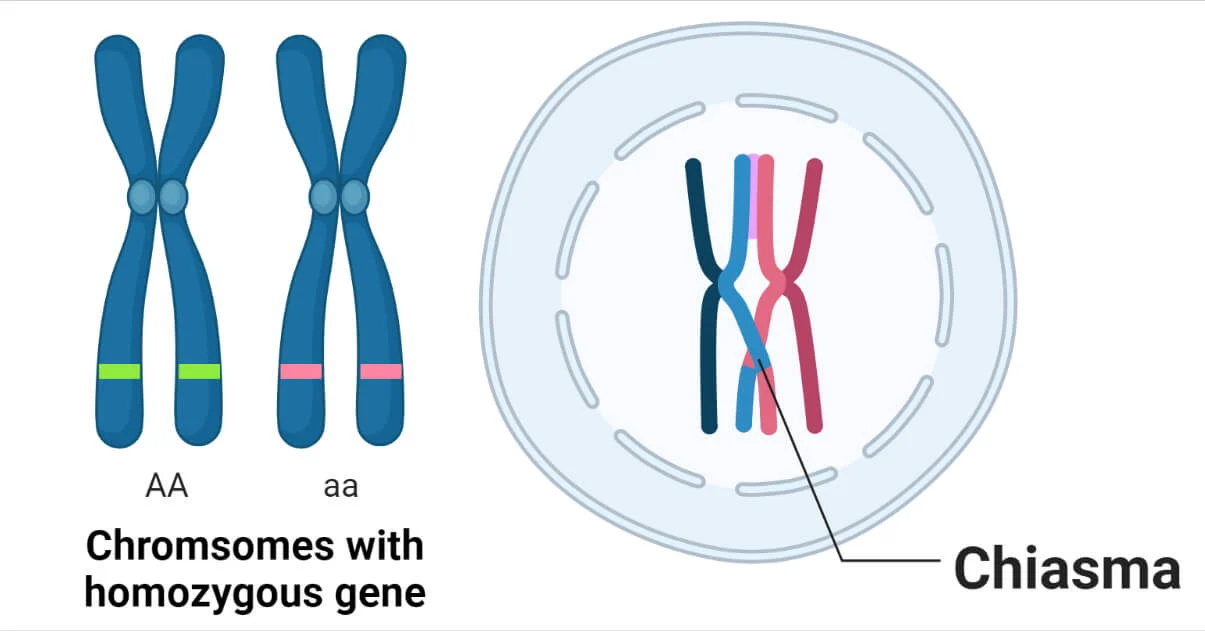
Homologous Chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that have the same genes at the same locations, but may have different versions of those genes. They come from each parent and are involved in genetic recombination during meiosis.
Chiasma
Site of genetic recombination during meiosis.
Diploid
The term for cells or organisms that have two sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. It represents the normal chromosome number in most body cells.
Haploid
The term used to describe cells that have half the number of chromosomes as a diploid cell. Cells are found in organisms during the process of sexual reproduction and are involved in the formation of gametes.
Meiosis
Process of cell division that produces four genetically unique haploid cells. The purpose is to to produce gametes, or sex cells.
Crossing Over
Process during meiosis where non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material, increasing genetic diversity, happens during Prophase I.
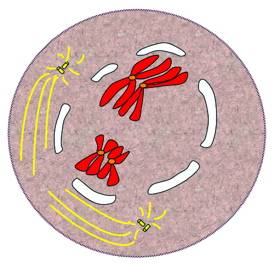
Prophase I
The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. crossing-over occurs, homologous chromosomes pair up. (diploid)
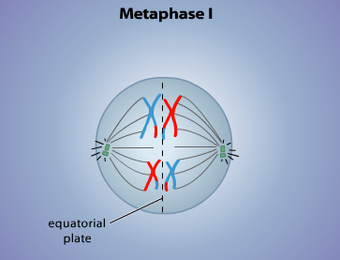
Metaphase I
Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell (diploid)
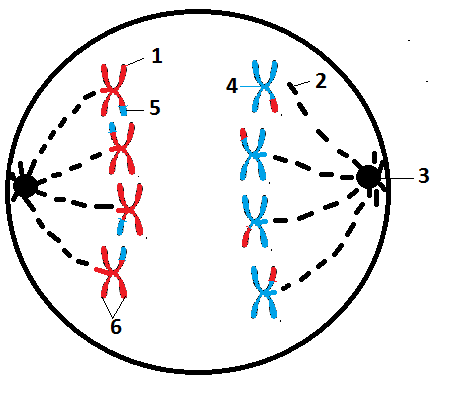
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell. (diploid)
Telophase I
The cytoplasm divides and two new cells form. Each new cell has one duplicated chromosome from each similar pair. (haploid)
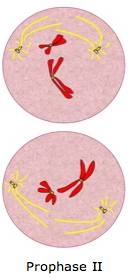
Prophase II
The duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell. (haploid)
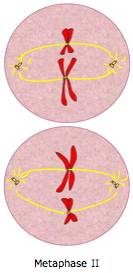
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up in the middle (haploid)
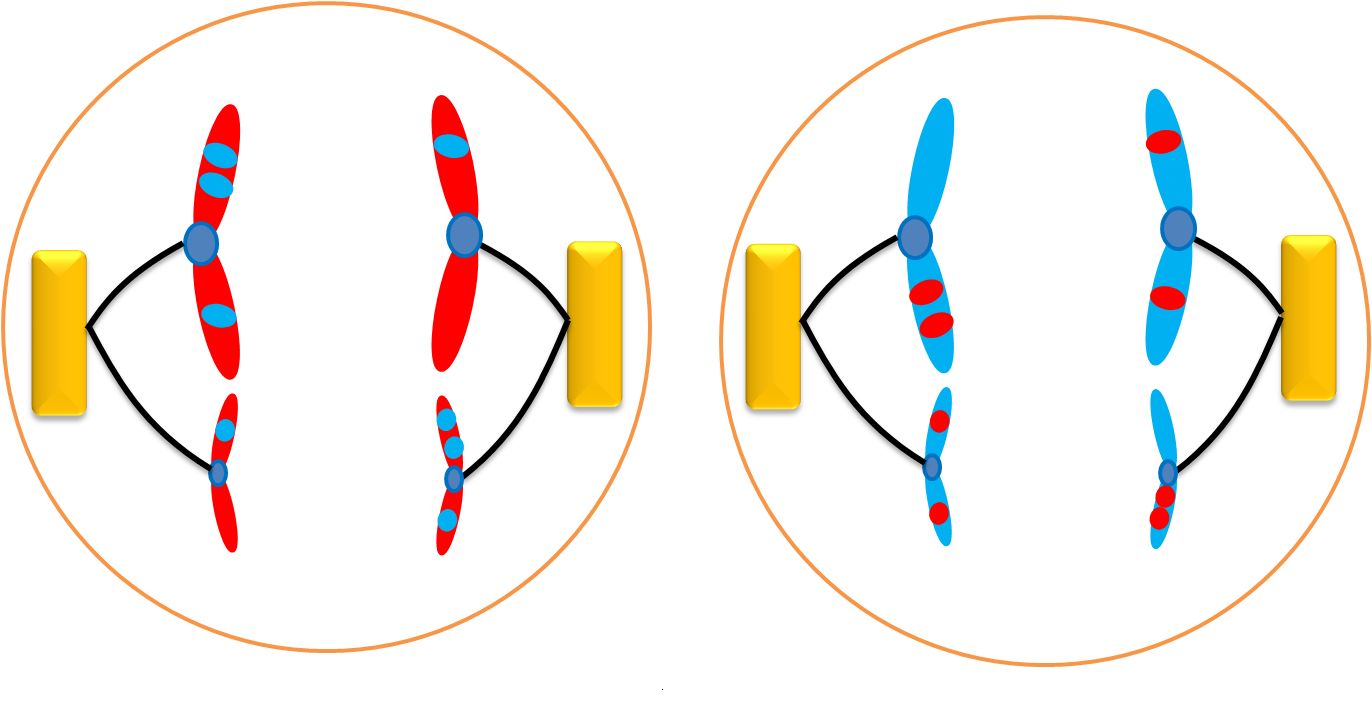
Anaphase II
The centromere divides. The chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Each chromatid is now an individual chromosome. (haploid)
Telophase II
Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed (haploid)
Recombinant
Offspring that show new gene combinations due to crossing over and unlinked genes.
