Instrumental Analysis Exam 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
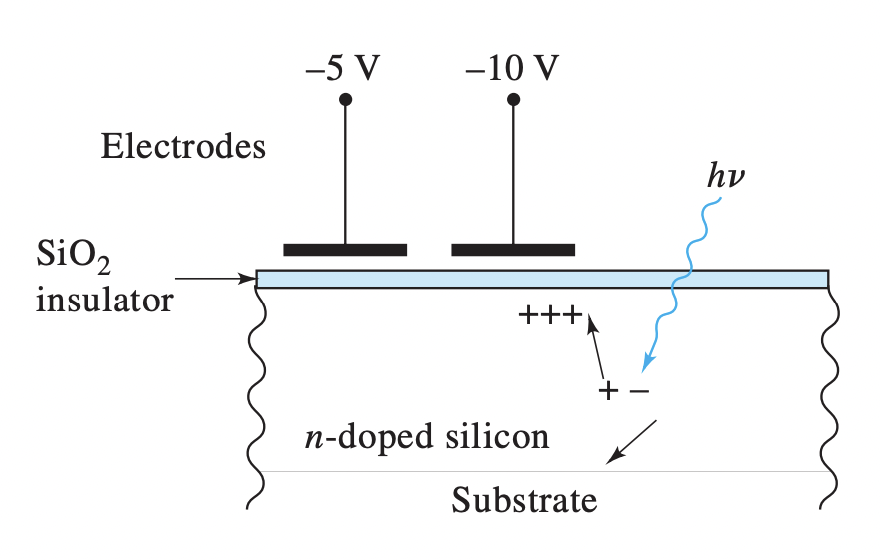
Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) - Diagram
(A) SiO2 insulators (B) Si electrode (C) Light (D) electrons stored beneath the positive electrode (E) Electron and hole generated by a photon (F) n-doped Si substrate
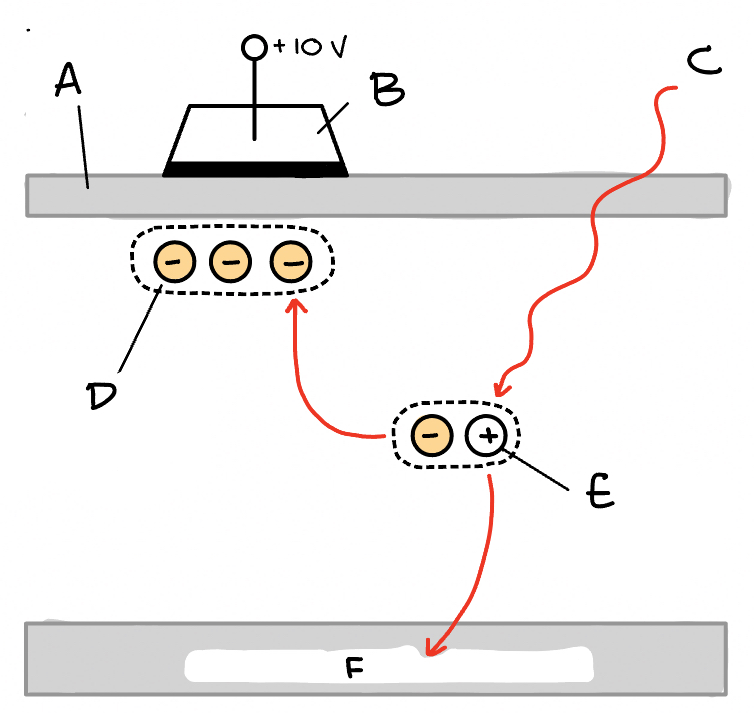
Charge-Injection Device (CID) - Diagram
(A) Charge formation and integration (B) Measure V1 (C) Measure V2 (D) Remove Charge (E) Substrate (F) n-type Si (G) SiO2 Insulator (H) Nondestructive readout mode (I) Destructive readout mode
