alkene addition reaction (mostly) product prediction | Quizlet
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
X2 (Br2), H2O
halohydrin formation
X and OH added anti
(markovnikov: H2O attacks more substituted side of halonium ion intermed —> OH on more substituted C)
H2, Pd/Pt/Ni
hydrogenation (reduction)
H and H added syn
1. O3
2. Zn/H+/DMS
ozonolysis
aldehyde and/or ketone (cut double bond down the middle, put O on each double bond)
HX (HBr, HCl)
hydrohalogenation
H and X added
markovnikov: X to more substituted C
not stereoselective - mixture of syn and anti
H2O, acid (H+ etc)
acid-catalyzed hydration
H and OH added
markovnikov: OH to more substituted C
no regioselectivity —> mix of syn and anti
1. BH3
2. H2O2, -OH
hydroboration oxidation
H and OH added
anti-markovnikov: OH to less substituted C
X2
halogenation
X and X added anti (vicinal dihalide created)
OsO4/KMnO4 (osmonium __, potasium manganate), cold dilute -OH
dihydroxylation (mild oxidation)
OH and OH added syn
(w other reagents, can include formation of an epoxide ring, addition is anti)
SOCl2 (thionyl chloride)
R-Cl
substitutes an OH group with a Cl (SN2)
NaNH2 (sodium amide)
form alkynes (C-=C) (when u have 2 NaNH2, one for each bond)
can create triple bond from dihalides by stealing e- from both X's in a dihalide, eliminating the X's (E2)
deprotonate terminal alkynes
create acetylide anion
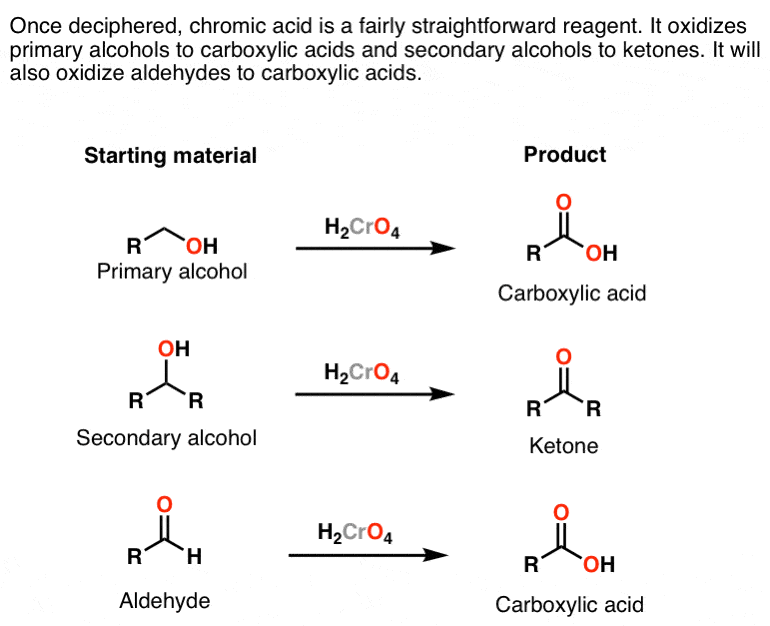
CrO3/H+ (H2CrO4)
chromic acid oxidation - oxidizes alcohols
primary alcohol —> carboxylic acid
secondary alcohol —> ketone
also oxidize aldehyde —> carboxylic acid
NaBH4 (sodium borohydride)
reduces aldehydes and ketones to alcohols (R-OH)
(splits the double bond to O, adds H to the O and to other single bond —> OH, H, R, R on the C)