Carbonyls and carboxyls
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Shape around the carbonyl bond
Trigonal planar
What is the nature of the C-O double bond
It is polar with the oxygen being +ve, and it is a pi bond with p orbitals and a sigma bond
What is the reagant for reduction of aldehydes/ketones
NaBH4 and water
What does the reaction of a ketone with HCN produce
a hydroxynitrile
What is the mechanism in reduction of aldehydes/ketones
Nucleophilic addition
What is the nucleophile reduction of ketones/aldehydes
Hydride
Mechanism for HCN added to propanal
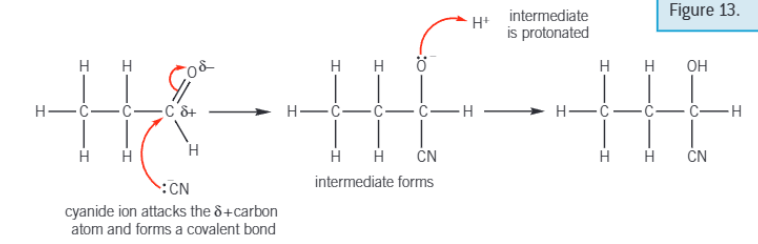
Test for carbonyls
Add 2,4-DNP and a yellow precipitate will form if an aldehyde or ketone are present, you can then filter the solid precipitate and recrystallise it to purify. Then find the melting point and compare this to a table of melting points to find what the original compound is
Test for aldehydes
Add tollens reagant, in the presence of aldehyde, the solution becomes a silver mirror
How soluble are carboxylic acids
Very soluble because they can form H bonds with water with the carbonyl bond and the O-H bond
How to test for carboxylic acids
Add to sodium carbonate, as this is the only organic molecule acidic enough to react with that weak base
How to name an ester
The alkyl chain added is the first word, for the second word remove the “-oic acid” and replace with “-oate”
How to name an acyl chloride
Remove the “oic acid” and replace with “oyl chloride”
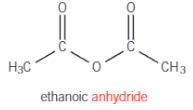
How to form acid anhydrides
Remove water from 2 carboxylic acids
Structure of ethanoic anhydride
Esterification reaction (including catalyst)
Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water (reversible with sulfuric acid catalyst)
What are esters used for
Perfumes and fragrances and flavourings
Why is esterification not a good method for synthesising esters
It is reversible so the yield will be low and does not work with phenol
Acid hydrolysis of an ester conditions
Heated under reflux with sulfuric acid
Acid hydrolysis of an ester reaction
ester + water → Carboxylic acid + alcohol (reversible with sulfuric acid catalyst)
Alkaline hydrolysis reaction
ester + water → Carboxylic acid + alcohol, then, carboxylic acid + alkali → water + salt
overall reaction: ester + alkali → salt + alcohol
Conditions of alkaline hydrolysis
Heated under refux with sulfuric acid
Reaction to make acyl chloride (and where should it be made)
Carboxylic acid + SOCl2 (thionyl chloride) → acyl chloride + sulfur dioxide + hydrogen chloride gas
Should be synthesised in a fume cupboard and in anhydrous conditions
Why would we use acyl chlorides to form esters instead of carboxylic acids
Reactions are not reversible and carboxylic acids could not react with phenol, also does not require a catalyst
Reaction of water and acyl chloride
acyl chloride + water → carboxylic acid + HCl. very vigorous and dangerous due to HCl fumes
Acyl chloride + ammonia → ?
Primary amide + ammonium chloride
Acyl chloride + primary amine
secondary amide + alkyl ammonium salt
Acid anhydride + alcohol → (catalyst?)
ester + carboxylic acid
(no catalyst)