Independent Assortment
The principle stating that genes for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes. This allows for the random combination of traits in offspring.
Meiosis vs Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division for somatic cells and for the asexual reproduction of unicellular eukaryotic cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division for the production of gametes in sexual reproduction.
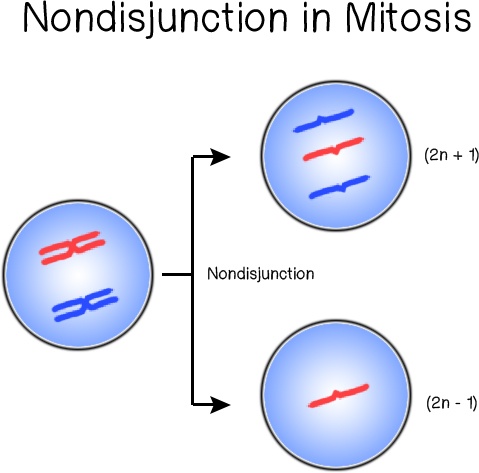
Nondisjunction
Failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate during meiosis or mitosis, resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in daughter cells.
Trait
A characteristic or feature that can be inherited or acquired by an organism.
True-Breeding
Describes organisms that, when self-fertilized or crossed with another true-breeding organism (homozygous recessive with homozygous dominant)
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, determined by the combination of alleles for a particular trait. It determines the characteristics and traits that an organism can inherit and pass on to its offspring.
Phenotype
The observable traits or characteristics of an organism resulting from the interaction between its genes and the environment.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene that occupy the same position on homologous chromosomes. They determine specific traits and can be dominant or recessive.
Dominant
The most influential or controlling trait or gene in an organism's genetic makeup, determining its physical characteristics or traits.
Recessive
Trait that is masked by a dominant trait in an organism's genetic makeup. It only manifests when an individual inherits two copies of the recessive allele.
P Generation
The initial generation of parents used in a genetic cross to study inheritance patterns.
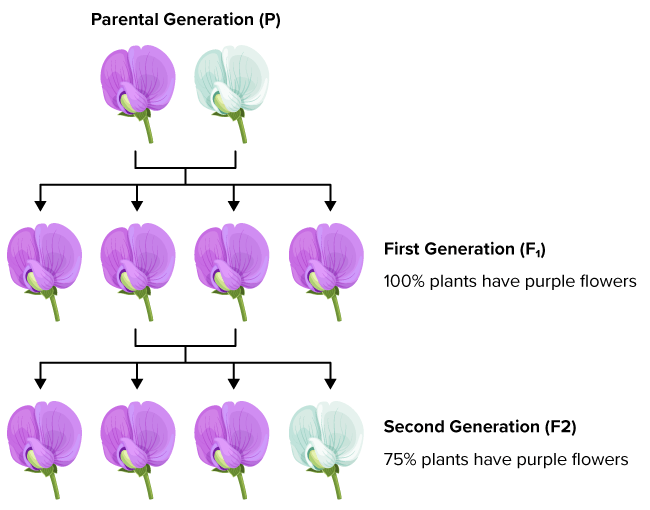
F1 Generation
Offspring resulting from the cross of two parental organisms with different genotypes.
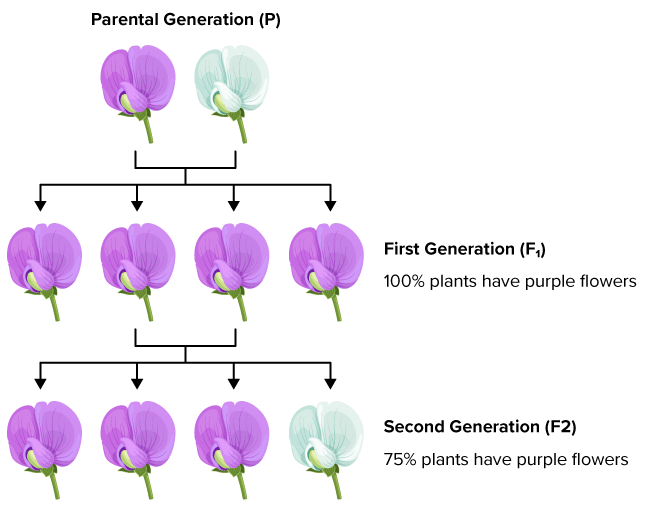
F2 Generation
Offspring resulting from the crossbreeding of two parental generations. Also known as the second filial generation.
Monohybrid Cross
A mating in which the parents differ with respect to the alleles of only one gene of interest.
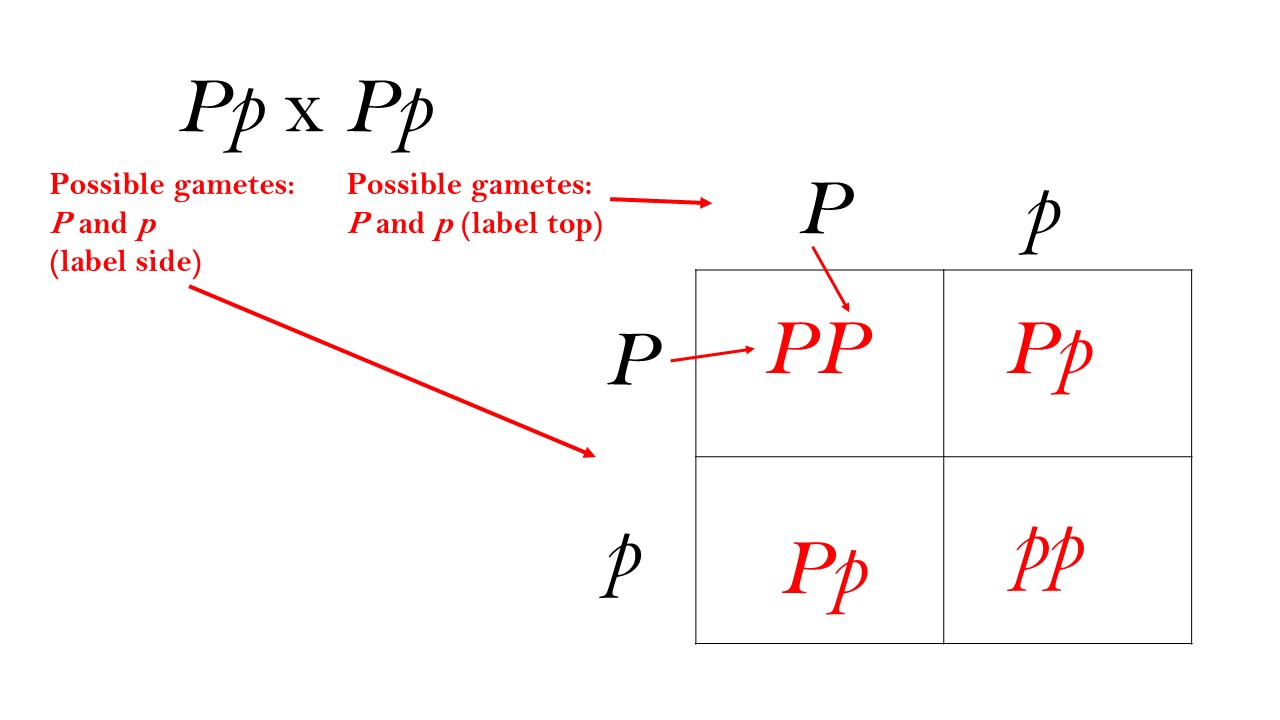
Dihybrid Cross
Breeding experiment that involves two traits. It examines the inheritance patterns of two different traits simultaneously.
