Fetal Syndromes, Chromosomal Abnormalities, and Other Complications in Pregnancy
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Severe generalized massive edema often seen with hydrops fetalis.
Anasarca
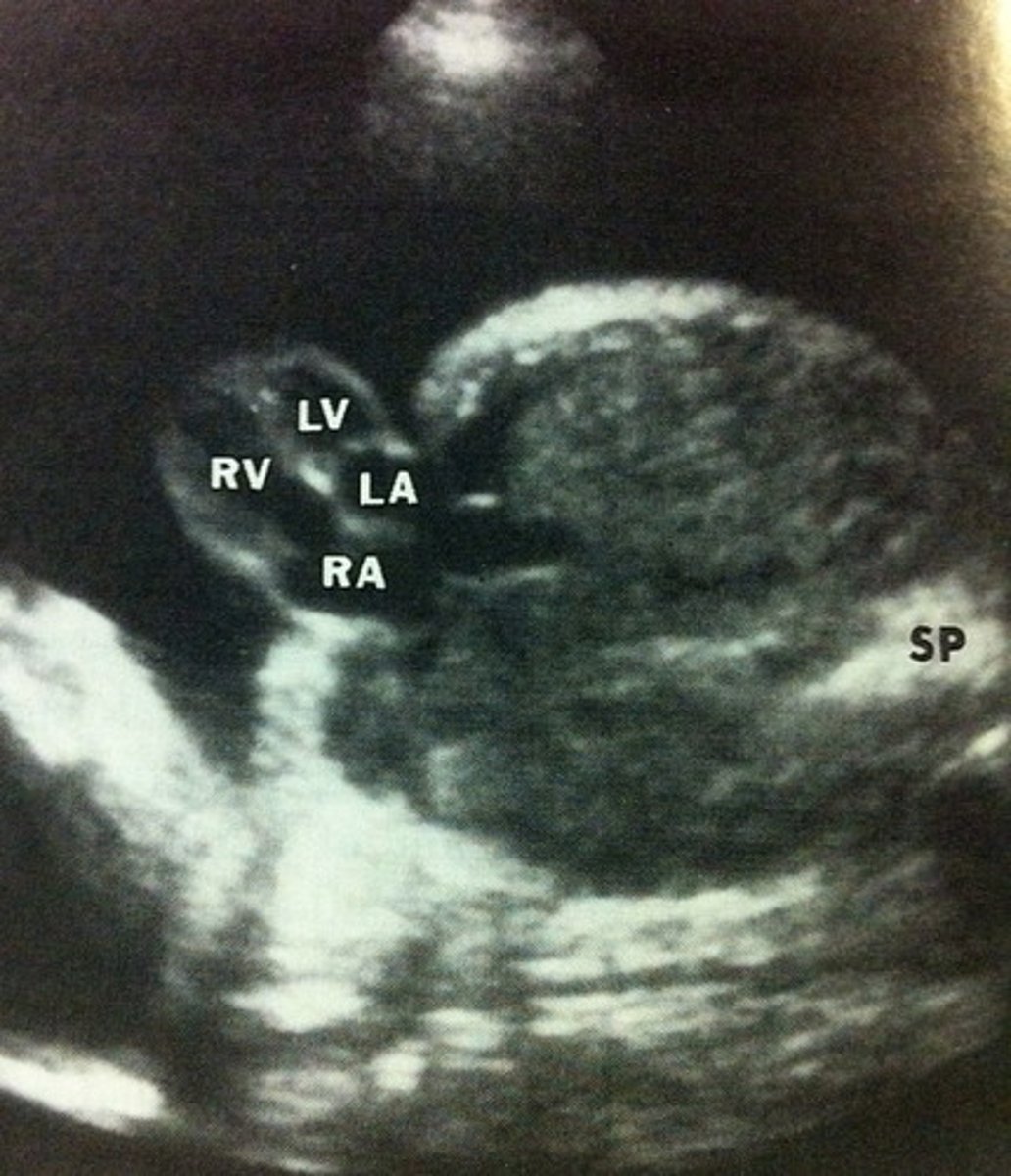
The presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes and is almost always associated with abnormalities of physical and cognitive development.
Aneuploidy
Inward curving of the fifth finger associated with Down syndrome.
Clinodactyly
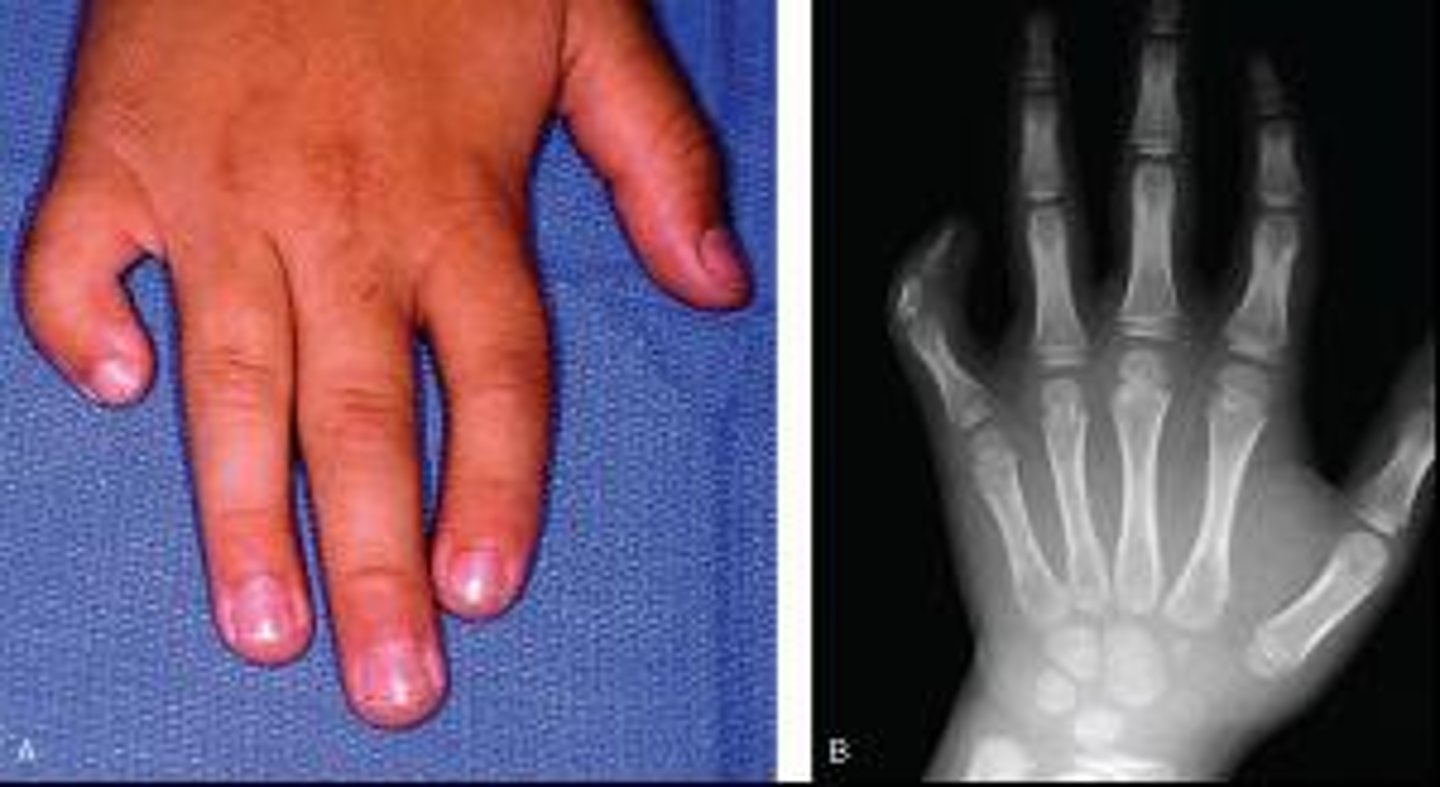
Clinodactyly is associated with trisomy ____.
21 - Down syndrome
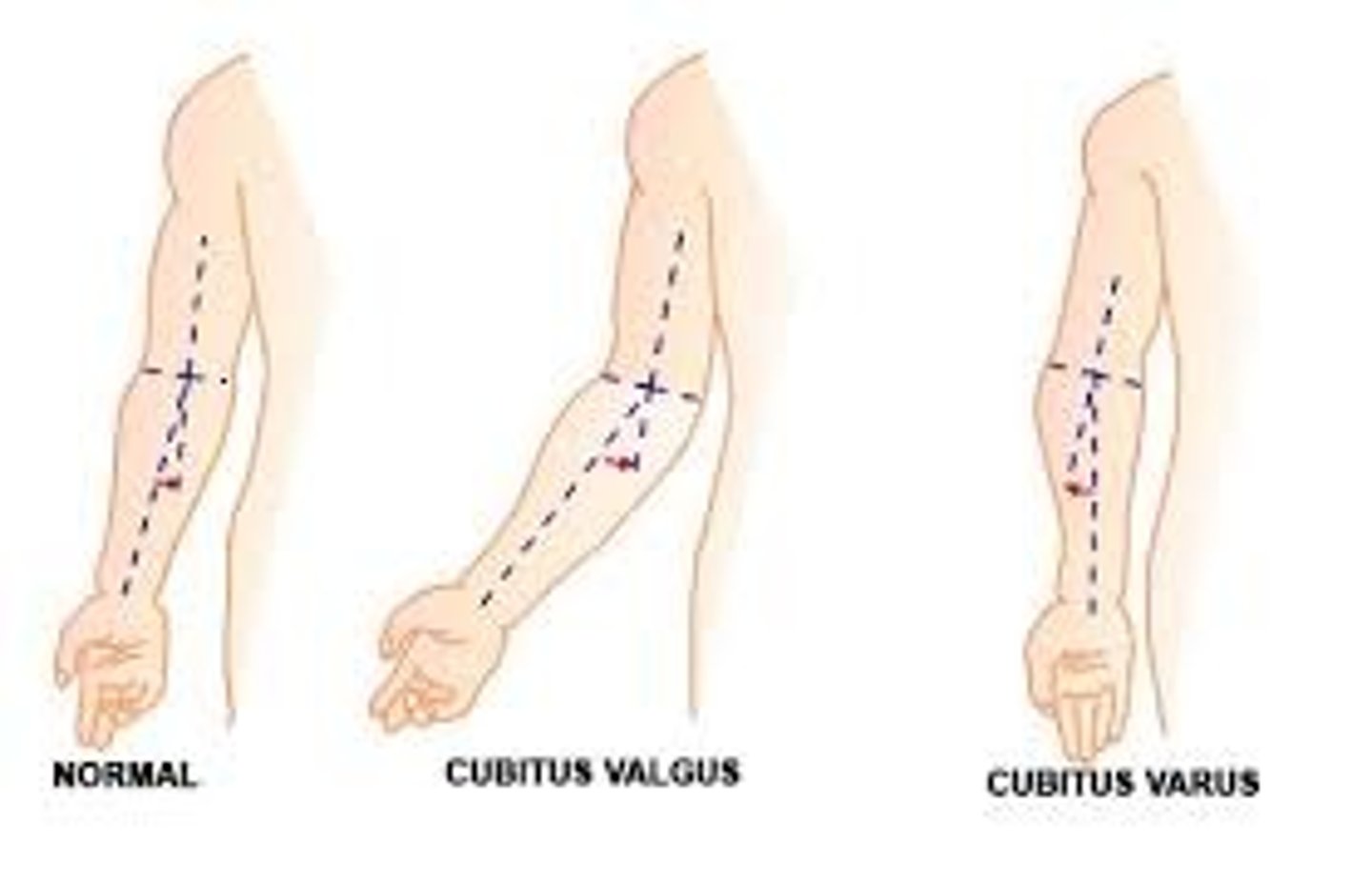
Abnormal outward bending or twisting of the elbow.
Cubitus valgus
Gravest form of pregnancy-induced maternal hypertension characterized by seizures, coma, proteinuria, and edema.
Eclampsia
A condition in which the ventral wall of the chest fails to close and the heart develops outside the chest.
