MS FINAL from KW
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
248 Terms
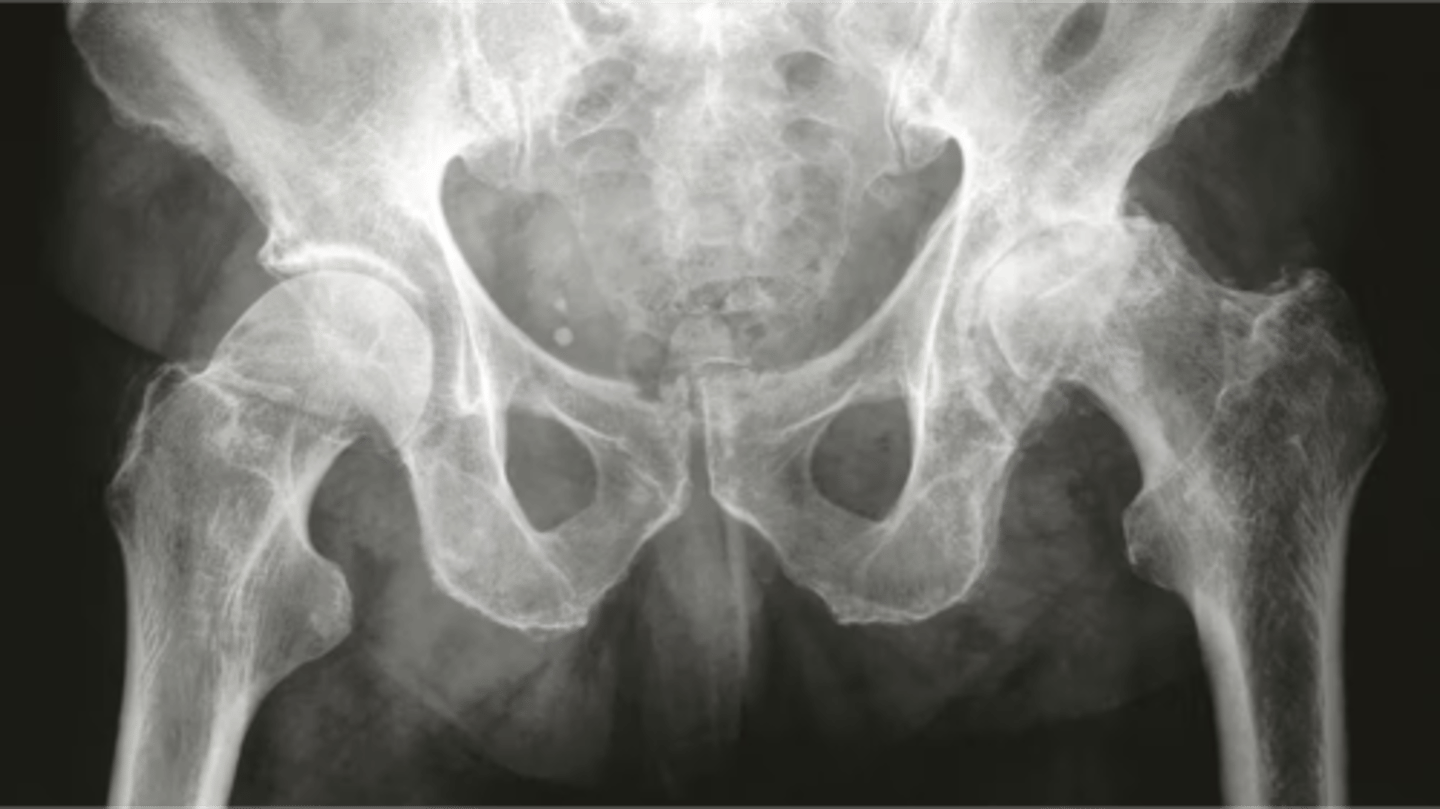
what does this x-ray show
osteoarthritis
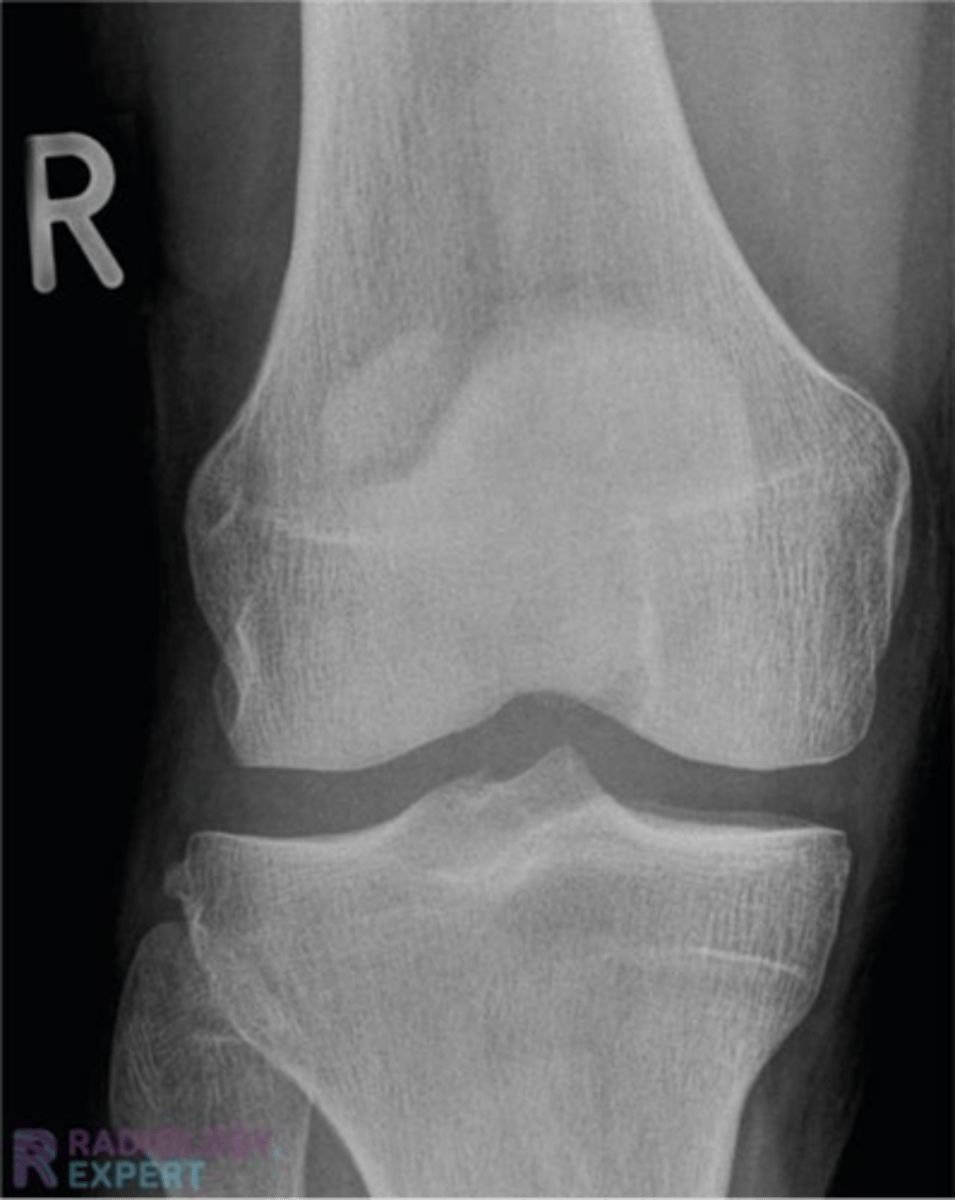
what does this x-ray show
something is wrong with the soft tissue
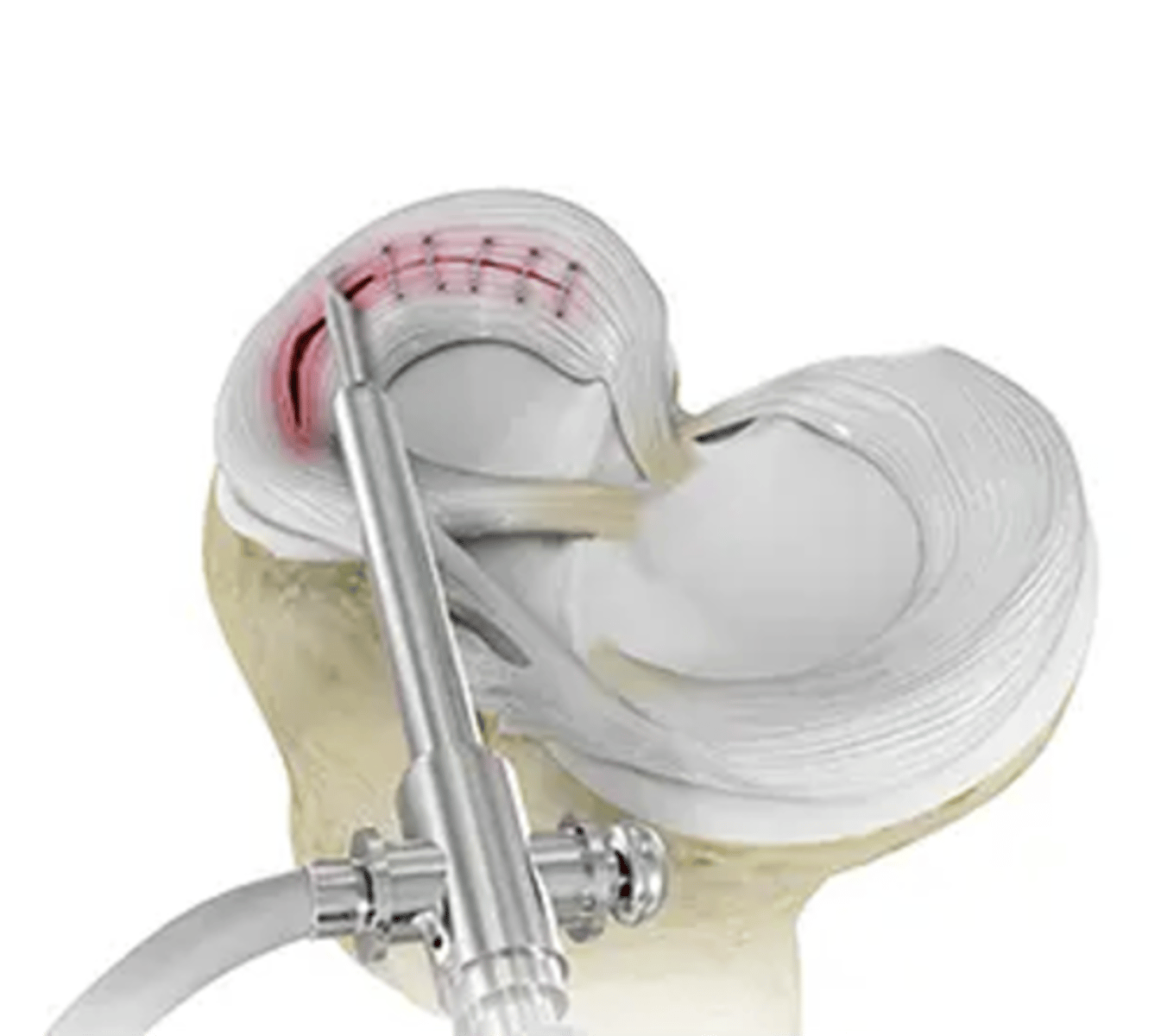
Which part of the meniscus can be repaired?
the lateral ridge of both menisci
What's the trade off with a meniscal repair?