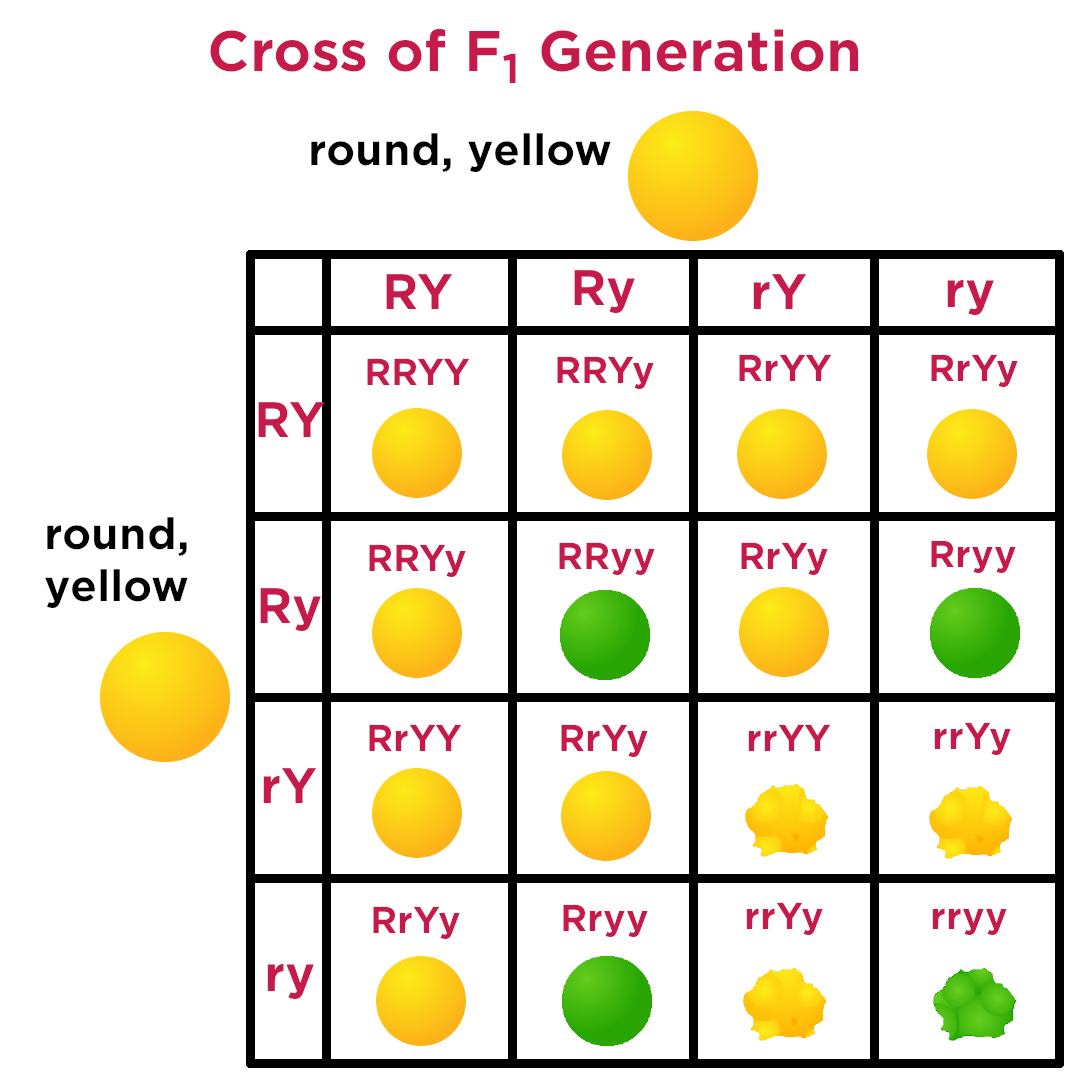
Test-Cross
A breeding technique used to determine the genotype of an individual showing a dominant trait. It involves crossing the individual with a known homozygous recessive individual.
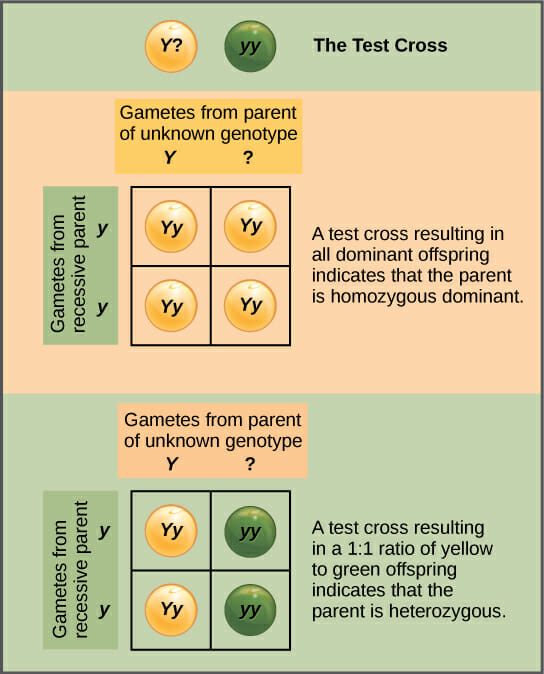
Mendel's First Law of Segregation
During gamete formation, the two alleles for a gene segregate from each other, so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene. Diploid → haploid gametes
Ex: Rr becomes R and r
Mendel's Second Law of Independent Assortment
Each pair of alleles segregates independently during gamete formation. This law states that the inheritance of one trait does not affect the inheritance of another trait.
Autosomal Dominant
Inheritance pattern where a single copy of a mutated gene from one parent is enough to cause the trait or disorder in an individual.
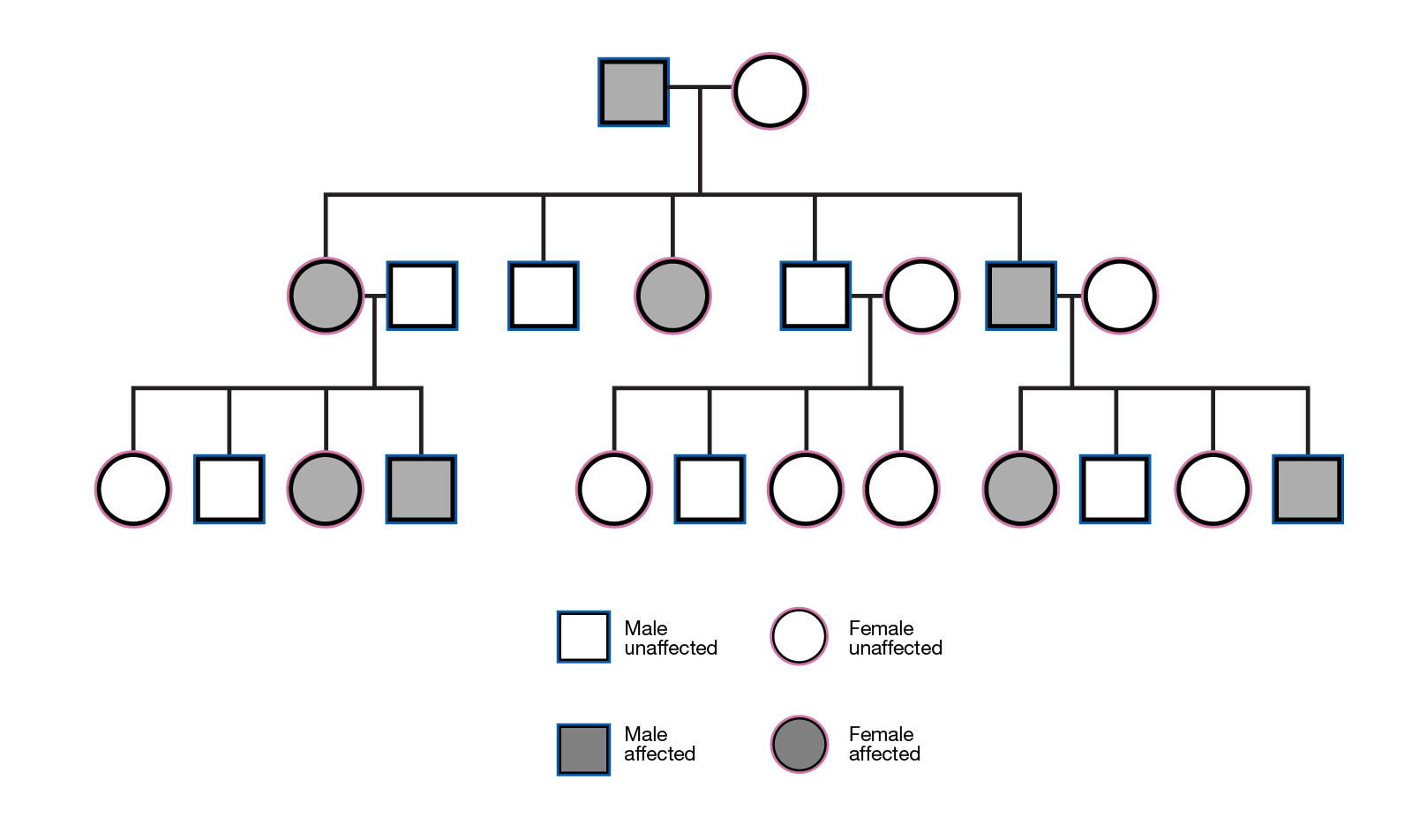
Autosomal Recessive
A genetic inheritance pattern where two copies of a recessive allele are needed for a trait or disorder to be expressed. It occurs on autosomal chromosomes, not sex chromosomes. Examples include cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia.