Ectopia cordis
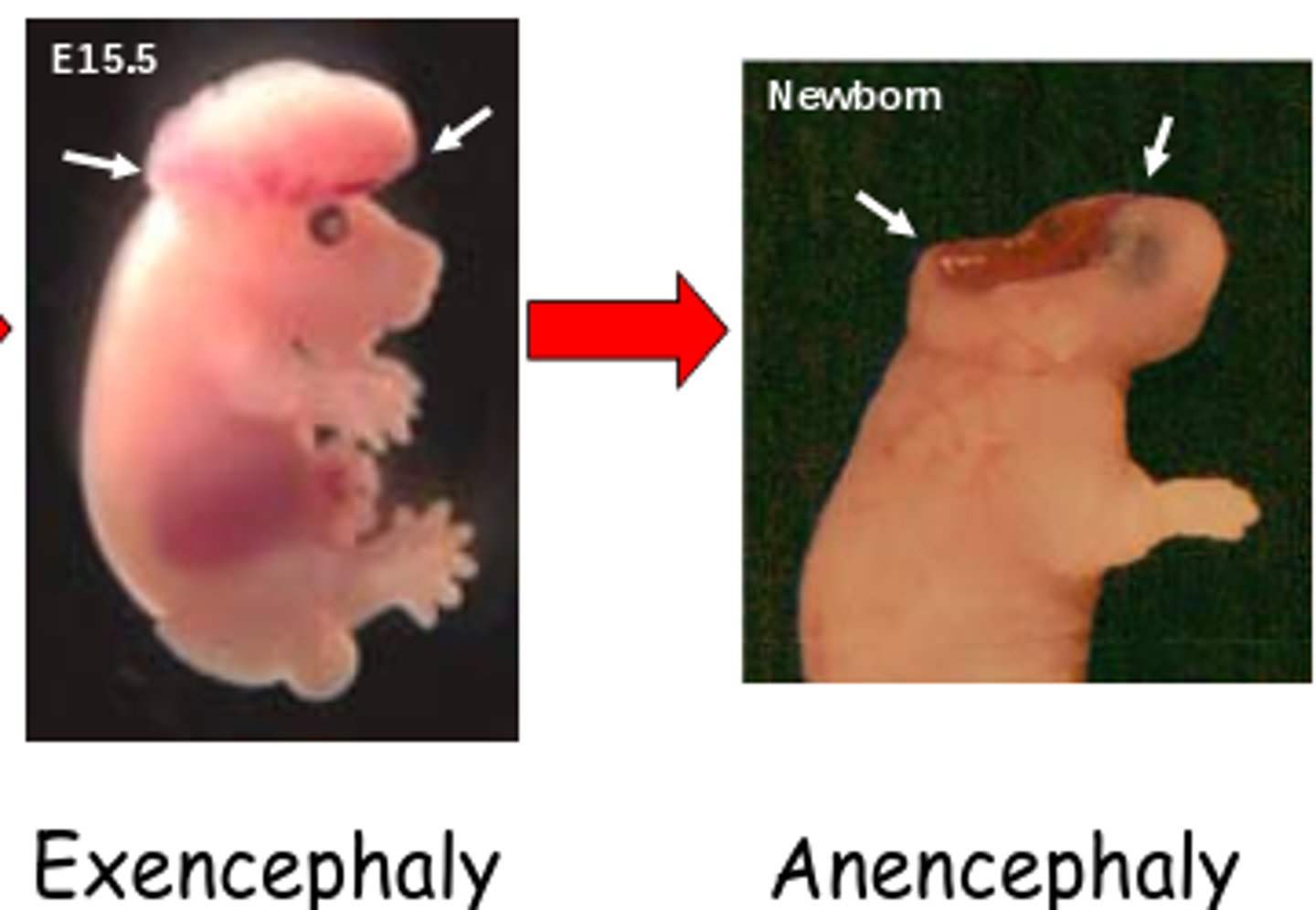
A condition where the skull is defective, causing exposure or extrusion of the brain.
Exencephaly
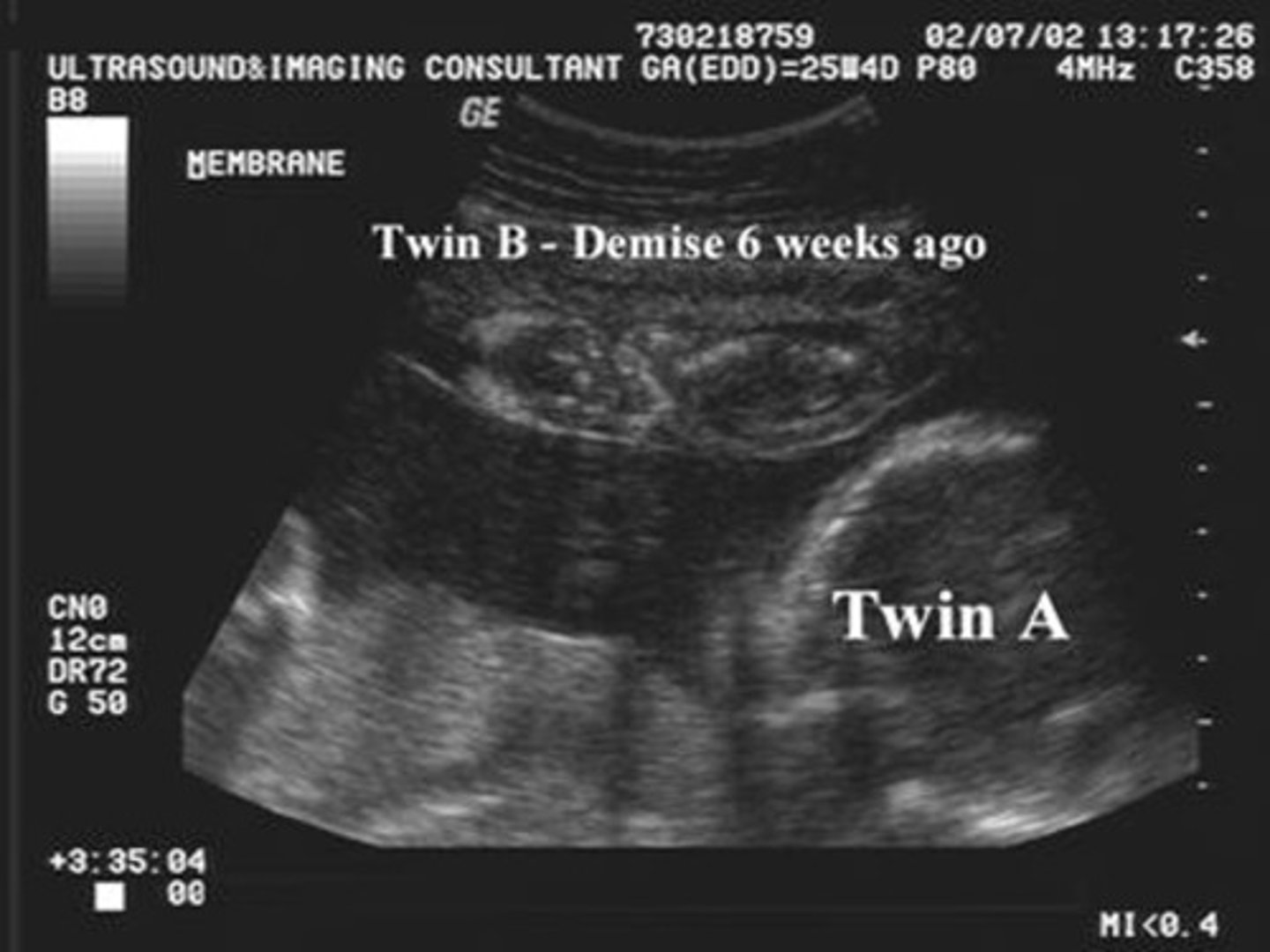
Demise of a twin that is too large to reabsorb.
Fetus papyraceus
Picture of chromosomes and how they look structurally.
Karyotype
Underdevelopment of the jaw, especially the mandible.
Micrognathia
Abnormal smallness of one or both eyes.
Microphthalmia
Congenital anomaly characterized by the presence of more than the normal number of digits.
Polydactyly
An abnormal condition characterized by the onset of acute hypertension after 24 weeks gestation. Classic triad includes maternal edema, proteinuria, and hypertension.
Preeclampsia
What is the classic triad for preeclampsia?
Maternal edema
Proteinuria
Hypertension
Preeclampsia is an abnormal condition characterized by the onset of acute hypertension after _____ weeks gestation.
24 weeks
Early rupture of the gestational sac with leakage of part or all of the amniotic fluid.
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
Onset of labour before 37 weeks gestation.
Preterm labour
Caused when the mother forms a corresponding antibody to the fetal blood, resulting in destruction of fetal red blood cells.
Rh disease
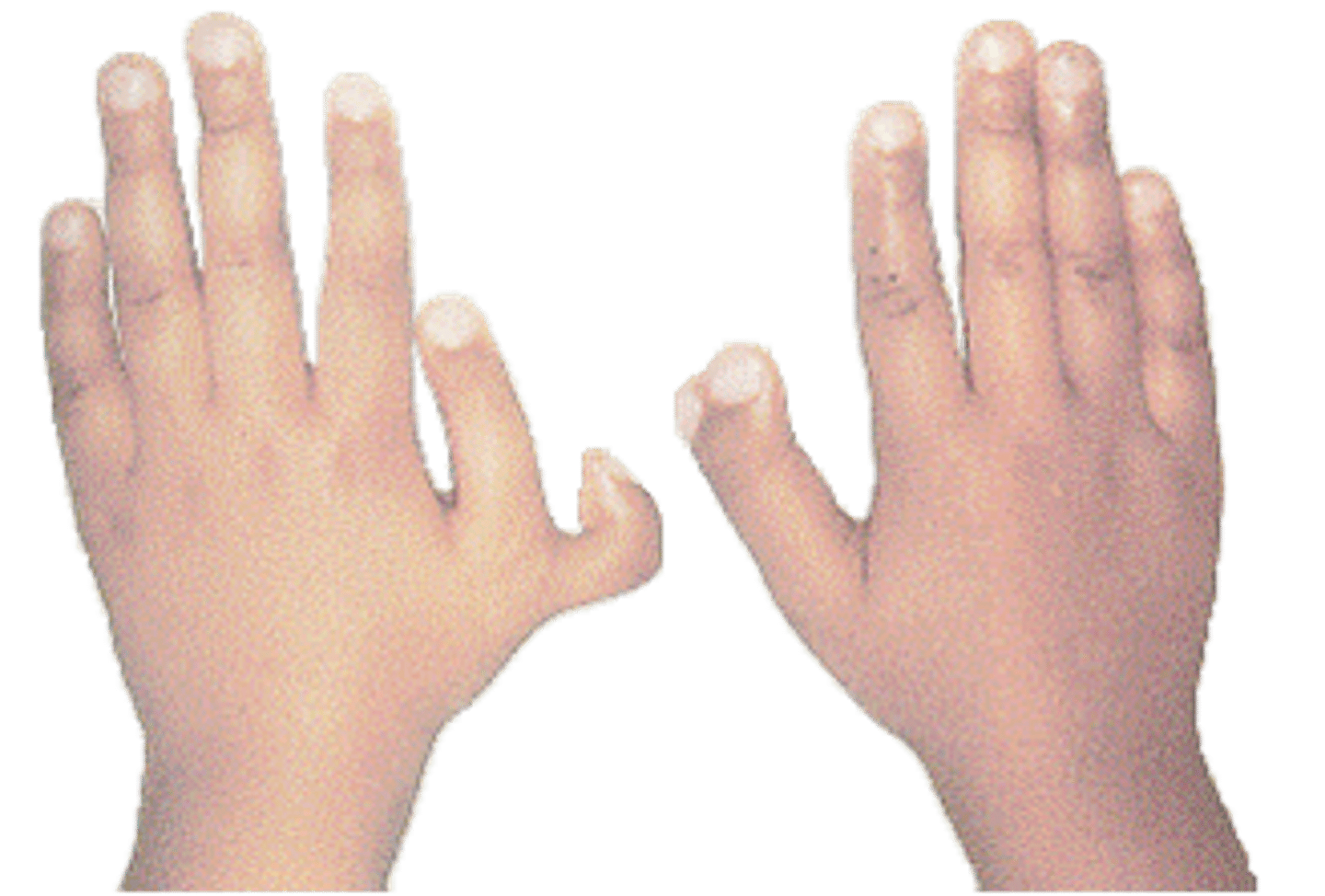
Increased distance between the first and second toes associated with Down syndrome.