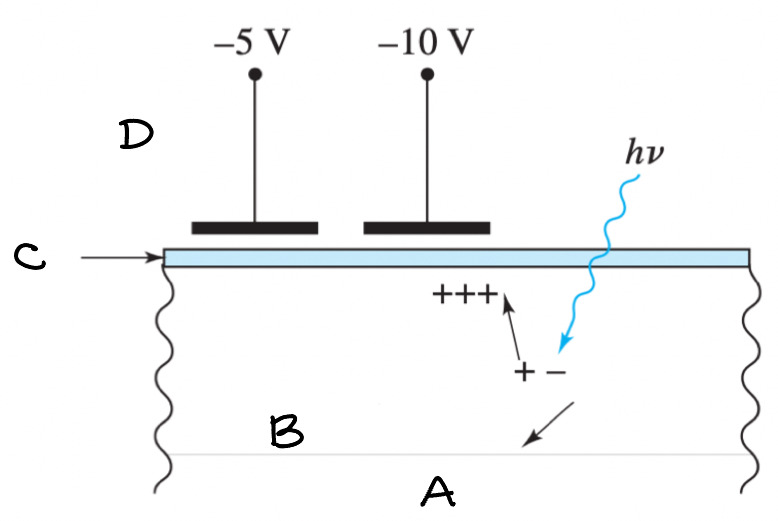
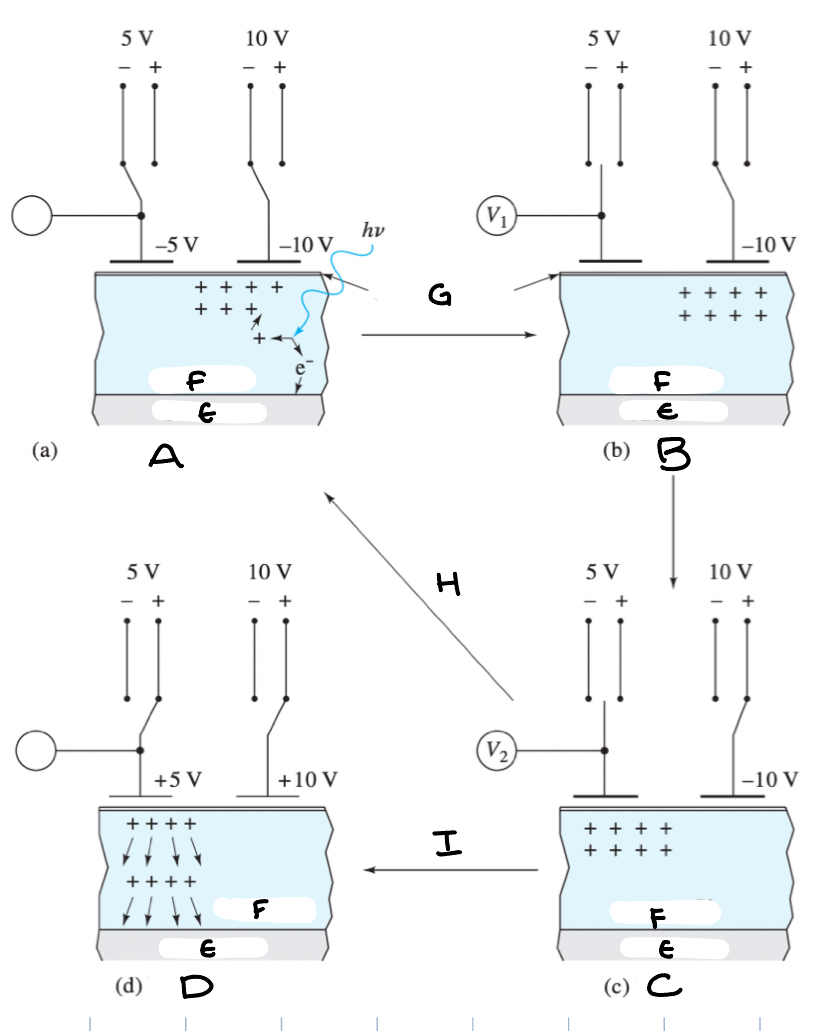
Charge Transfer Device - Diagram
(A) Substrate (B) n-doped silicon (C) SiO2 insulator (D) electrodes
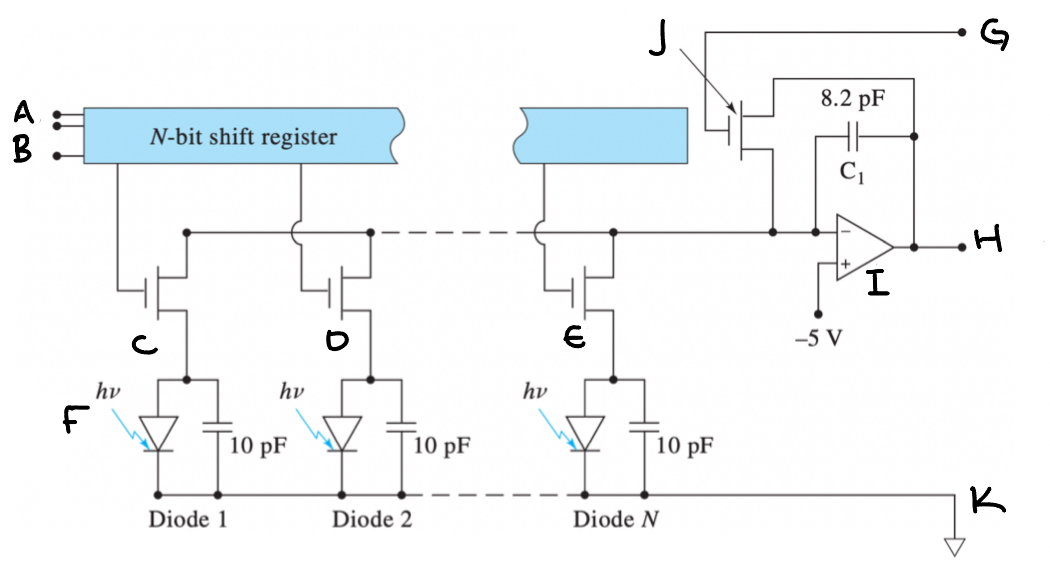
Photodiode-Array (PDA) - Diagram
(A) Clock (B) Start (C) Switch 1 (D) Switch 2 (E) Switch N (F) Photodiodes (G) Reset (H) Output (I) Integrator (J) Integrator reset Switch (K) Common
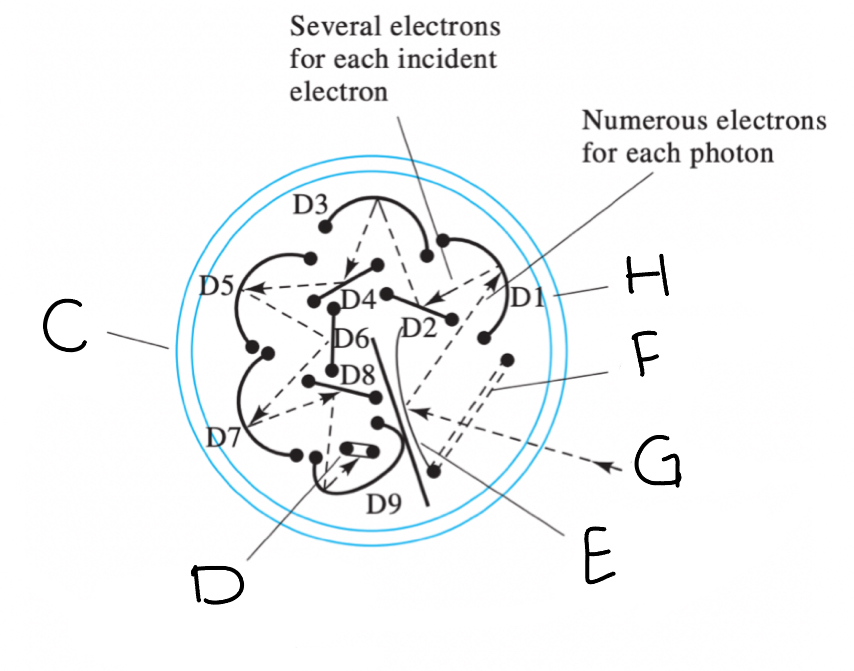
Photomultiplier Tube - Diagram
(C) Quartz envelope (D) Anode (E) Photoemissive cathode (F) Grill (G) Radiation (H) Dynodes