repair=can't weight bear for a few weeks
partial menisectomy=can walk to your car right after
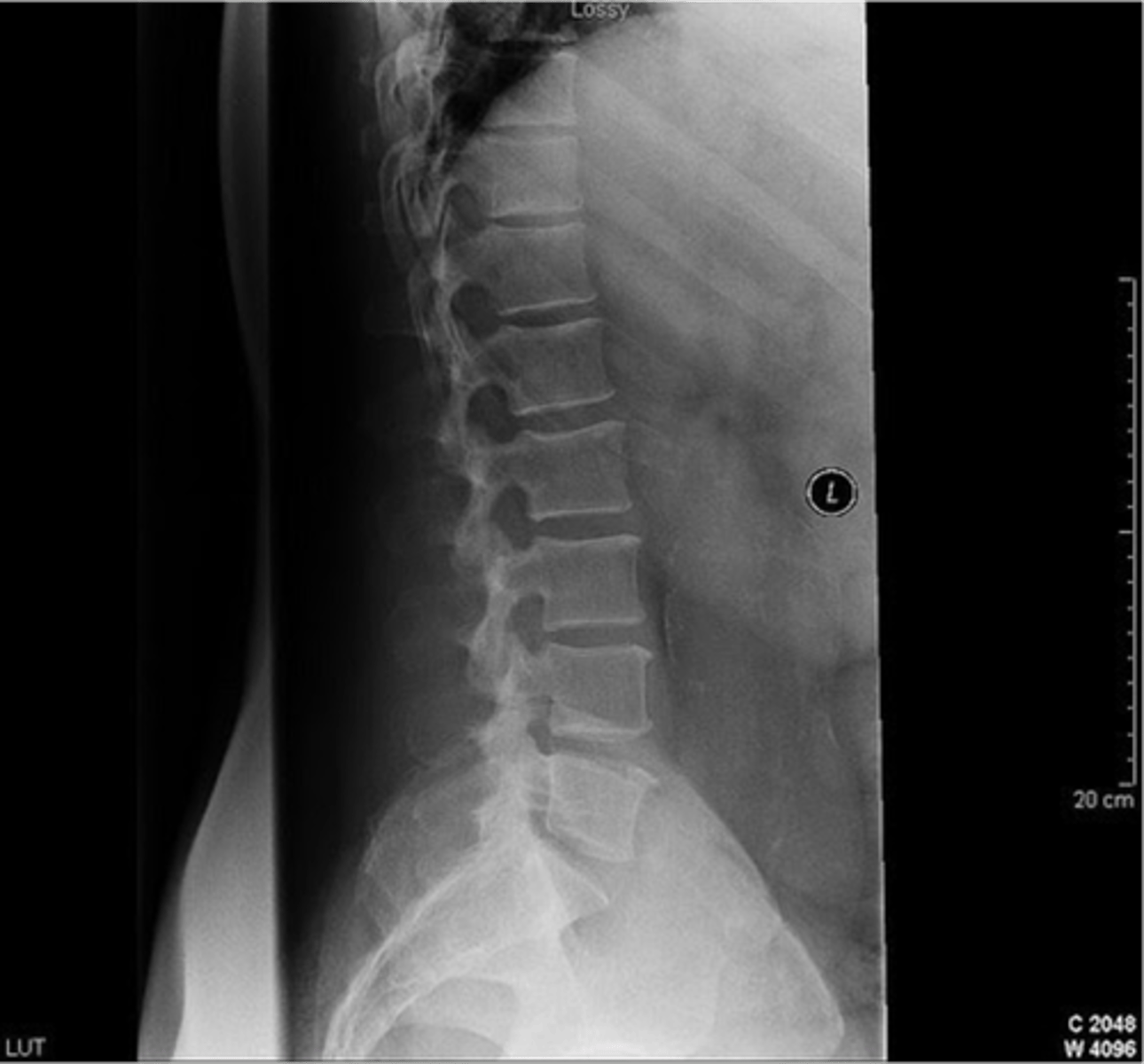
what is wrong
could be muscle strain or a HNP
difference between cauda equina and HNP
cauda equina comes out medially
HNP comes out laterally
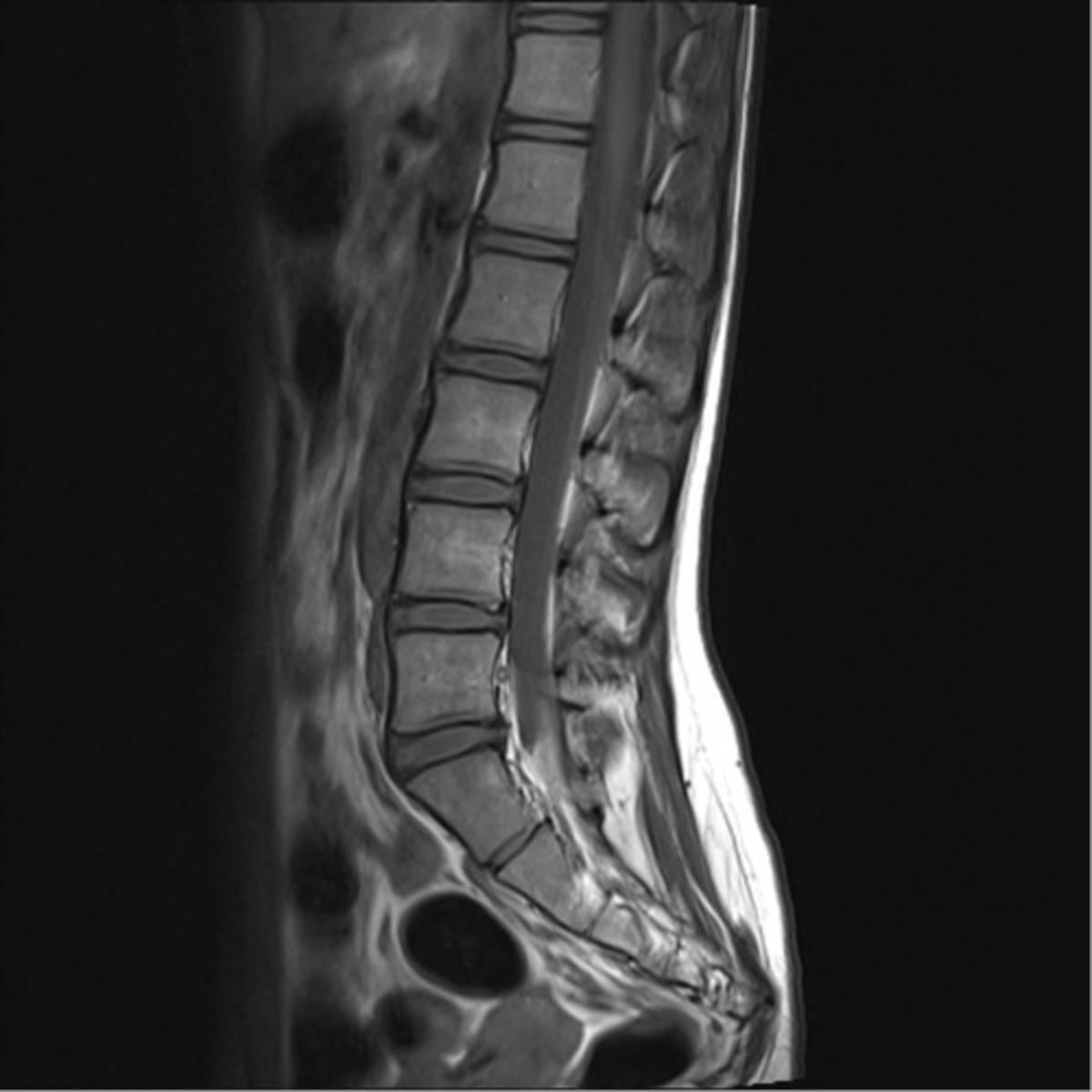
describe
normal MRI
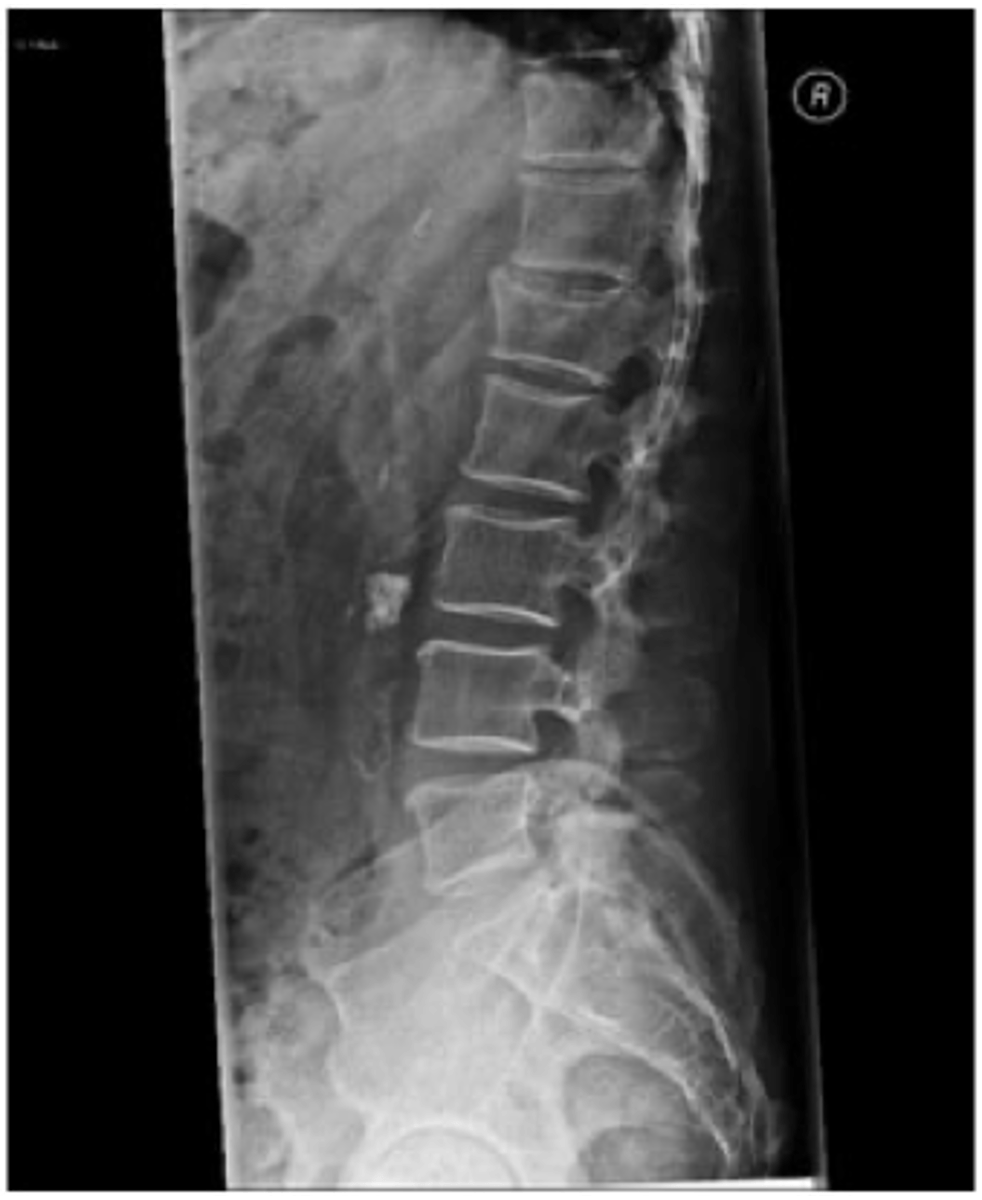
what is wrong
there's a compression fracture on the third one down
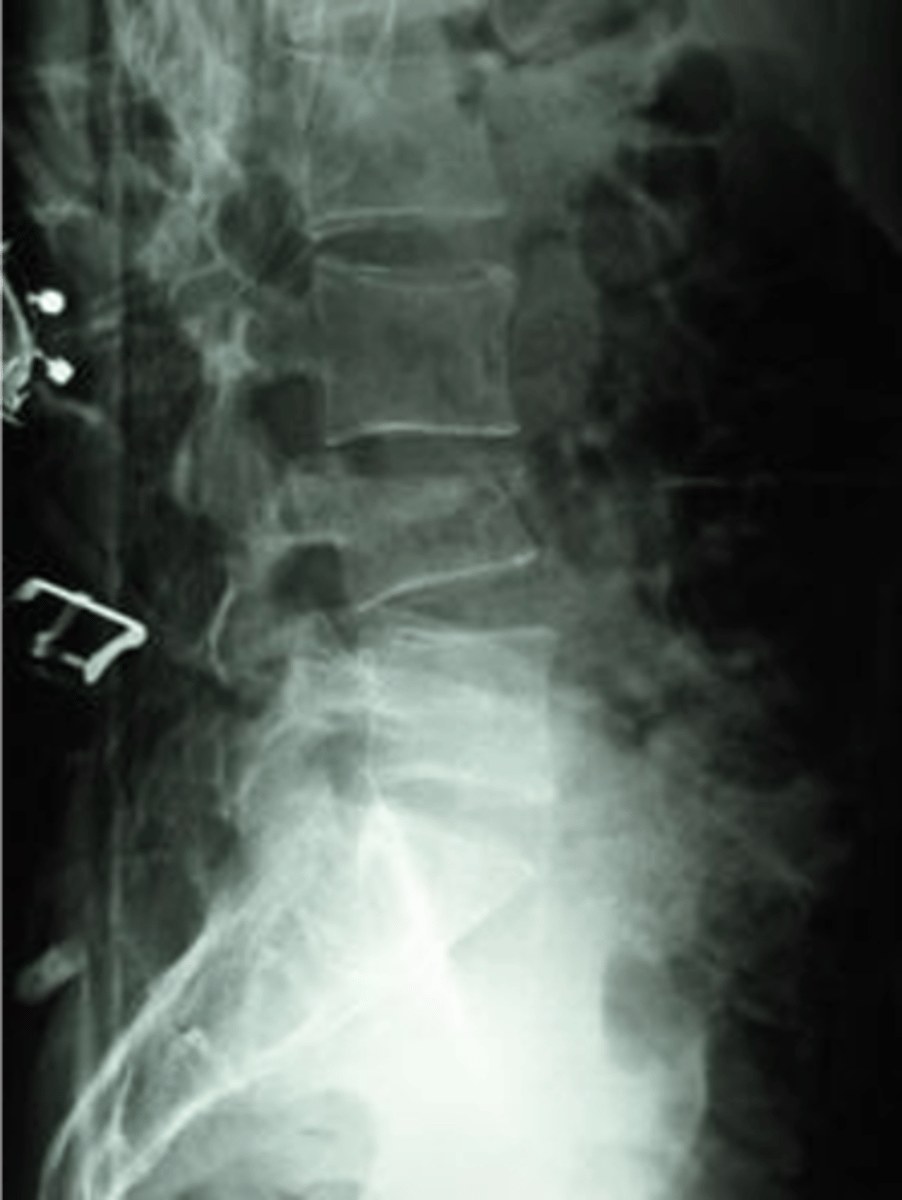
what is wrong
vertebral compression fracture
If the patient says I lost weight without trying and I get night sweats
he has some form of osteosarcoma
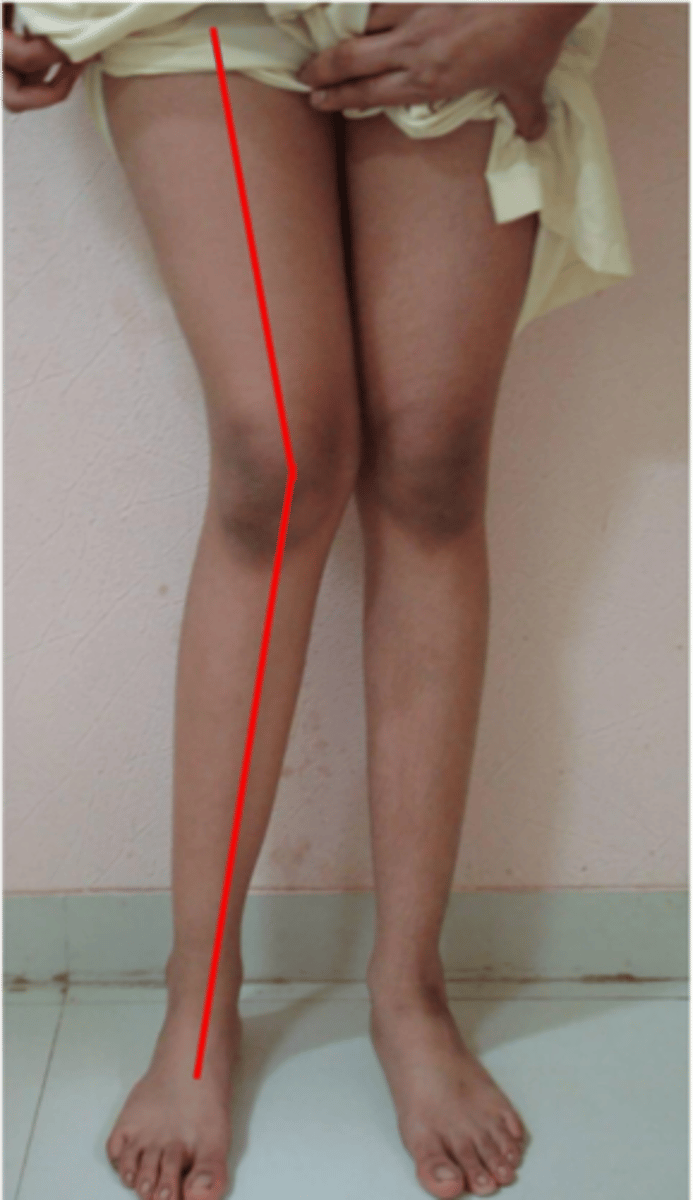
what will happen
lateral meniscus will wear out

medial joint space narrowed