Sandal toe deformity
Sandal toe deformity is associated with trisomy _____.
21 - Down syndrome
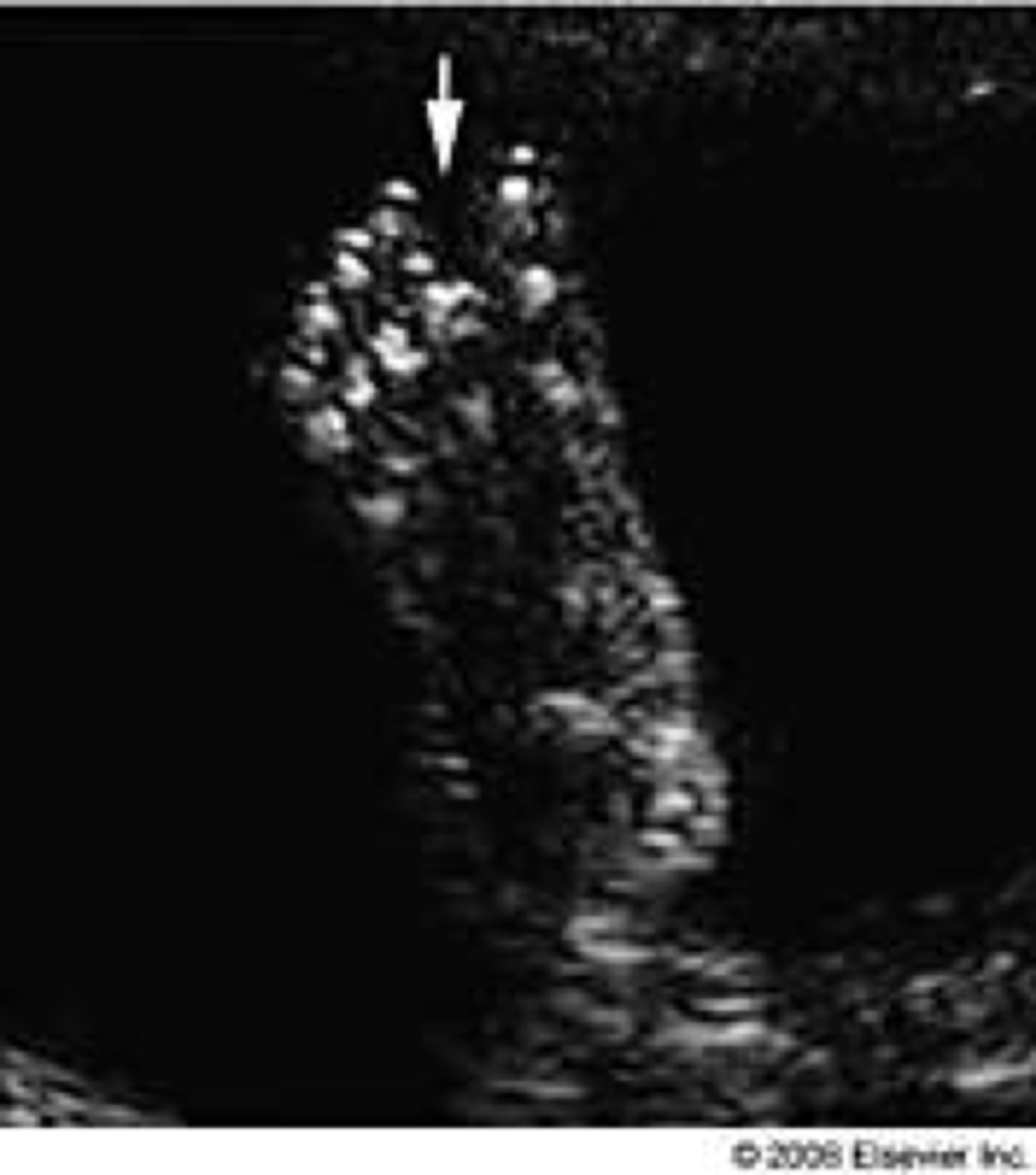
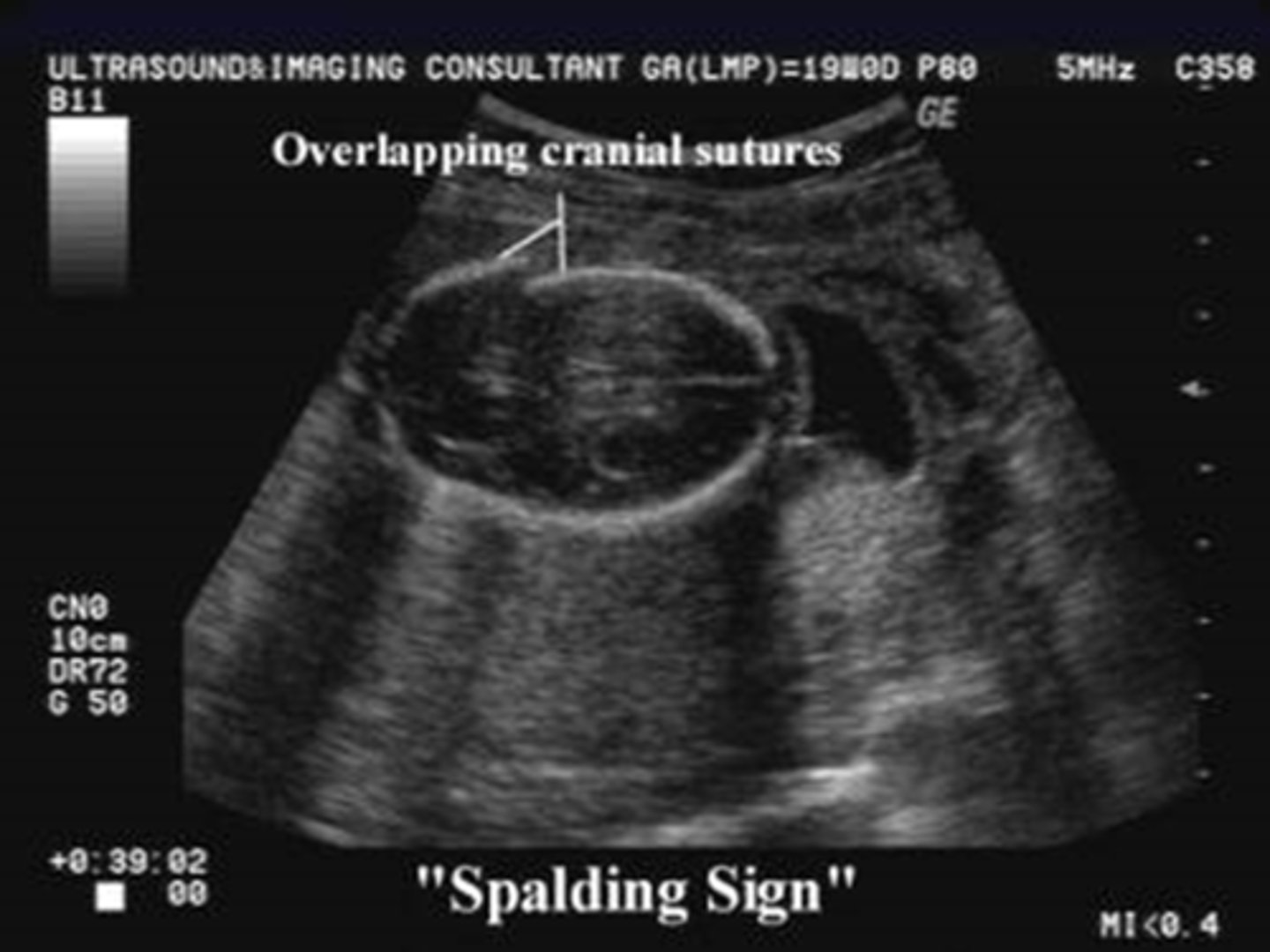
Overlapping of the cranial bones associated with fetal demise.
Spalding sign
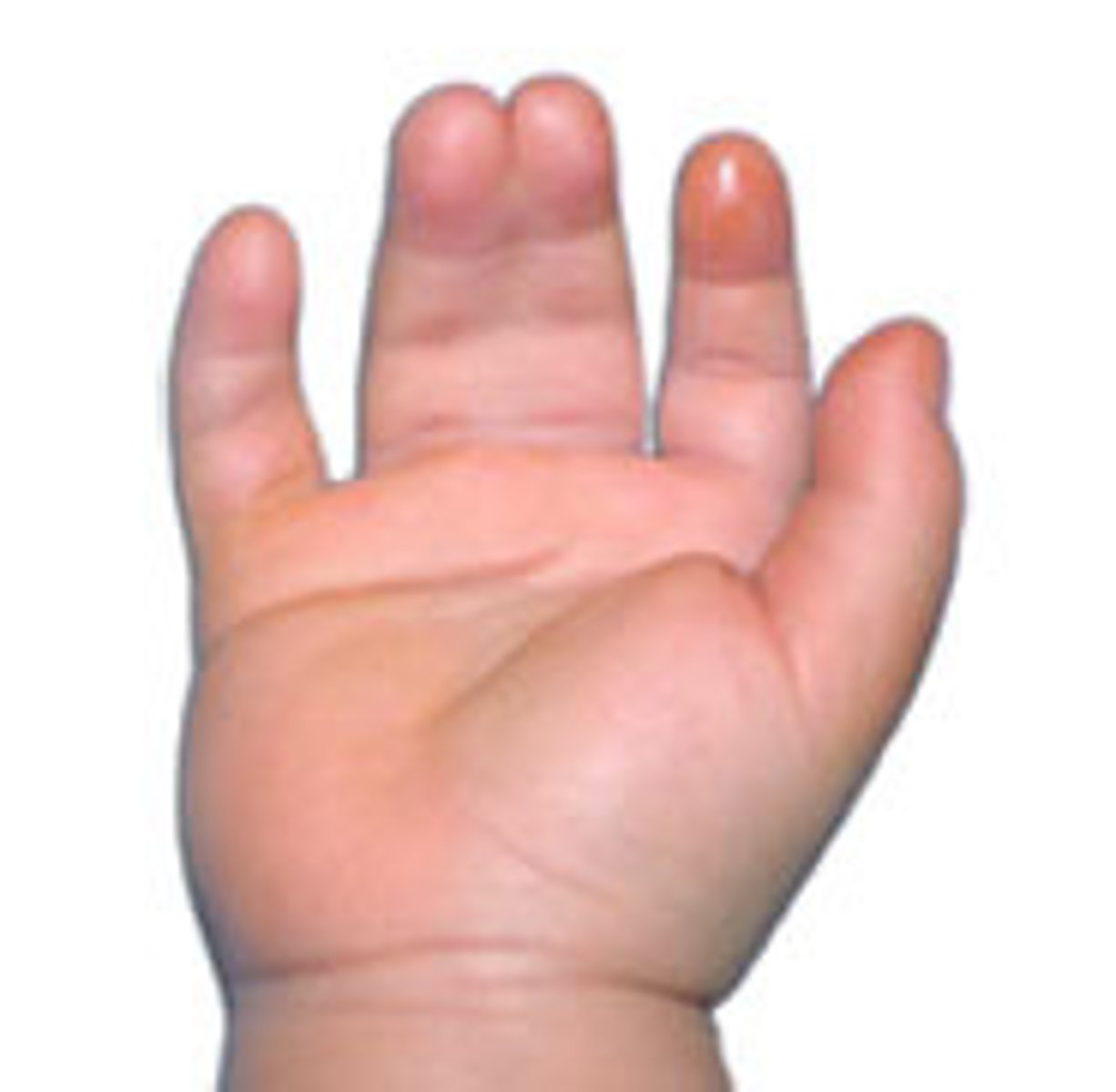
Congenital anomaly characterized by the fusion of the fingers or toes.