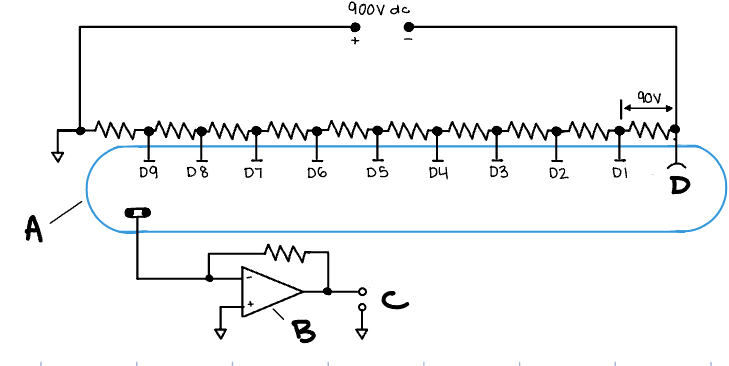
Photomultipler Tube Electrical Diagram
(A) Quartz envelope (B) Amplifier (C) To readout (D) Cathode
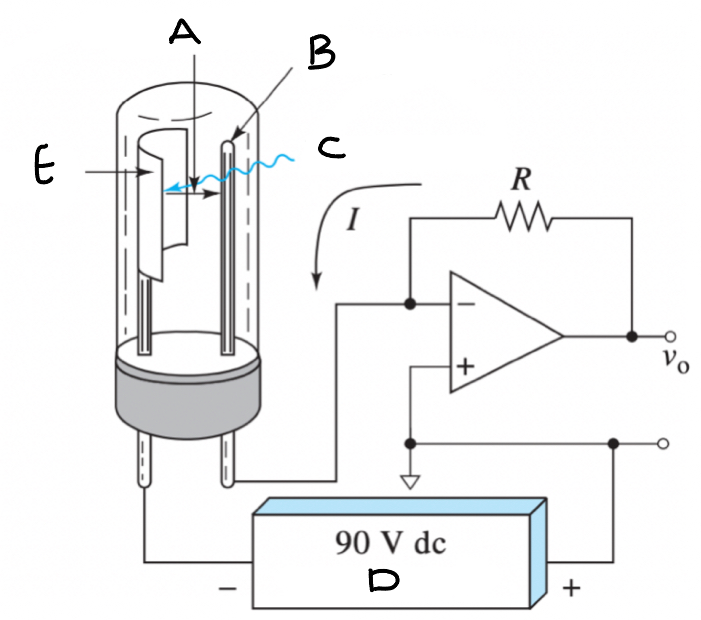
Phototube - Diagram
(A) Electrons (B) Wire anode (C) Photon Beam (D) power supply (E) Cathode
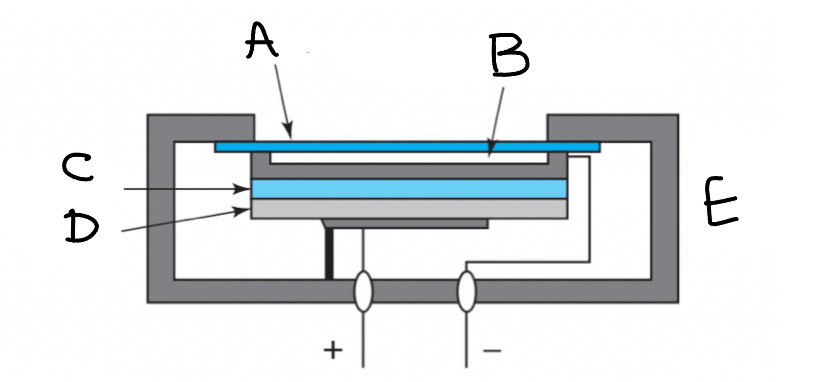
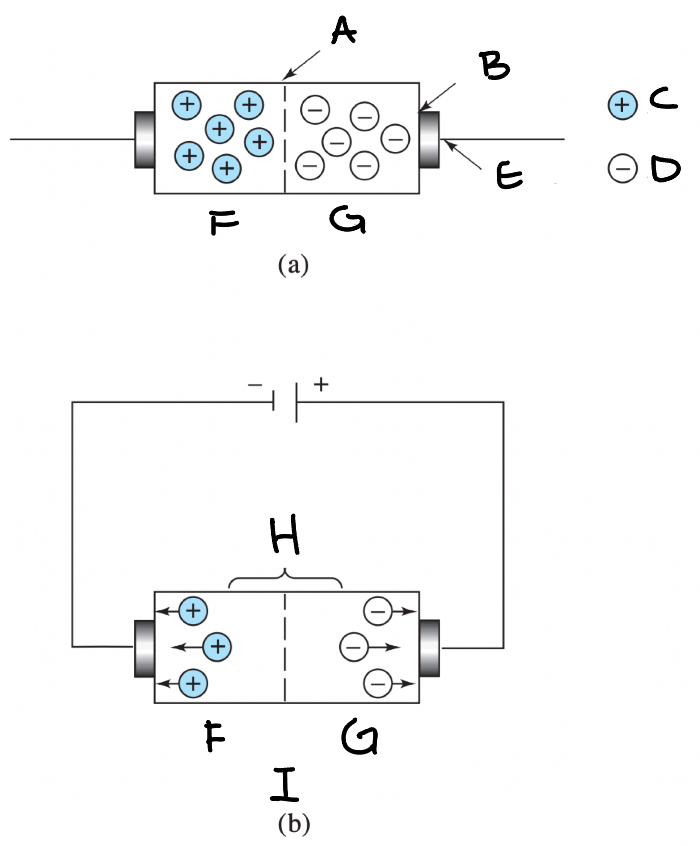
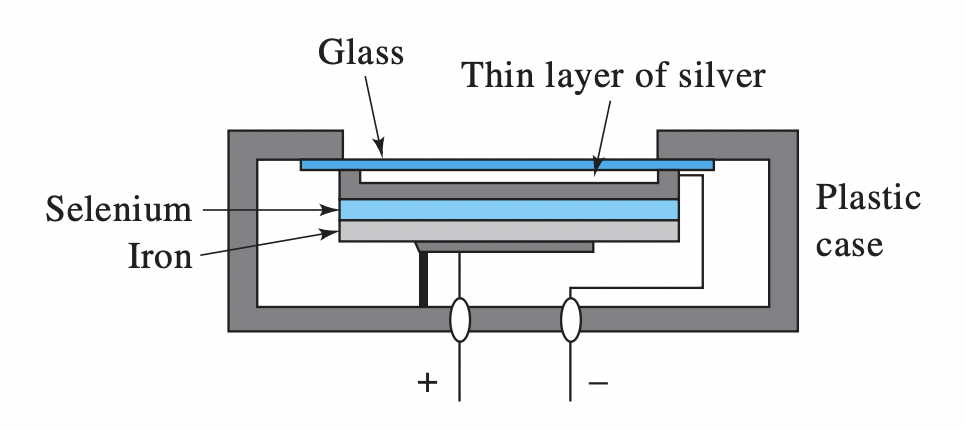
Photovoltaic Cell - Diagram
(A) Glass (B) thin layer of silver (C) Selenium (D) Iron (E) Plastic Case
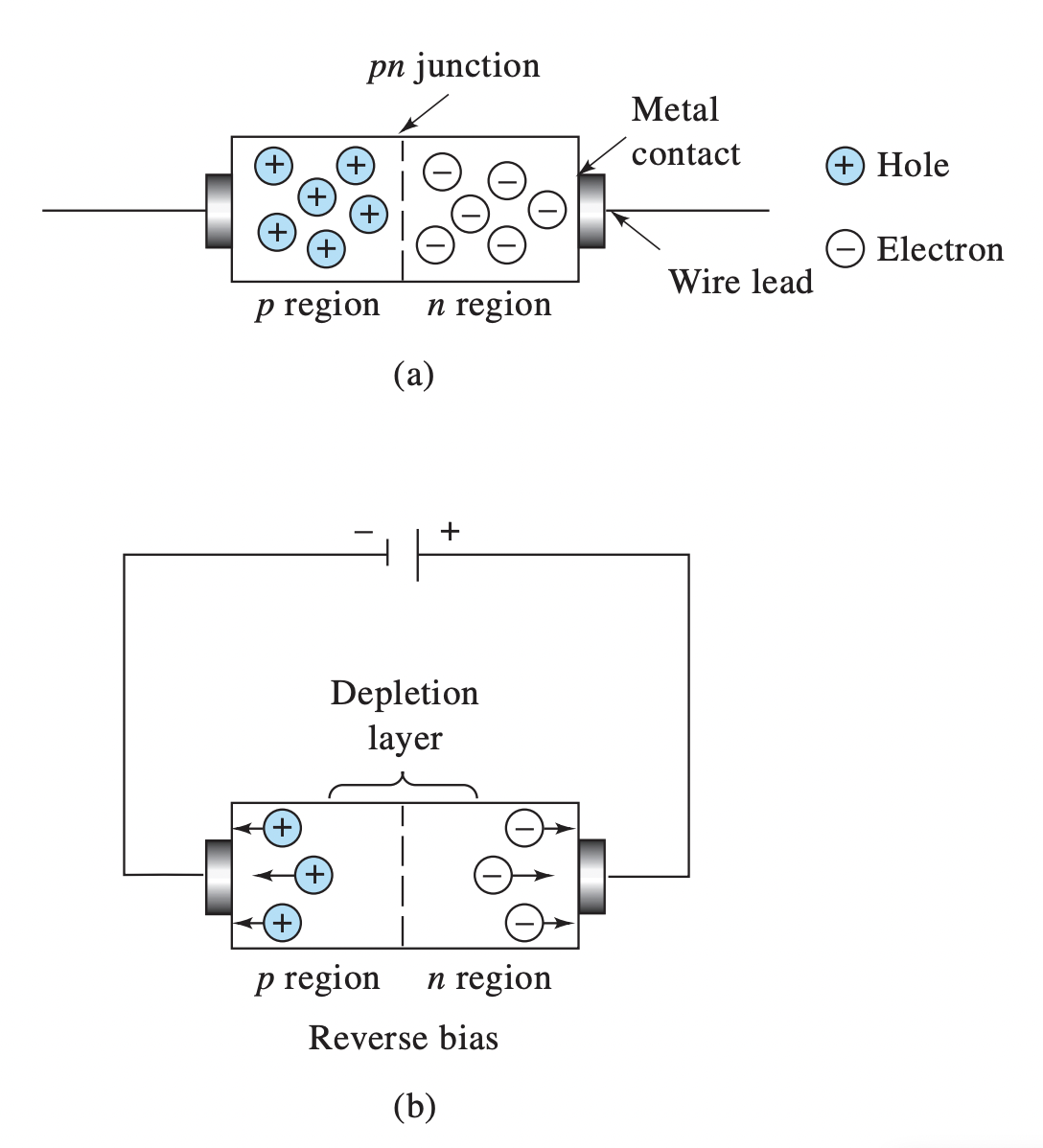
Silicon Diode - Diagram
