Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nerve Tissue
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
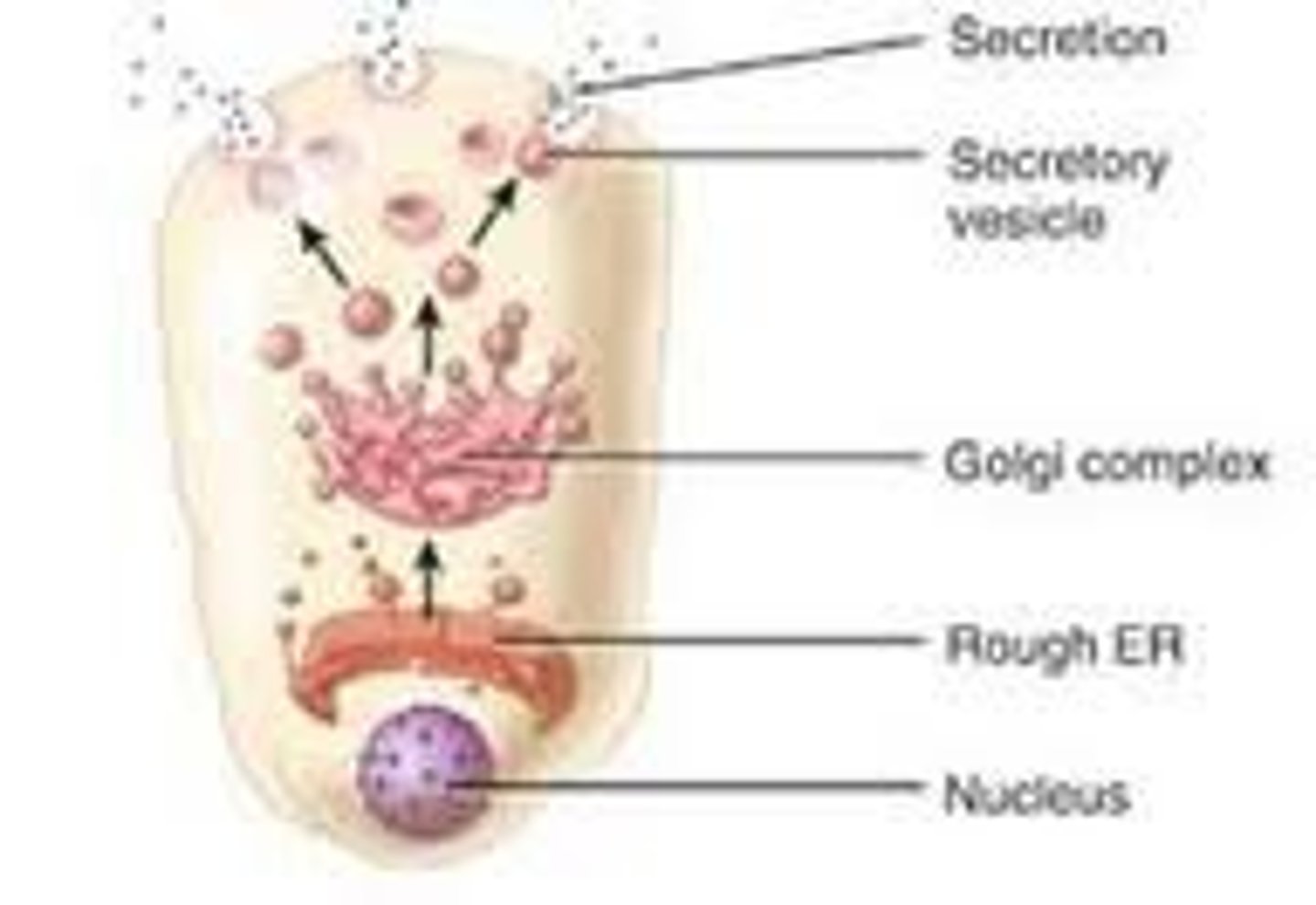
Merocrine
No part of the cell is lost with the secretion - salivary glands
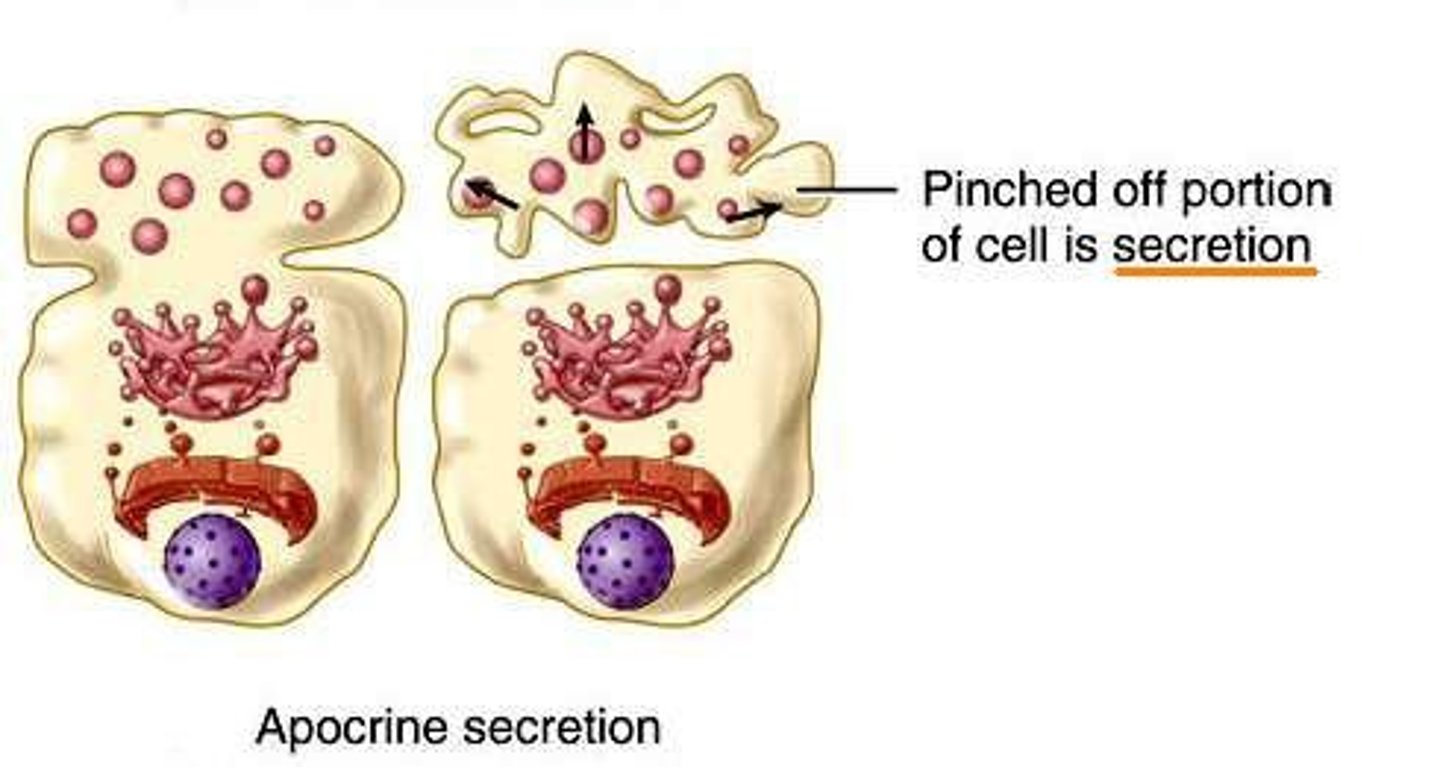
apocrine
The top of the cell is lost with the secretion - mammary glands
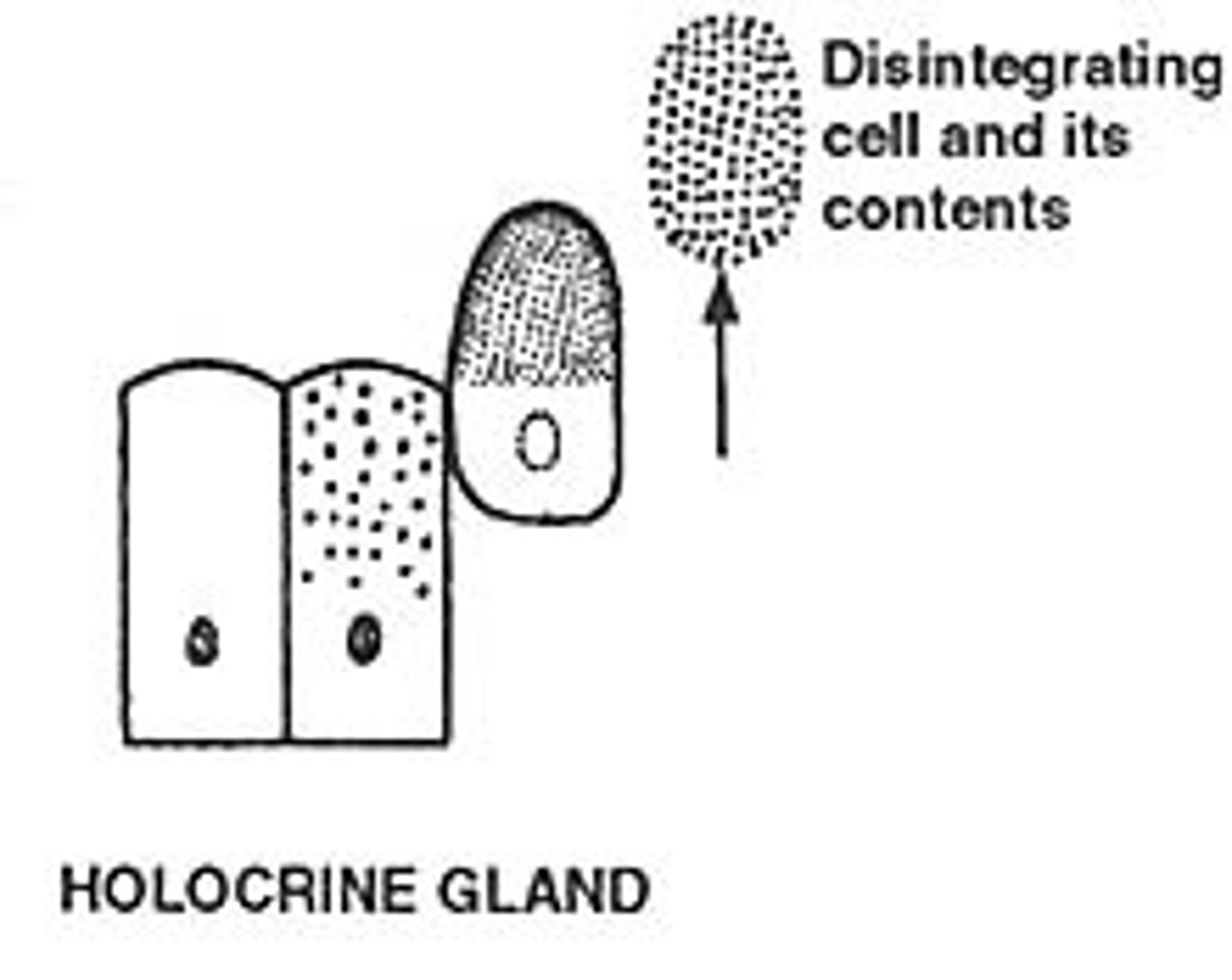
holocrine
The whole cell detaches with the secretion
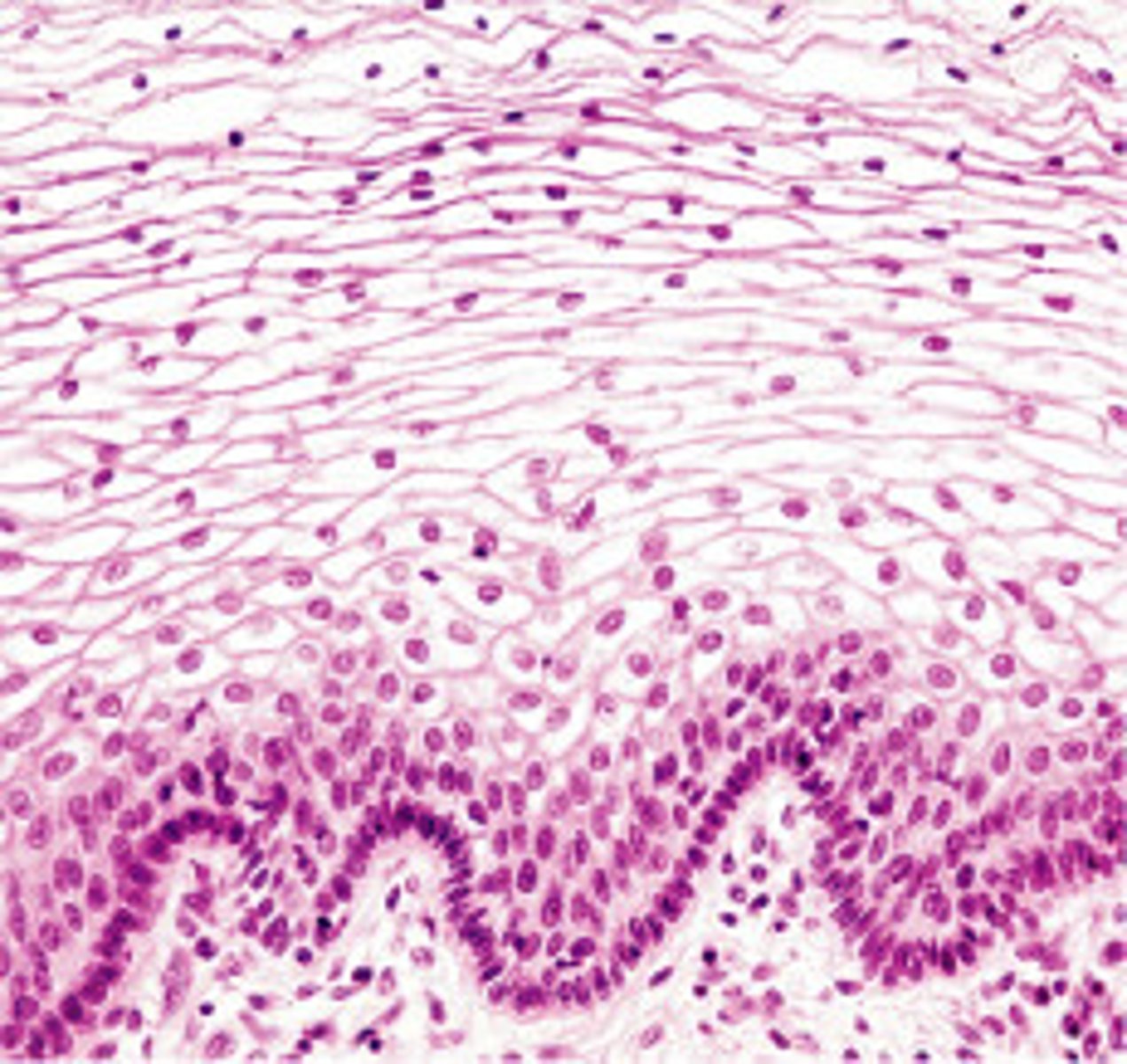
stratified squamous epithelium
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
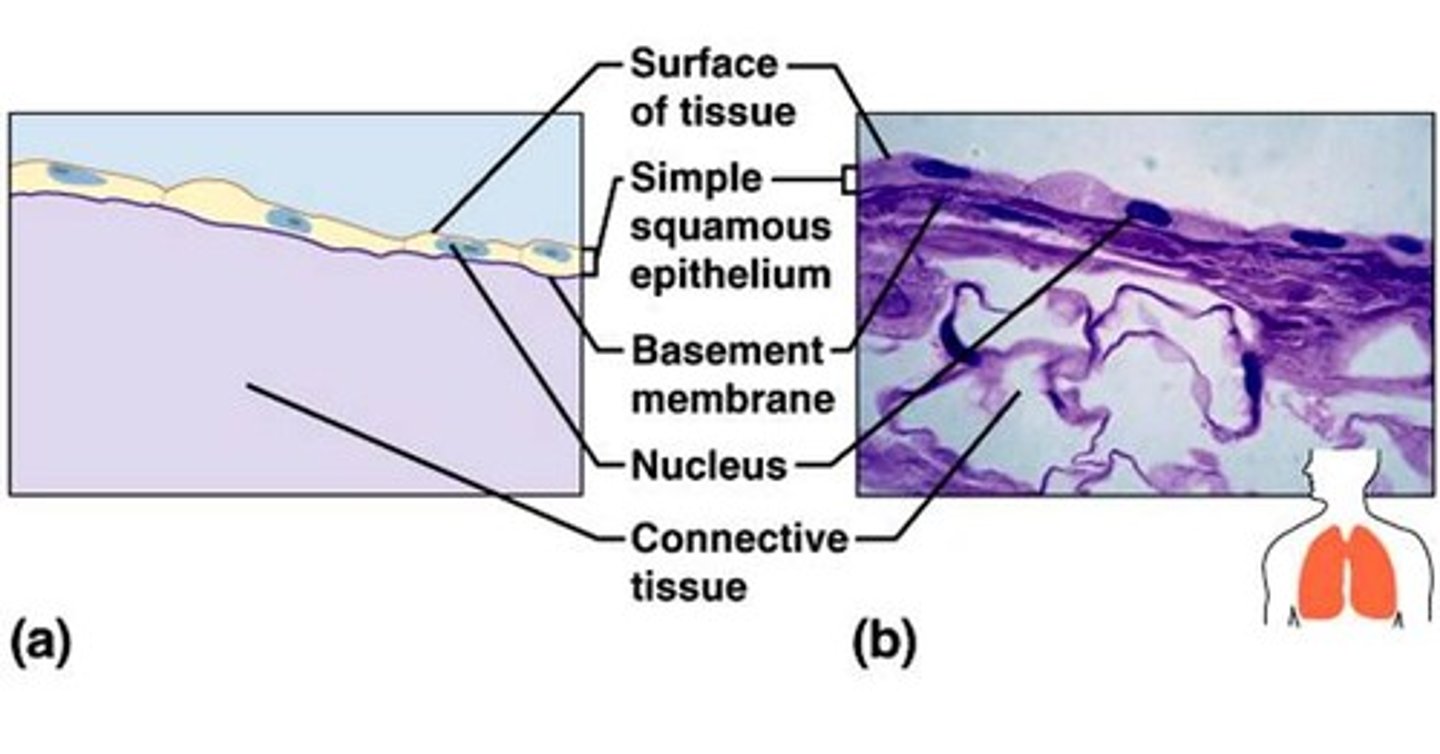
simple squamous epithelium