Syndactyly
The arterial blood of the donor twin pumps into the venous system of the receiving twin.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)
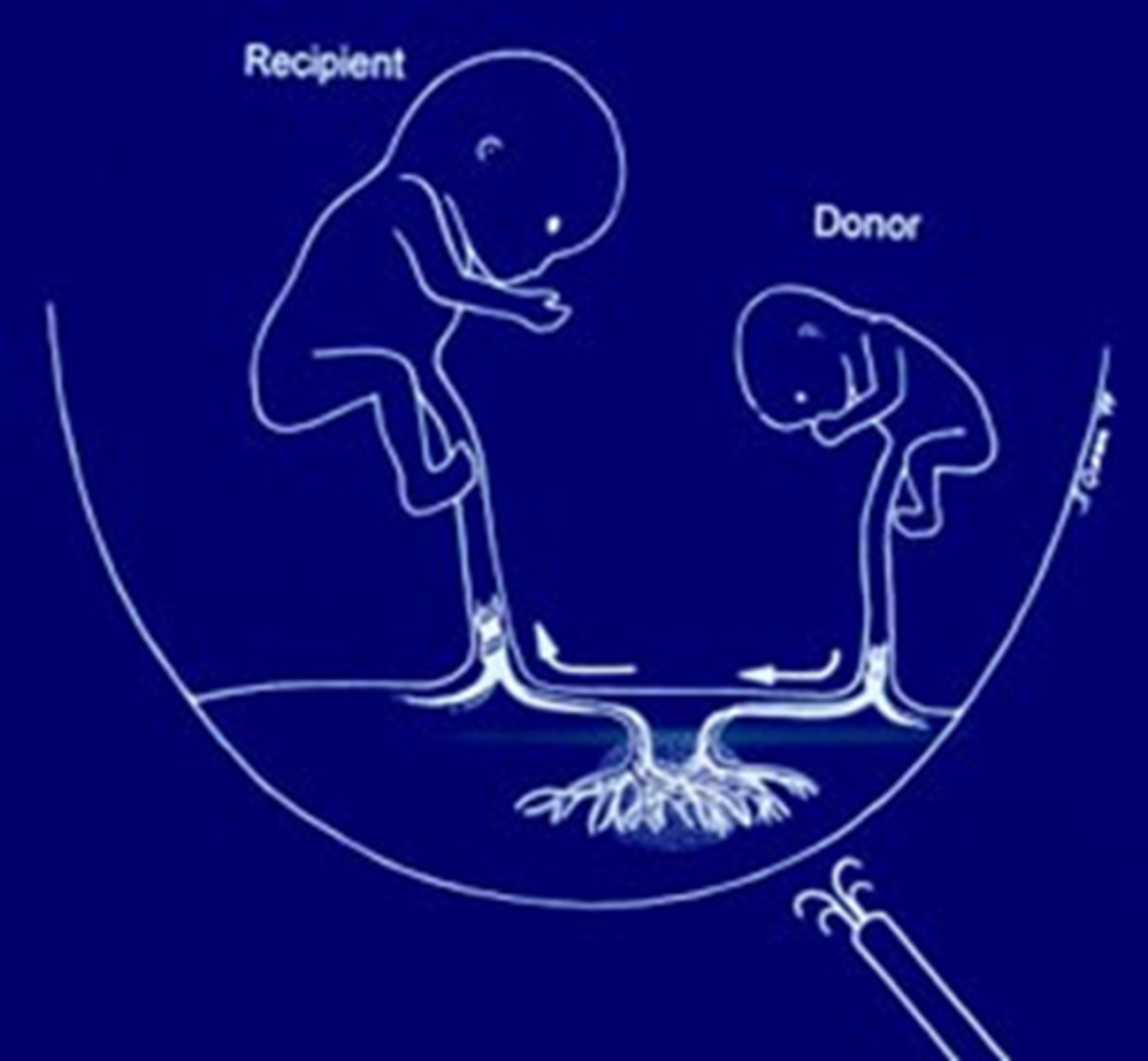
Chromosomal abnormalities can be either numeric or structural. 95% of chromosomally abnormal conceptions are _____ before term.
Lost
What is another name for Edward syndrome?
Trisomy 18
A clenched fist is often associated with which trisomy?
18 - Edward's syndrome
Is AFP affected with trisomy 18?
Yes - Decreased AFP
True or false:
Trisomy 18 has an overall good prognosis.
FALSE
Overall poor prognosis
Does trisomy 18/Edward's syndrome have a male or female prevalence?
Female
Edward syndrome/trisomy 18:
-80% of cases display a _____
-Decrease in _____
-Overall _____ prognosis
-95% spontaneously _____
-_____ prevalence
80% display a clenched fist
Decreased AFP (alpha-fetoprotein)
Overall poor prognosis
95% spontaneously abort
Female prevalence
The following sonographic findings are associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
-Cardiac defects (especially VSD)
-Choroid plexus cysts
-Clenched hands
-Micrognathia
-Clubbed or rocker bottom feet
-Cleft lip or palate
-Renal anomalies
-Omphalocele
-Spina bifida
-Cystic hygroma
-Diaphragmatic hernia
-Two-vessel cord
-Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
Edward syndrome (trisomy 18)
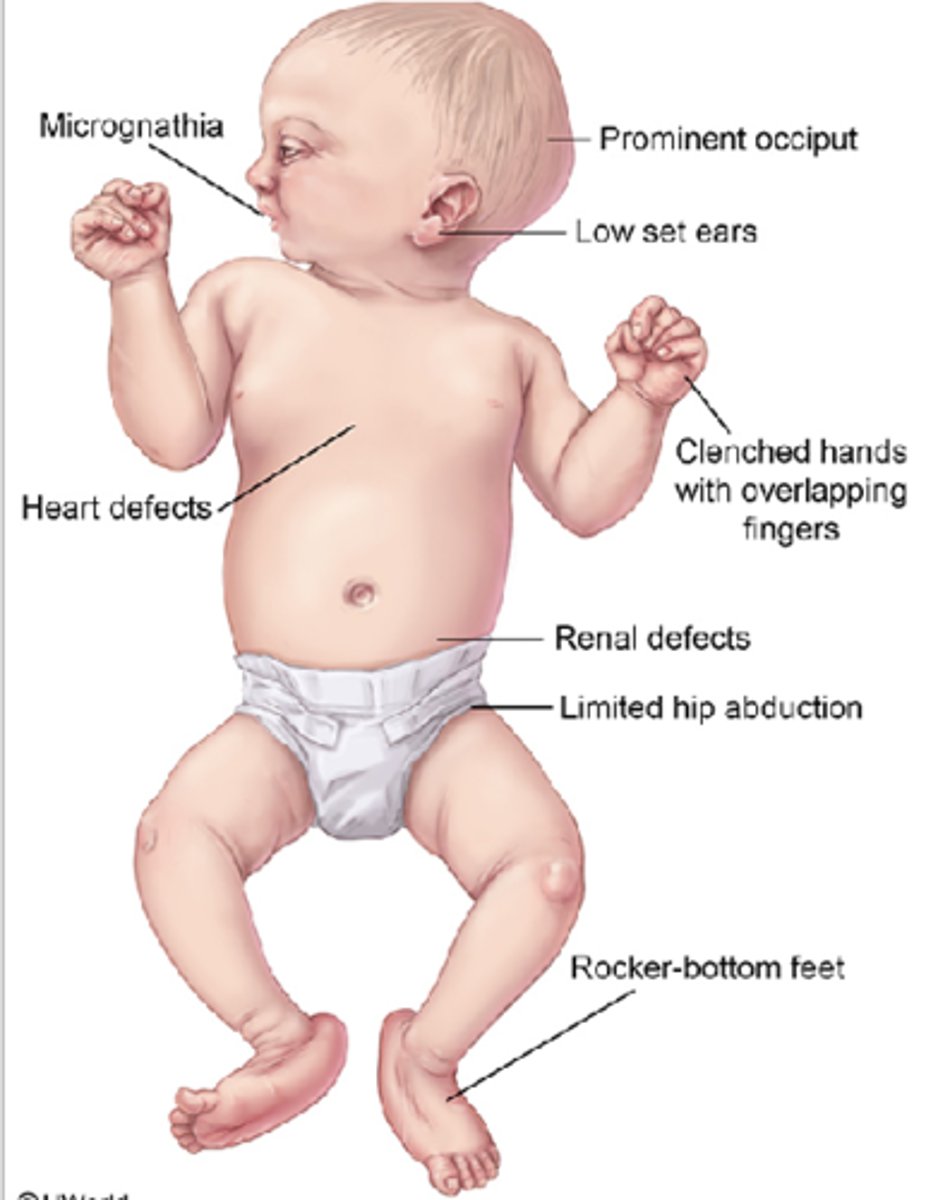
List some of the sonographic findings associated with trisomy 18.
-Cardiac defects (VSD)
-Choroid plexus cysts
-Clenched hands
-Micrognathia
-Clubbed or rocker bottom feet
-Cleft lip or palate
-Renal anomalies
-Omphalocele
-Spina bifida
-Cystic hygroma
-Diaphragmatic hernia
-Two-vessel cord
-Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
-Short ears
What is another name for Down syndrome?
Trisomy 21
Which of the trisomies is the most common?
Trisomy 21 (extra copy of chromosome 21)
What is the primary risk factor for trisomy 21?
Maternal age
Is AFP affected with trisomy 21?
Yes - decrease in AFP levels
What is the prognosis for down syndrome (trisomy 21)?
Coexisting anomalies dictate overall prognosis
Duodenal atresia is seen in 30% of trisomy _____ cases.