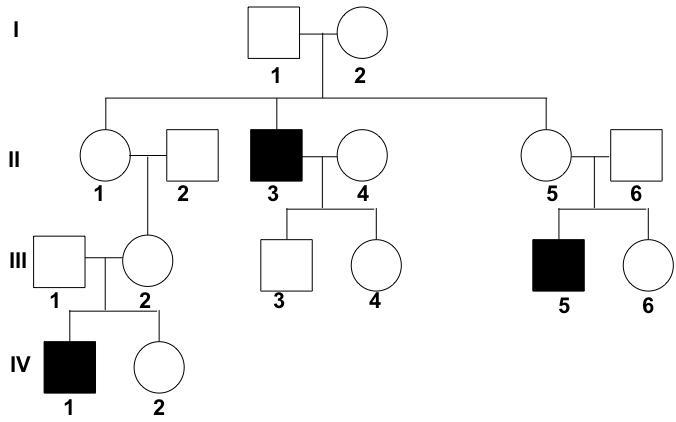
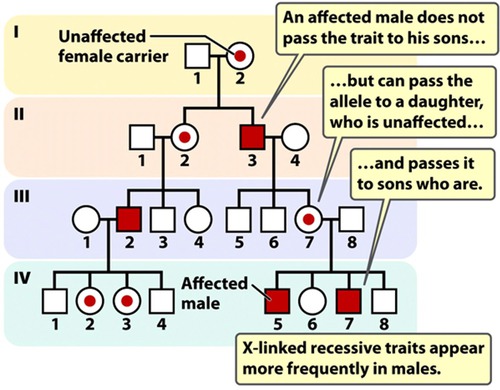
X-Linked Dominant
Inheritance pattern where a mutated gene on the X chromosome leads to a dominant trait or disorder. Affected fathers pass the trait to all daughters, but not sons. Affected mothers can pass the trait to both sons and daughters.
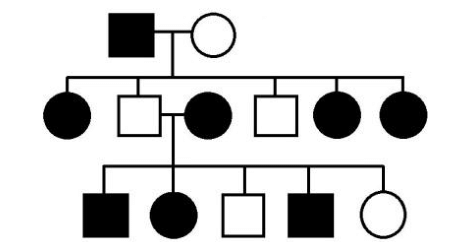
X-Linked Recessive
A mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation
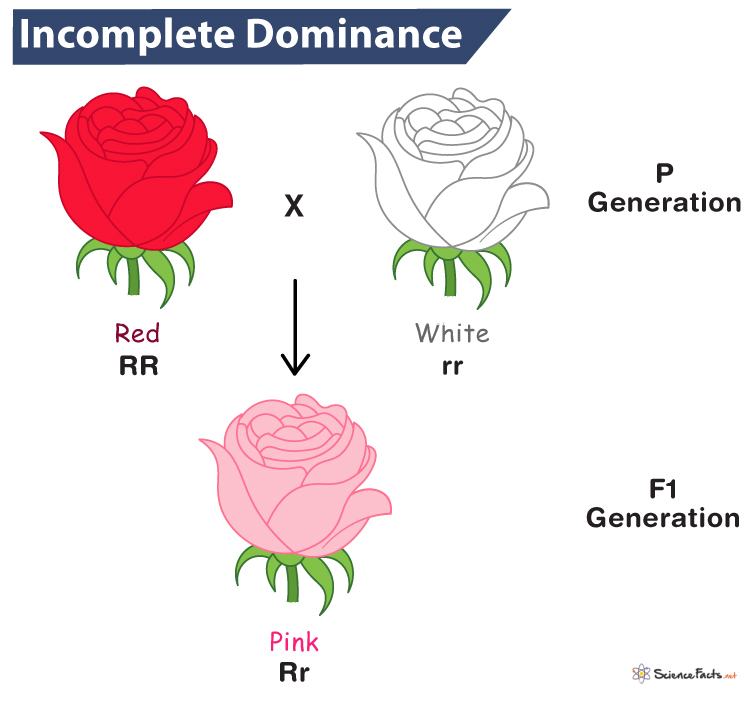
Incomplete Dominance
Type of genetic inheritance where neither allele is completely dominant over the other, resulting in a blended phenotype.
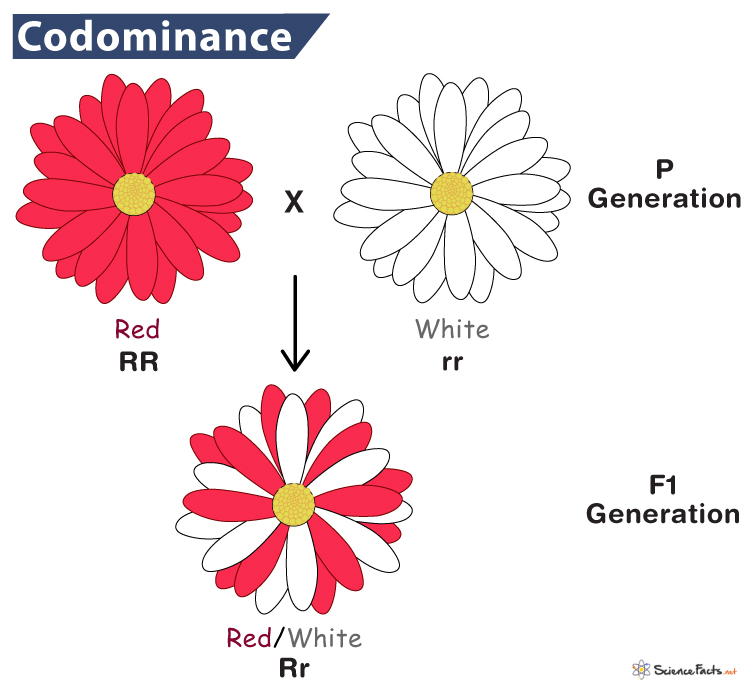
Codominance
A genetic scenario where both alleles of a gene are fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual. Neither allele is dominant or recessive, resulting in a unique phenotype that shows traits from both alleles.
