Inferential Statistics III
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What two properties must the null and alternative hypotheses satisfy?
They must be mutually exclusive (cannot both be true) and exhaustive (cover all possible outcomes).
What is a directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that predicts the direction of the effect (e.g., “Expensive price will increase perceived quality”).
What is a non-directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that predicts a difference but not the direction (e.g., “Price will change perceived quality in some way”).
Example of directional hypotheses for the bag price study?
H₀: Expensive price will not affect perceived quality positively (x̄EC ≤ x̄IC).
H₁: Expensive price will increase perceived quality (x̄EC > x̄IC).
What are t-tests used for?
To determine whether the difference between two means is large enough to conclude that they are statistically different (not due to chance).
What is the general logic of the t-ratio?
t = signal / noise
Signal: difference between group means
Noise: variability in the data (spread, variance)
What increases the signal in a t-test?
Larger differences between group means.
What increases the noise?
High variance
Small sample size
Poorly worded questions
Confounds
Uncontrolled extraneous variables
What is the obtained t-value (t-obt)?
A statistic representing the strength of the observed effect in your data.
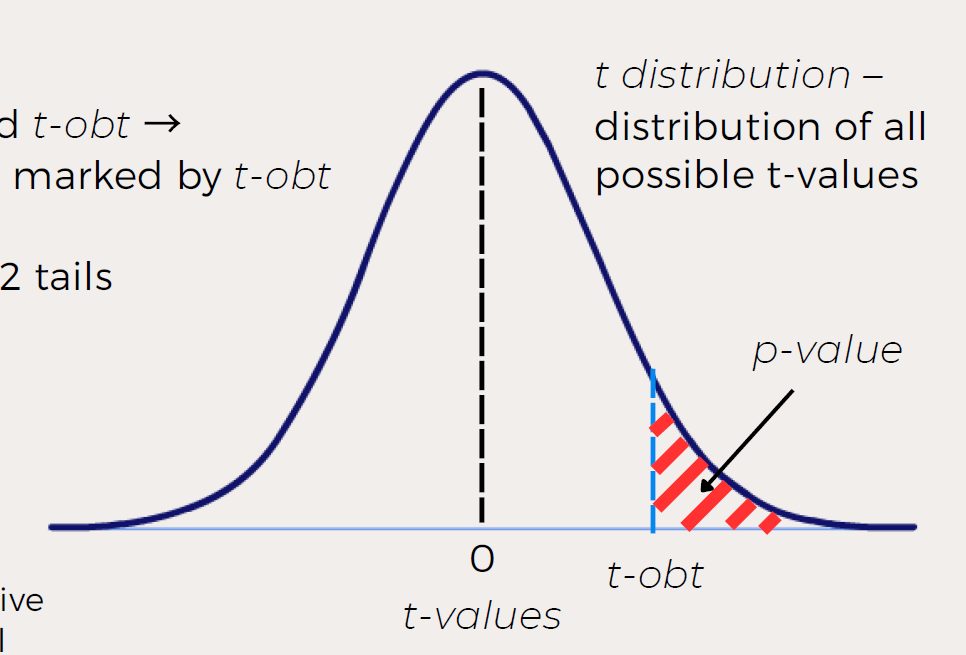
What increases t-obt?
Bigger numerator → bigger difference between means
Smaller denominator → less variability
What does a larger t-obt imply?
A stronger effect; more evidence against the null hypothesis.
What is the p-value in a t-test?
The area under the tails of the t-distribution beyond your t-obt:
→ Probability of obtaining a result as or more extreme than what you found if the null were true.
What is the difference between 1-tailed and 2-tailed tests?
1-tail: used for directional hypotheses; examines only one tail.
2-tail: used for non-directional hypotheses; examines both tails.
What is the critical t-value (t-crit)?
The value that marks the cutoff for the most extreme 5% (or chosen alpha) of the t-distribution. It corresponds to alpha (commonly 0.05).