Function: Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae.
Location: blood vessels and lungs
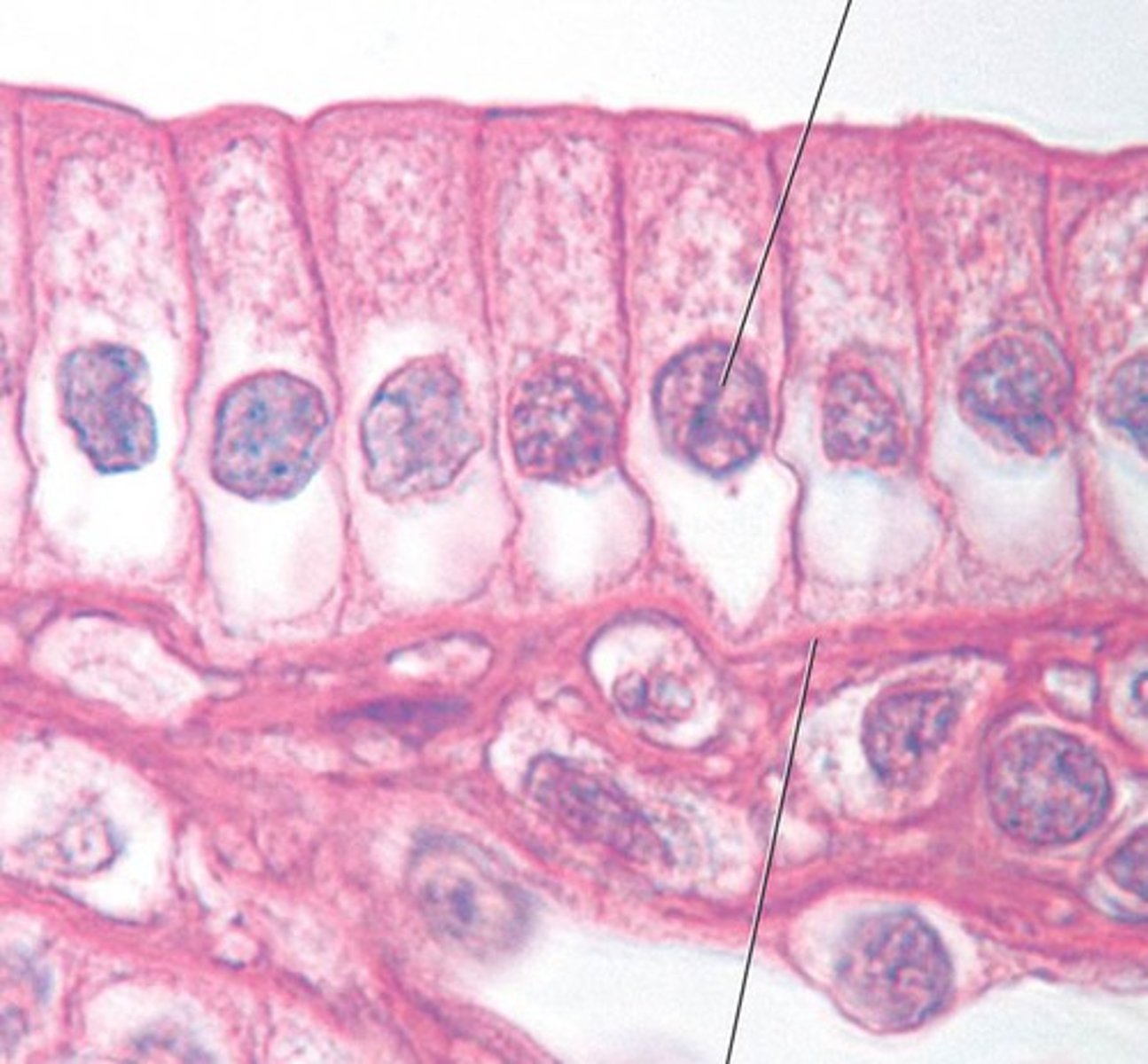
simple columnar epithelium
Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliated action.
Location: digestive tract
simple cuboidal epithelium
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: Kidney
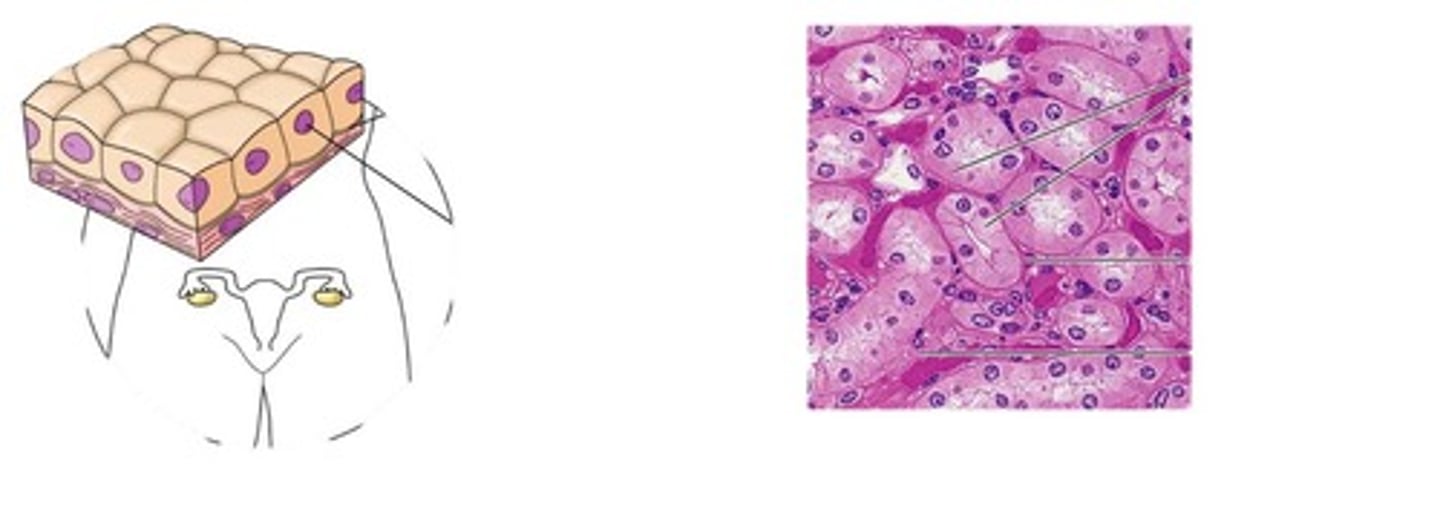
stratified columnar epithelium
Function: protection and secretion
Location: rare in the body; small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
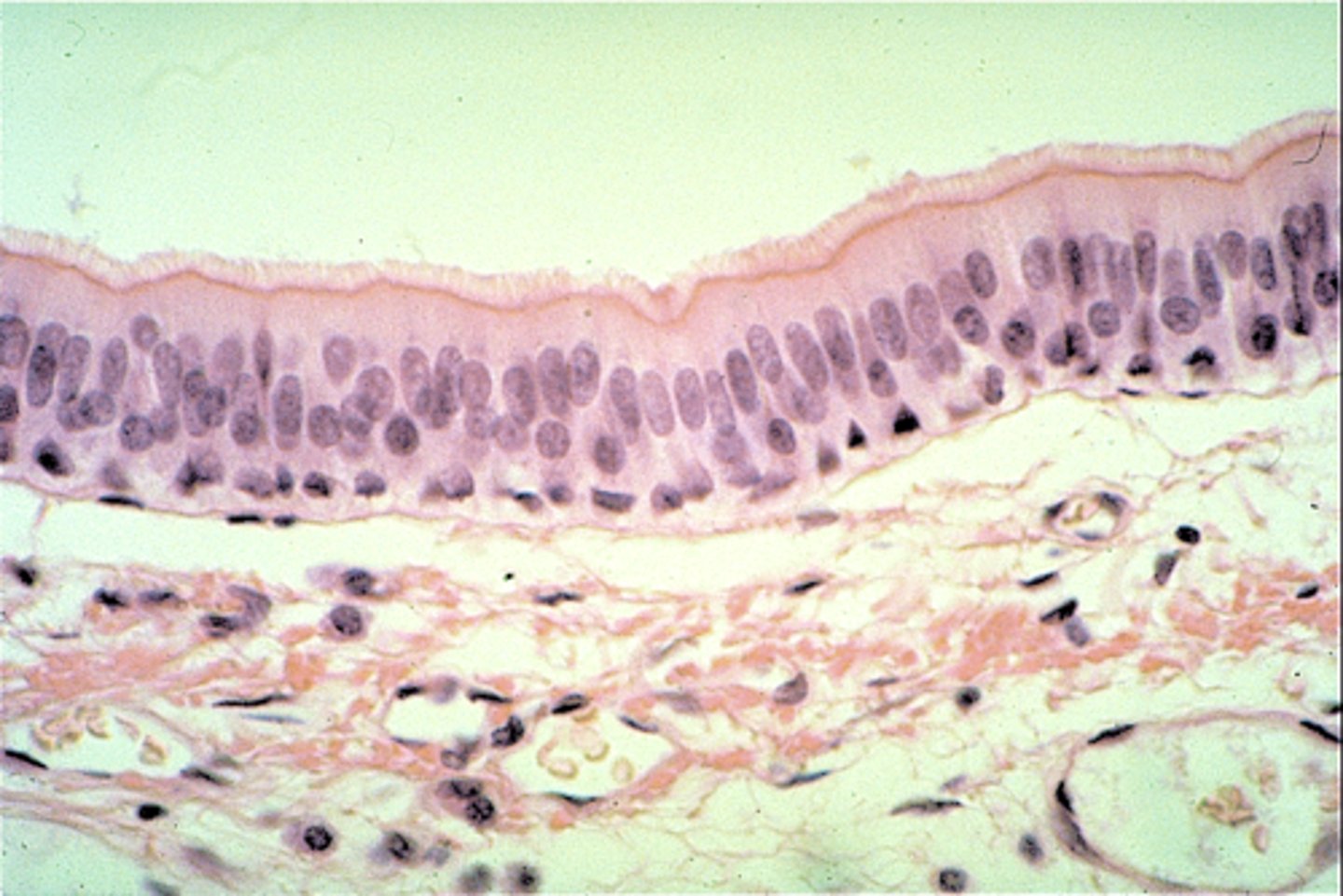
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities.