Epistasis
A genetic phenomenon where one gene masks or influences the expression of another gene. It occurs when the alleles of one gene interact with alleles of another gene to determine the phenotype.
Hybrid Vigor
The term that describes the phenomenon where the offspring of two different breeds or species show improved traits compared to their parents.
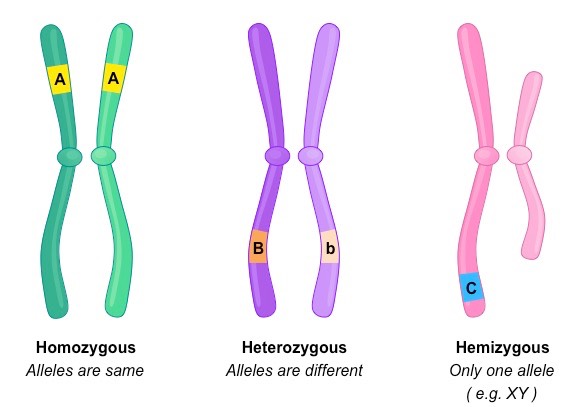
Hemizygous
Having only one copy of a particular gene instead of the usual two copies. This occurs in males for genes located on the X chromosome, as they have only one X chromosome.
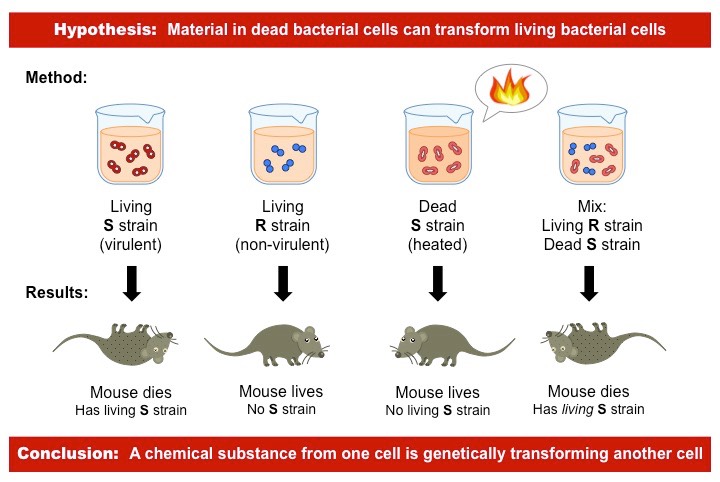
Griffith Experiment
Landmark experiment conducted in 1928, demonstrating the concept of bacterial transformation. Showed that genetic material can be transferred between bacteria, leading to the discovery of DNA as the molecule responsible for inheritance.
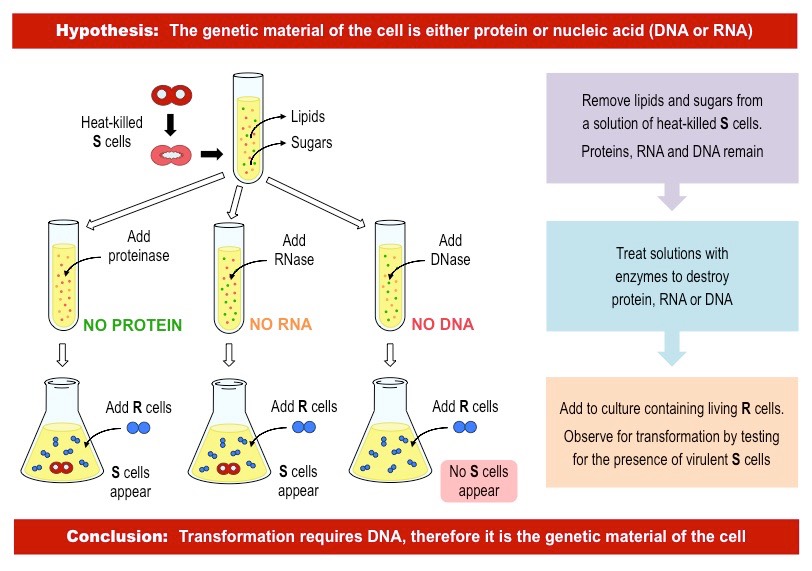
Avery Experiment
Experiment that showed that DNA is the hereditary material in bacteria, not proteins. Extracted DNA from a virulent strain of bacteria and transferred it to a non-virulent strain, which became virulent. Proved DNA's role in genetic transformation.
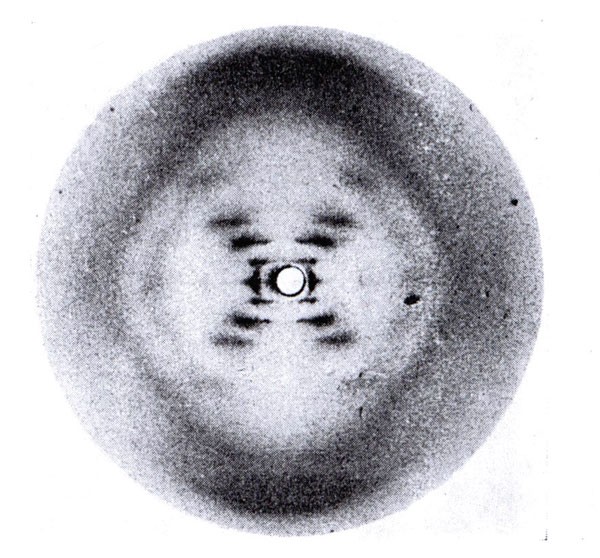
Rosalind Franklin
Scientist who played a crucial role in discovering the structure of DNA. Her X-ray diffraction images provided evidence for the double helix shape.
Watson and Crick
"Discoverers of DNA structure using X-ray crystallography, proposed the double helix model in 1953. Their work revolutionized our understanding of genetic information and laid the foundation for modern molecular biology."
Structure of DNA
The arrangement of nucleotides in a double helix, consisting of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine). 5’ Carbon (sugar) attaches to phosphate group, 1’ carbon attaches to nucleotide, 3’ carbon has a free hydroxyl group. Antiparallel, right handed, major and minor grooves.
DNA Replication
Process in which DNA molecules are duplicated, resulting in two identical copies. It occurs during cell division and involves unwinding of the DNA double helix, synthesis of new DNA strands, and proofreading for accuracy.
Limitations of DNA Polymerase
Cannot add nucleotides de novo. Therefore, needs a primer. Can only catalyze the addition of a nucleotide to the 3’ end. Therefore, replication occurs in the 5’-3’ direction.
Origin of Replication
Specific DNA sequence where DNA replication begins. It serves as a starting point for DNA polymerase to unwind and replicate the DNA molecule. Multiple origins of replication exist in eukaryotes, while prokaryotes usually have a single origin.
Replication Fork
The site where DNA strands separate and new strands are synthesized during DNA replication.
Template Strand
The DNA strand that serves as a template for RNA synthesis during transcription. It is complementary to the coding strand and has the same sequence as the RNA transcript, except for the substitution of thymine with uracil.
Leading Strand
The DNA strand synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction during DNA replication. It follows the replication fork and requires only one primer for initiation.
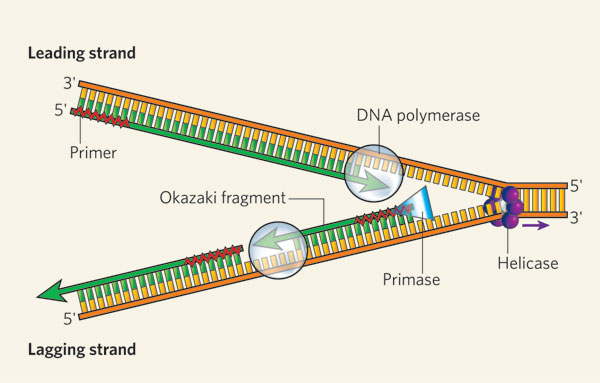
Lagging Strand
The strand of DNA that is synthesized discontinuously during DNA replication. It is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments.