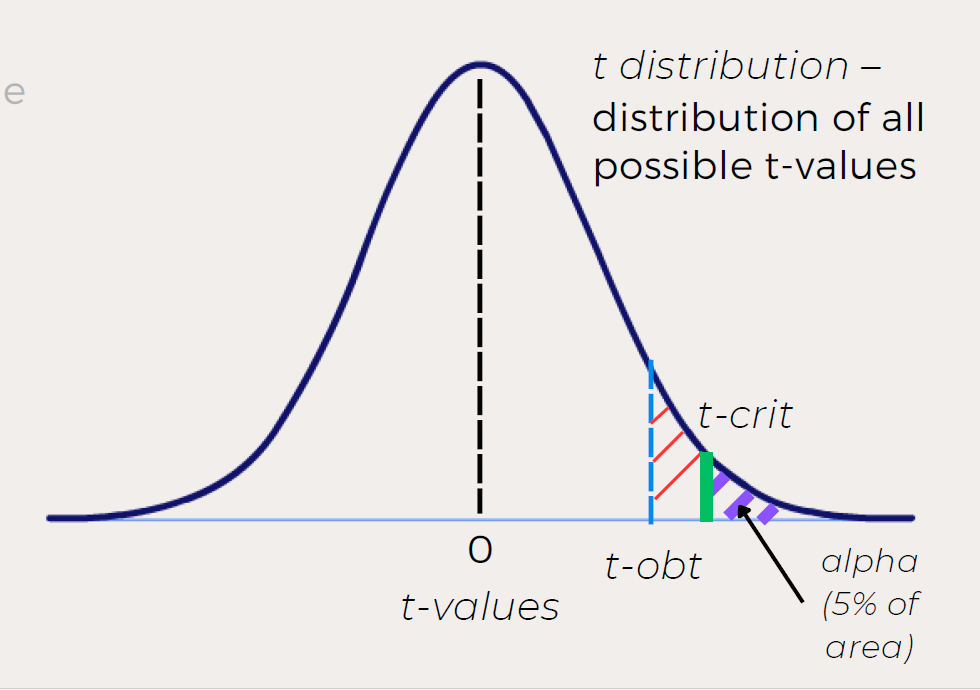
How do t-obt and t-crit determine decisions?
t-obt < t-crit → retain null
t-obt ≥ t-crit → reject null
This matches the decision rule for p-values:
p > α → retain null
p ≤ α → reject null
What are the steps of NHST for t-tests?
Formulate hypotheses; assume H₀ is true.
Collect data.
Compute t-obt and/or p-value.
Compare t-obt to t-crit (or p to α).
Decide whether to reject or retain the null.