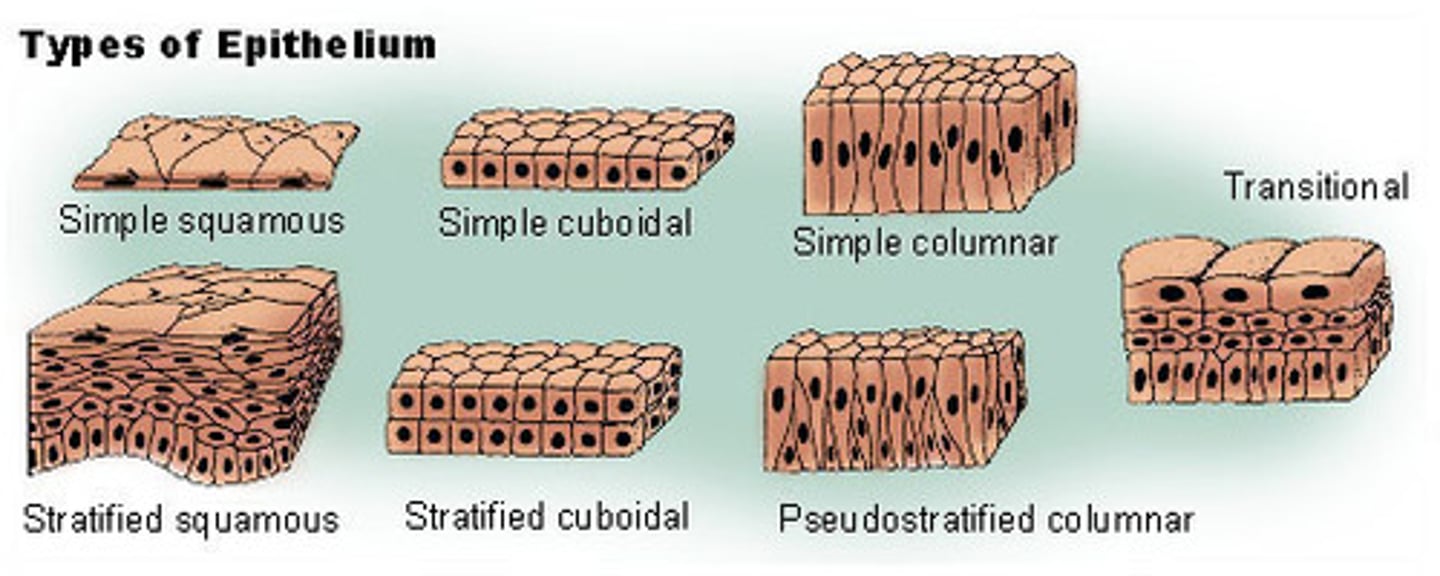
Function of Epithelial tissue
protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration
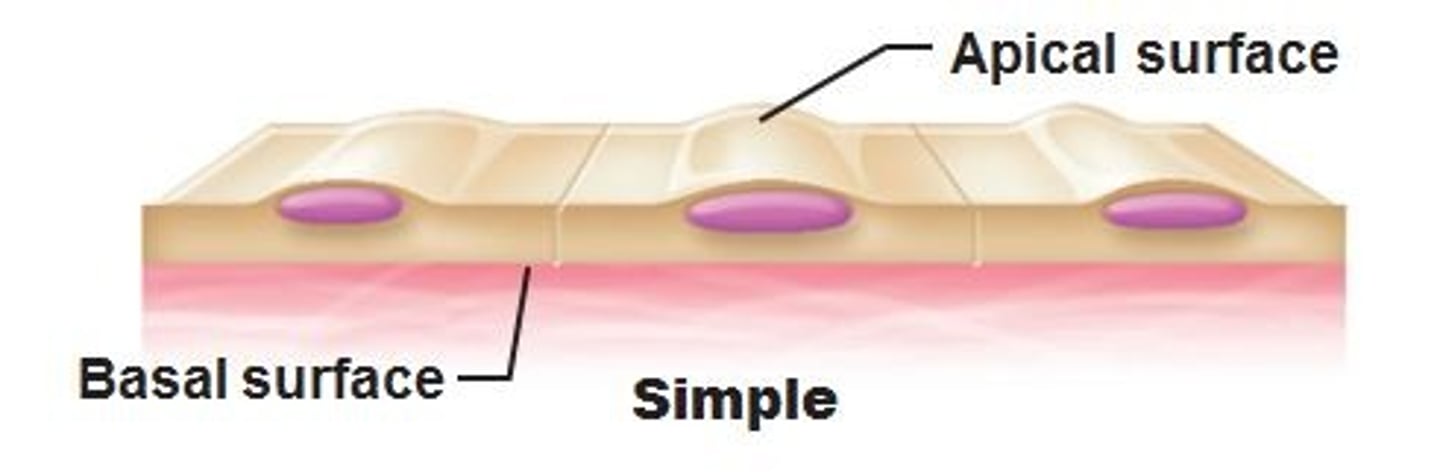
apical surface
upper free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ
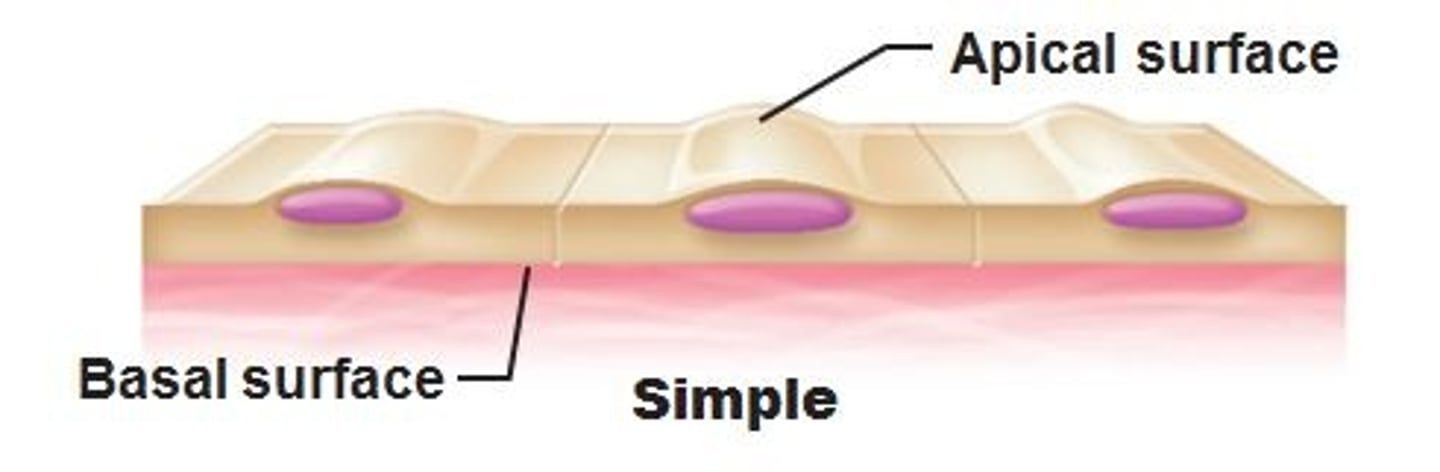
basal surface of epithelial tissue
attached to basement membrane
basement membrane
Layer between epithelium and underlying connective tissue
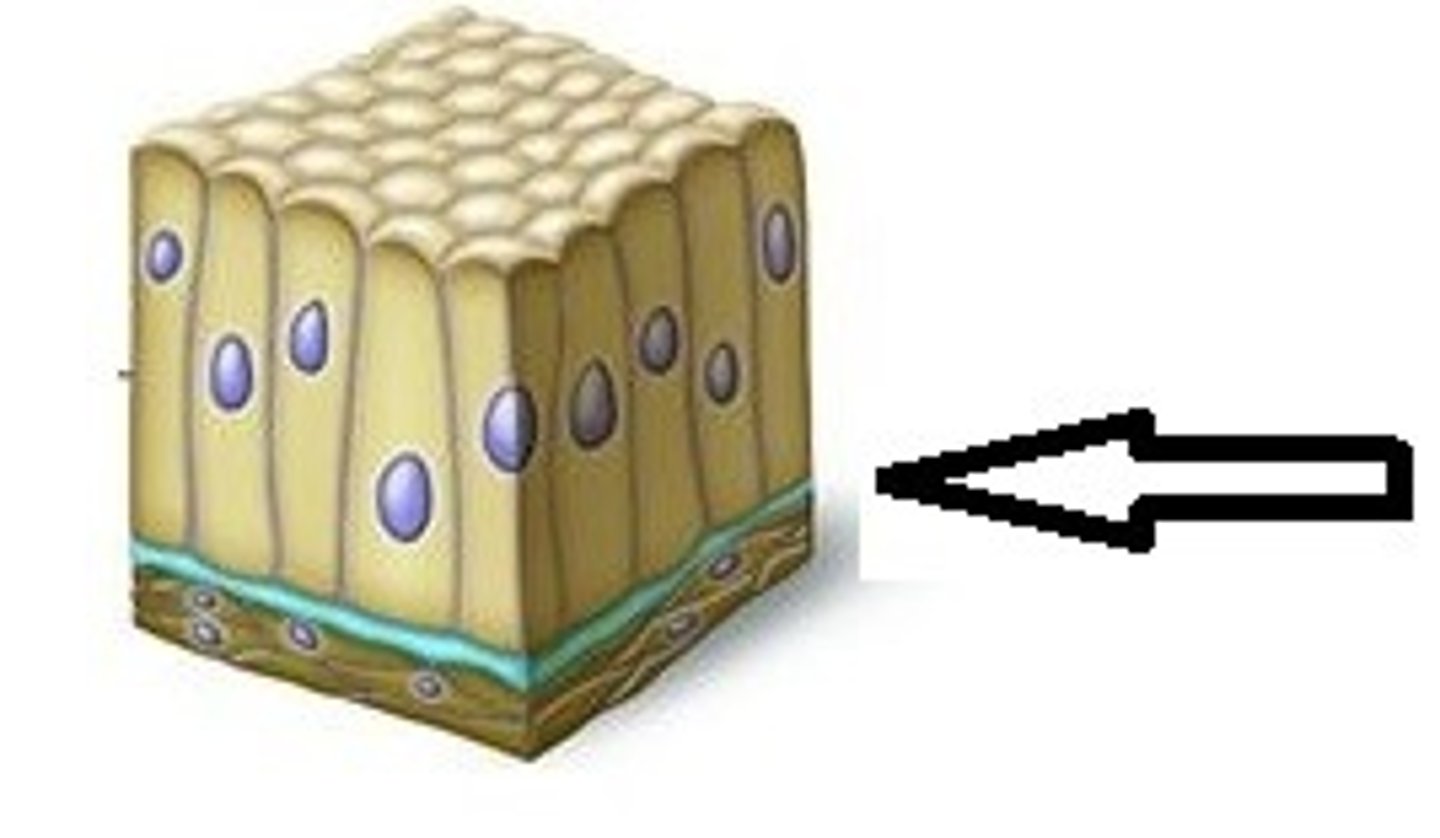
Avascular
without blood vessels - epithelial tissue is this
ground substance of connective tissue
Gelatinous or rubbery material found in between cells-protects by absorbing compressive forces.