21 (down syndrome)
Down syndrome/trisomy 21:
-_____ in AFP levels
-Coexisting anomalies dictate overall _____
-Approx. 30% of cases demonstrate _____
Decreased AFP
Coexisting anomalies dictate prognosis
30% demonstrate duodenal atresia
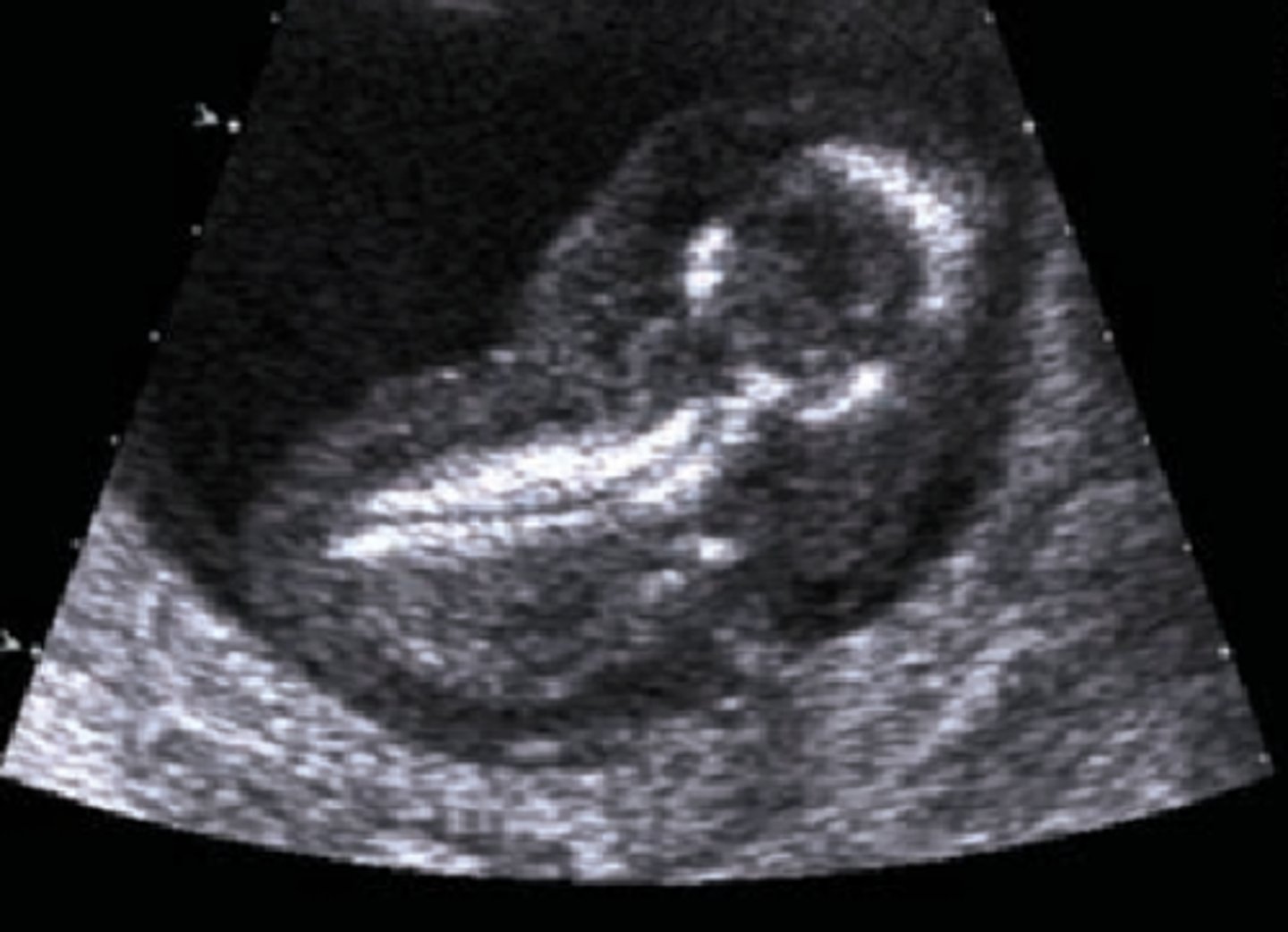
The following sonographic findings are associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
-Subtle anomalies
-Atrioventricular defect
-Ventricular septal defect
-Nuchal thickening
-Small or absent nasal bone
-Macroglossia
-Mild ventriculomegaly
-Duodenal atresia
-Pyelectasis
-Hyperechoic bowel
-Nonimmune hydrops
-Sandal toe deformity
-Clinodactyly
-Low-set ears
-Shortened limbs
-Femur length below the 10th percentile for gestational age
-Small humeral length
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
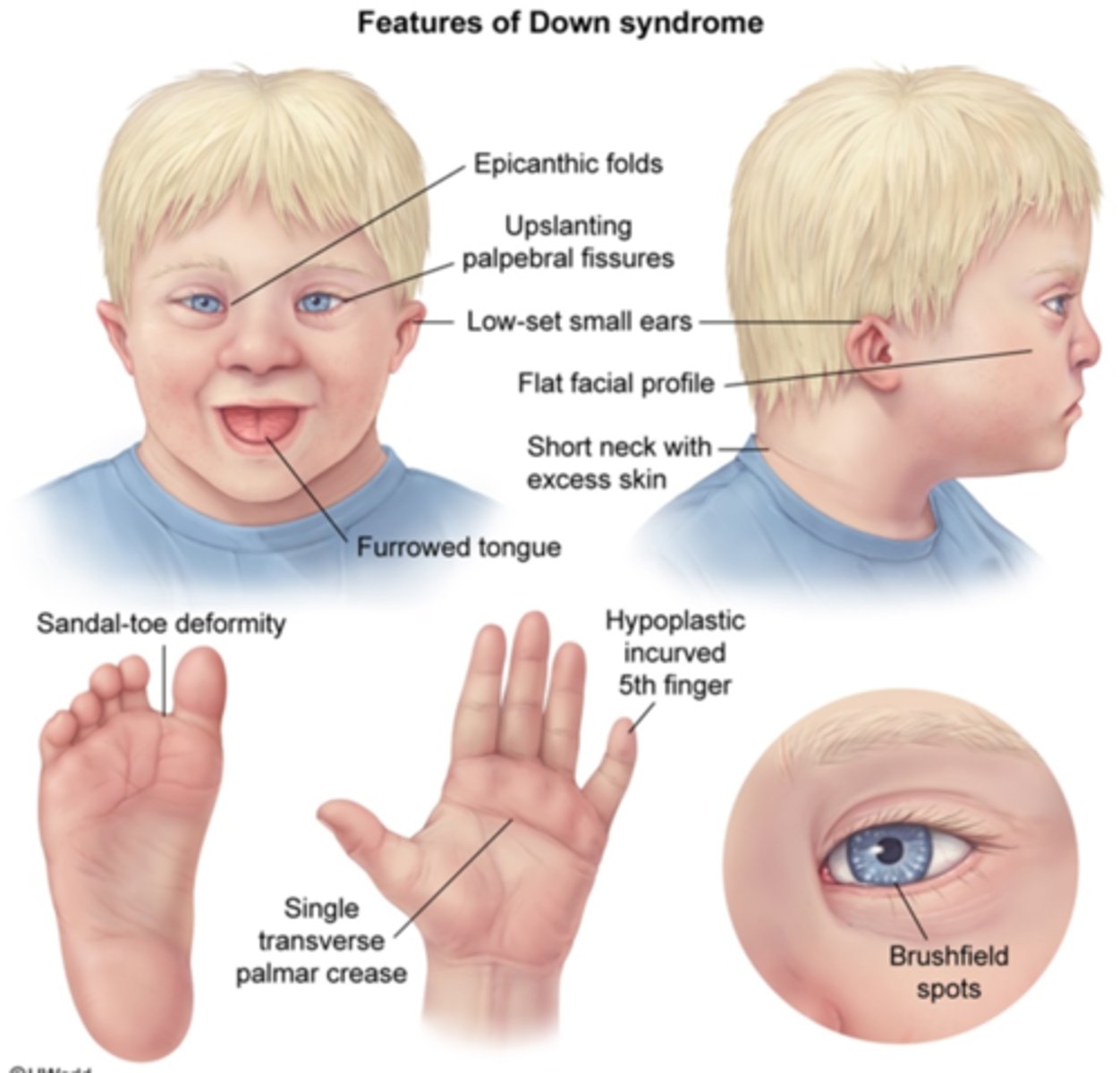
List some of the sonographic findings associated with down syndrome (trisomy 21).
-Subtle anomalies
-Atrioventricular defect
-Ventricular septal defect
-Nuchal thickening
-Small or absent nasal bone
-Macroglossia
-Mild ventriculomegaly
-Duodenal atresia
-Pyelectasis
-Hyperechoic bowel
-Nonimmune hydrops
-Sandal toe deformity
-Clinodactyly
-Low-set ears
-Shortened limbs
-Femur length below the 10th percentile for gestational age
-Small humeral length
What are 2 differential considerations for Edward syndrome?
Trisomy 13
Triploidy
Which trisomy is associated with low set ears?
Trisomy 21
What is the differential consideration for down syndrome/trisomy 21
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
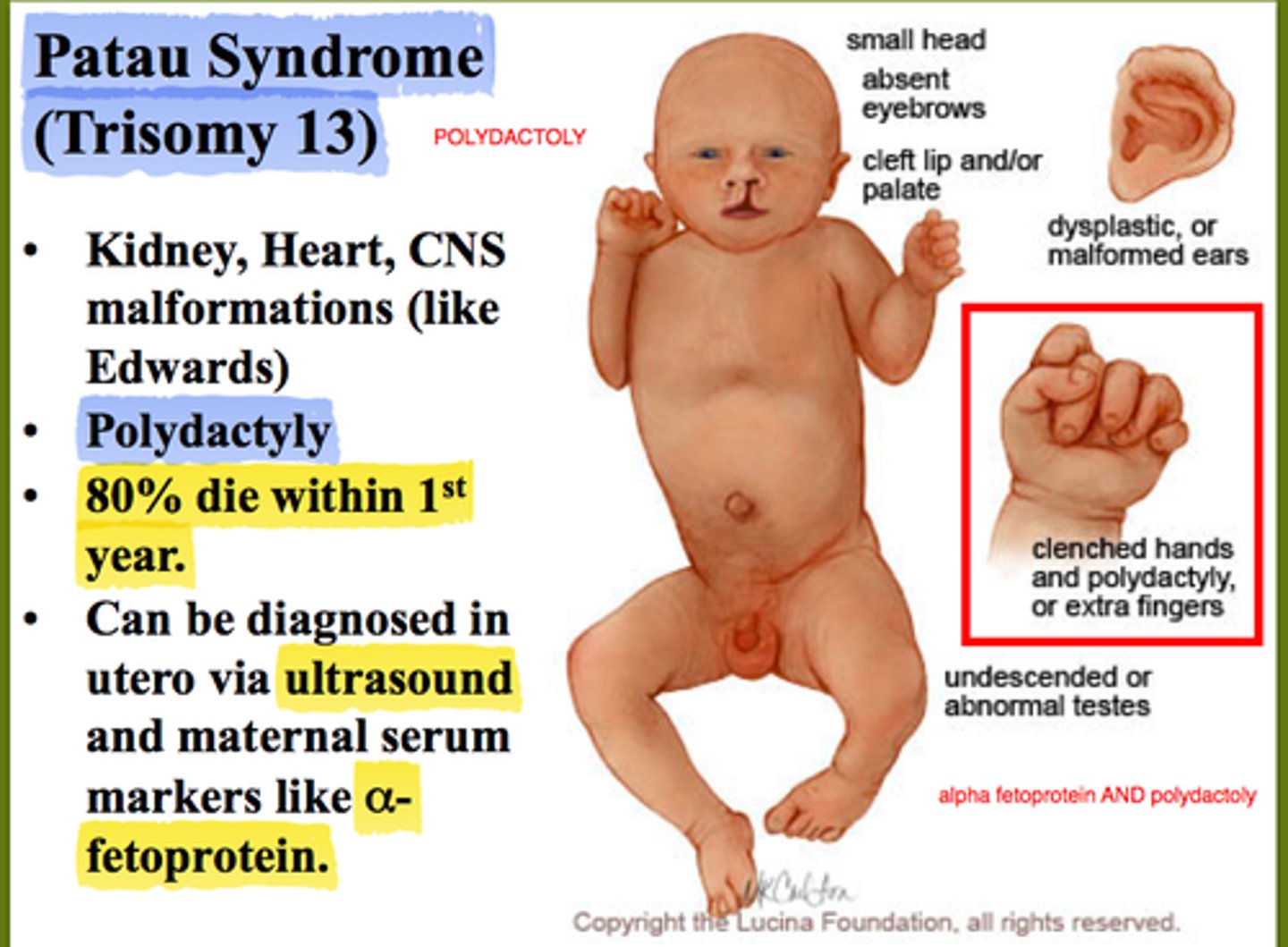
What is another name for Patau syndrome?
Trisomy 13 (extra 13th chromosome)
Which autosomal trisomy is the least common but the most severe?
Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
Which trisomy is the "syndrome of midline defects"?
13 - Patau syndrome
What is the prognosis for Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)?
Poor prognosis
90% of trisomy ____ cases display cardiac defects.
13
Trisomy 13 is associated with multiple anomalies, many involving the _____.