(A) pn junction (B) Metal contact (C) Hole (D) Electron (E) Wire Lead (F) p region (G) n region (H) Depletion layer (I) Reverse bias
Photovoltaic Cell - Definition
radiant energy generates a current at the interface of a semiconductor layer and a metal
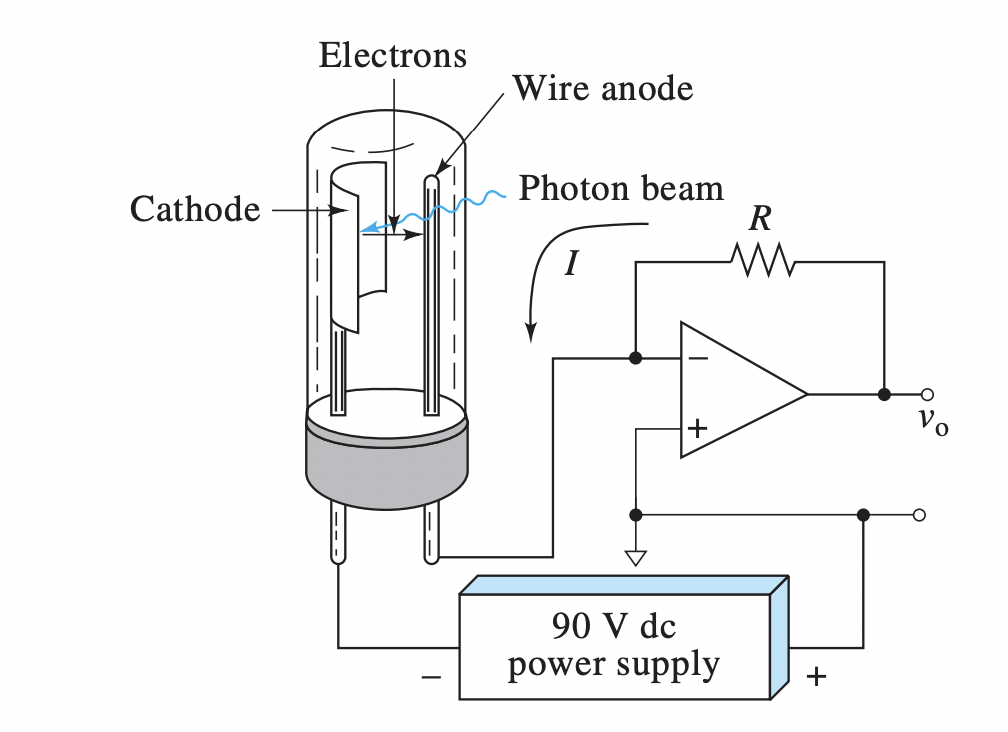
Phototubes - Definiton
radiation causes emission of electrons from a photosensitive solid surface
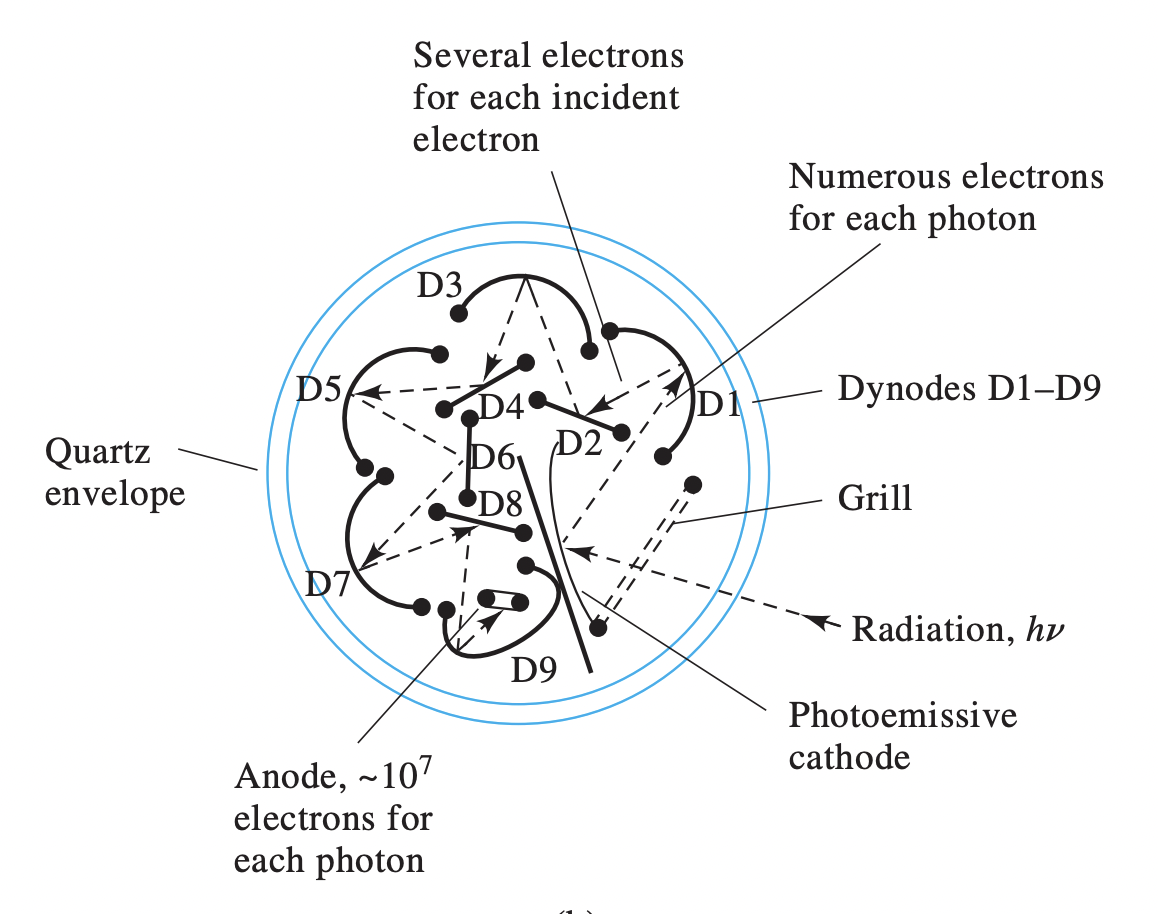
Photomultipler - Definition
Contains a photoemissive surface and several additional surfaces which emit a cascade of electrons when struck by electrons from the photosensitive area
Photoconductivity - Definition