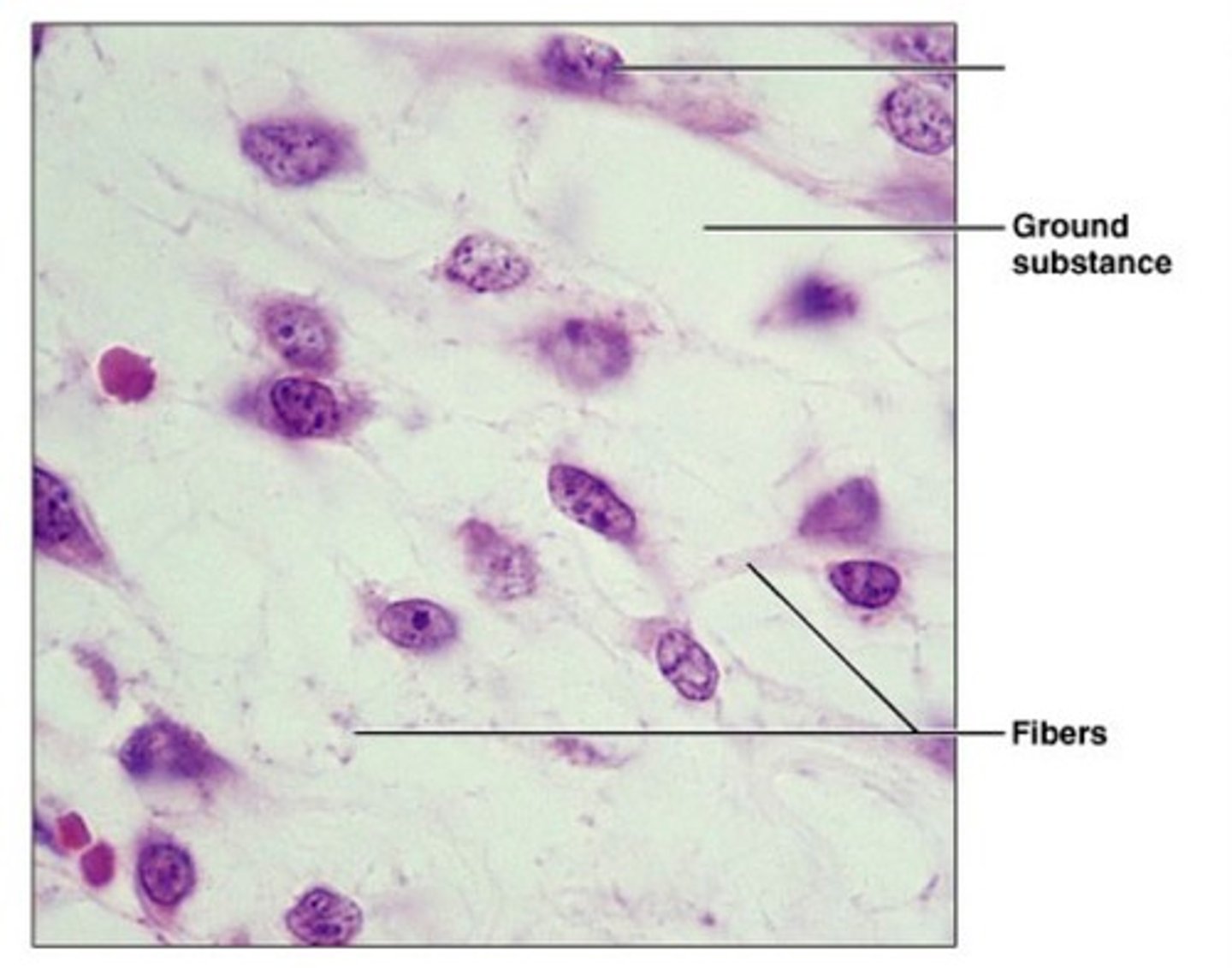
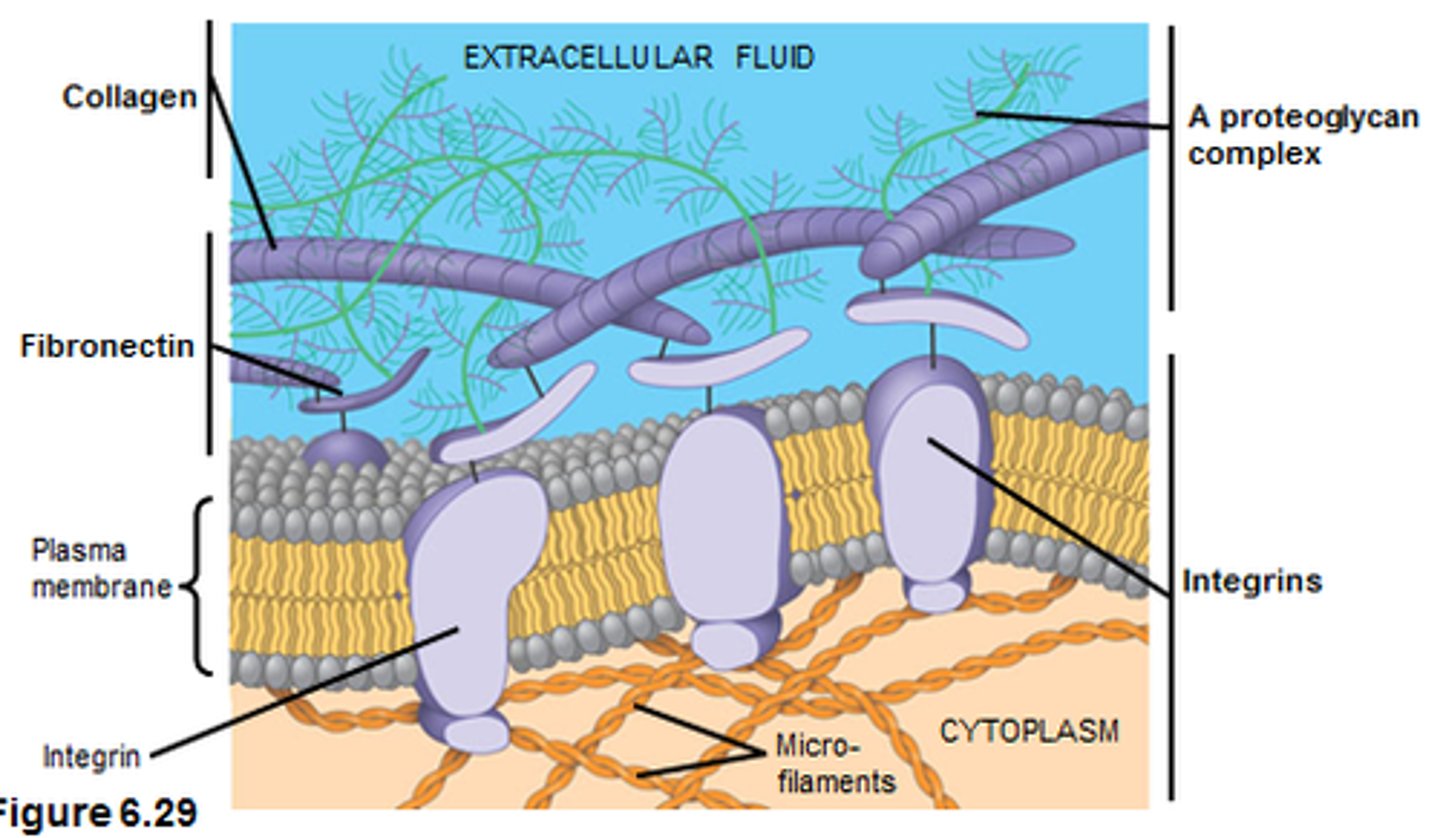
extracellular matrix
The chemical substances located between connective tissue cells
areolar connective tissue
-mostly open space
-holds water and salt for surrounding tissue
-found under epithelium and around organs
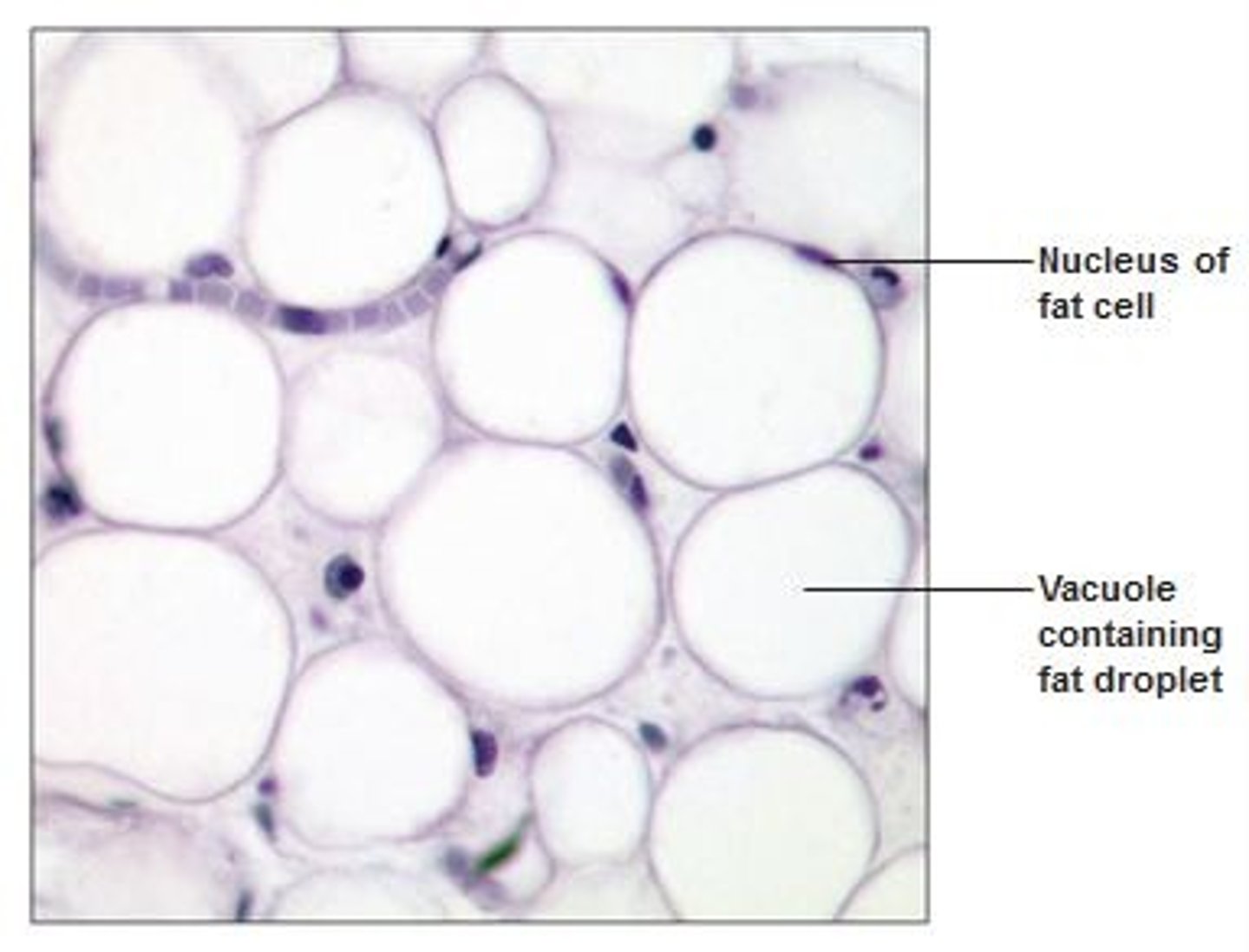
adipose tissue
-Tissue that stores fat.
- insulates, warms, provides nutrients
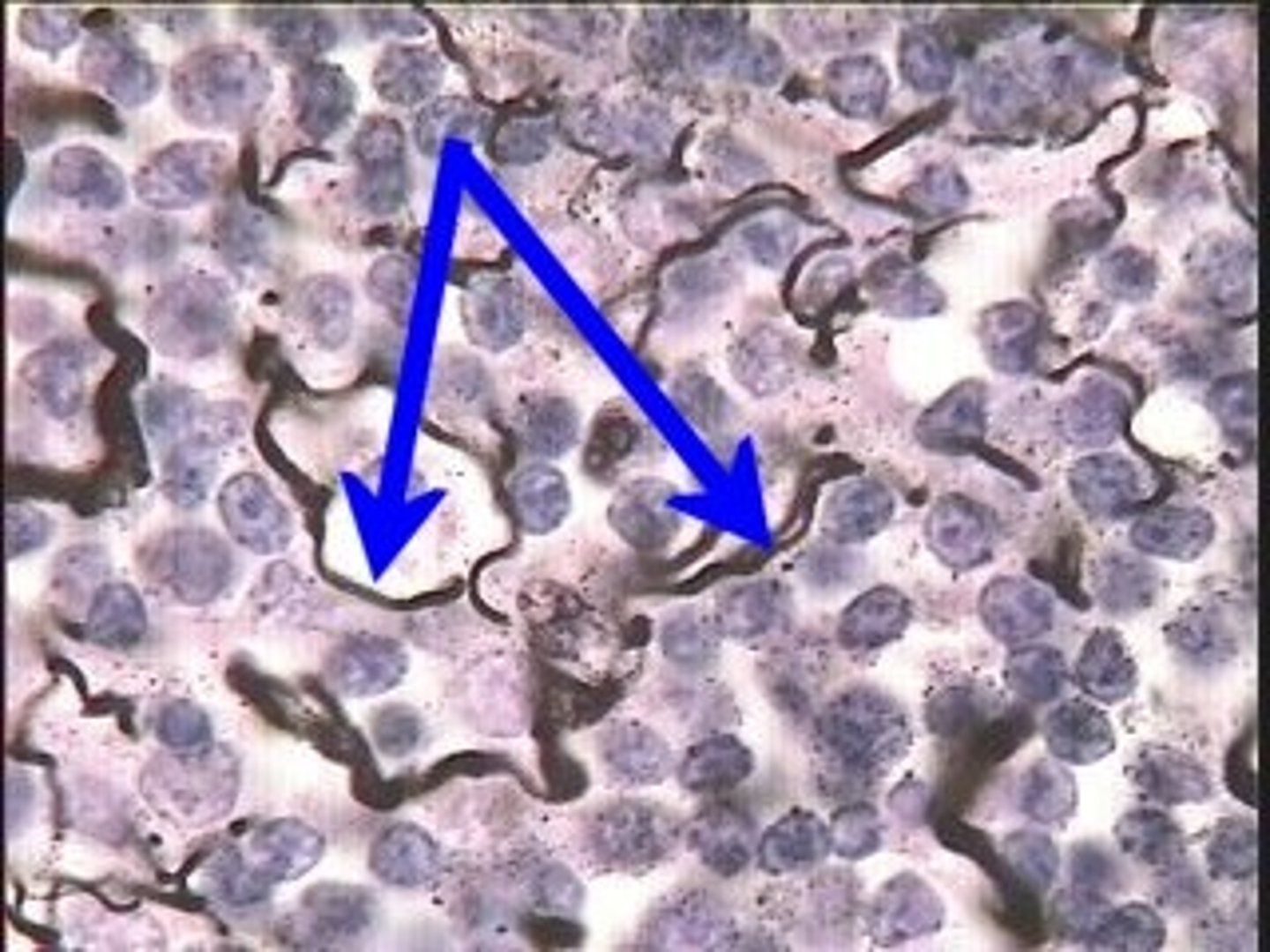
reticular fibers
Fibers found near blood vessels that add strength and support
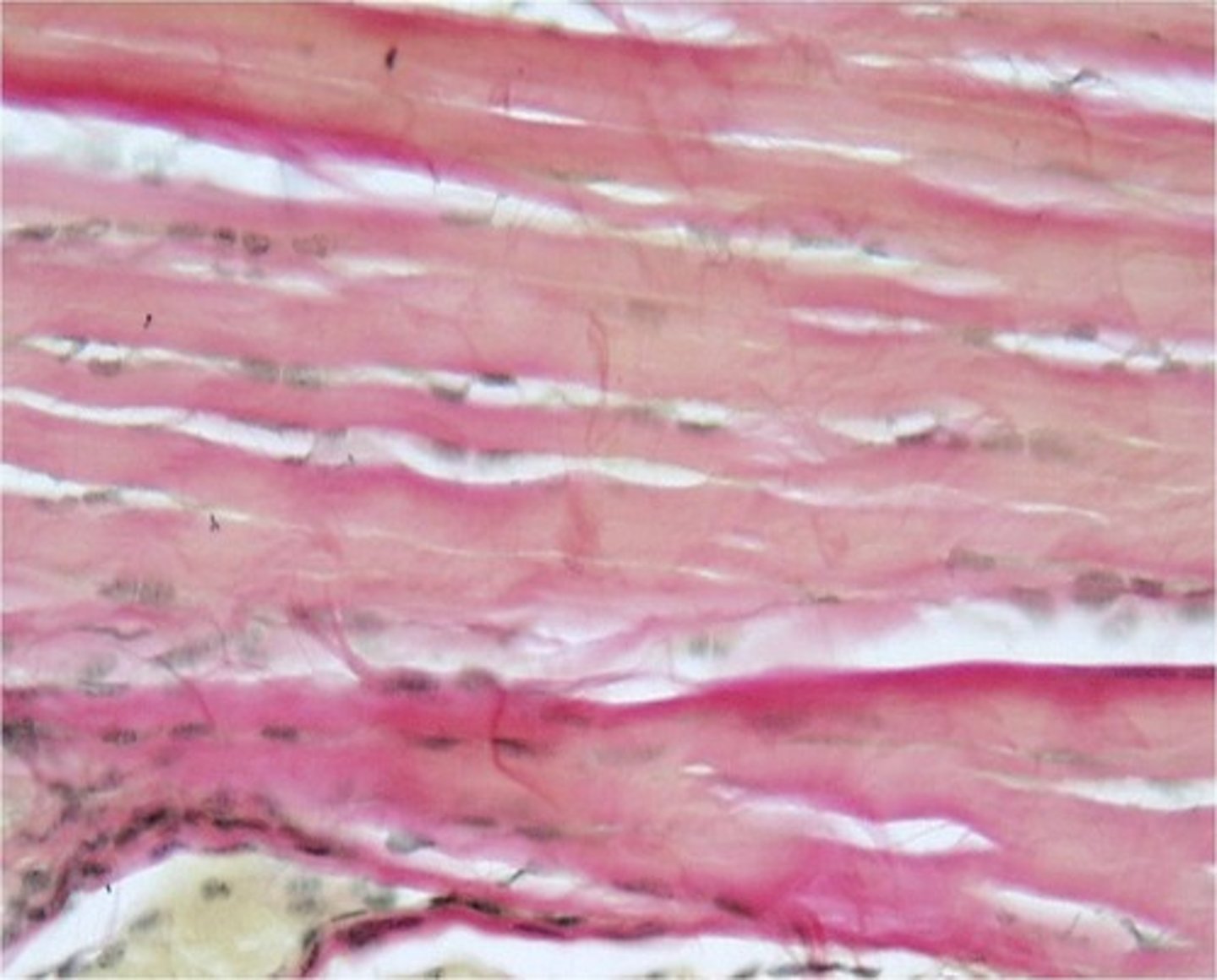