A) is correct
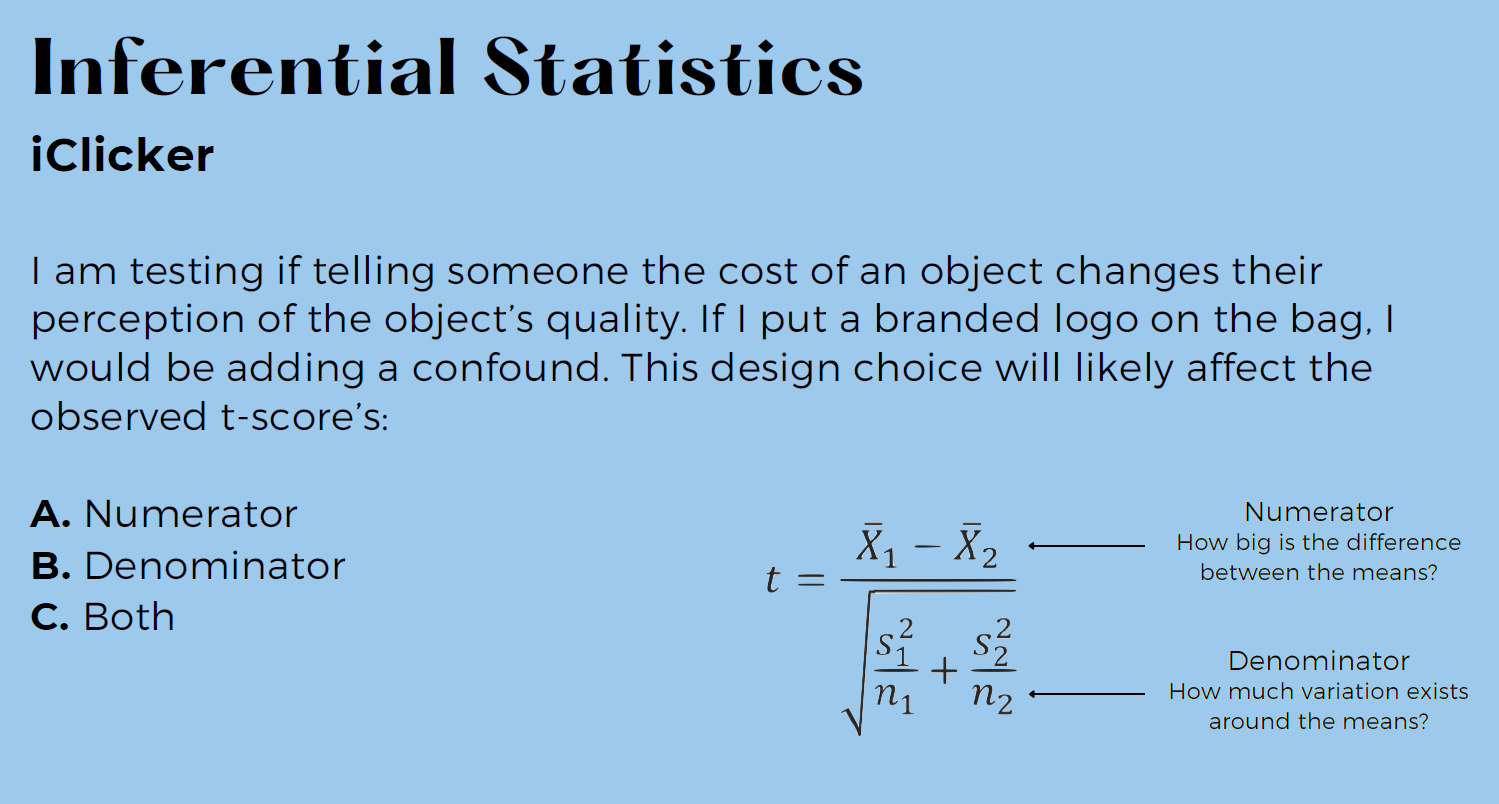
c) is correct
Numerator → more indirect but both means will change due to this confound
But it will more so affect the denominator over the numerator
Denominator = noise; adding confound adds more noise
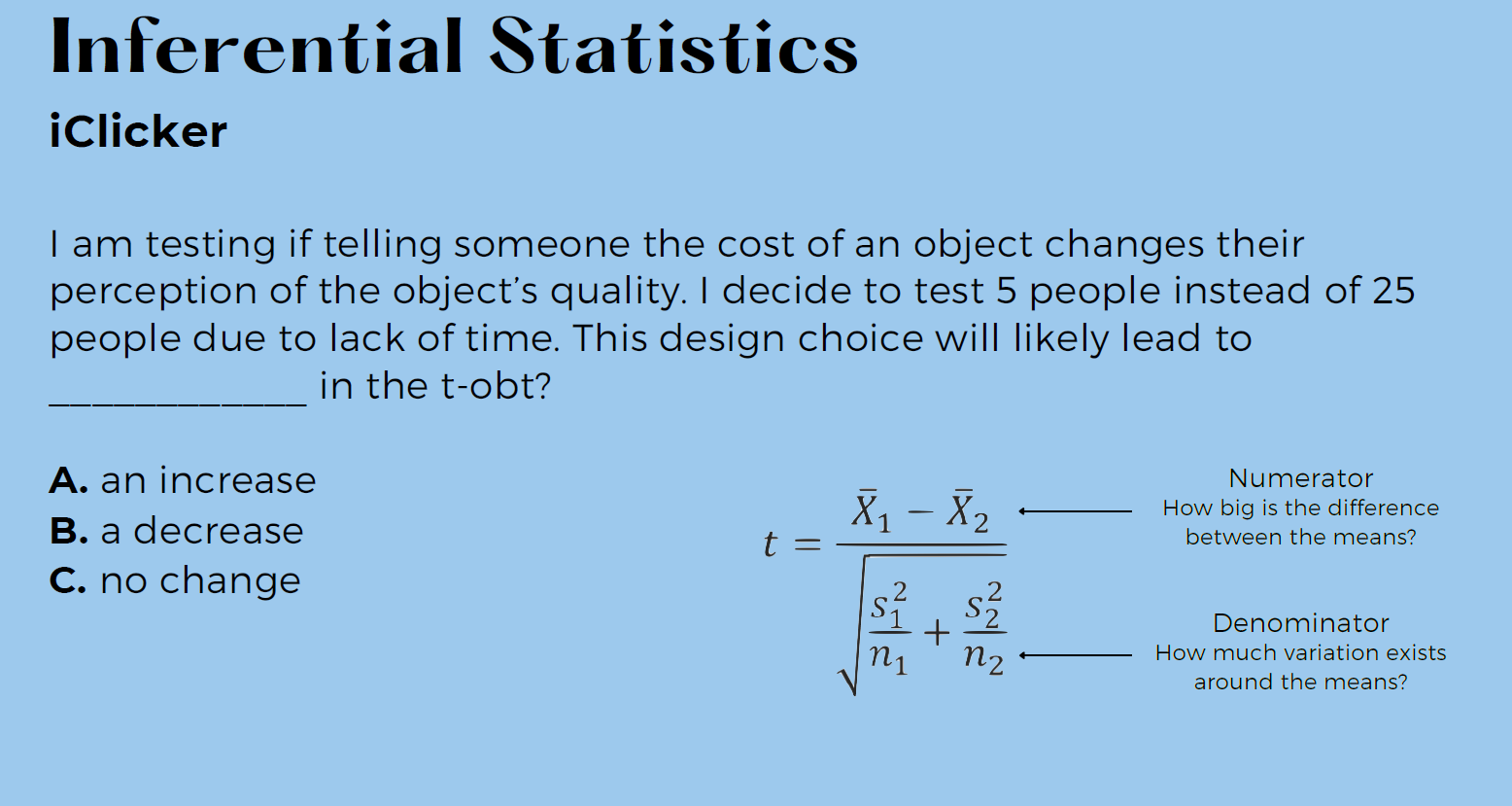
b) is correct
Smaller sample size = increased variability
What else would be decreasing if we use a small sample size?
