Respiration
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Define “Anatomy”
The study of organisms structure and the relations of their parts
Define “Physiology”
The study of the function of the living organisms and their parts
What are the 4 speech subsystems?
Articulatory, Phonation, Respiration, Resonatory,
What does Anterior/Ventral mean?
toward the front
What does Posterior/Dorsal mean?
toward the back
What does Lateral mean?
toward the outside
What does Medial mean?
toward the middle
What does Superior mean?
toward the head
What does Inferior mean?
toward the feet
What does Superficial mean?
toward the surface
What does Deep mean?
away from the surface
What are the 5 systems of the Resonator-Resonatory passageway in order?
Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli,
What do the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi have for support? What purpose does this support serve? What shape are they?
cartilaginous rings that keep the airway open, they’re U-shaped open to the dorsal
What do the mucus and cilia do?
Filter debris and microorganisms from the respiratory system
How are cilia shaped? Where are they found in what proportions? How do they move?
hair-like structures found in the nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, and larger bronchioles with less of them in smaller airways, they move in a coordinated wave-like motion
What are alveoli? How do they work? What are they covered in?
Small sacs of air that diffuse CO2 and Oxygen from the blood, they are covered with a capillary bed which is a woven net of tiny veins
What are the lobes of the right and left lungs (top to bottom)?
R - superior lobe, middle lobe, inferior lobe,
L - superior lobe, inferior lobe,
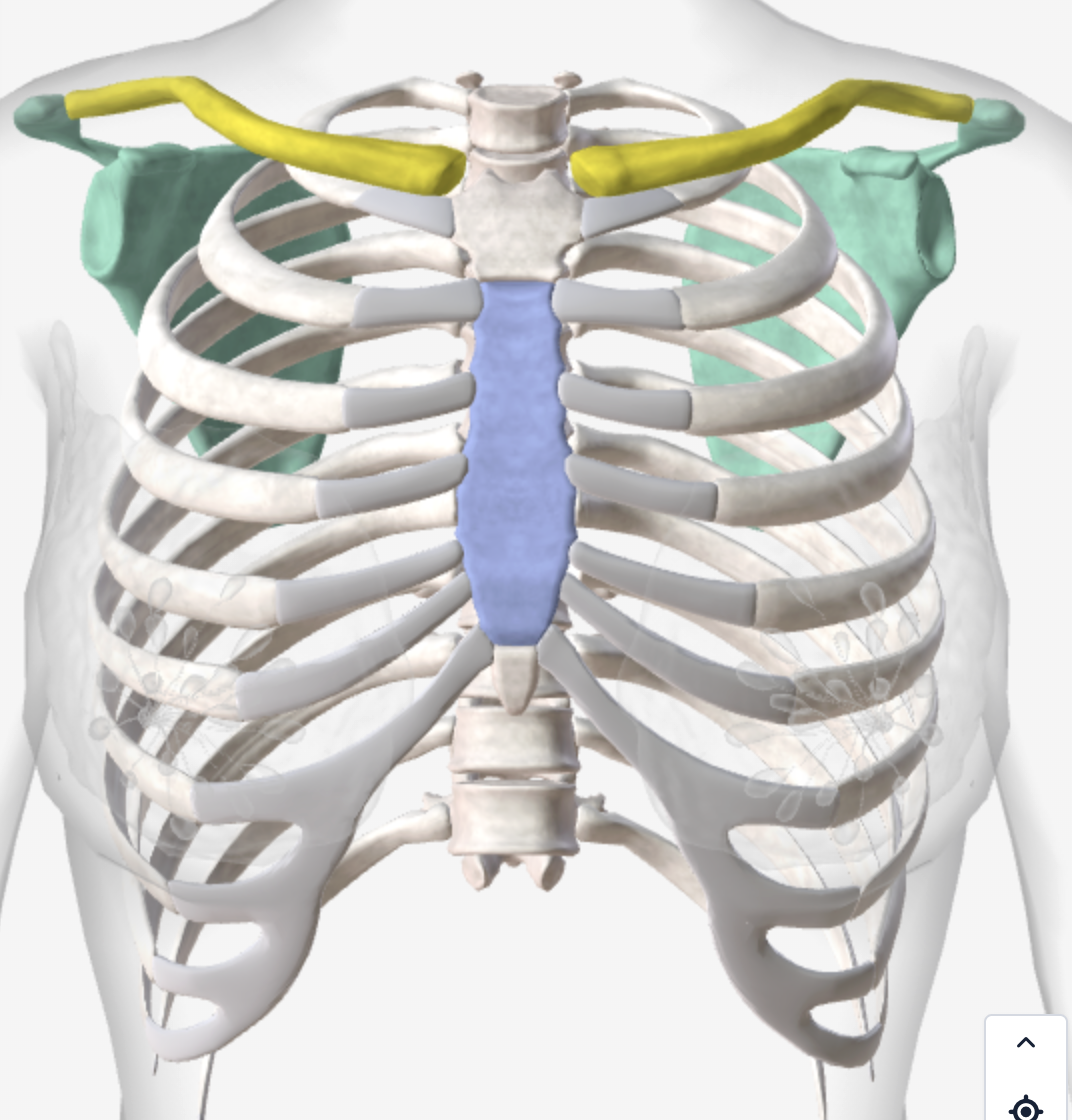
What bones are these? What do they do?