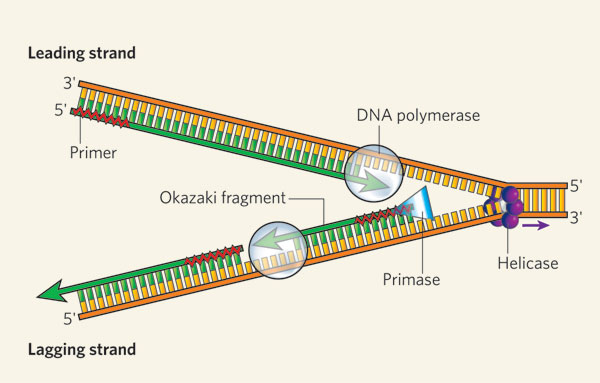
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds and separates the DNA double helix during DNA replication.
DNA Binding Proteins (SSBP)
Keep the template strands separated
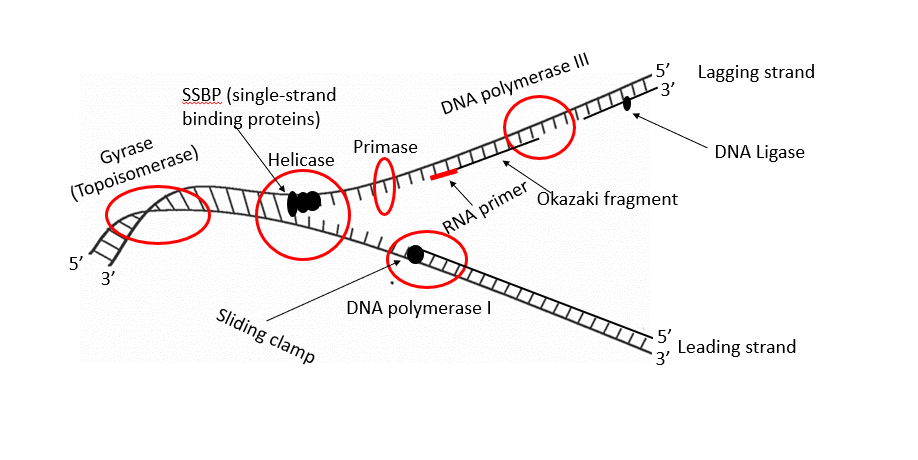
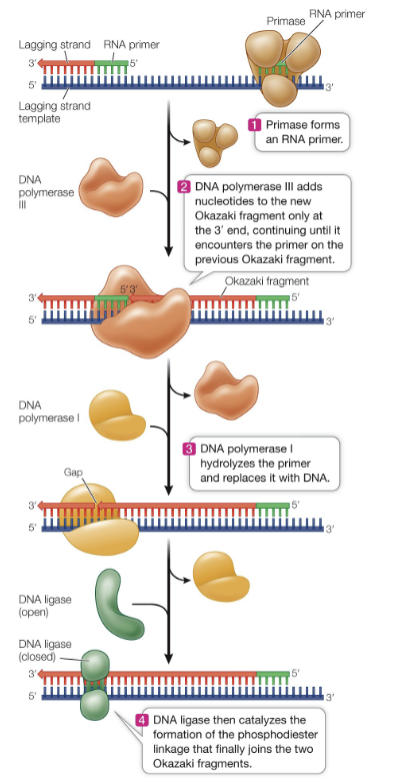
Primase
Enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers during DNA replication.

RNA Primer
Short segment of RNA that serves as a starting point for DNA synthesis during replication. It provides a free 3' OH group for DNA polymerase to attach and initiate synthesis of a new DNA strand. RNA primers are later removed and replaced with DNA nucleotides.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing DNA template during DNA replication.
Ligase
Enzyme that joins DNA fragments together by catalyzing the formation of phosphodiester bonds. Crucial in DNA replication, repair, and recombination.
Telomerase
Enzyme responsible for maintenance of the length of telomeres by addition of guanine-rich repetitive sequences. Reverses reversing the loss/shortening of DNA from each round of replication.
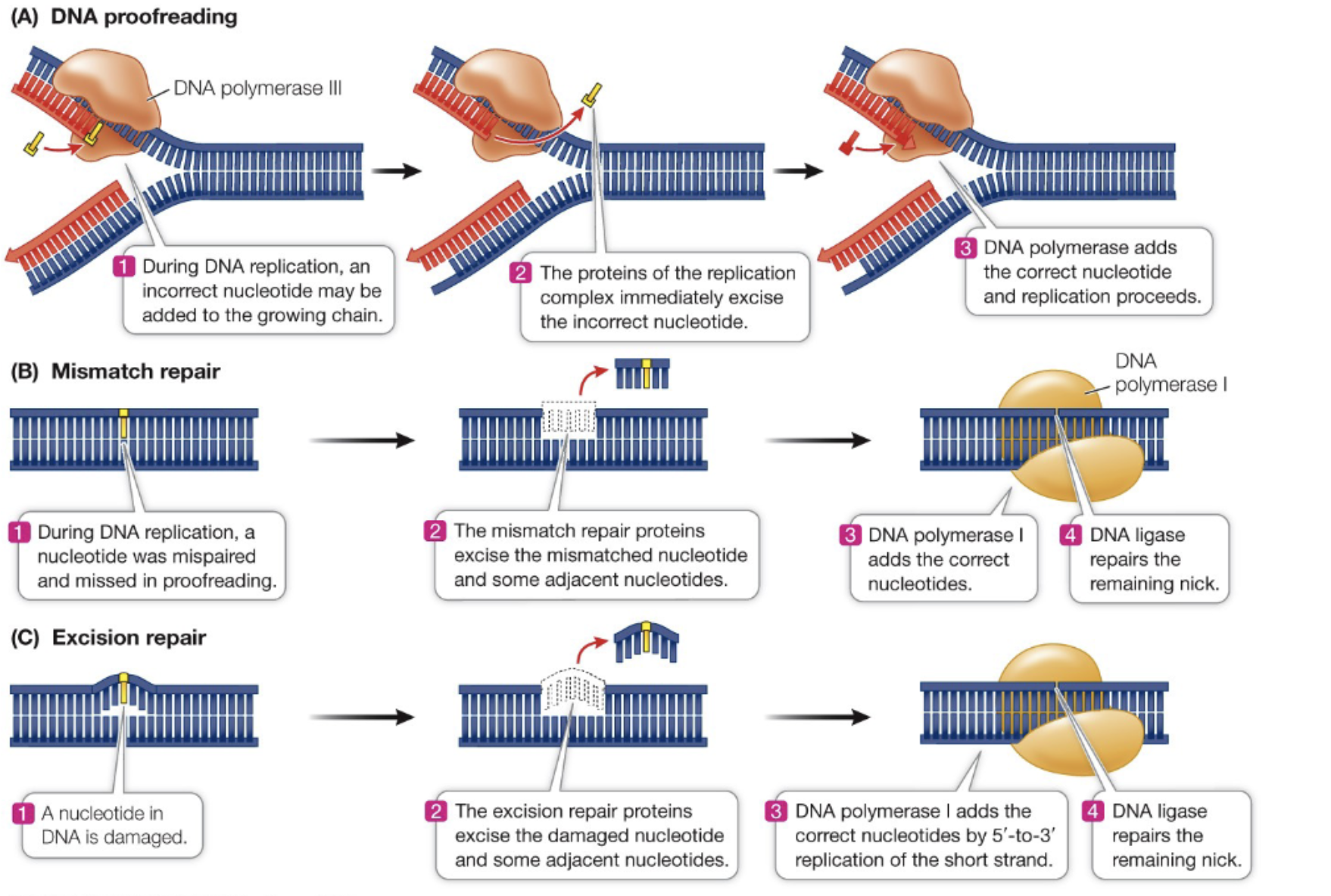
DNA Proofreading
Process by which DNA polymerase III checks for errors during DNA replication and corrects them. Ensures accuracy of DNA sequence.