transducers in which absorption of radiation by a semiconductor produces electrons and holes, thus leading to enhanced conductivity
Silicon photo diodes - Definition
photons cause the formation of electron and hole pairs and a current across a reverse biased pn-junction
Charge-transfer transducers - Definition
the charges developed in a silicon crustal as a result of absorption of photons are collected and measured
A number of cycles per unit time is called
frequency
Amperometry is based on what principle?
Electrical properties
Atomic absorption spectroscopy is based on what principle?
interaction with electromagnetic radiation
Capillary electrophoresis is based on what principle?
separation and resolution
Consider the use of photomultiplier tube measuring the intensity of a light source. In which type of domain is the transduced information?
analog
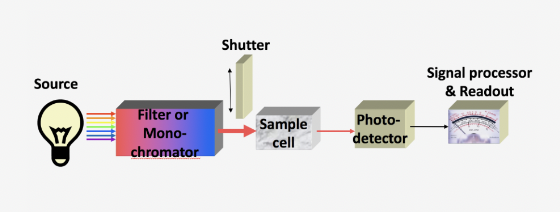
Consider this schematic of a ultraviolet-visible spectrometer, which measures light intensity at a particular wavelength. What purpose does the monochromator play?
information sorter
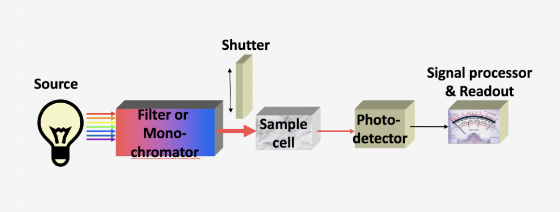
Which piece of the instrument serves as the input transducer?