what is this
fall on outstretched hand

what is this
FOOSH
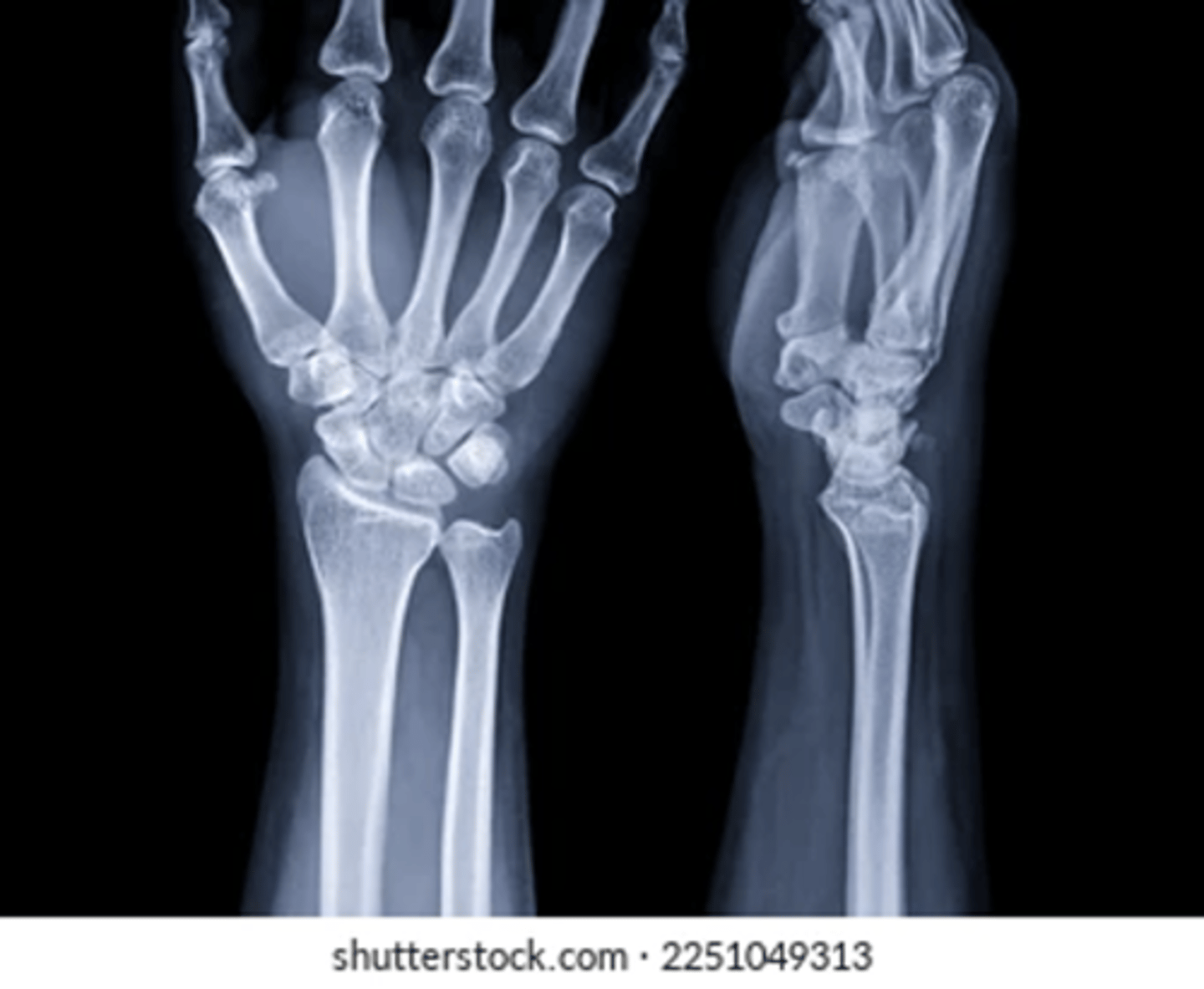
describe
no fracture
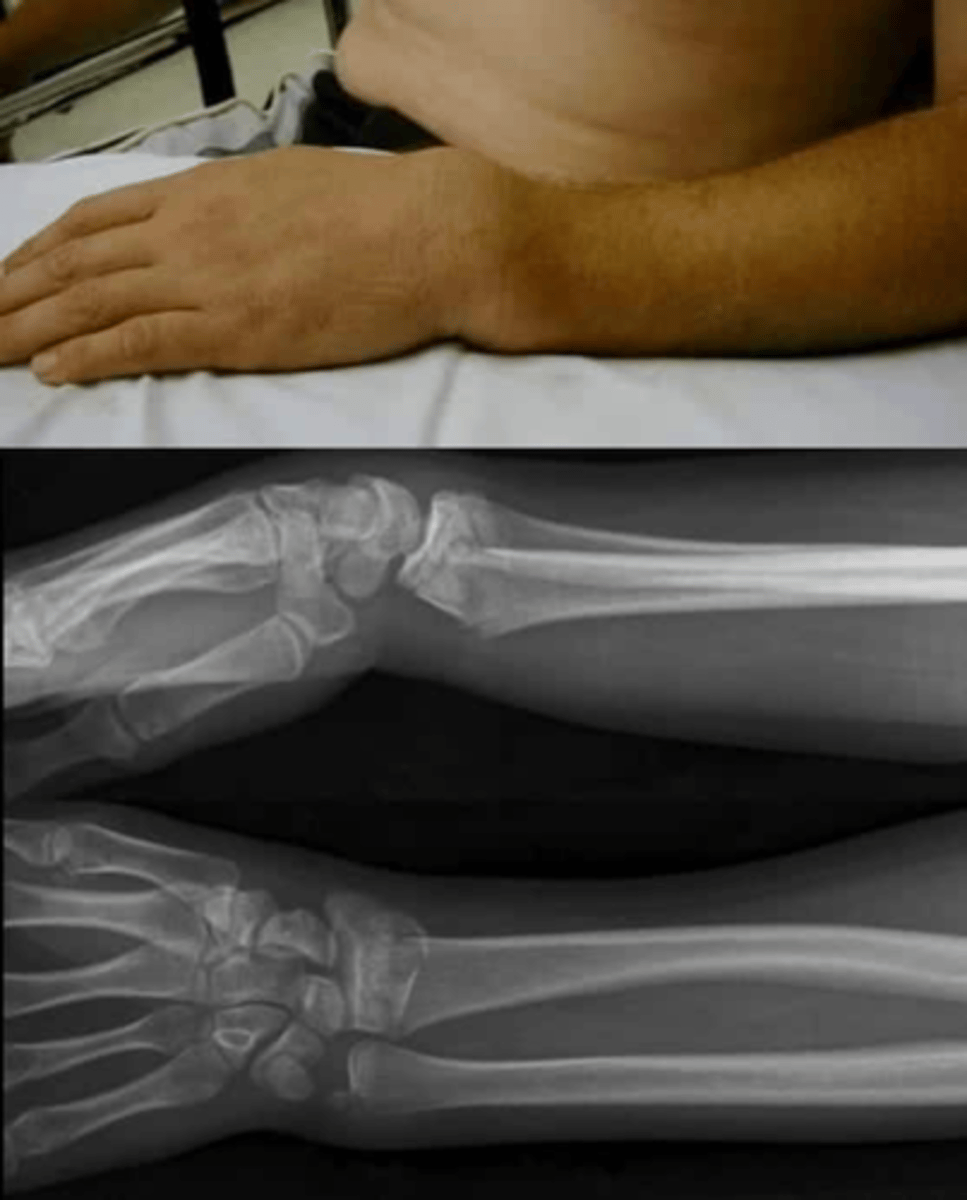
describe
FOOSH, distal radial fracture
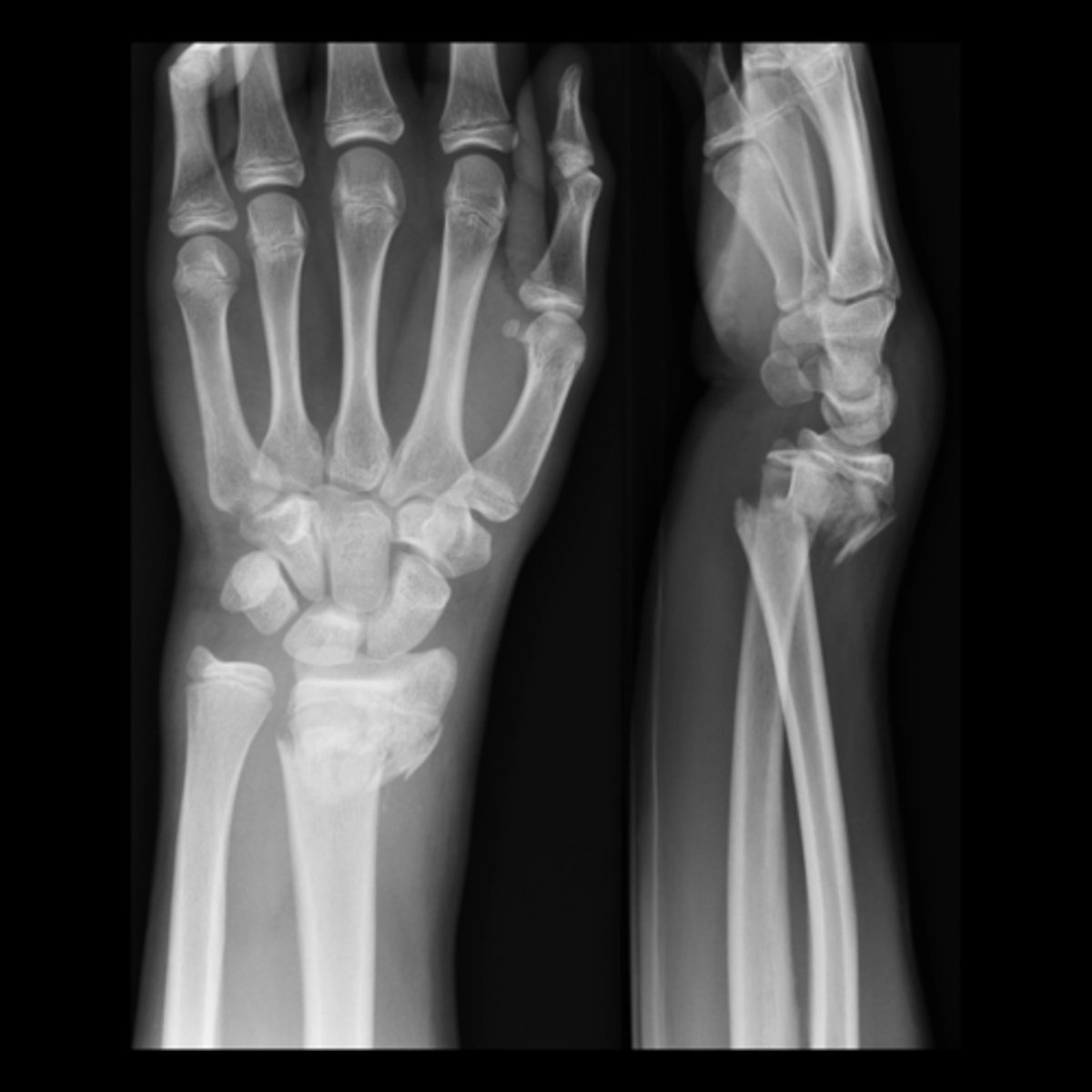
what is this
distal radial fracture
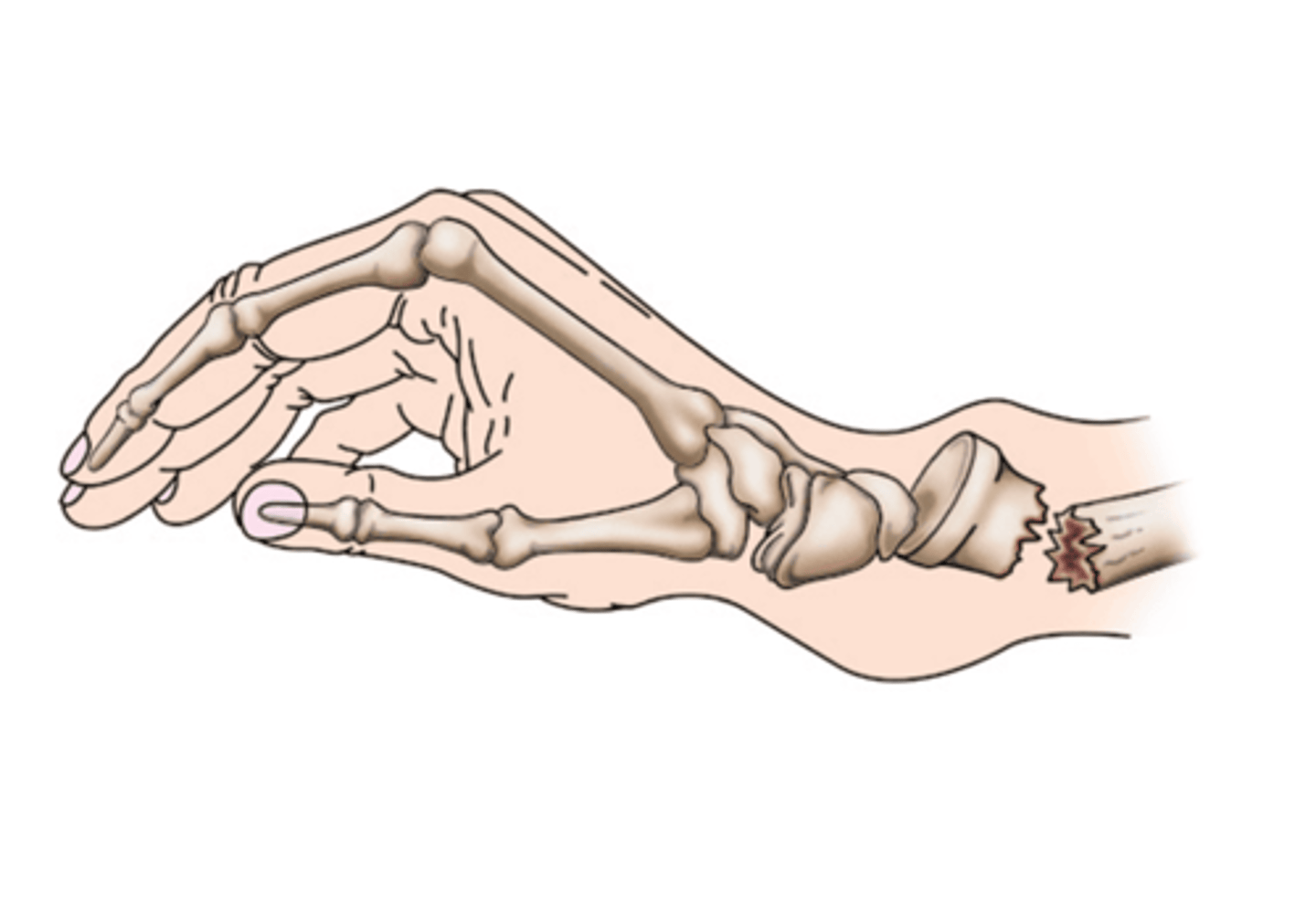
distal portion of the distal bone pointing towards the dorsum (back) of the hand
Colles Fractures
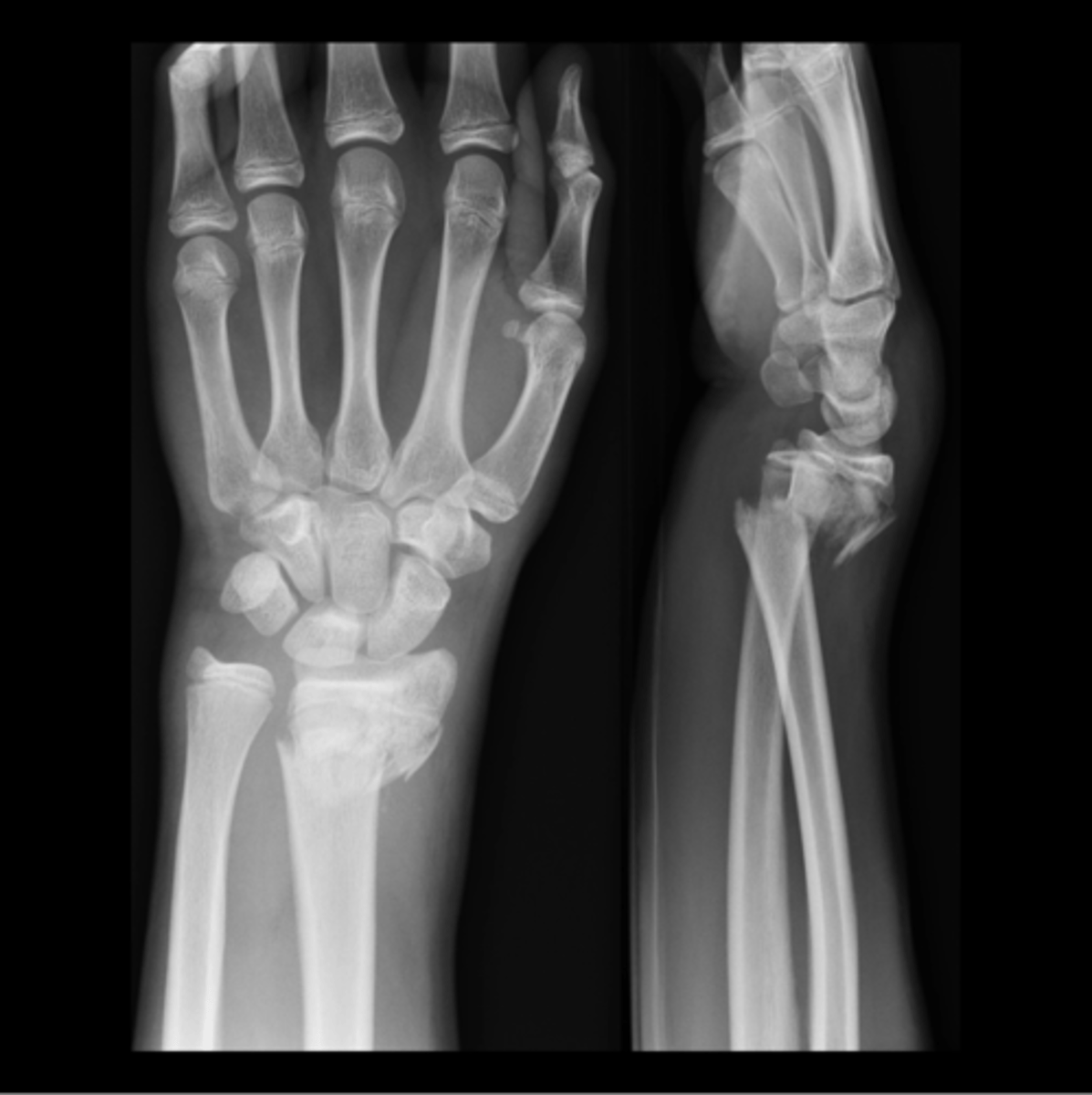
what is this
colles fracture
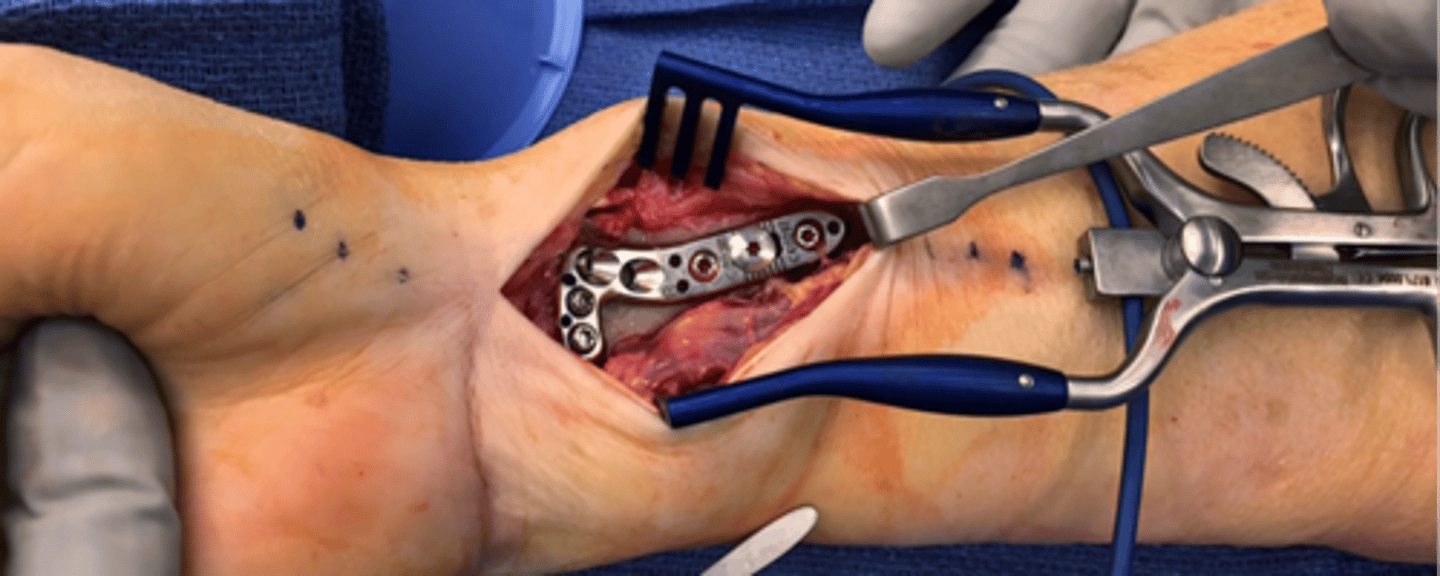
what is this
open reduction internal fixation (colles fracture)
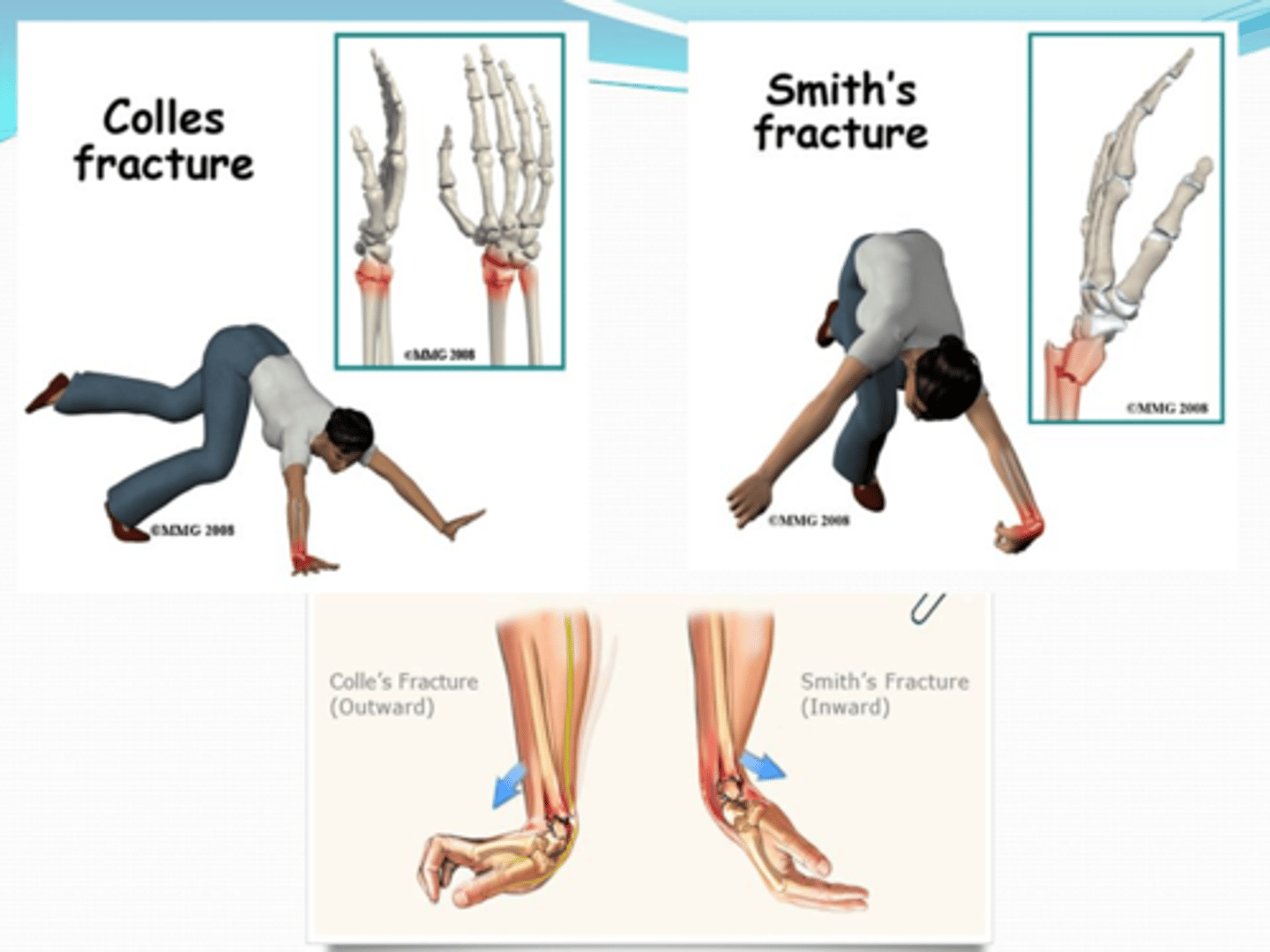
MOI of Colles Fracture
FOOSH
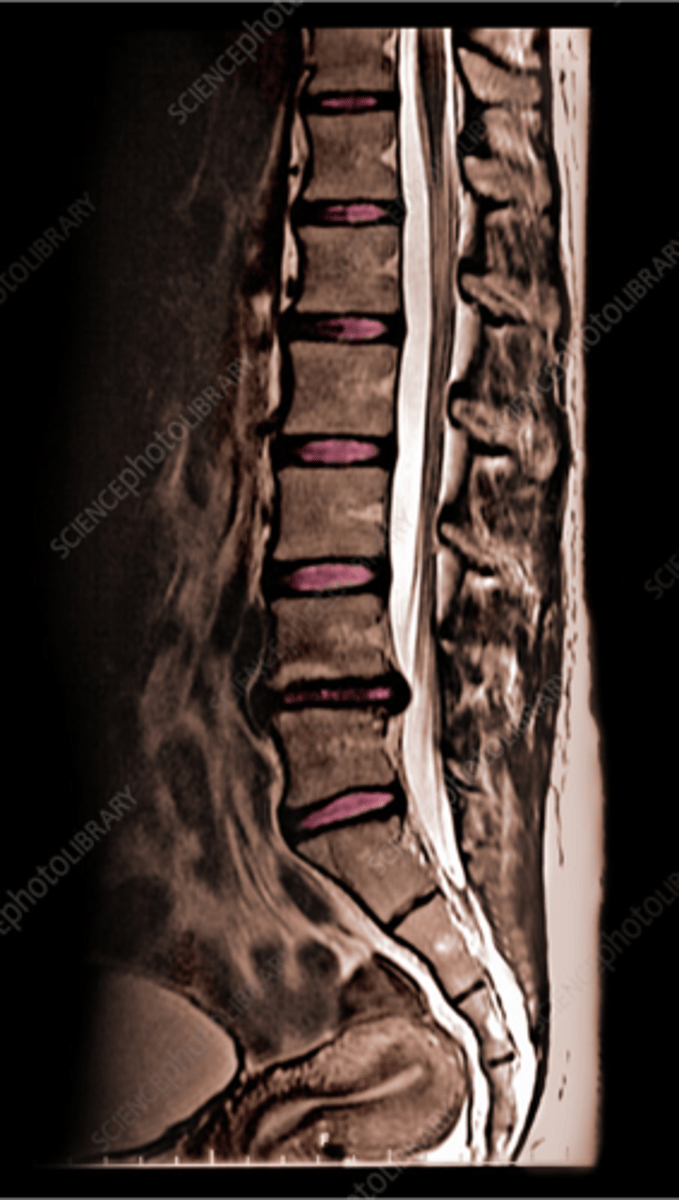
what is this
L5 herniation
prevalence of OA and RA
OA – 20.7 million
RA - 2.1 million
osteoarthritis
A degenerative disorder with minimal articular inflammation.
No systemic symptoms.
Pain relieved by rest; morning stiffness brief.
Radiographic findings: narrowed joint space, osteophytes
OA general information
non-inflammatory disease
characterized by progressive degeneration of joint cartilage with bone margin involvement and osteophyte formation
· Osteoarthritis is a chronic long-term, degenerative disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage in the joints leading to pain and stiffness.
cortical steroids (risk factor for osteoporosis)
Before the age of 45, osteoarthritis predominantly affects men. After 55 the condition is more frequent in women.