Blue = Sternum - attachment for ribs and protects the lungs
Yellow = Clavicles - attachment for accessory muscles, pull up rib cage
Green = Scapula
Which ribs are the true ribs? Which ribs are the false ribs? Which ribs are floating ribs? Explain why each of these are what they are.
True ribs = 1-7, they attach directly to the sternum via intercostal cartilage
False ribs = 8-10, they attach to the intercostal cartilage of rib 7 to the sternum
Floating ribs = 11-12, they don’t attach to the sternum
What are the two phases are aspiration? What happens during them?
Inspiration - taking in air, Expiration - exhaling air
What is Boyle’s law?
As volume increases pressure decreases and vise versa.
An area of high pressure will move to…
an area of low pressure
Where are the visceral pleurae located? Where are the parietal pleurae located? What is the space between them called and what is in it? What kind of pressure does this space have and what does it do?
Visceral pleurae - outside of the lungs, Parietal pleurae - inside of the rib cage
The space between them is the intrapleural place with intrapleural fluid, has negative pressure for a gentle suction
How many cycles of respiration do adults complete in 1 minute?
12-20
What is tidal volume? What is male and female average volumes?
the volume of air exchanged in one cycle of respiration when breathing quietly
Male - 600 mc/mL, Female - 450 cc/mL
What is vital capacity? Why can’t we achieve total capacity + what is the name for the air?
the volume of air that can be inhaled following a maximal exhalation
total capacity can’t be achieved because we cannot fully removed all the air from the lungs, called residual volume
What percent range of the vital capacity is used for life breathing, speech breathing, loud speech breathing, and child speech breathing?
Life breathing - 40-50%
Speech breathing - 40-60%
Loud speech breathing - 40-80%
Child speech breathing - 25-60%
What are the two types of breathing? Descibe them.
Quiet breathing - typical, slow, relaxed breathing
Active breathing - faster breaths and quick inhales during exercise and speech
What are the muscles of quiet breathing inspiration? What do they do?
Diaphragm - shifts lungs down
External intercostals - expands rib cage
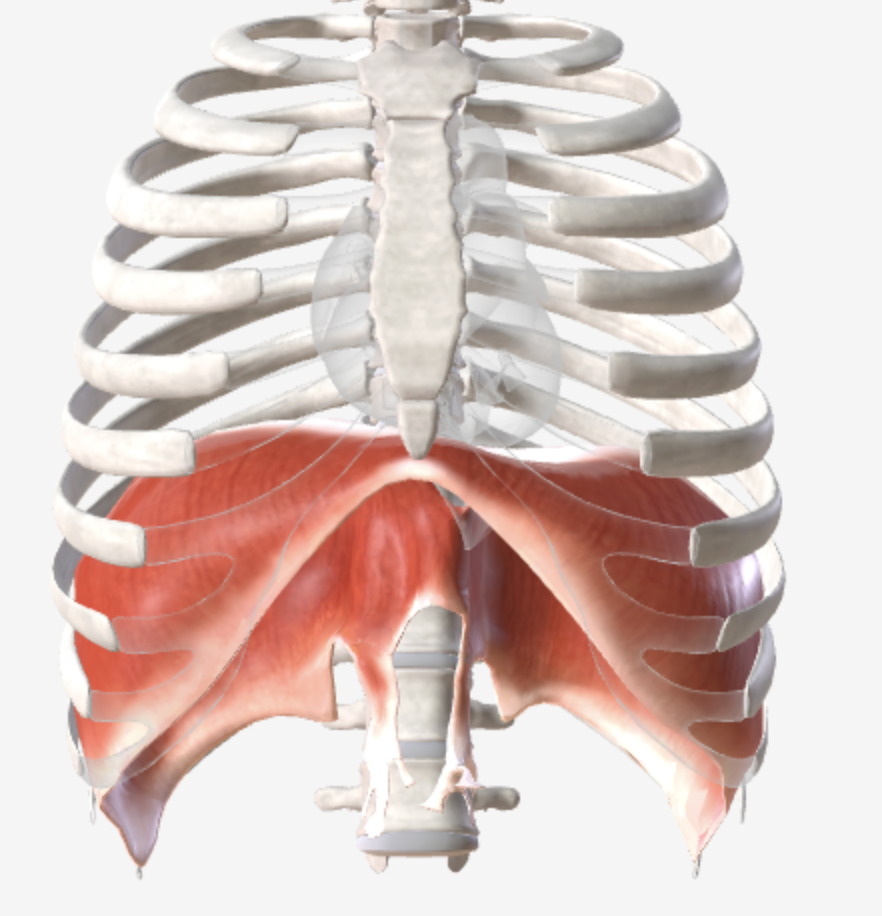
What is diaphragm made of? What does it attach to? How and where does it move?
Made of muscles and tendons
Attaches to the lower rib cage, sternum, spine, and itself
Contracting muscles pulls it flat and pushes against lower organs to expand lungs
What muscles are needed for quiet breathing inhalation? Why?