photodetector
Which of the following represents an electrical data domain?
the readout of a pH meter
Which has a longer wavelength blue light or red light?
red
Again compare blue light and red light. Which has a higher frequency?
blue
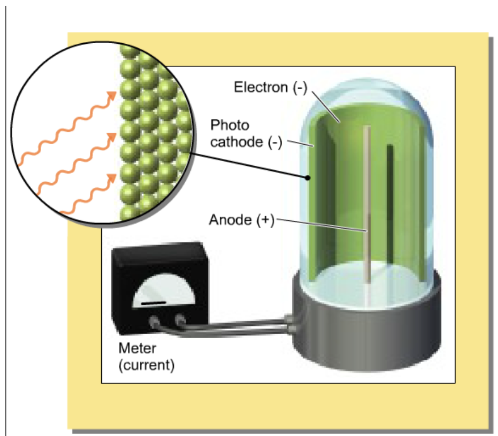
Which of the following describes the trend you see in the number of ejected electrons vs. frequency?
there is a certain frequency, above which electrons are ejected
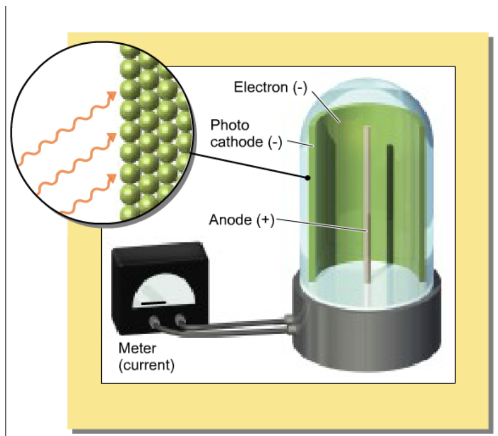
What is the effect of the light intensity if the light frequency is fairly low?
increasing intensity has no effect
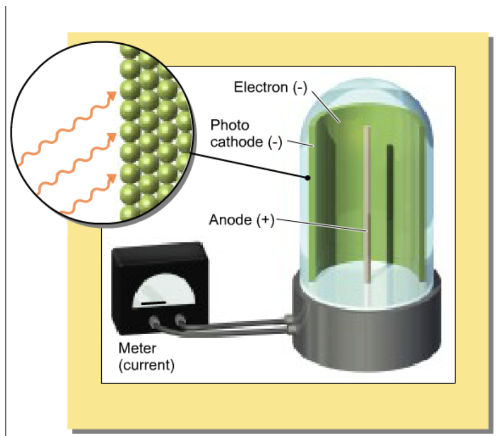
Now repeat the same experiment, but with the high frequency of light. What happens?
increasing intensity leads to more ejected electrons
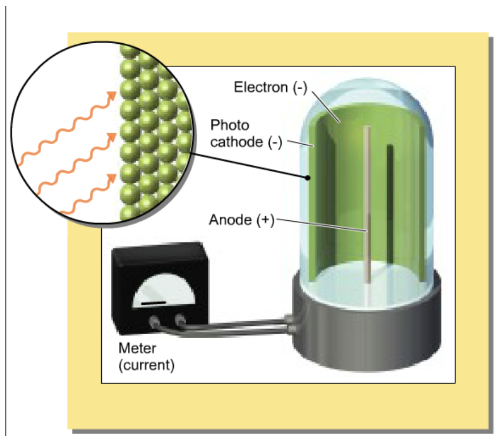
The energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency. The energy needed to remove an electron form the metal surface is equal to the energy of photons of a frequency equal to the cutoff frequency. When radiation of higher energy is used, what happens to the excess energy?
it increases the kinetic energy of the ejected electron
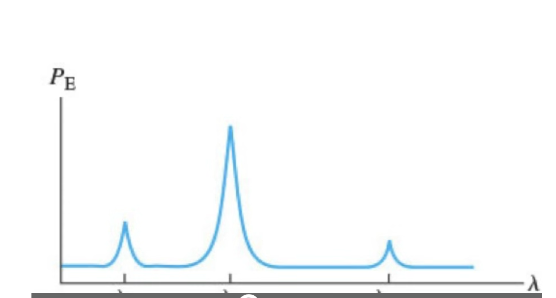
What electronic transition is responsible for the first peak (medium intensity, shortest wavelength)?
lambda 2
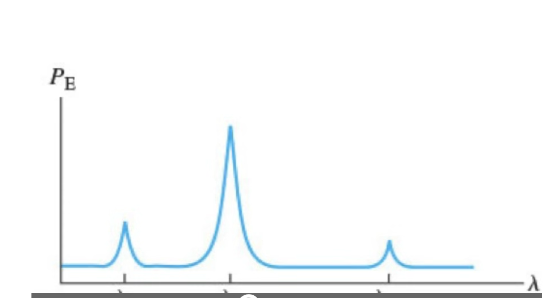
What electronic transition is responsible for the second peak (largest intensity, medium wavelength)?
lambda 1
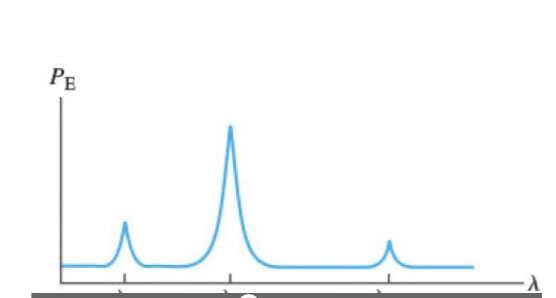
What electronic transition is responsible for the third peak (lowest intensity, longest wavelength)?
lambda 21
if a sample has an absorbance of 1.0, what percent of incoming radiation (P0) is the transmitted through the sample (P)?