Fifty percent of people over 60 years of age are affected in at least one joint. It is estimated that everyone over the age of 75 suffers from osteoarthritis.
primary osteoarthritis
· an unknown cause but is generally associated with aging. It is sometimes referred to as "wear and tear" arthritis.
secondary osteoarthritis
the destruction of cartilage from a known cause. Conditions that lead to cartilage loss include repetitive trauma, obesity, crystal deposits, infection, congenital abnormalities, injury or joint surge (obesity, gonorrhea, gout)
joints most commonly affected include
hips and knees
joints where thumb meets hand (carpometacarpal joint/basal joint), two distal joints to the knuckle
OA signs and symptoms
Pain
Pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis and usually increases with joint use.
Pain can also restrict mobility.
Stiffness
Swelling
Deformity
Painless, irregular bony enlargements
Heberden's nodes
Bouchard's nodes
“Harley-Davidsons raise your Blood Pressure”
Crepitus
stiffness with OA
Stiffness of the affected joint is often noticed first thing in the morning, and after resting. < 15 minutes
crepitus
Grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage
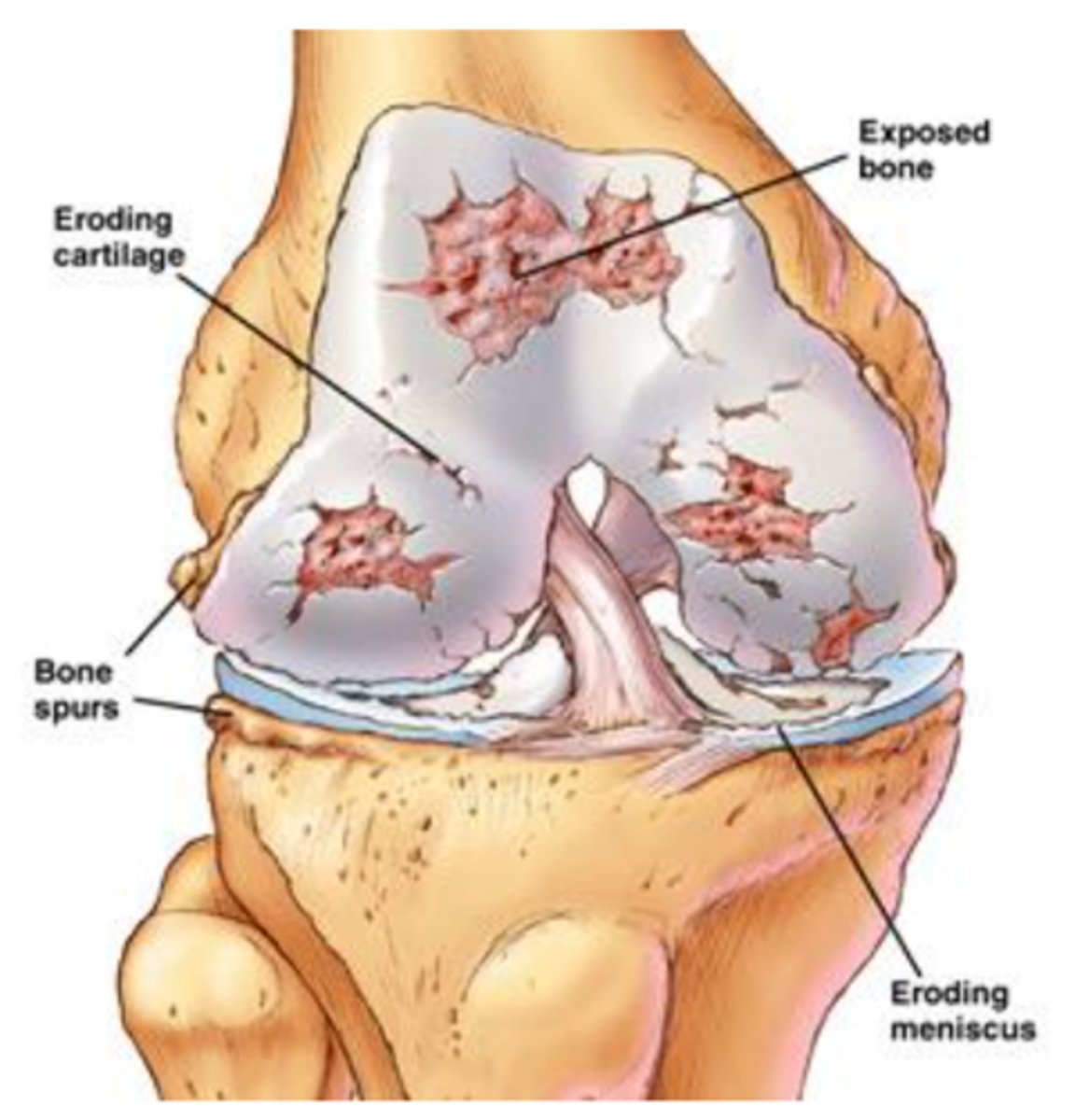
what is this
eroding cartilage
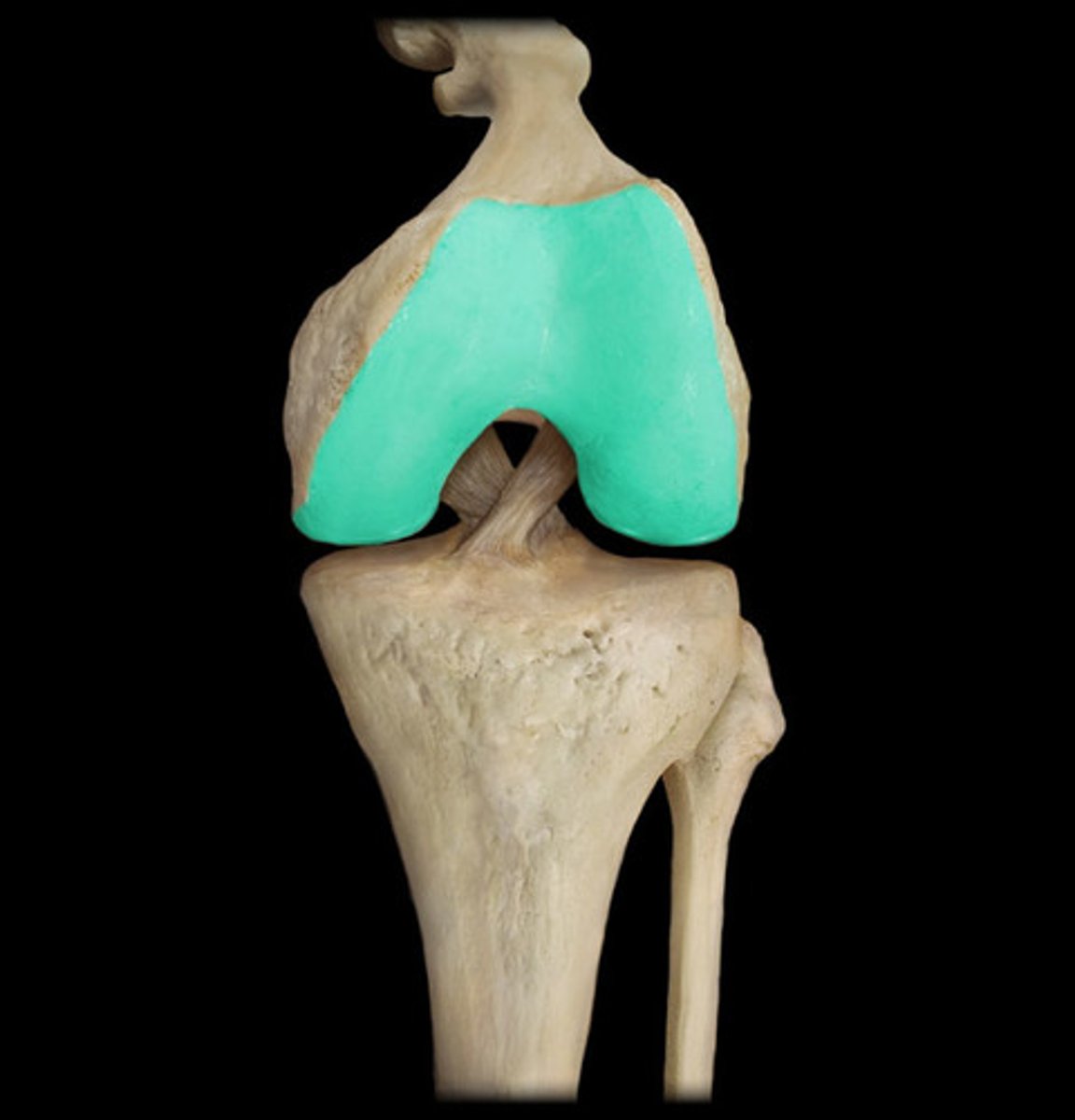
what is this
cartilage
what is this
osteoarthritis
What symptoms can you see on an x-ray?
bone spurs, narrowing space
Why can't cartilage grow back?
it's avascular
Heberden's nodes
bony growths of DIP
Bouchard's nodes
bony growths of PIP
OA risk factors
Obesity
Trauma
Genetics - predilection for cartilage breakdown
Increased age (>40)
Repetitive movements (sports or employment - manual laborers)
radiograph "LOSS"
a. Loss of joint space
b. Osteophytes - spurs of bone
c. Subarticular sclerosis
Increased density of bone on joint line
d. Subchondral cysts
Small fluid filled holes in bone on the joint line
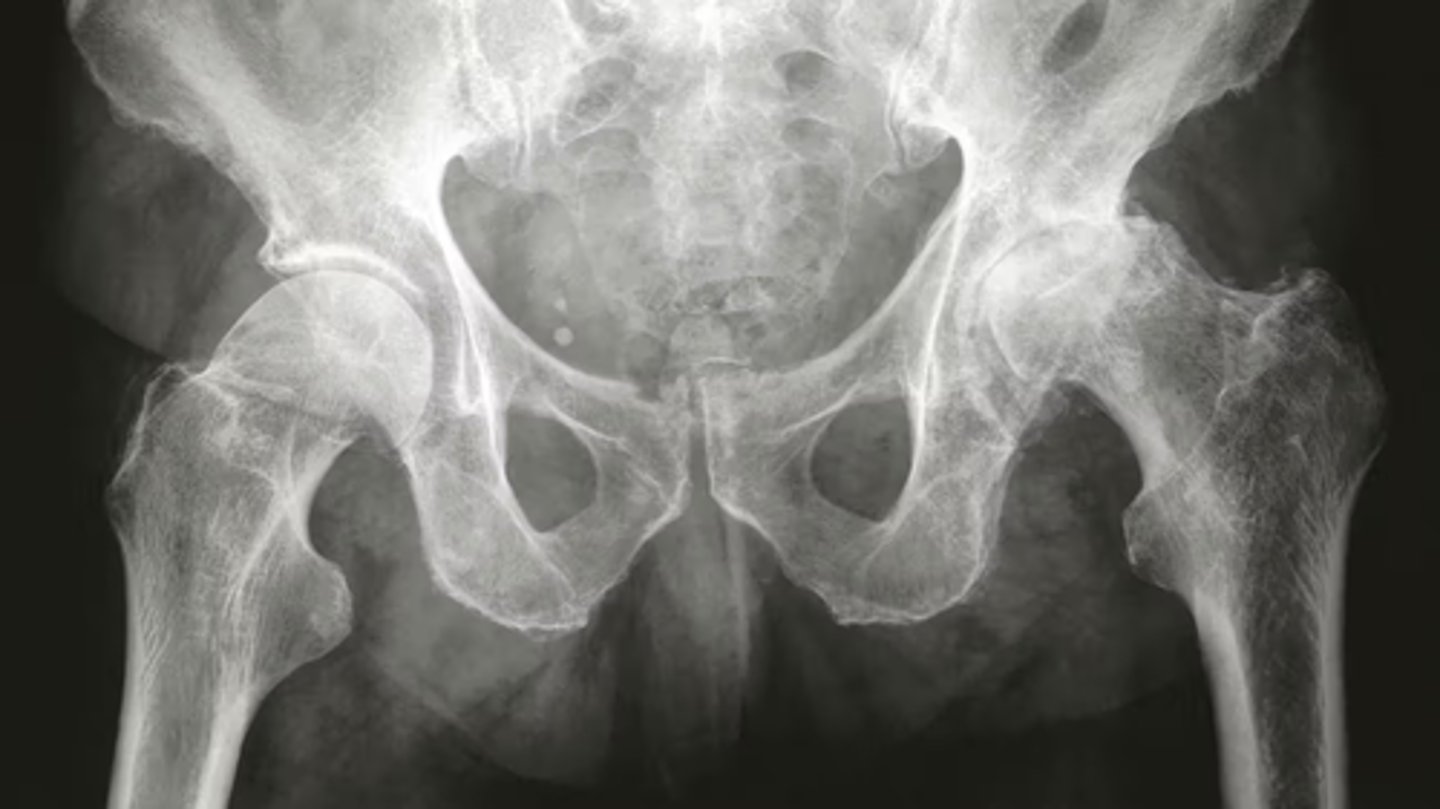
what is this
OA on left hip
OA labs
none
OA medical treatment
1.Acetaminophen – Tylenol
2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs)
Motrin
Advil
Celebrex
Intra-articular injections of triamcinolone ((corticosteroid) often
with lidocaine)
surgical intervention-joint arthroplasty
Total hip and knee replacements provide excellent symptomatic and functional improvement when involvement of that joint severely restricts walking or causes pain at rest, particularly at night.