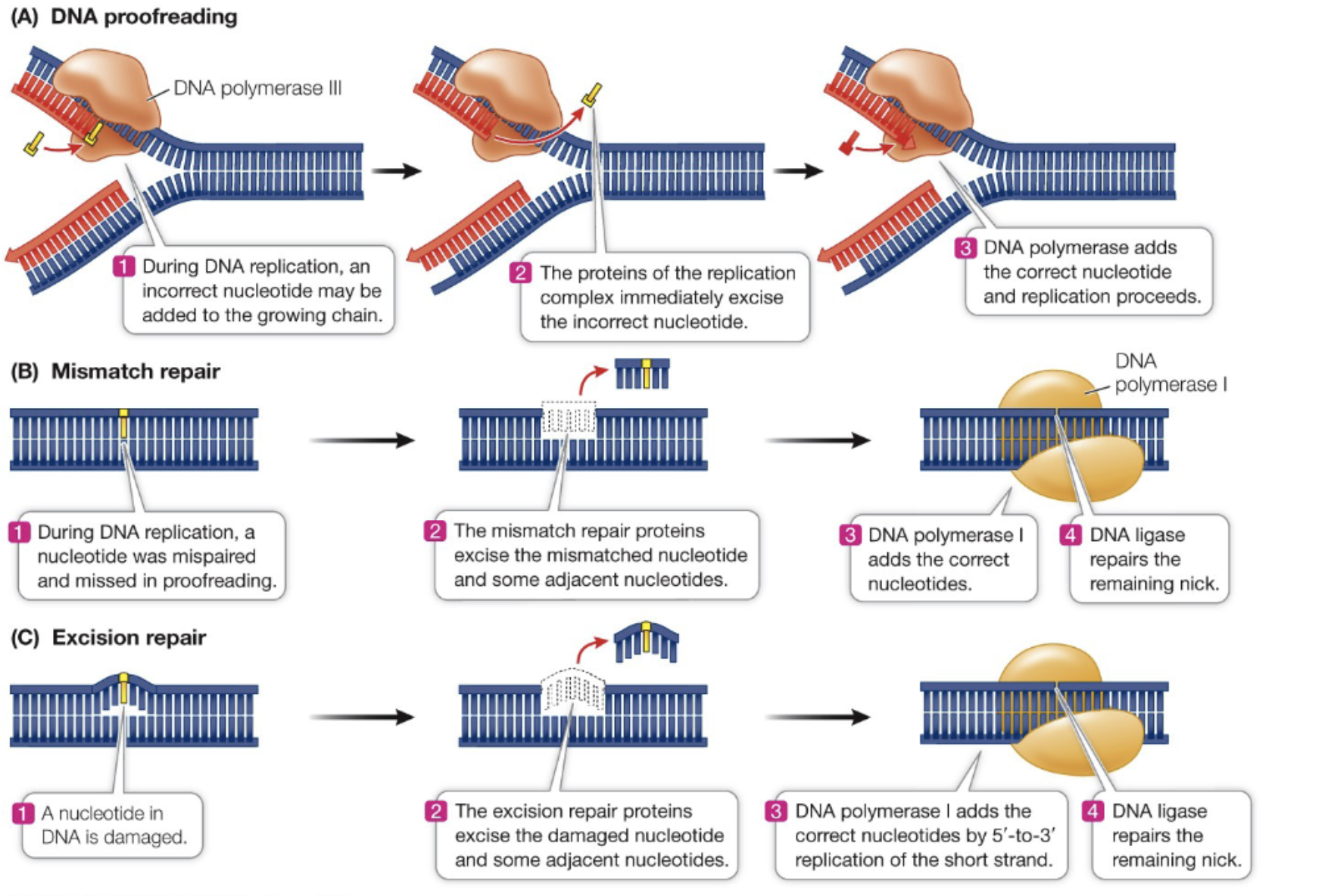
Mismatch Repair
Process that corrects errors in DNA replication by identifying and removing mispaired nucleotides using DNA polymerase I. Essential for maintaining the integrity of genetic information.
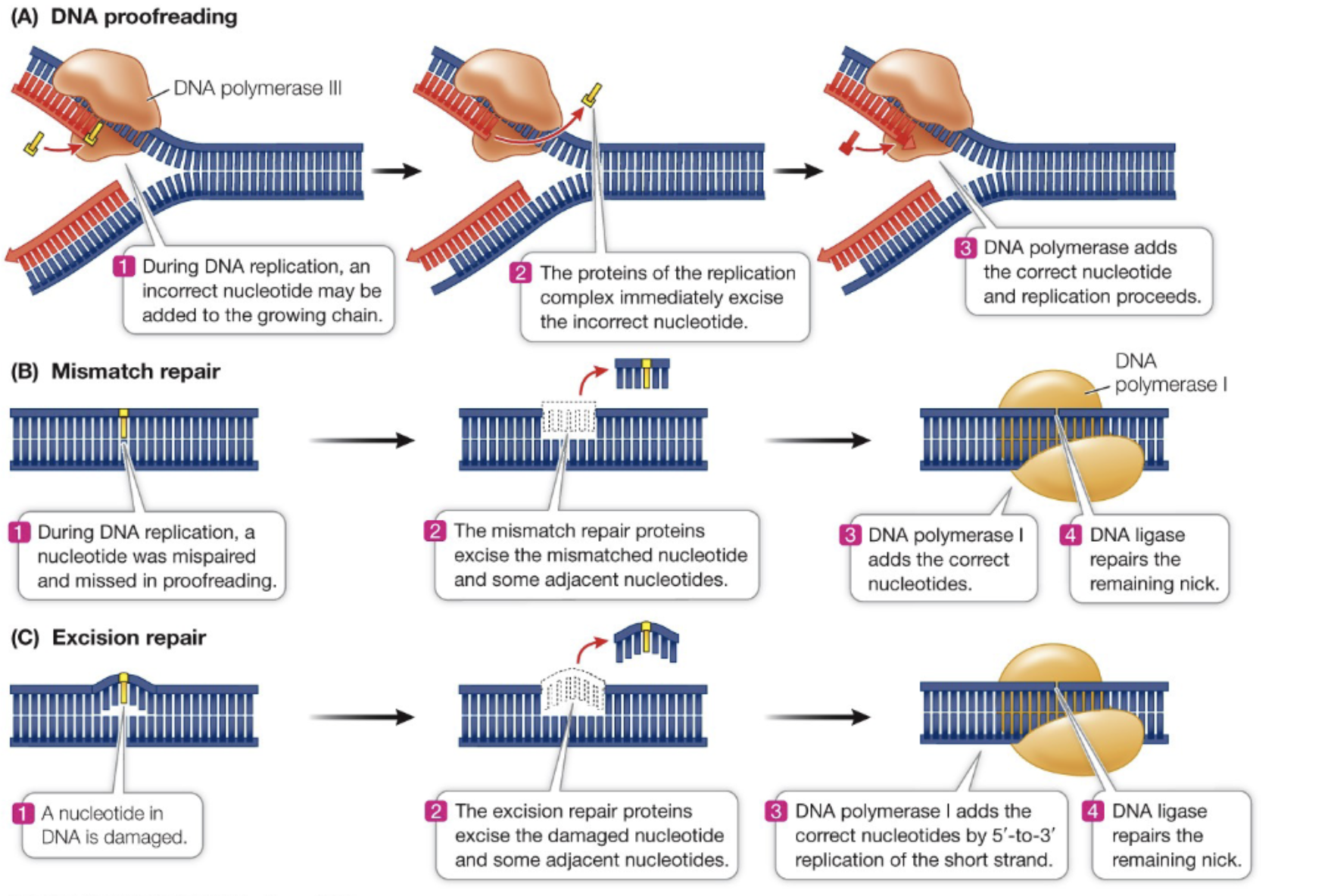
Excision Repair
Process by which damaged DNA is repaired by removing the damaged section and replacing it with the correct nucleotides using DNA polymerase I.