Brain
Patau syndrome/trisomy 13:
-90% of cases display _____ defects
-Syndrome of _____ defects
-Overall _____ prognosis
-Multiple anomalies, many involving the _____
90% display cardiac defects
Syndrome of midline defects
Overall poor prognosis
Many anomalies involving the brain
The following sonographic findings are associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
-Holoprosencephaly
-Microcephaly
-Cystic hygroma
-Absent or small eyes
-Facial clefts
-Cardiac defects
-Omphalocele
-Echogenic kidneys
-Diaphragmatic hernia
-Clubfoot
-Polydactyly
-IUGR
-Polyhydramnios
-Cutis aplsaia (protrusions of scalp)
Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
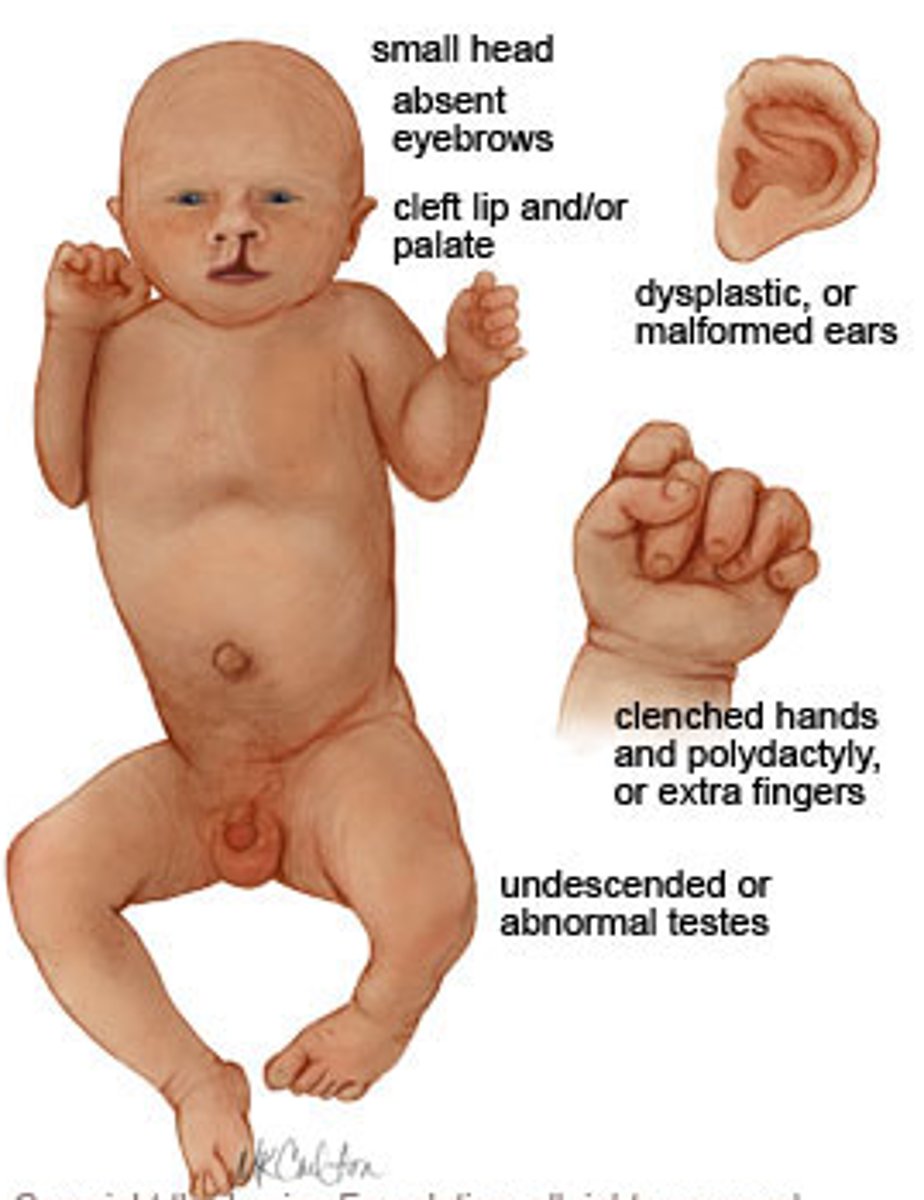
List some of the sonographic findings associated with trisomy 13.
-Holoprosencephaly
-Microcephaly
-Cystic hygroma
-Absent or small eyes
-Facial clefts
-Cardiac defects
-Omphalocele
-Echogenic kidneys
-Diaphragmatic hernia
-Clubfoot
-Polydactyly
-IUGR
-Polyhydramnios
-Cutis aplsaia (protrusions of scalp)
Which trisomy is associated with holoprosencephaly?
13
What is the differential consideration for Patau syndrome/trisomy 13?
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
What is the term for three complete sets of chromosomes?
Triploidy (69 chromosomes)
69 XXY or 69 XXX
True or false:
Most triploidy cases will abort spontaneously.
TRUE
The following sonographic findings are associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
-Early onset IUGR
-Holoprosencephaly
-Hypertelorism
-Micrognathia
-Microphthalmia
-Ventriculomegaly
-Oligohydramnios
-Two-vessel cord
-Cardiac abnormalities
-Clubfeet
-Syndactyly
Triploidy
What are the differential considerations for triploidy? (2)
Trisomy 13
Trisomy 18
True or false:
Maternal age has no influence on the trisomies (13, 18, 21)
FALSE
Increased maternal age increases risk for trisomies.
Which syndrome is classically characterised by the absence of one X chromosome copy (45 XO), with the missing chromosome most frequently (two-thirds) being the paternal one? Most cases occur as a sporadic event.
Turner syndrome
However, the classic genetic change is not present in all cases. Three main subtypes include:
1) complete monosomy (45XO): ~60%
2) partial monosomy (structurally-altered X chromosome): ~15%
3) mosaicism (XO and another sex karyotype): ~30%
Is the missing chromosome in Turner Syndrome most frequently maternal or paternal?
Paternal
What gender is a fetus with turner syndrome?
Female
How many chromosomes does a fetus with Turner syndrome have?
45 chromosomes, including a single X chromosome
Is AFP affected with Turner syndrome?
Yes - Elevated AFP levels
The following sonographic findings are associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
-Cystic hygroma
-Cardiac defects
-Renal anomalies
-Cubitus valgus
-Short femurs
-Nonimmune hydrops
Turner syndrome
Fetal syndromes:
-Demonstrate normal karyotype
-______ refers to a defect of an organ that results from an intrinsically abnormal development process
-______ refers to an abnormal form, shape, or position of a part caused by mechanical forces antenatally
-______ is a defect of an organ resulting from the breakdown of previously normal tissue
-______ refers to a pattern of multiple anomalies that result from a single anomaly or mechanical factor
-Malformation refers to a defect of an organ that results from an intrinsically abnormal development process
-Deformation refers to an abnormal form, shape, or position of a part caused by mechanical forces antenatally
-Disruption is a defect of an organ resulting from the breakdown of previously normal tissue
-Sequence refers to a pattern of multiple anomalies that result from a single anomaly or mechanical factor
The following info describes which fetal syndrome?
-Ruptured amnion sticks and entangles fetal parts
-Associated with fetal abnormalities and amputations
Amniotic band syndrome
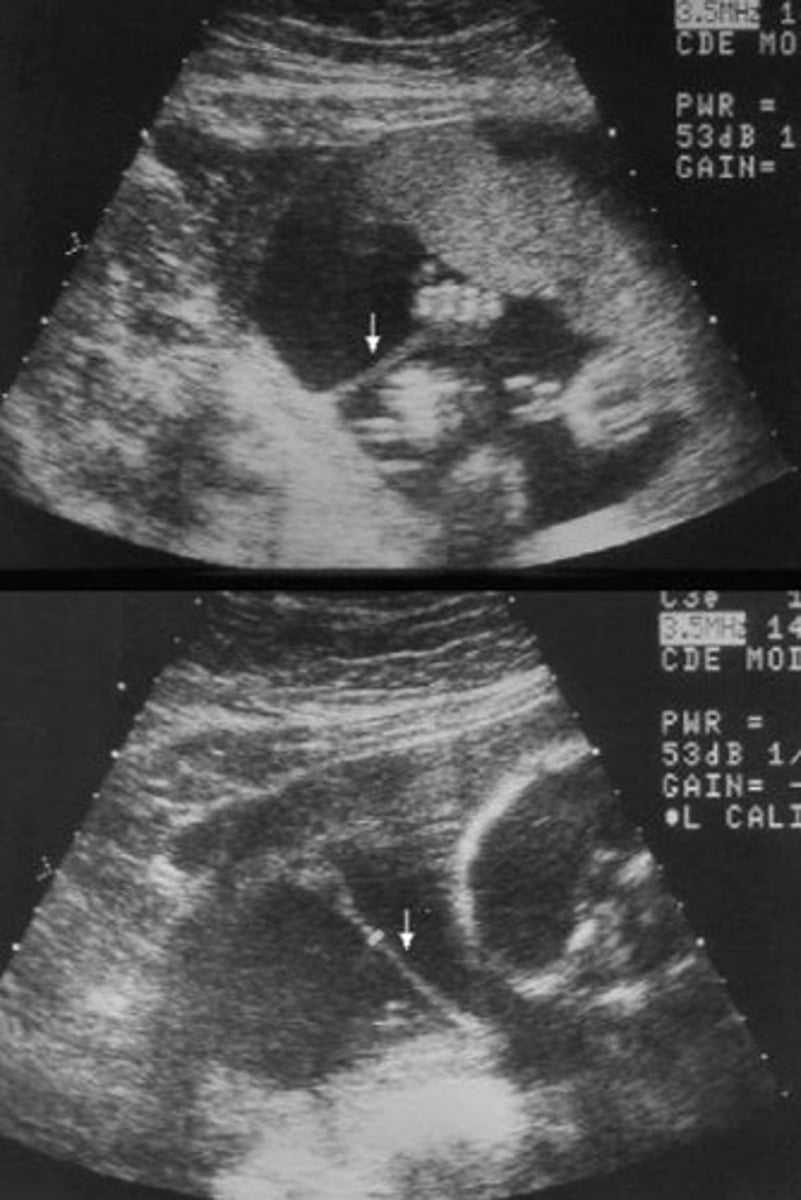
The following sonographic findings describe which fetal syndrome?
-Thin hyperechoic linear structure floating within the amniotic cavity
-Fetal abnormalities
Amniotic band syndrome
What are the differential considerations for amniotic band syndrome? (4)
-Synechia
-Amniotic chorionic separation
-Limb-body wall complex
-Placental shelf
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome is an _____ syndrome with alteration in chromosome _____.
Overgrowth
Chromosome 11
What is the classic triad seen with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
1) Macrosomia (large fetus)
2) Omphalocele
3) Macroglossia
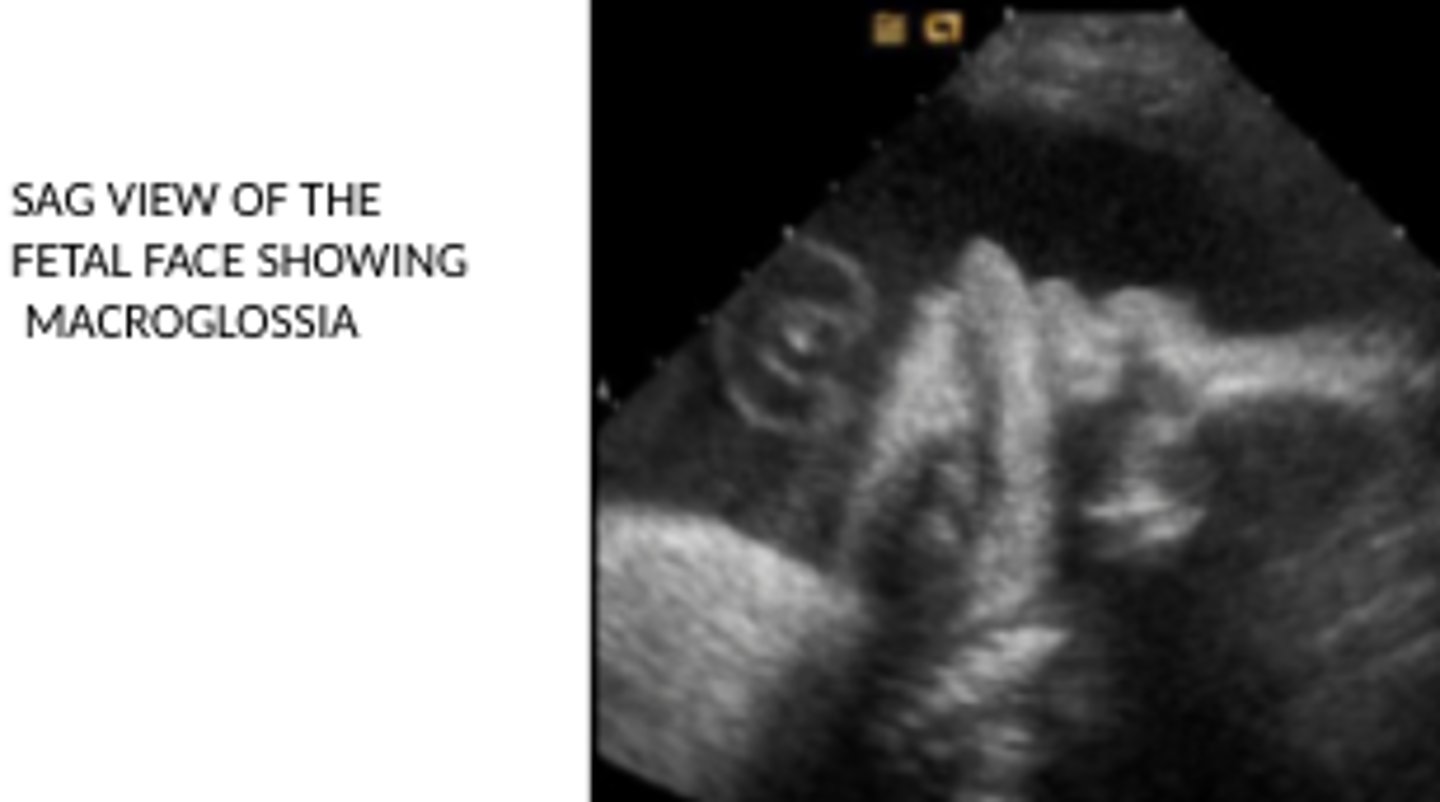
The following triad is often seen with which fetal syndrome?