Statistical power → how large is the effect we see
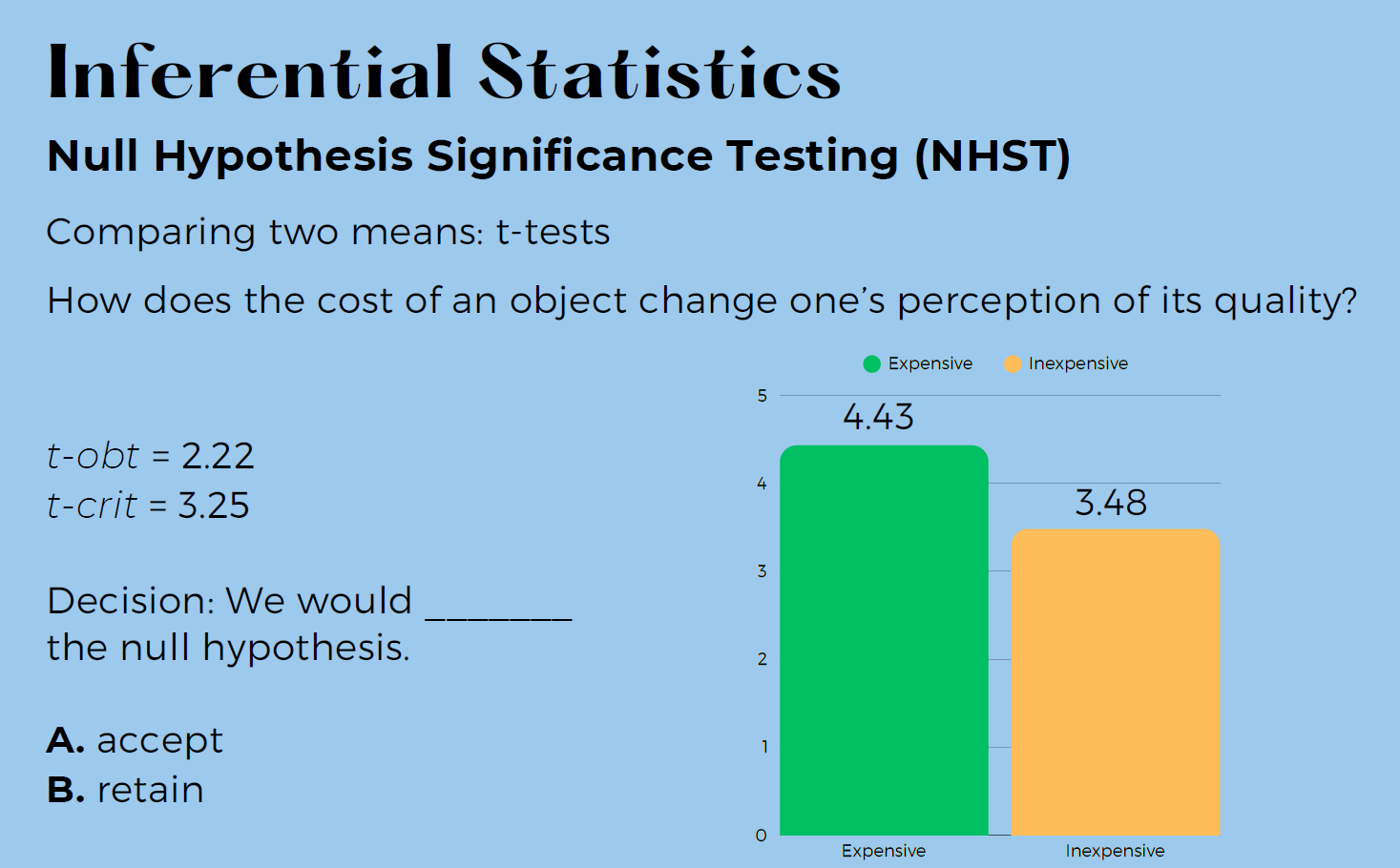