regular dense connective tissue
-has mostly collagenous fibers, but are in a regular, parallel alignment
-provides tensile strength
-tendons and ligaments
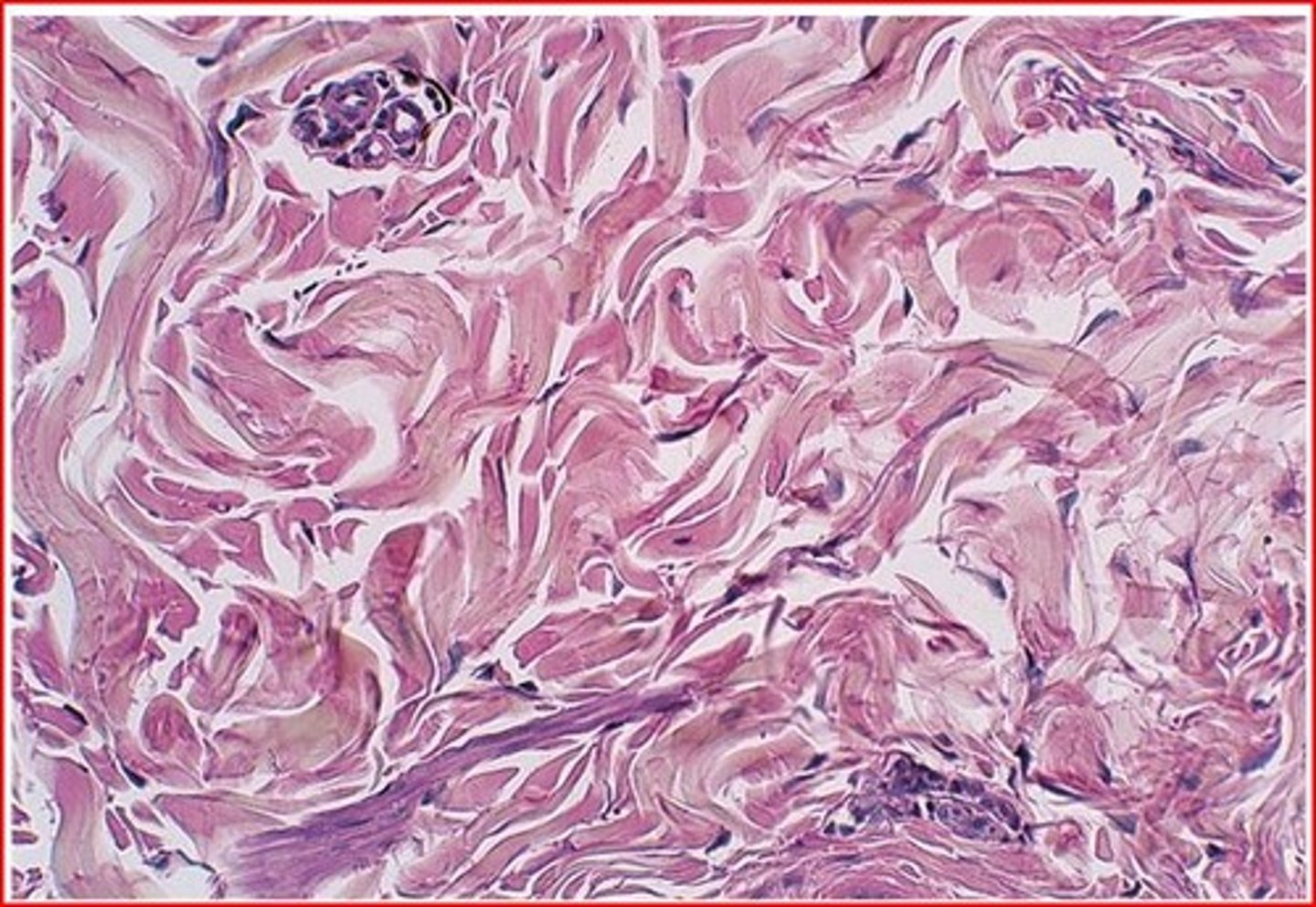
irregular dense connective tissue
-has mostly collagenous fibers in random arrangement
-provides strength in lots of directions
- capsules around organs
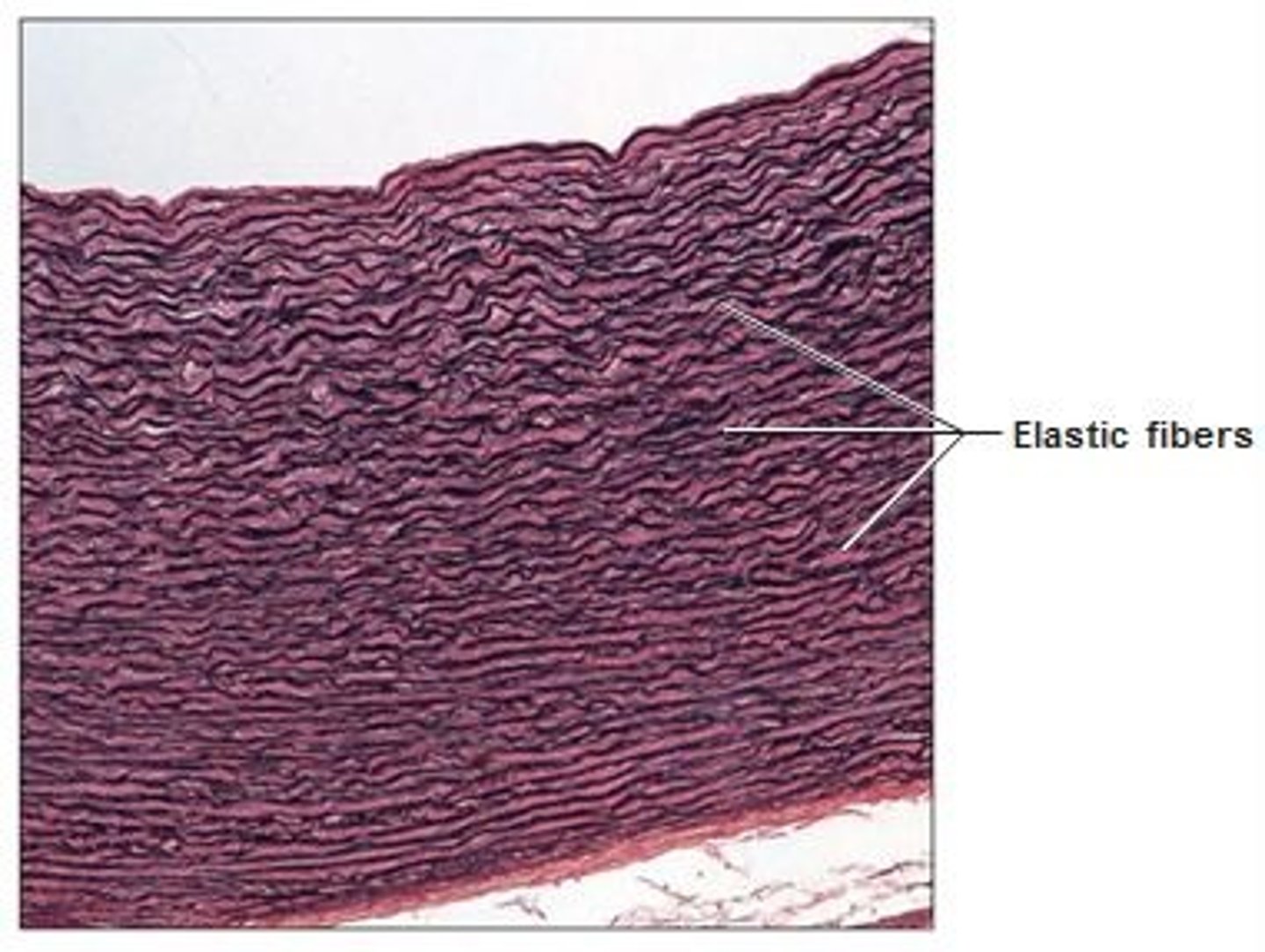
elastic dense connective tissue
provides flexible cushioning, found between vertebrae and in arteries
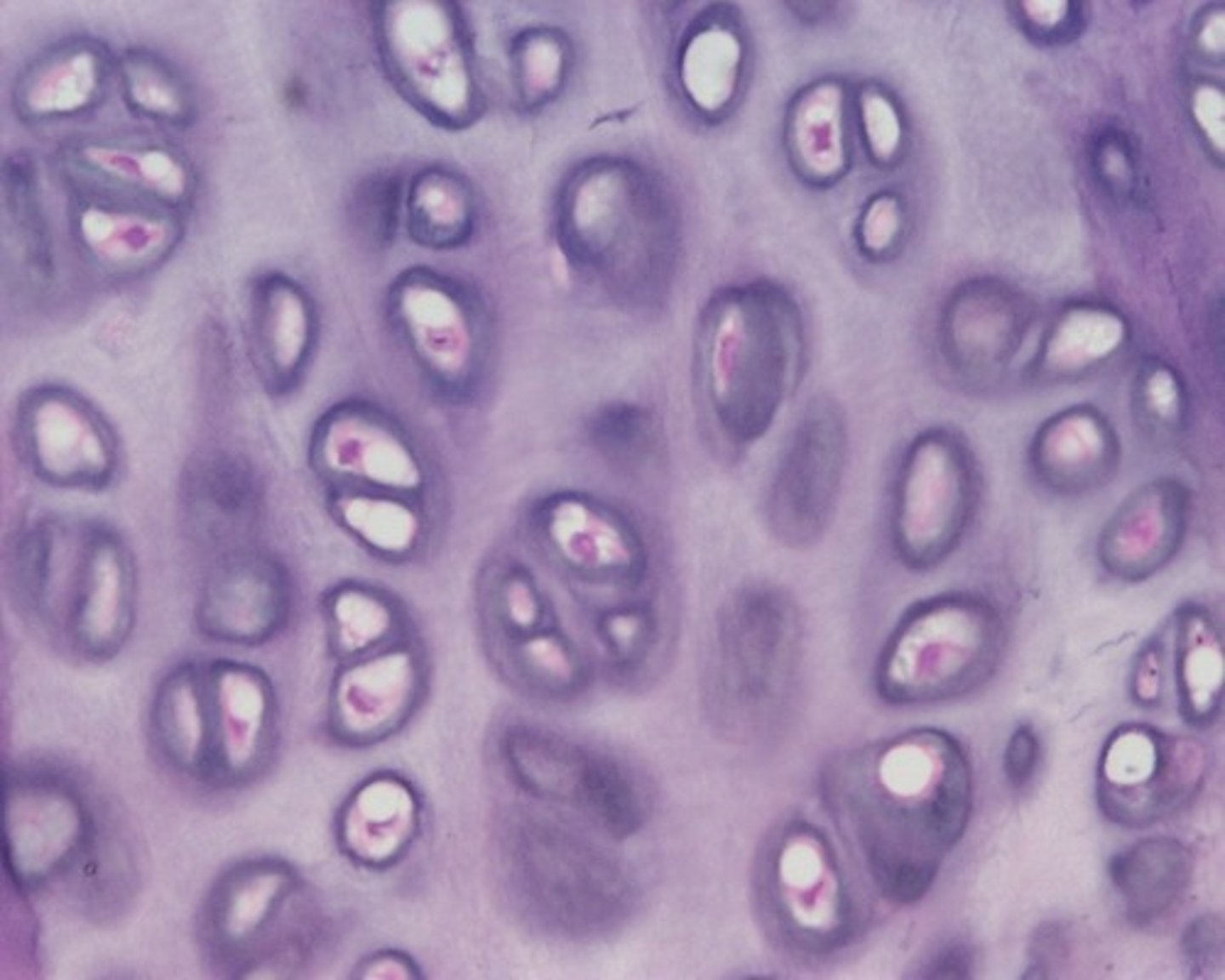
hyaline