1) Macrosomia (large fetus)
2) Omphalocele
3) Macroglossia
Beckwith-Wiedemann
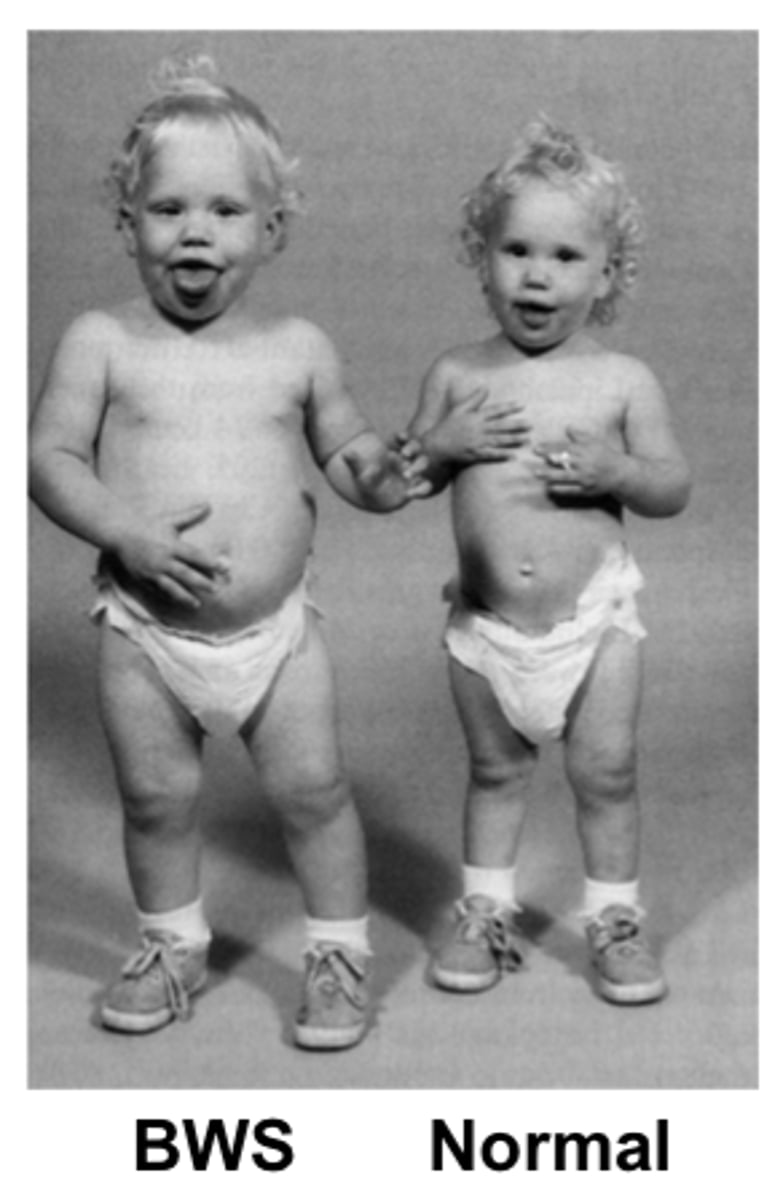
The following information describes which fetal syndrome?
-Normal karyotype
-Increases risk of developing Wilm's tumor, hemihypertrophy, renal anomalies, and hepatosplenomegaly
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
The following sonographic findings are associated with which fetal syndrome?
-Hemihypertrophy
-Macroglossia
-Omphalocele
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
What are 3 Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome sonographic findings?
Hemihypertrophy
Macroglossia
Omphalocele
What is the differential consideration for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
Down syndrome
What is another name for Eagle-Barrett syndrome?
Prune belly syndrome
The following info describes which fetal syndrome?
-Hypotonic abdominal wall muscles
-Associated with dilated fetal bladder, small thorax, and imperforate anus
Prune Belly/Eagle-Barrett syndrome
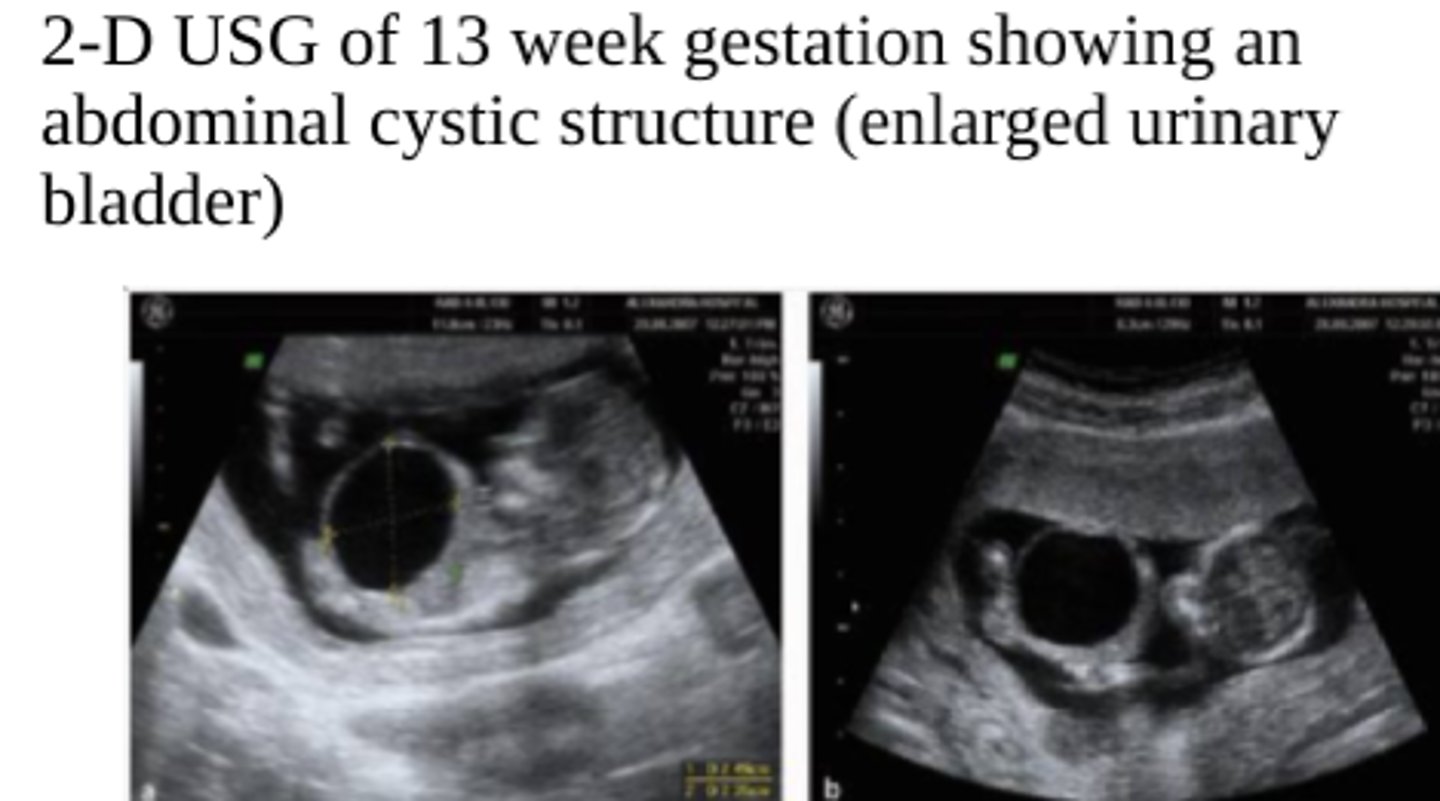
What is another name for Prune Belly Syndrome?
Eagle-Barrett syndrome
The following sonographic findings are associated with which fetal syndrome?
-Hydronephrosis
-Megaureter
-Oligohydramnios
-Small thorax
-Large abdomen
-Cryptorchidism
-Hip dislocation
-Scoliosis
Eagle-Barrett / Prune Belly
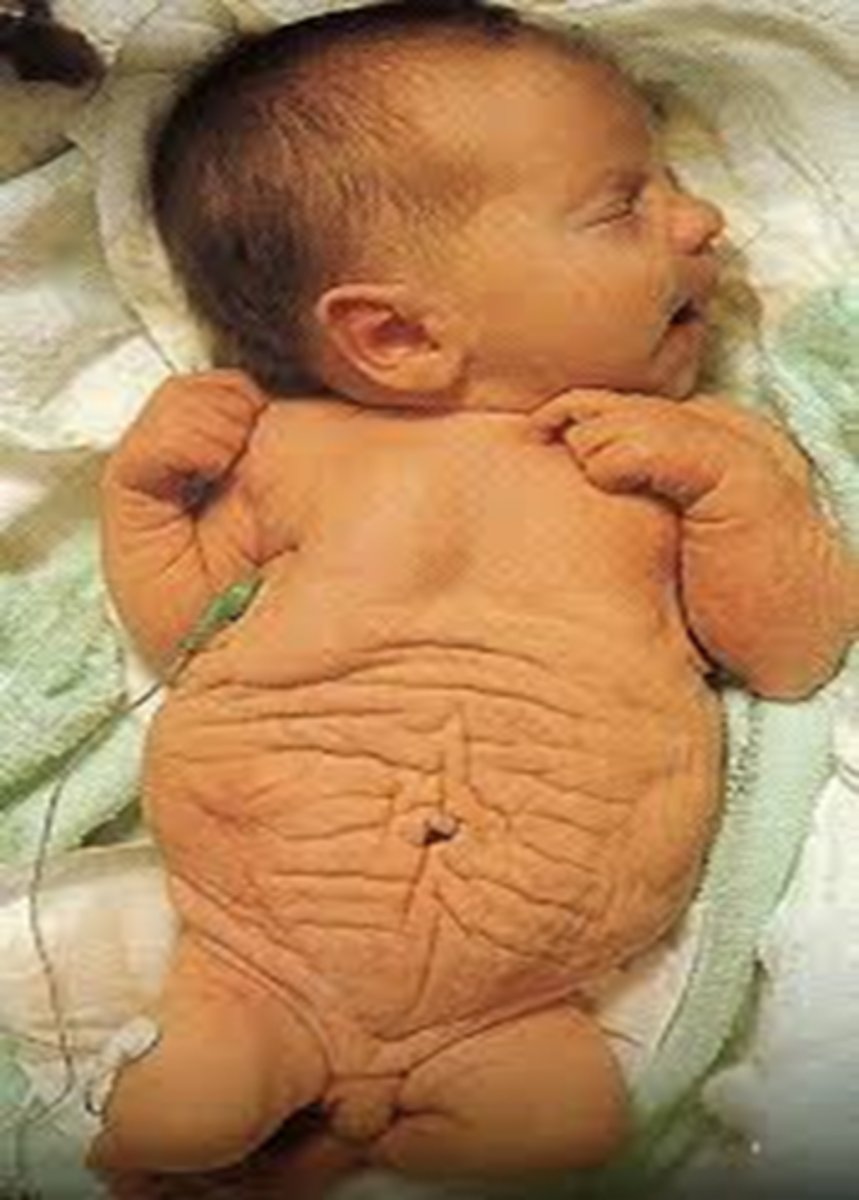
What is the triad associated with prune belly syndrome?