Genes
Units of heredity that carry instructions for building and maintaining an organism. They are composed of DNA and determine an individual's traits and characteristics.
Promoter
A DNA sequence that initiates gene expression. It is located at the beginning of a gene and acts as a binding site for RNA polymerase, allowing transcription to occur.
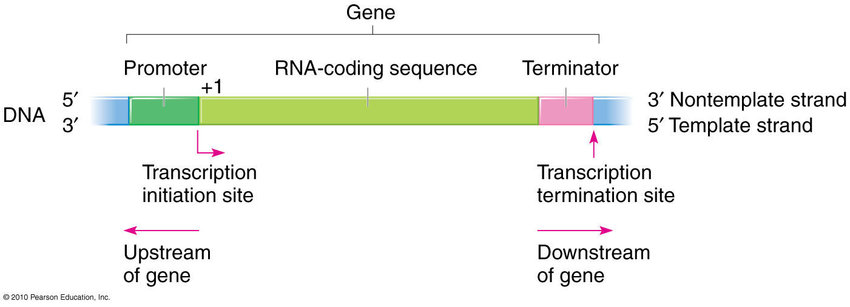
Coding Region
The part of a gene that contains the instructions for building a protein. It is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into amino acids by ribosomes.
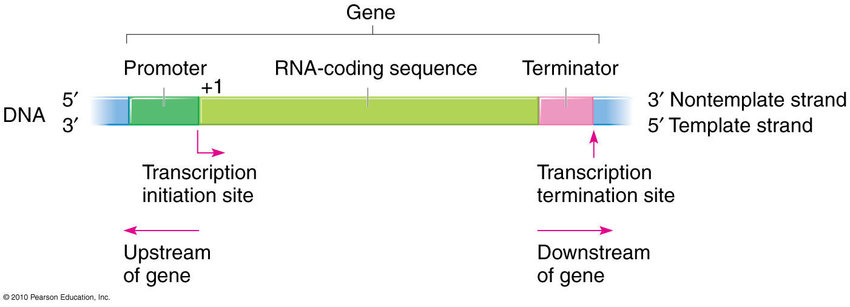
Terminator
A DNA sequence that signals the end of gene transcription. It helps in halting the production of mRNA and prevents further synthesis of proteins.
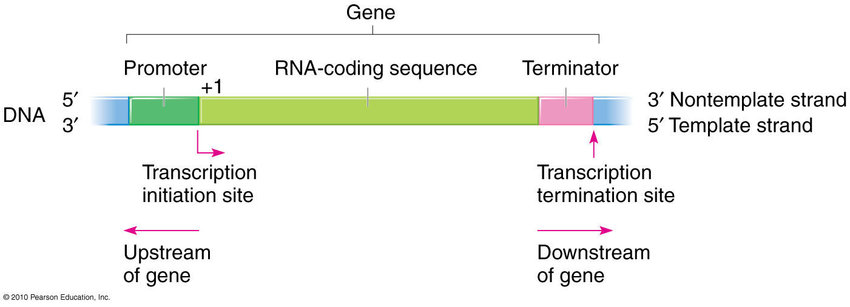
Transcription
Process of synthesizing an RNA molecule using DNA as a template. RNA is synthesized 5’ to 3’, 3’ to 5’ is used as a template, Uracil replaces Thymine. Happens in the nucleus.
Initiation
The process where RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter region to begin synthesizing an RNA molecule.
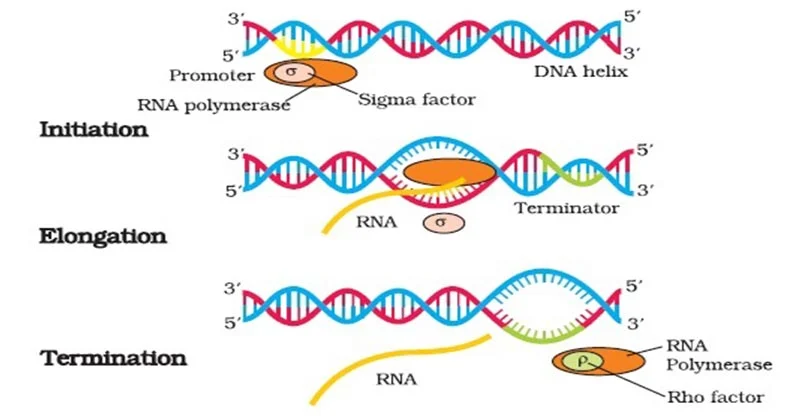
Elongation
Process where RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing RNA strand during transcription.
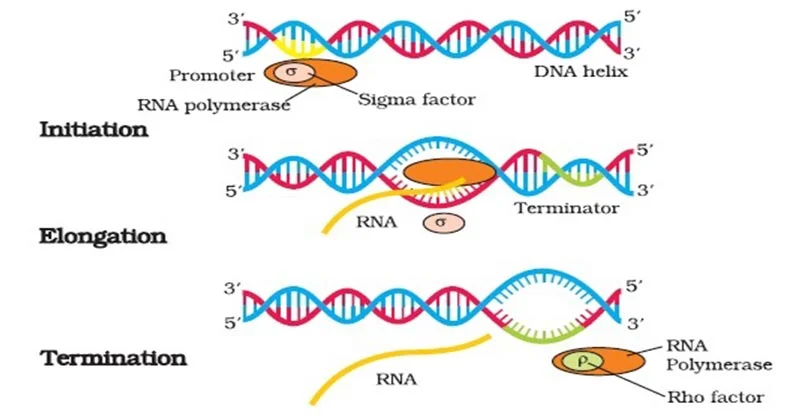
Termination (Transcription)
A specific DNA base sequence stops transcription
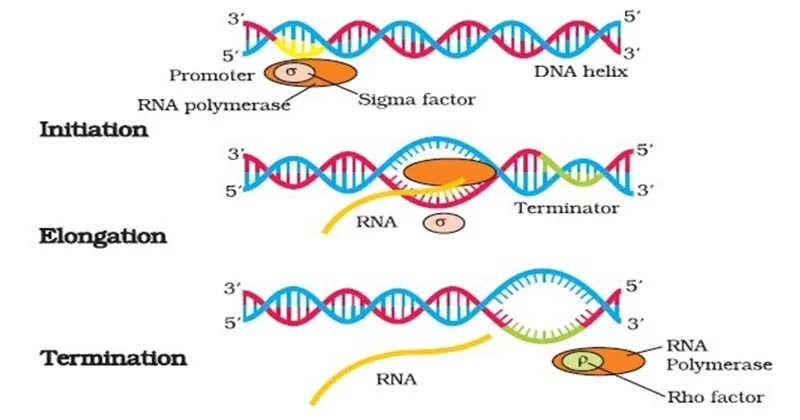
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme responsible for transcription in cells. It synthesizes RNA molecules by reading the DNA template strand and adding complementary RNA nucleotides.
Nucleoside Triphosphate
Molecules composed of a nucleoside (a nitrogenous base linked to a sugar) and three phosphate groups. They are essential for various cellular processes, including DNA and RNA synthesis, energy transfer, and signaling pathways. Examples of NTPs include adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triphosphate (UTP). These molecules provide the necessary energy and building blocks for cellular activities.
Splicing
Process by which introns are removed from pre-mRNA molecules, and exons are joined together to form a mature mRNA. It occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and is essential for producing functional proteins.
G Cap
A regulatory element found at the 5' end of mRNA molecules. It is recognized by proteins that help initiate translation, ensuring efficient protein synthesis.
Poly A Tail
A sequence of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of mRNA during post-transcriptional processing. It protects the mRNA from degradation and helps in the export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation.
Translation
Process in which the genetic information carried by mRNA is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a protein molecule. Occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid or serves as a start or stop signal in protein synthesis.