10%
If a sample has an absorbance of 2.0, what percent of incoming radiation (P0) is transmitted through the sample (P)?
1%
If a sample has a transmittance (P/P0) of 0.25, what is the absorbance of the sample?
0.602
which of the following is a unique property of laser?
coherence
Which of the following is an example of optical pumping?
Ruby laser
Calculate the wavelength of radiation emitted by an LED made up of semiconducting material with a band gap energy of 2.8 eV.
4430.8 Å
what is the need to achieve population inversion?
to excite most of the atoms
Lasing species loses all or part of its excess energy in the form of fluorescence or phosphorescence radiation in the process called:
spontaneous emission
Voltage dividers are used to ___________.
produce a fixed fraction of the input
In a voltage divider, resistors are connected _____.
in series
In a voltage divider, all resistors _____.
Share the same current
In most modern monochromator (also known as wavelength selectors), reflection gratings are preferred over prisms. The disadvantage(s) of prisms compared to gratings include:
grating have a linear dispersion of light along a focal plane, while prisms do not disperse light lineraly along a focal plane
In general for qualitative analysis one uses _____ slit settings on a monochromator an for quantitative analysis one uses _______ split settings on a monochromator
narrower, wider
In what device an icident beam of photons causes production of electron-hole pairs which when separated produce a voltage related to the photon flux
photovoltaic cells
In what device photoelectrons are emitted as a result of photon bombardment and attracted to the positively charged anode to produce a small photocurrent proportional to the photon flux
phototube
What is the most sensitve photon transducer?
photomultiplier tube
What device does not require external power supplies?
photovoltaic cell
Basic, single-beam spectrophotometers like the Spectronic 20 use simple phototubes for detecting electromagnetic radiation in the visible range. These are useful as transducers because at saturation potential the current is ________ to the radiation power of light striking the cathode. At the same time, one must consider that such detectors have a measurable __________ that must be accounted for.
proportional, dark currrent
Charge transfer devices and photodiodes are often used in instruments where there is simultaneous detection of a range of wavelengths of light. For this type of detection, individual transducers are arranged in two-dimensional __________ which detect light after it has been separated by a polychromator.
arrary
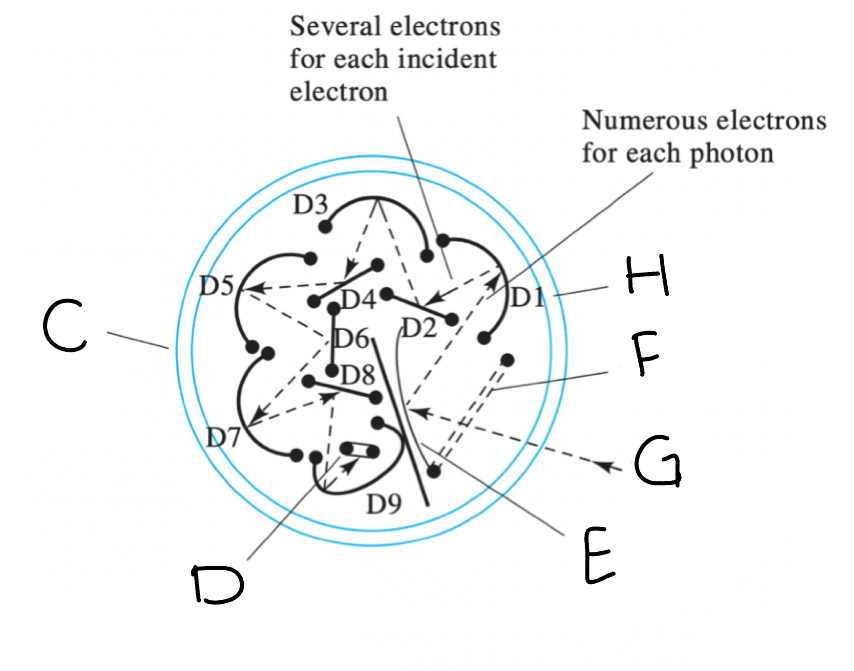
Referring to the diagram, identify the relevant components of a photomultiplier tube. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are among the most sensitive radiation transducers for ultraviolet and visible light. Light (G) entering a PMT first passes through a ________(F) before striking a photoemissive _________(E). The resulting photoelectrons (b) strike a series of ________ (H) before being collected at the _________(D). The entire PMT assembly is encased in a __________ (C) which is sealed and evacuated to allow the photoelectrons (B) and secondary electrons (A) to travel without interference.
(F) grill (E) cathode (H) dynodes (D) anodes (C) quartz envelope
What type of charge-storing device is used to record the radiant intensity of light that impinges upon photodiode array detectors?
capacitor