No muscles are needed, elastic recoil move diaphragm to its original position and gravity moves the ribs back down
During active inhalation and expiration why are accessory muscles required?
Inhalation - additional muscles to push the ribs and clavicles up and out
Expiration - additional muscles to pull the ribs and diaphragm back down
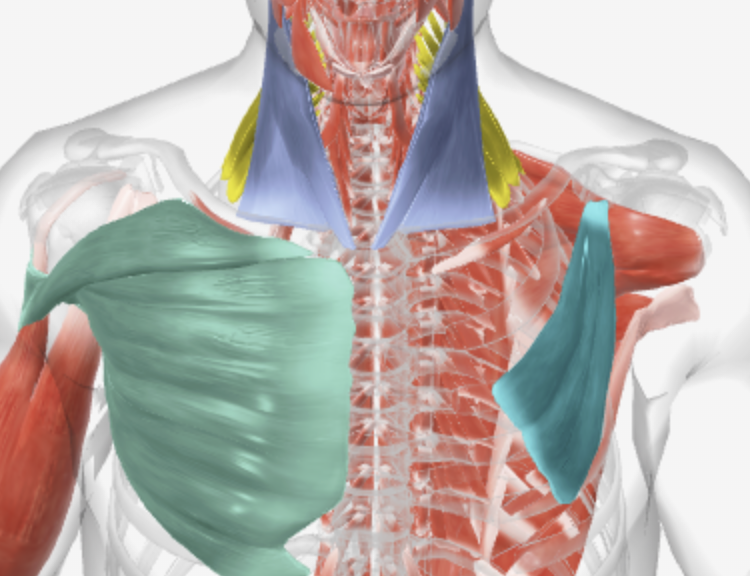
What are these muscles for active breathing inspiration? What do they do?
Blue = Sternocleidomastoid, pulls up on the top ribs
Yellow = Scalene, pulls up on the top ribs
Green = Pectoralis Major, pulls rib cage up and out
Teal = Pectoralis Minor, pulls ribs outwards
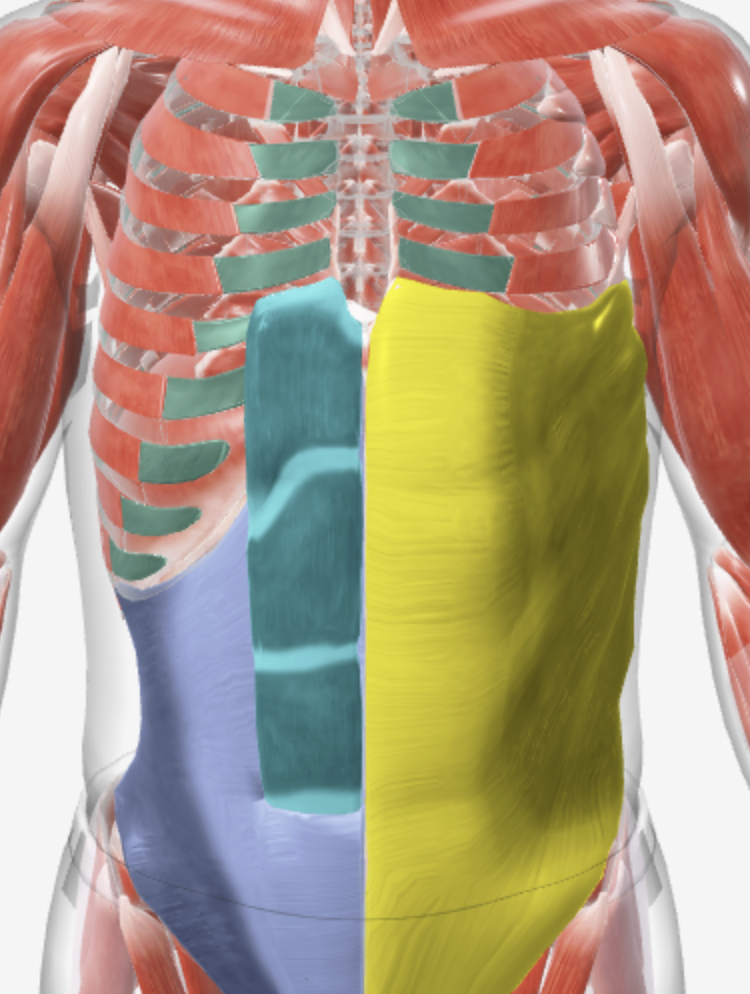
What are these muscles (+the one under the yellow not pictured)? What do they do (only specific answer for muscle pictured in green)?
Green = Internal intercostals, pulls ribs back together
Blue = Rectus Abdominus,
Purple = Transverse Abdominus
Yellow = External Oblique
Under the yellow = Internal Oblique
They help push all the air out
Where is the breathing for life breathing done? What is the inhale/exhale %-ration? Where is the breathing for speech done? What is the inhale/exhale %-ration?
Life Breathing: the nose, 40% inhale 60% exhale
Speech breathing: the mouth, 10% inhale 90% exhale