Typo: B) should be reject
A) is correct → t-crit > t-obt
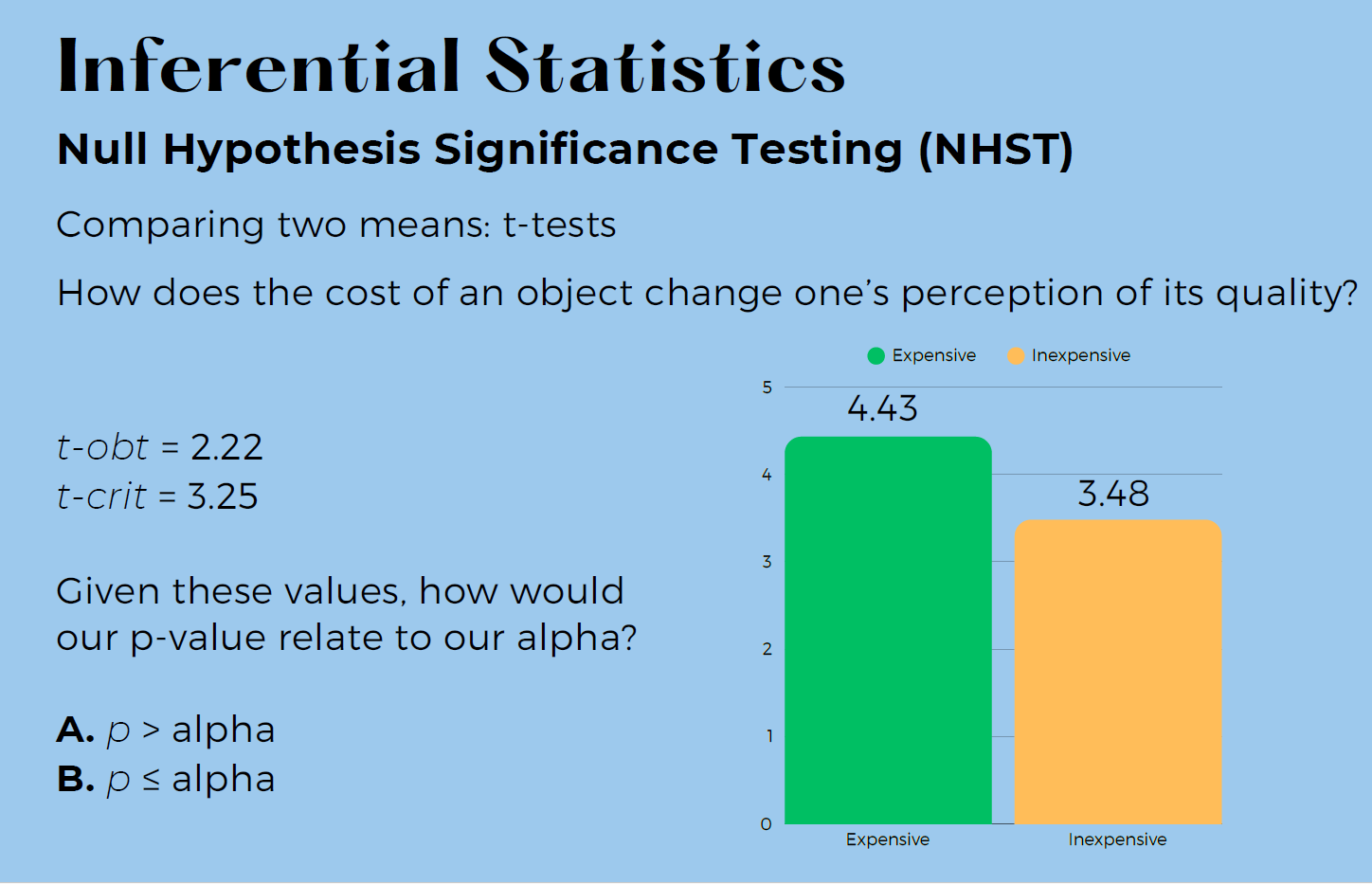
A) is correct