-most common type of cartilage
-found in larynx, bridge of nose, ribs
-glassy looking
- spaces for cells
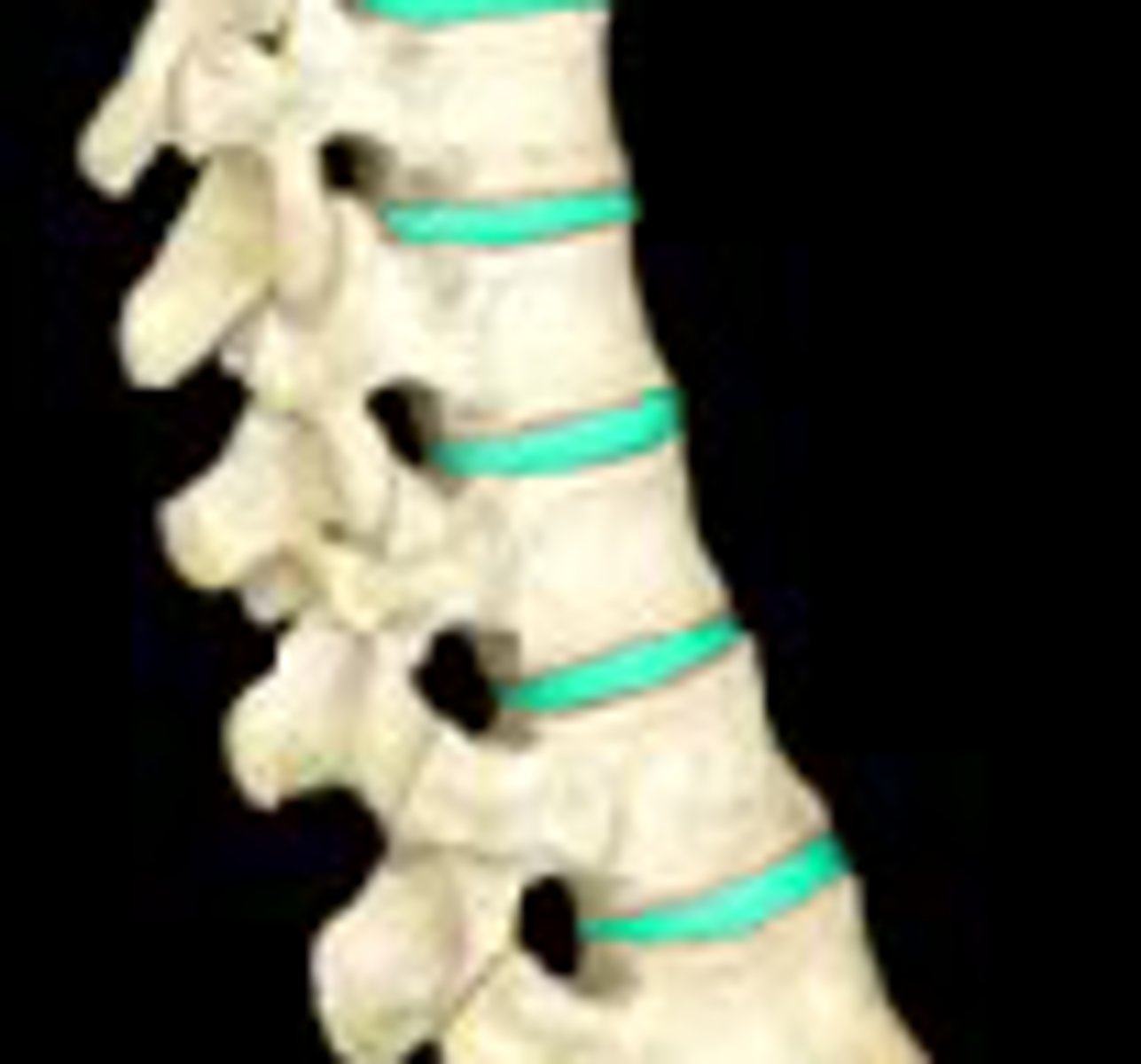
Fibrocartilage
-Pads between vertebrae that are shock absorbers
-contains lots of collagen, mostly running parallel
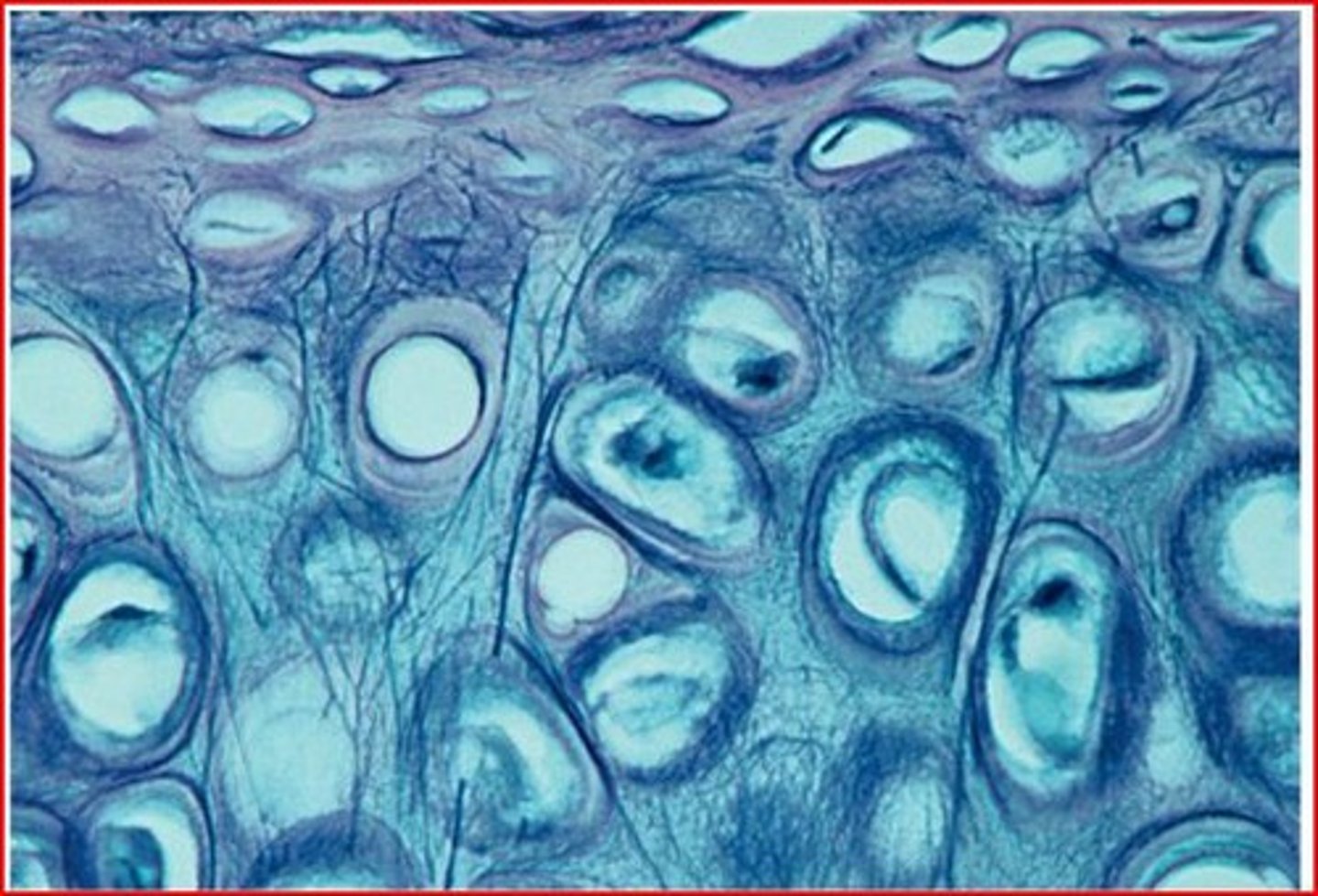
elastic cartilage
-cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
-found in outer ear and tip of nose
osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix
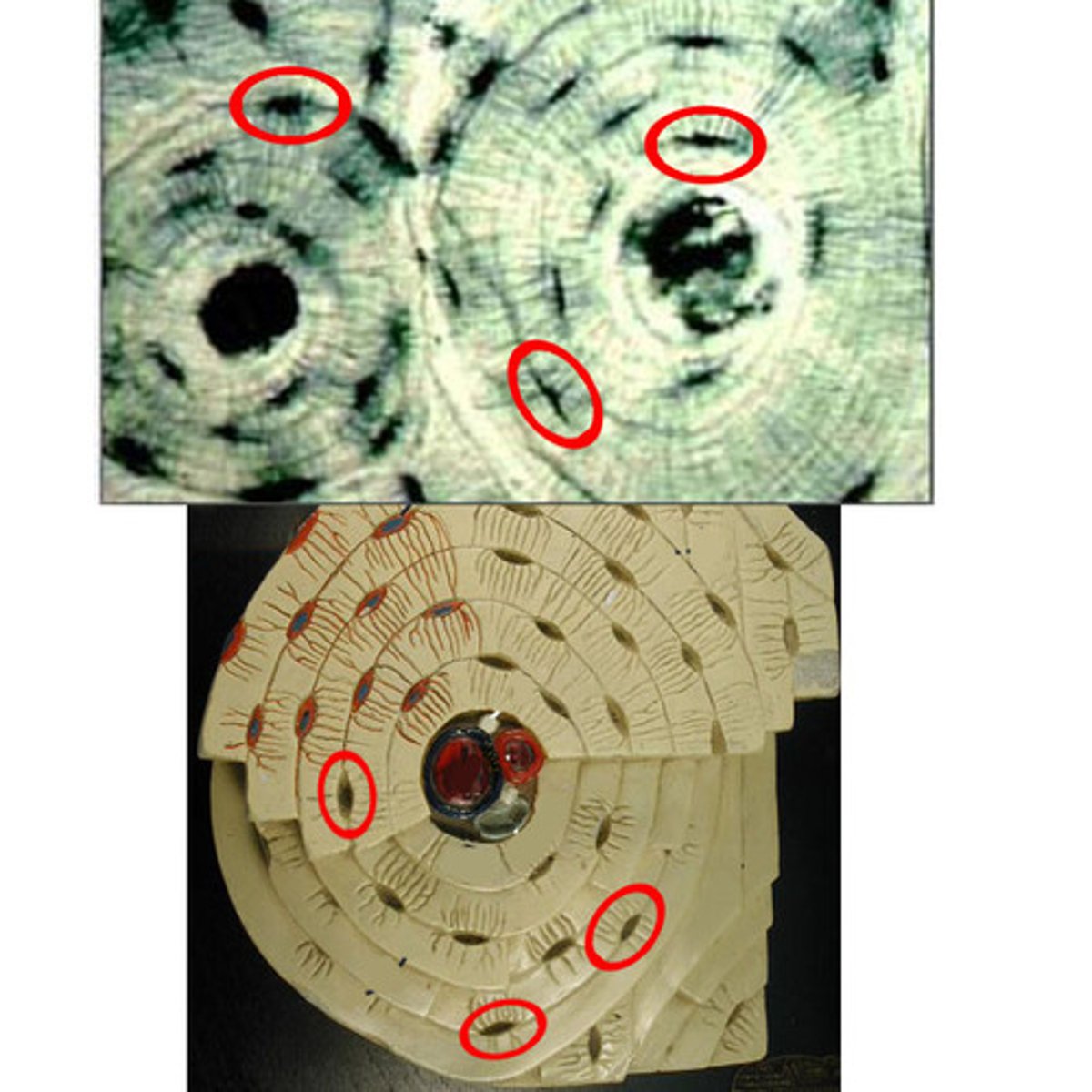
calcified
inflexible, hardened
spongy bone tissue