What's a risk of arthroplasty?
infection
micro-fracture surgery
quick fix to help delay an arthroplasty, wet paint on knee, you can't weight bear for a 5 weeks. A lot of people
OA prognosis
a. No cure
b. Manage pain and minimize disability
c. Maintain quality of life
d. Encourage exercise - strength and joint function
e. Depression associated with chronic pain
DIP
distal interphalengeal
rheumatoid arthritis
a chronic, system, autoimmune inflammatory disease
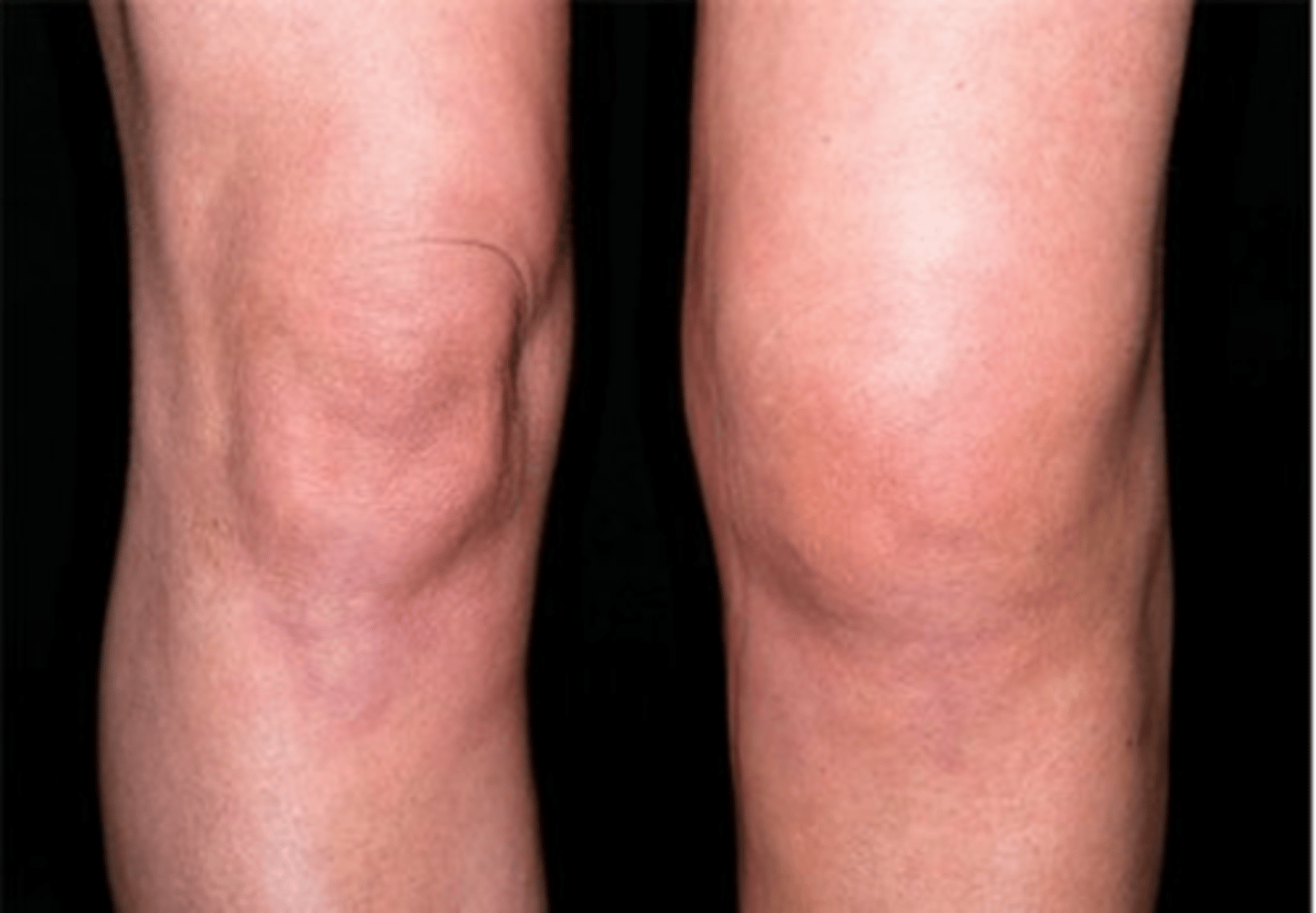
RA essentials
Usually insidious onset with morning stiffness and joint pain.
Symmetric polyarthritis with predilection for small joints of the hands and feet; deformities common with progressive disease.
Rheumatoid factor and antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP) are present in 70-80%.
Extra-articular manifestations: subcutaneous nodules, interstitial lung disease, pleural effusion, pericarditis
What is the most common inflammatory arthropathy?
rheumatoid arthritis
Are men or women more likely to get RA?
females (3:1 ratio)
When is RA onset?
4th or 5th decade
RA environmental factors
tobacco; known to be a major trigger both for new onset RA and as an exacerbating agent for existing RA
RA genetic factors
HLA DR beta 1 alleles - genetic trait that increases the incidence of the condition. There is a strong familiar relationship associated with RA. (can be passed on)
inflammatory response
chronic inflammation of the synovium (synovitis) erodes cartilage, bone, ligaments, and tendons.
Effusion and other manifestations of inflammation are common.
unbated
without any reduction in intensity or strength (disability becomes pronounced)
RA symptoms
Patients have flares (OA is constant) RA can get worst sometimes and have asymptomatic days
Usually insidious onset with morning stiffness and joint pain.
Symmetric polyarthritis with predilection for small joints of the hands and feet
Wt loss, fatigue, muscle weakness and vague m/s discomfort that eventually settles in joints
Morning stiffness that lasts about one hour
What joints are affected by RA?
Although any joint may be affected the most commonly involved joints are:
i. PIP joints of the fingers
ii. MCP joints
iii. Wrists
iv. Knees
v. Ankles
vi. MTPs
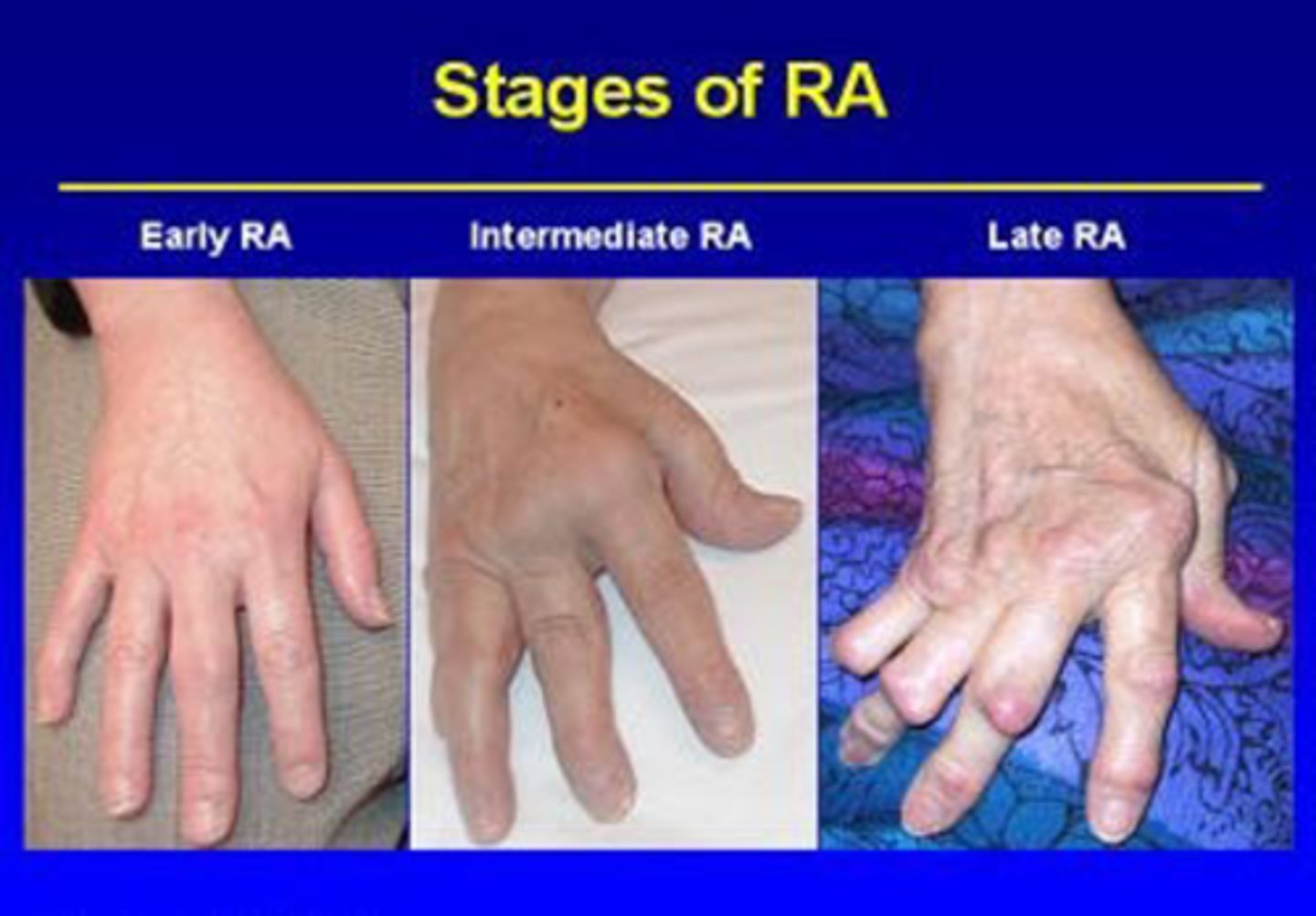
Stages of RA
it's a progressive disease-deformities caused by disruption/erosion of ligaments and tendons
Early RA -> Intermediate RA -> Late RA
Physical exam findings
1. Joint findings (we want to fend off inflammation with medication before deformities occur and we can't help them)
2. Rheumatoid nodules
3. Ocular symptoms
4. Systemic disease (must do a good pulmonary and cardiac exam)
joint findings
A. Polyarticular joint edema, erythema and pain, often at rest (red, painful, warm to touch)
B Swan-neck and Boutonniere deformities
C Ulnar deviation at MCPs
Swan neck deformity
hyperextension at PIP and Flexion at DIP
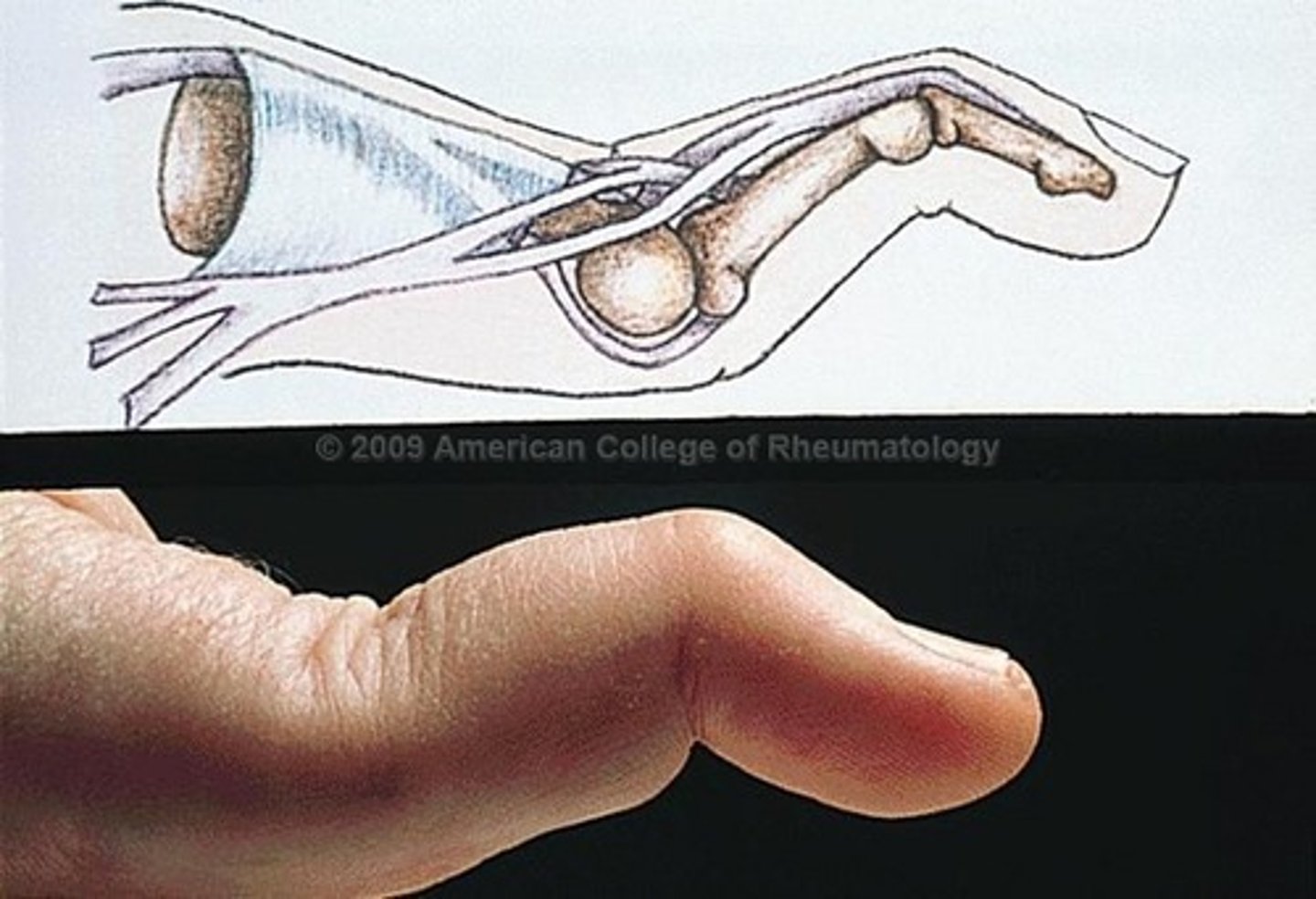
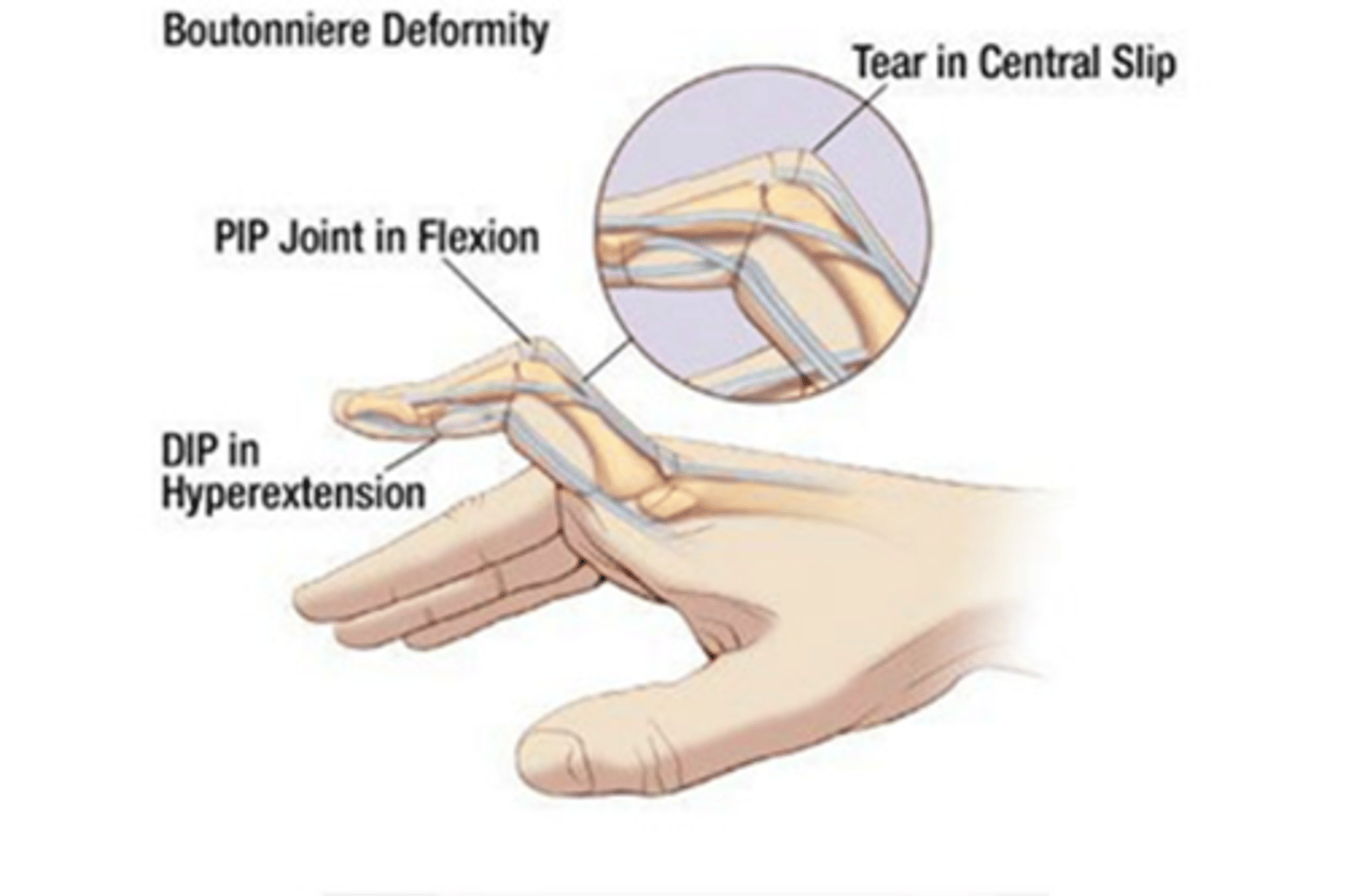
Buotonniere Deformity
flexion at PIP and hyperextension at DIP
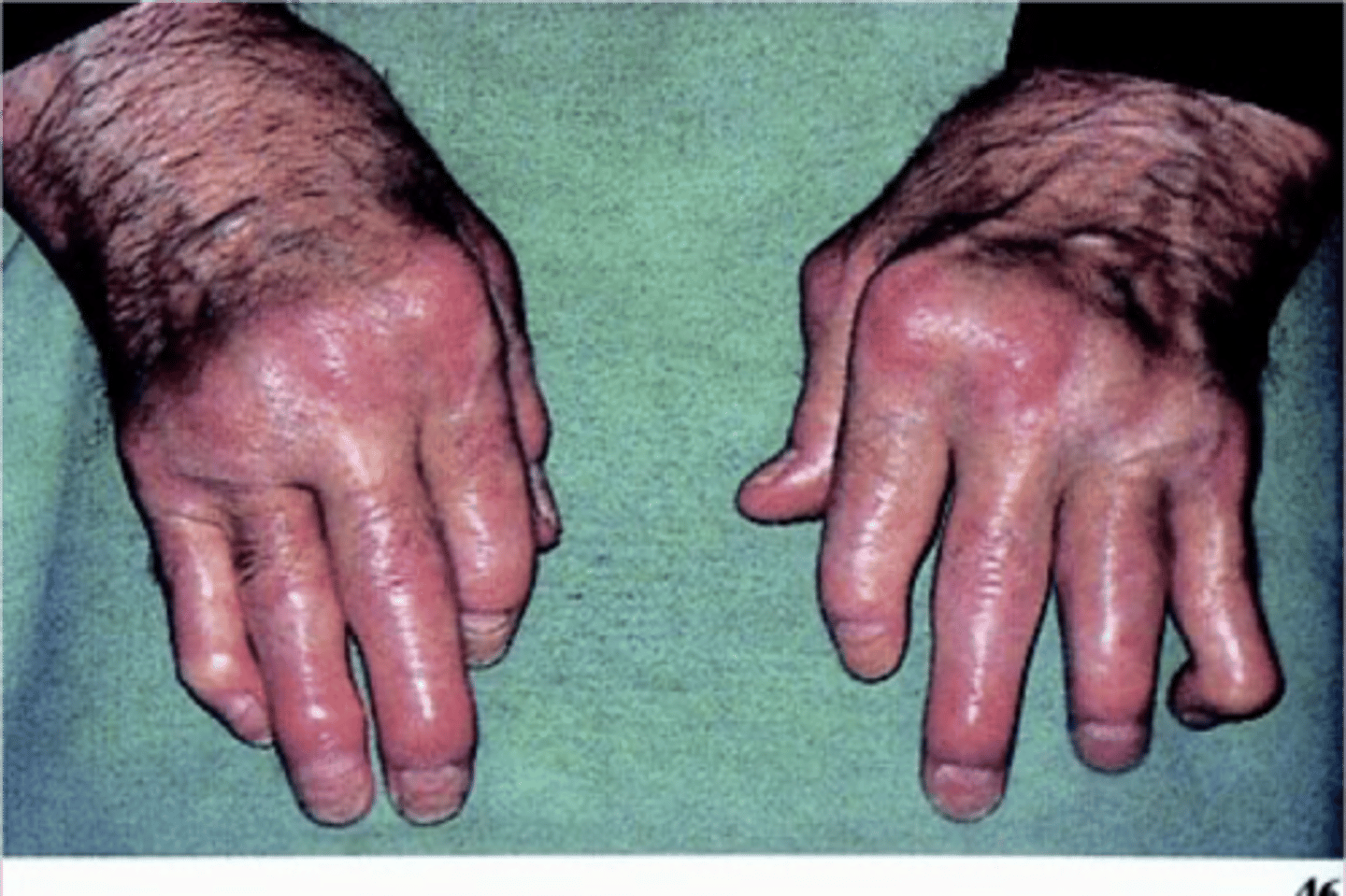
ulnar deviation at MCPs
thickening of fingers-sausage fingers, edematous- important to take rings off so they don't have to be cut off
rheumatoid nodules
Twenty percent of patients have subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules, most commonly situated over bony prominences but also observed in the bursae and tendon sheaths

ocular symptoms
Dryness of the eyes, mouth, and other mucous membranes is found especially in advanced disease
systemic disease
A Interstitial lung disease -decreased ability to gas exchange
B Pericarditis -inflammation of the pericardial sac in which the heart sits
C Disease of the lung pleura
**because the immune system attacks more than joints - thus we must be
concerned with systemic manifestations
RA classic complaint
I woke up and my ____ was sore and I couldn't move it and I couldn't _____ but now it feels fine (they had a flare but it went away before we saw them)
RA labs
1 Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
Anti-CCP antibodies are the most specific blood test for rheumatoid arthritis
Anti-CCP is an autoantibody produced by the patient’s immune system that attacks the body. These attacks can produce inflammatory symptoms most commonly experienced in rheumatoid arthritis.