1) Abdominal wall defects
2) Urinary tract dilatation secondary to urethral obstruction
3) Cryptorchidism
Does prune belly syndrome occur predominately in males or females?
Males
The following info describes which fetal syndrome?
-Rare complex malformation caused by the failure of the closure of the ventral body wall
Two or more of the following:
-Limb defects
-Lateral wall defects (esp. left)
-Encephalocele
-Exencephaly
-Facial defects
-Scoliosis
Limb-body wall complex
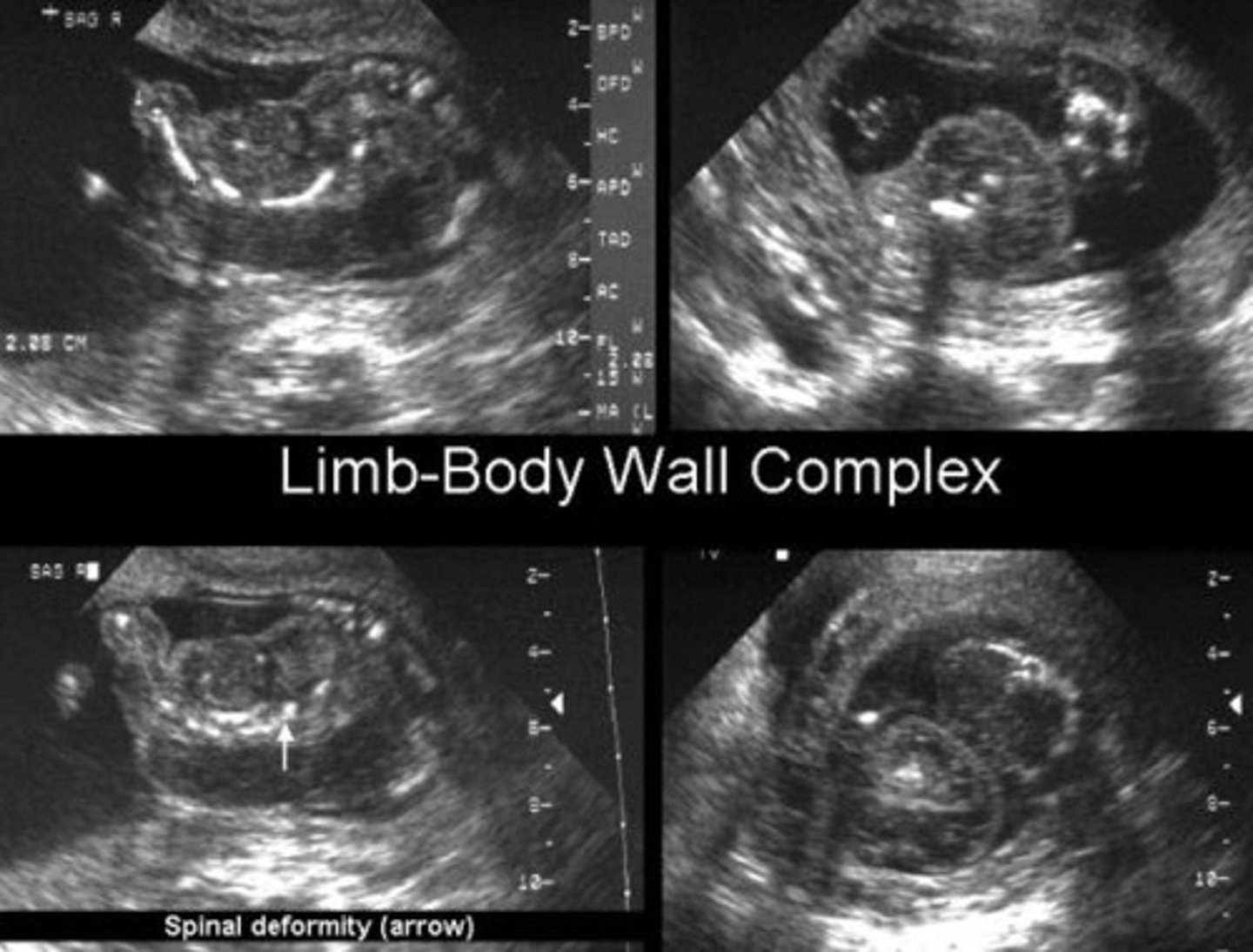
The following sonographic findings are associated with which fetal syndrome?
-Ventral wall defect
-Cranial anomalies
-Marked scoliosis
-Limb defects
-Short umbilical cord
-AMniotic bands
Limb-body wall complex
What are the differential considerations for limb-body wall complex (LBWC)? (2)
Amniotic band syndrome
Trisomy 13
True or false:
Meckel-Gruber syndrome is a non-lethal condition.
FALSE
It is lethal
Does Meckel-Gruber syndrome occur more in males or females?
Occurs equally in males and females
Is Meckel-Gruber syndrome autosomal dominant or recessive?
Recessive
The following sonographic findings describe which fetal syndrome?
-Encephalocele
-Infantile polycystic kidneys (b/l enlarged hyperechoic kidneys)
-Oligohydramnios
-Bladder not visualized
-Polydactyly
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
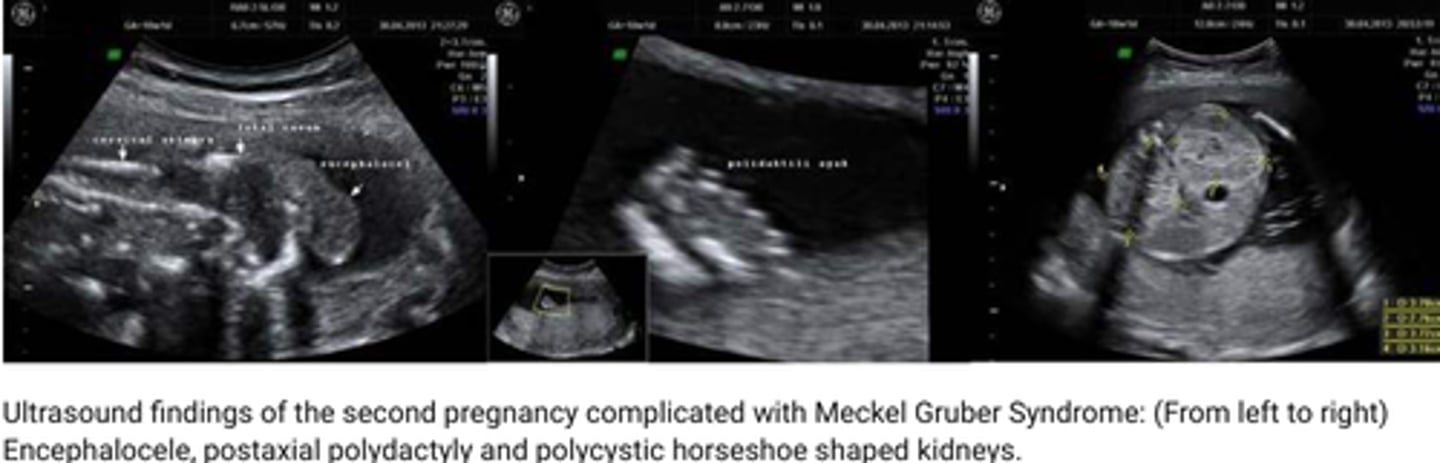
How is the fetal bladder and amniotic fluid level affected with Meckel-Gruber syndrome?
-Oligohydramnios
-Bladder not visualized
What are the differential considerations for Meckel-Gruber syndrome? (2)
Trisomy 13
Infantile polycystic disease
Pentalogy of Cantrell is a congenital disorder characterized by two out of five major defects. List the 5 major defects.
1. Cardiac defect
2. Abdominal wall defect
3.Diaphragmatic hernia
4. Defect of diaphragmatic pericardium
5. Ectopia cordis
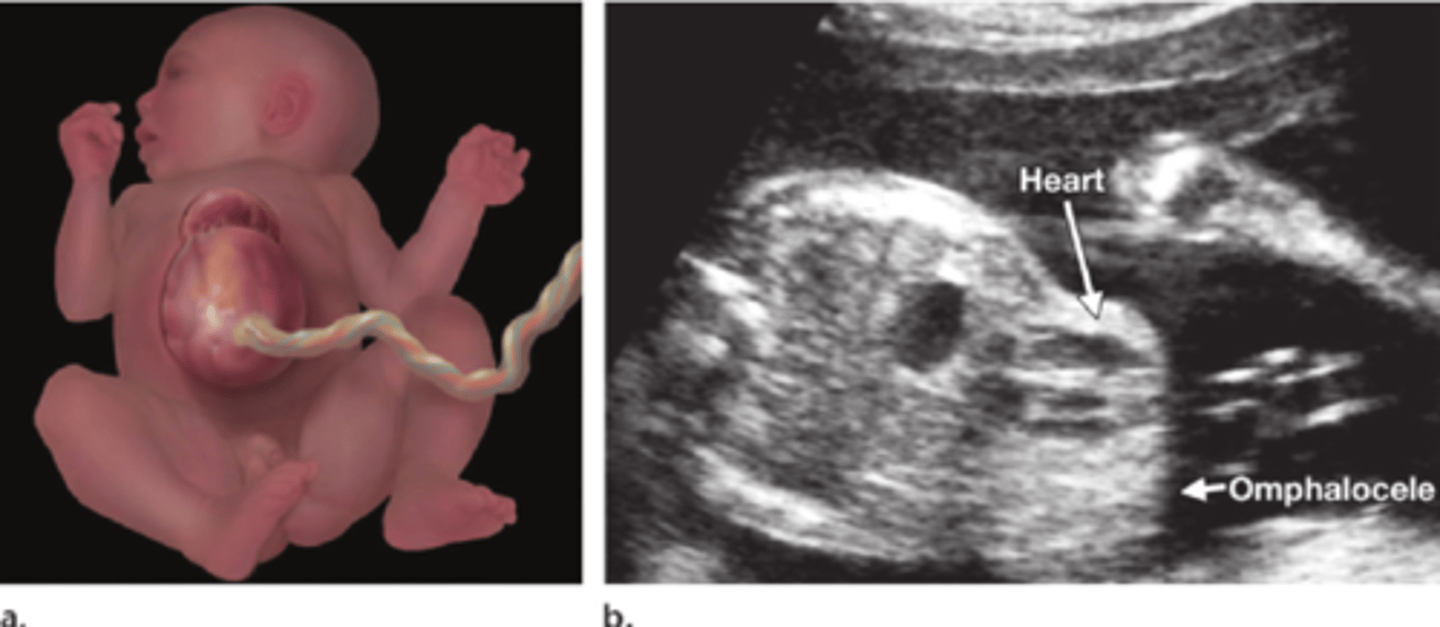
The following sonographic findings are seen with which fetal syndrome?
-Pulsating mass outside of the chest cavity
-Omphalocele
-Gastroschisis
-Diaphragmatic hernia
Pentalogy of Cantrell
What are the differential considerations for Pentalogy of Cantrell? (2)
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Acardiac twin
VACTERL is a group of complex anomalies.
It is associated with maternal _____ and _____ exposure.
Diabetes
Lead
What are the sonographic findings of VACTERL?
-Vertebral defects
-Anal atresia
-Cardiac anomalies
-Tracheoesophageal fistula
-Esophageal atresia
-Renal anomalies
-Limb anomalies
Other:
-Polyhydramnios
-Collapsed stomach
VATER is a group of complex anomalies.
Associated with maternal _____ and _____ exposure.
Diabetes
Lead
What are the sonographic findings of VATER?
-Vertebral defects
-Anal atresia
-Tracheo-Esophageal fistula
-Renal anomalies
Other:
-Polyhydramnios
-Collapsed stomach