hard, lightweight tissue of bone that has many spaces
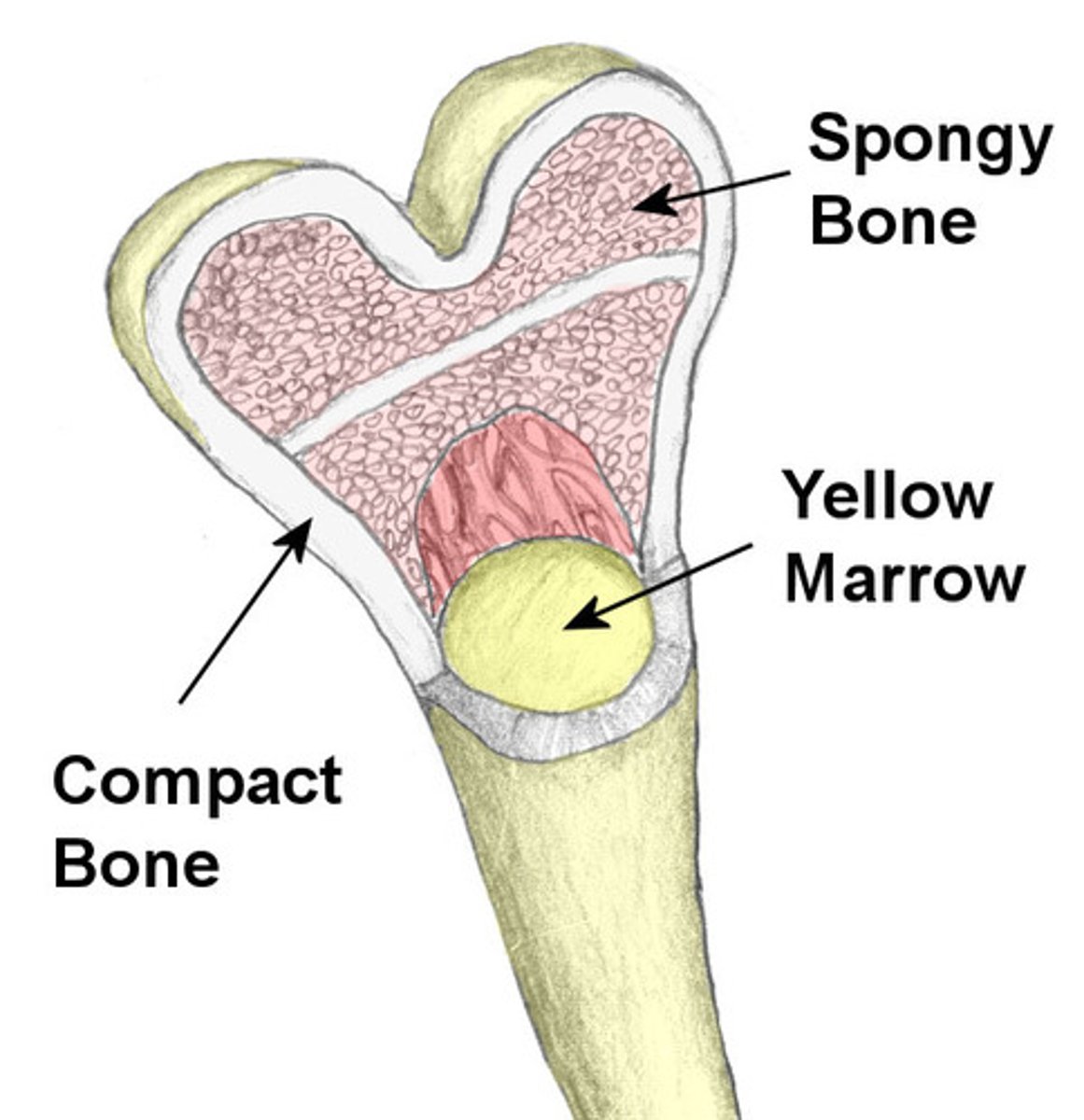
compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
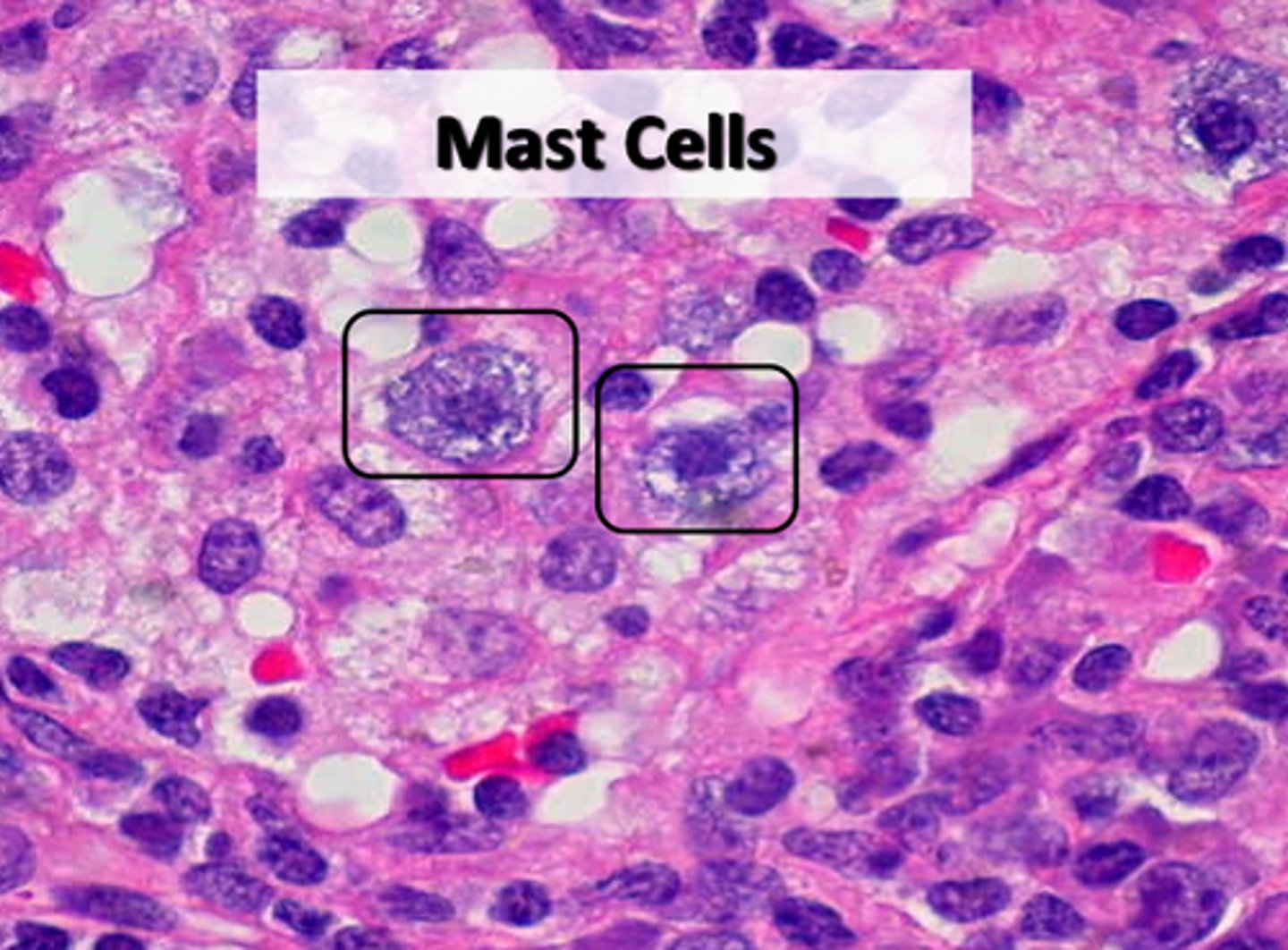
mast cells
Cells that release chemicals (such as histamine) that promote inflammation.
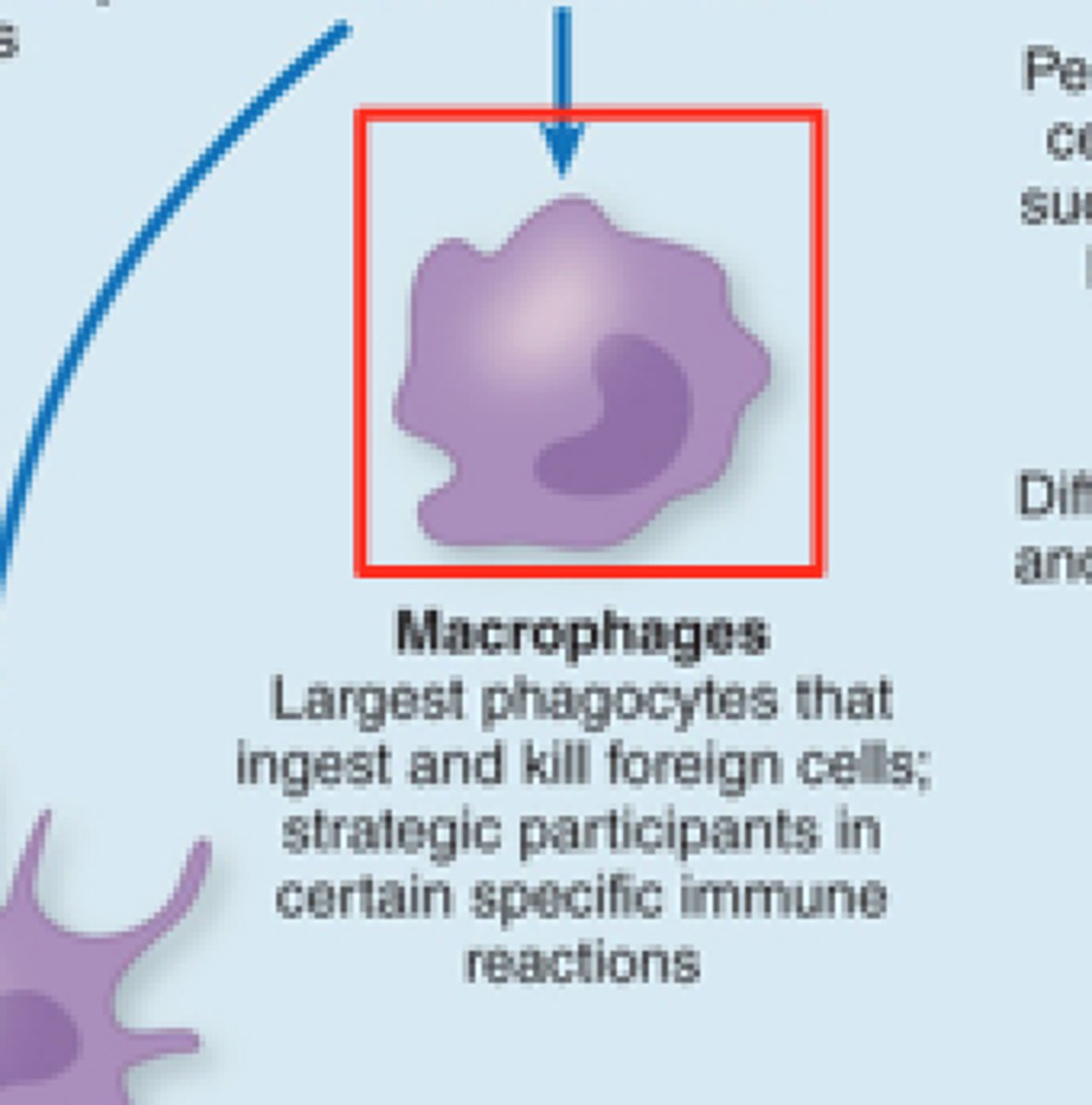
macrophages
blob-like cells that engulf invading substances
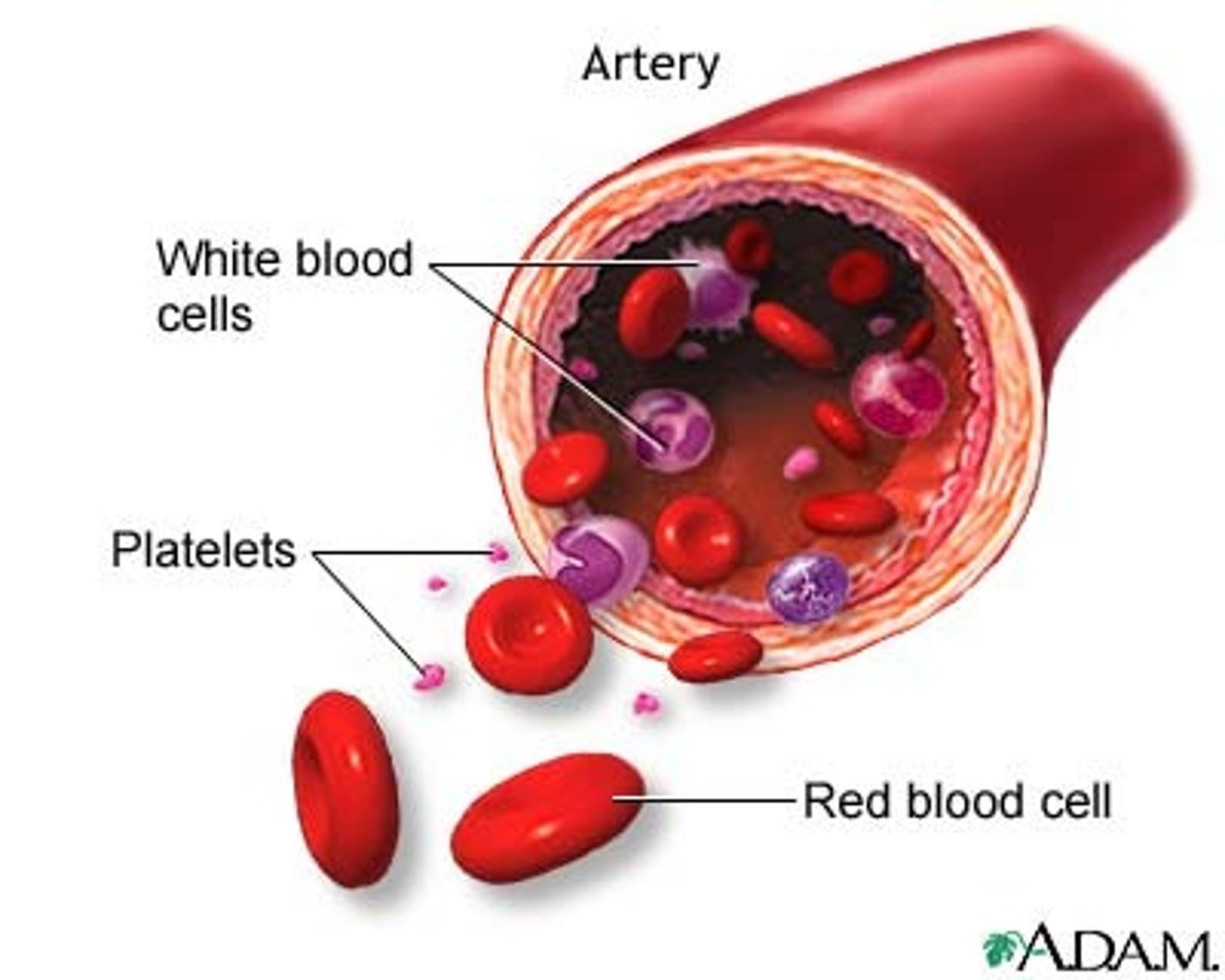
blood cells
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
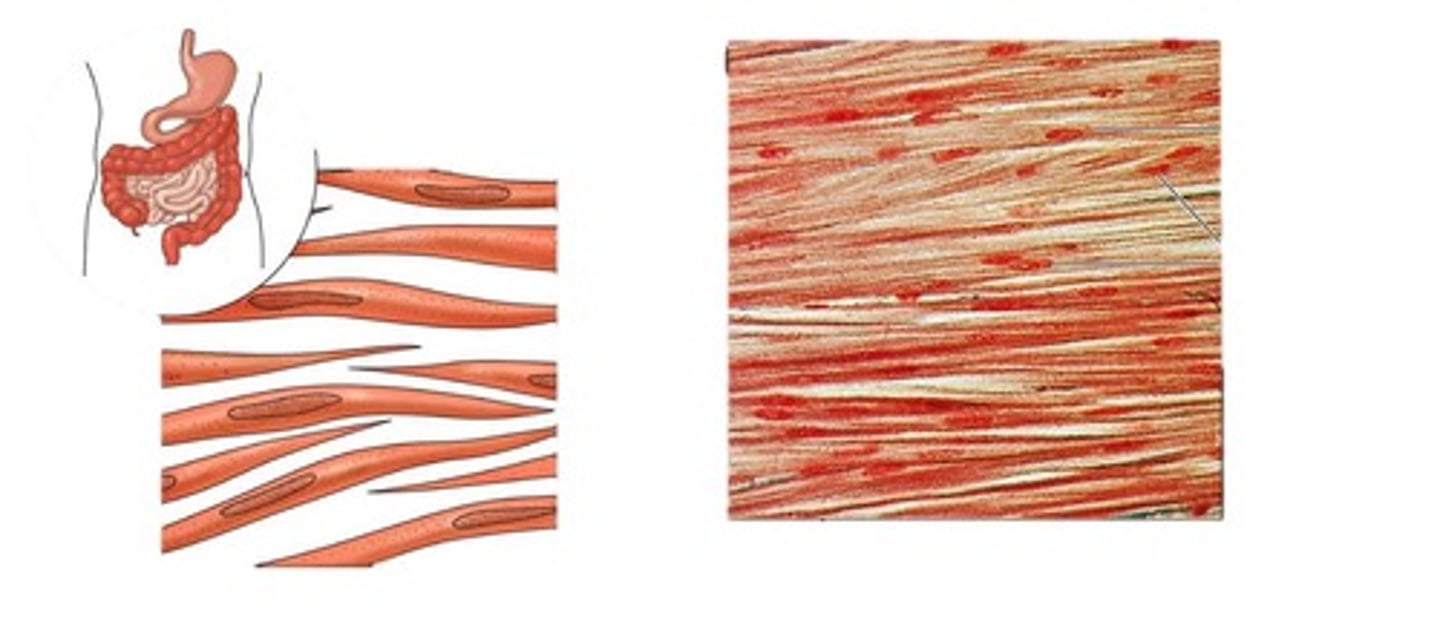
smooth muscle
-Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body like the walls of stomach, uterus, intestines, bladder, arteries, veins and eyes
-non striated
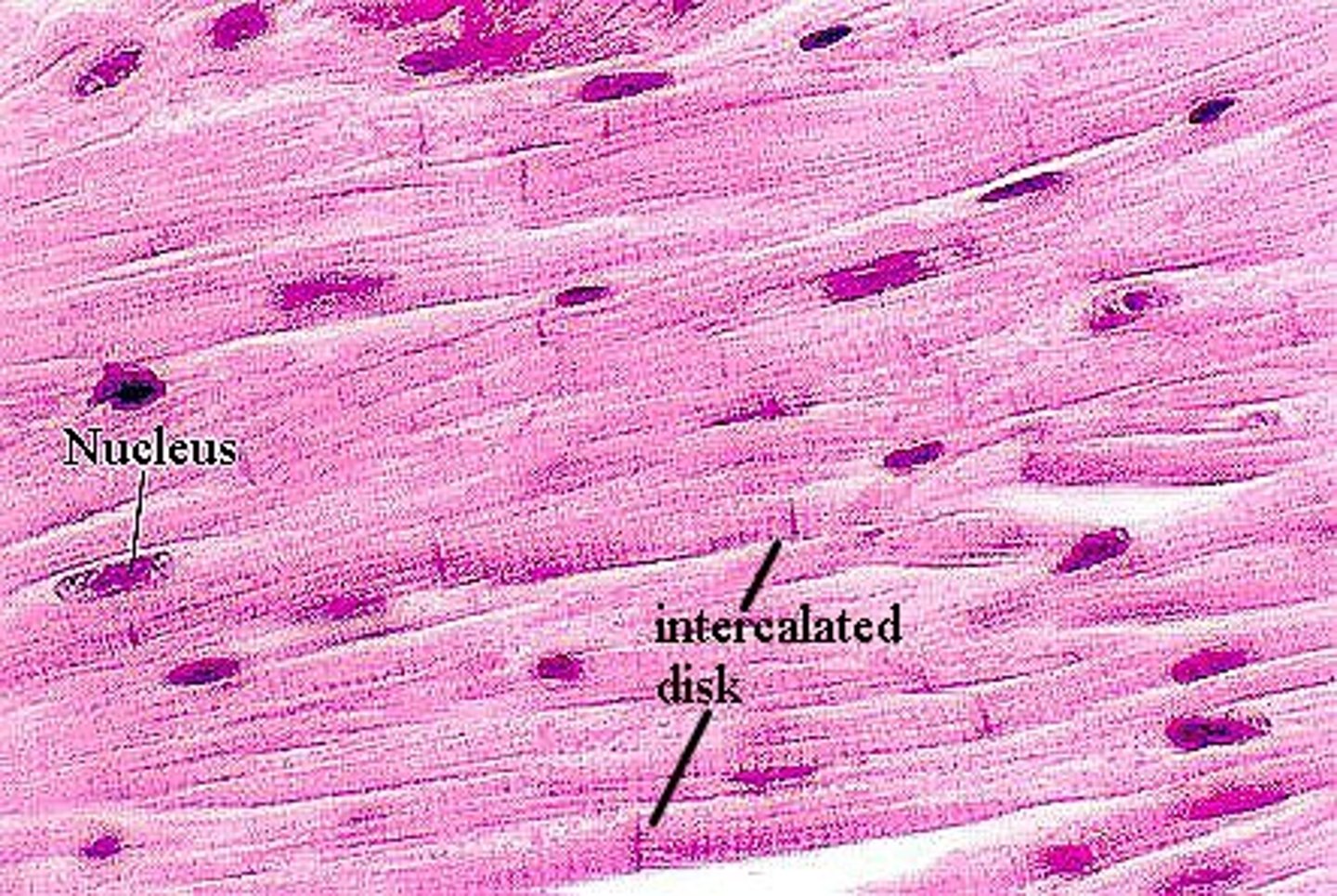
cardiac muscle tissue
-striated and involuntary
-heart
-activated by brain and hormones
skeletal muscle tissue
-striated and voluntary
-bones of skeleton
-somatic nervous system
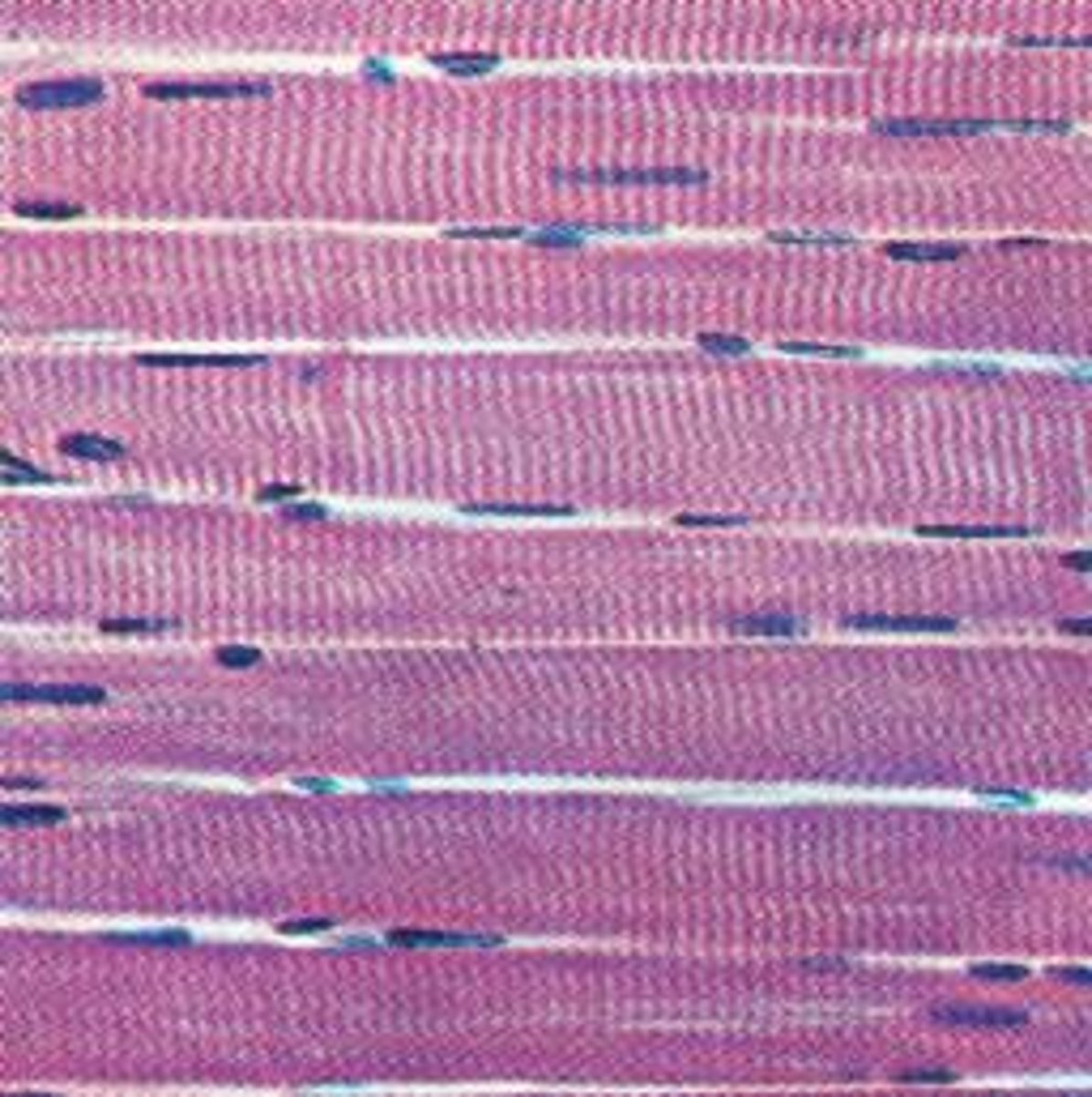
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles
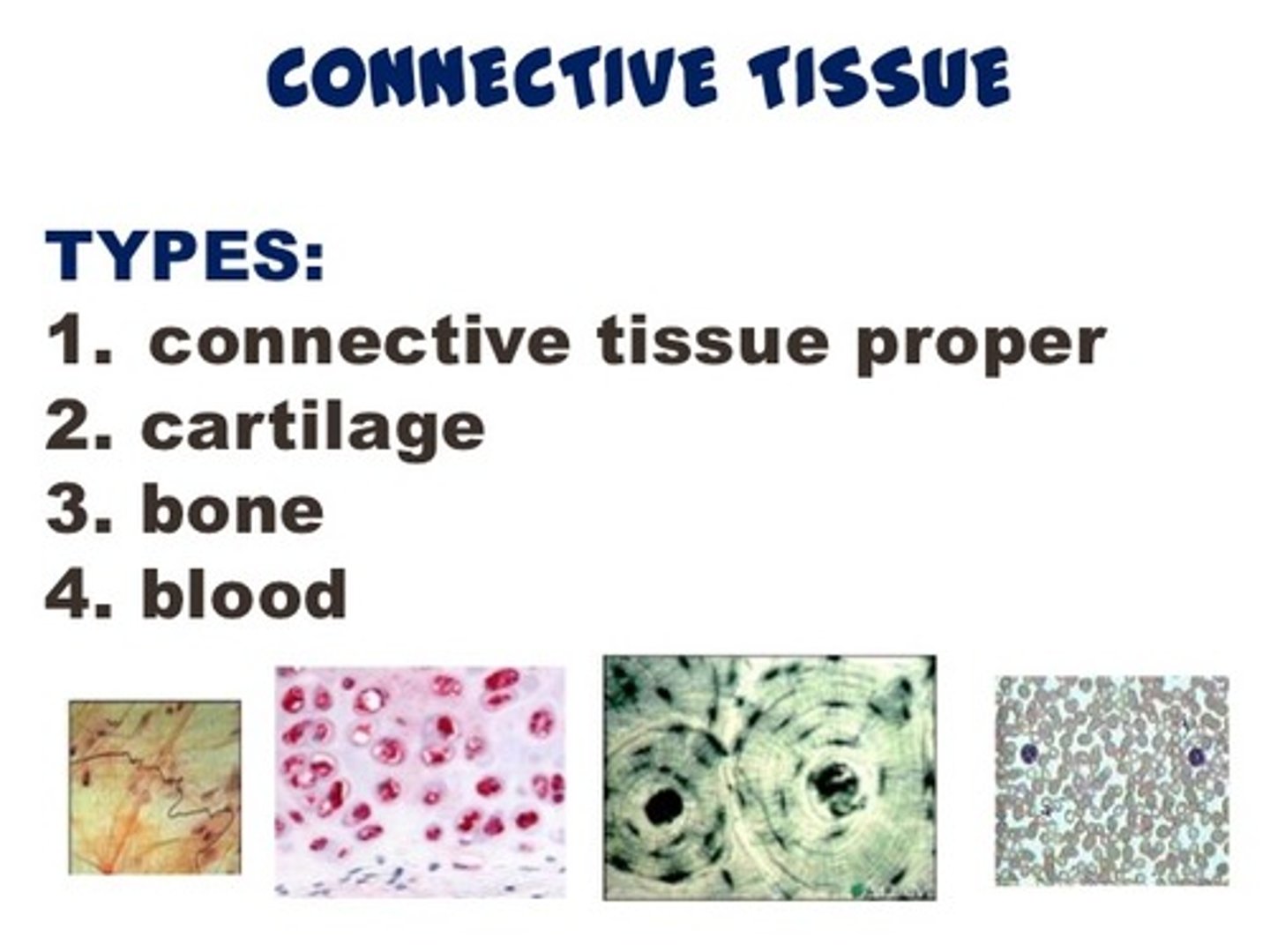
4 types of connective tissue
connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, blood