2 Rheumatoid factor
An antibody that is detectable in the blood of approximately 80% of adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
RA prognosis
Aggressive RA can shorten life by 10-15 years (cardiac/pulmonary issues)
Decreases quality of life = some depression involved
Early aggressive therapy is warranted by rheumatologist
RA treatment
“The primary objectives in treating rheumatoid arthritis are reduction of inflammation and pain, preservation of function, and prevention of deformity.”
“Early recognition and diagnosis of RA may allow intervention with appropriate medications with a decrease in the destructive arthropathy that can occur with the disorder.” JAAPA DiBaise and Kohn
If medications do not achieve the target of remission of symptoms or low disease activity, additional medications should be added to the therapeutic regimen.
Immunosuppressive agents increase a patient’s risk of infection including Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C. (should be the first in line for vaccines every year)
low-dose corticosteroids (prednisone)
produce a prompt anti-inflammatory effect and slow the rate of articular erosion. These should only be used for short term control for patients with acute "flares". (keep in mind they increase risk for osteoporosis)
disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
sulfasalazine, methotrexate, and biological response modifiers
sulfasalazine
similar to methotrexate in terms of medication category.
This medication is a good choice for women with RA who are interested in becoming pregnant. Sulfasalazine is not teratogenic and will allow her to safely become pregnant.
LFT should be obtained at the onset of medication and then every 3 months thereafter and after increasing the dose.
methotrexate
a long standing medication used to treat RA
Methotrexate increases adenosine levels. Adenosine
promotes an anti-inflammatory state.
Taken once per week - by mouth or IM injection (thigh)
Adversely impacts body's folic acid levels via GI tract - thus patients often take folic acid supplements along with methotrexate.
Known teratogenic effects make this medication CONTRAINDICATED in pregnancy.
Obtain a pregnancy test prior to starting the medication.
Adverse effect - possible liver damage - pts are often advised to avoid alcohol and monitor LFTs (liver function tests). LFT should be obtained at the onset of medication and then every 3 months thereafter.
Anencephaly
fetus taken to gestation but born without CNS (lack of folic acid)
spina bifida
spinal cord grown outside of skin (lack of folic acid)
What is needed in CNS production?
folic acid
biological response modifiers
newest class of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
They are genetically engineered to act like natural proteins in the patient’s immune system.
Biologics don’t cure RA, but they can dramatically slow its progression.
Generic Name Trade Name
A Etanercept Enbrel
B Adalimumab Humira
C Infliximab Remicade
*These are injectable medications*
info about DMARDs
All three of these drugs are tumor necrosis factor blockers. TNF is a protein in the immune system that contributes to inflammation and joint damage. TNF blockers block the action of TNF that leads to damage from abnormal inflammation.
Medications in this class cause the patient to be at increased for serious infections such as tuberculosis, herpes zoster and fungal infections
What are concerns about a patient on steroids for too long?
impaired immune system and bone density problems
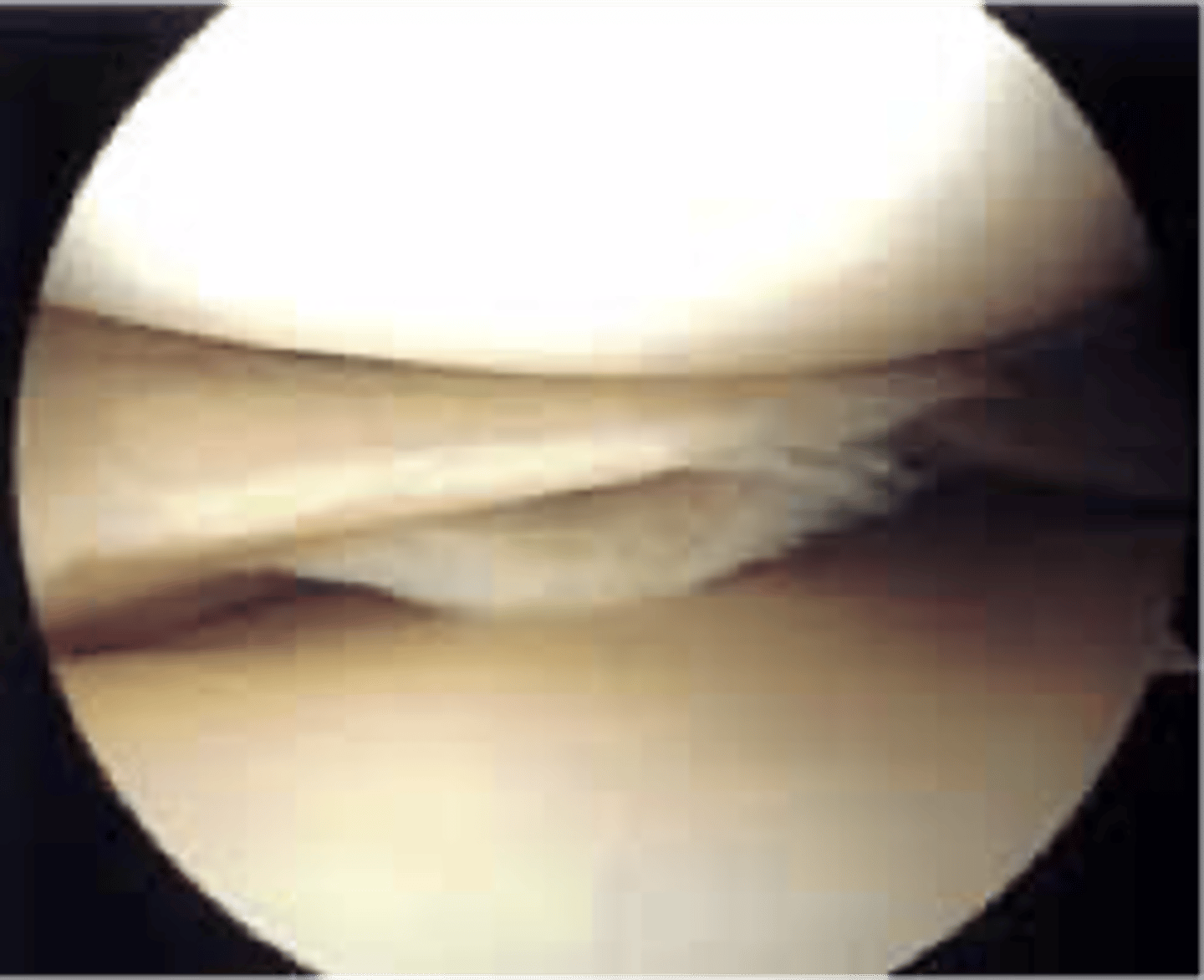
meniscus
c-shaped wedges of fibrocartilage between tibial plateau and femoral condyle
What happens to the meniscus over time?
it wears down and joint space narrows
Which meniscus is more likely to tear?
the medial meniscus because it is larger and more tethered down
x-ray
shows us things with high levels of calcium
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
shows us bones and soft tissues (diagnostic modality of choice for soft tissue and thus the knee)
common age groups affected by meniscal tears
young athletic people or men or women over the age of 55
Why are older people affected by meniscus tears?
the meniscus gets thinner as we get older so it's more likely to tear
MOI
mechanism of injury
meniscal tears MOI
a rotational force
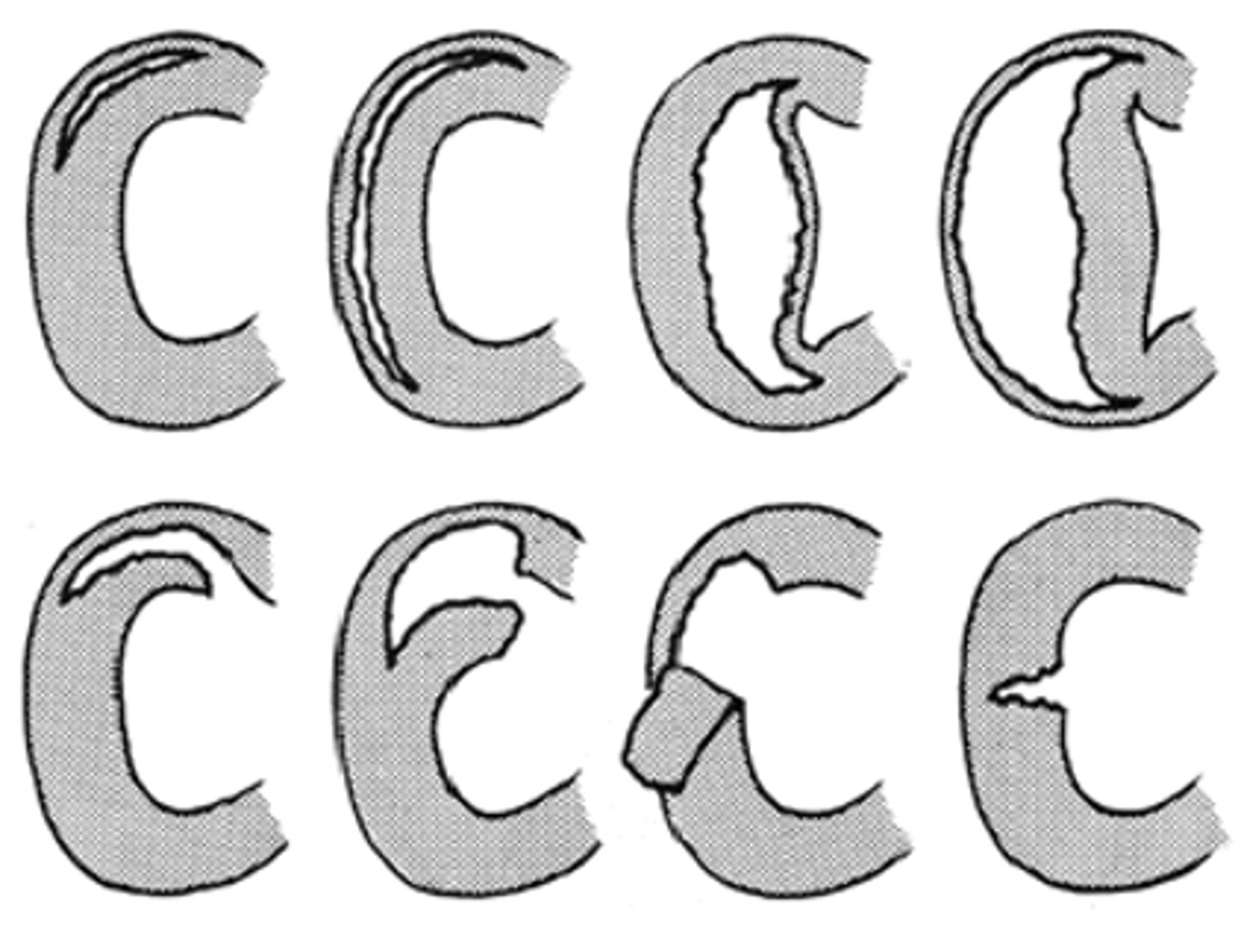
Are all meniscal tears the same?
no
symptoms of meniscal tear
Locking (difficulty bending)/popping
Will feel weak but if asked to stand on it will not fall to the ground (ACL tears you will fall to the ground)
Catching
Painful clicking
“Giving way”
signs of meniscal tear
Edema/Hemarthrosis: develops gradually slower than ACL
(will happen much later than an ACL tear-those usually happen within minutes to first hour) takes much longer than an hour
decreased range of motion
McMurray Test, Thessaly Test
hemarthrosis
blood within a joint
decreased ROM for meniscus
evaluate ability to fully extend - a meniscus injury can block full extension
non-surgical treatment for torn meniscus
RICE - - with no mechanical symptoms and in the case of a degenerative tear
RICE
rest (crutches, relax), ice (15-20 minutes), compression (compression sleeve), elevation (laying supine and raise injury above level of heart)
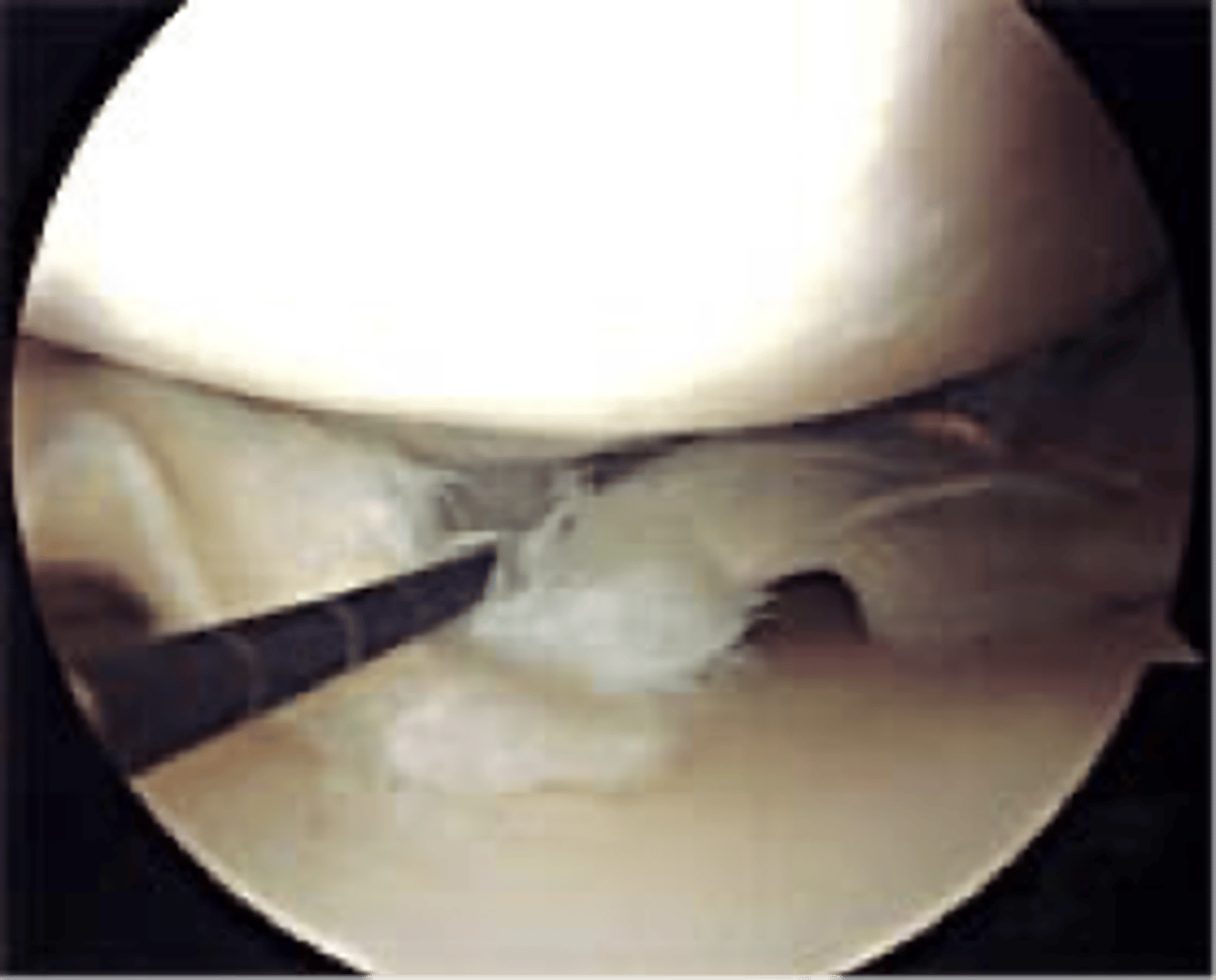
surgical treatment for meniscal tear
arthroscopic debridement or repair
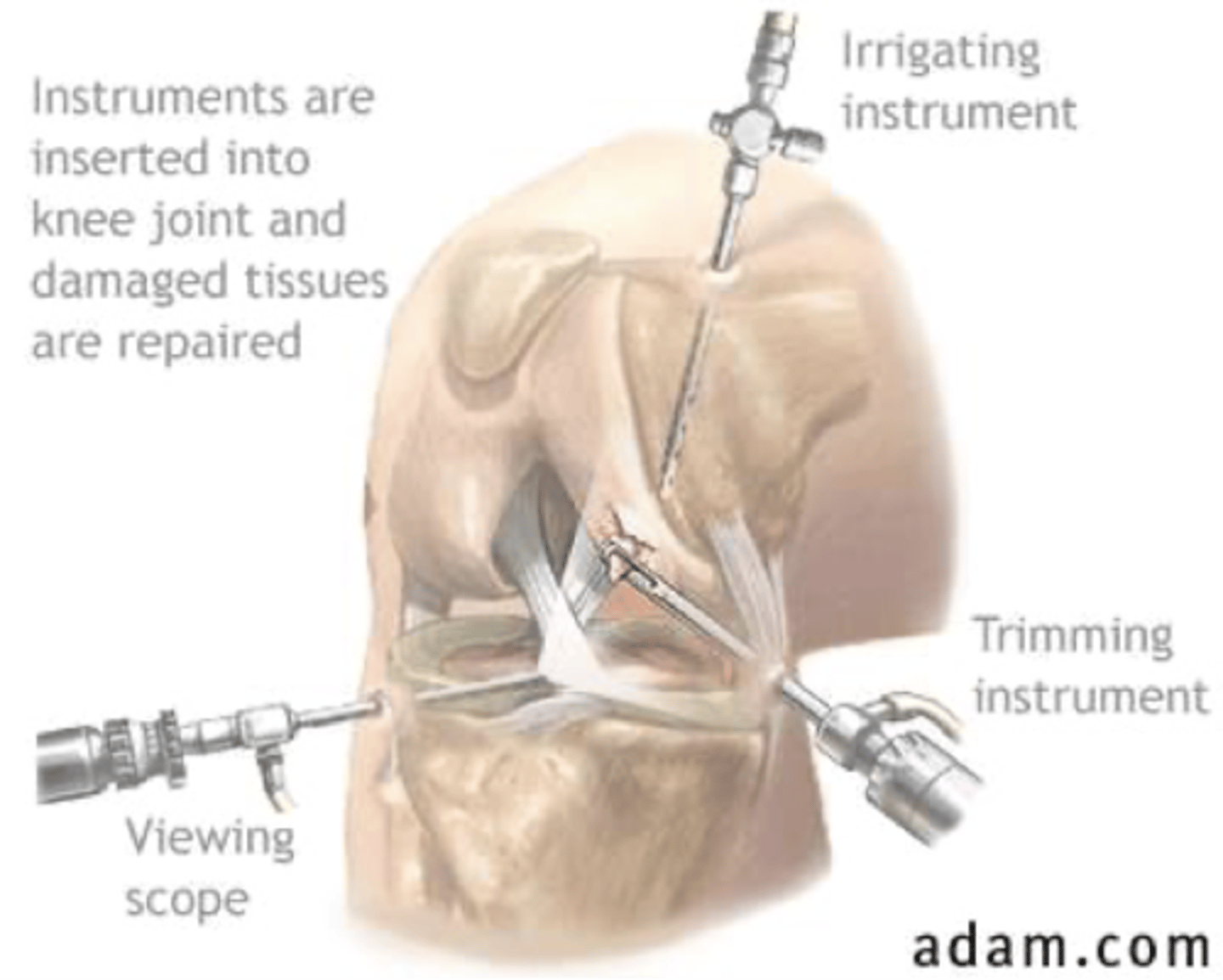
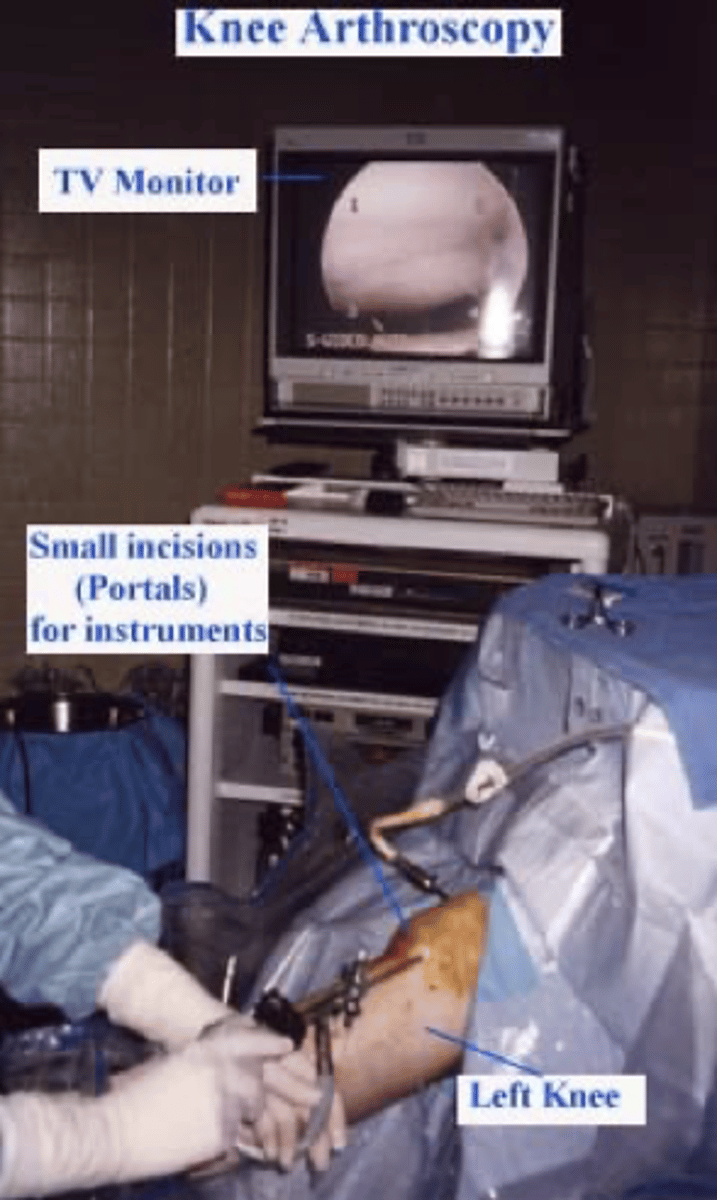
How many ports enter the knee in arthroscopic surgery?
1. camera
2. irrigating instrument (lets in sterile saline)
3. trimming instrument