L85b: microanatomy of large intestines
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
MCQ: what mucosal feature is common to both small and large intestines?
intestinal glands within the lamina propria
what do all segments of the large intestine lack?
villi
paneth cells
plicae circulares
what does the cecum have a substantial number of?
lymphatic nodules
where are lymph nodes concentrated in the cecum of pigs. ruminants, and dogs?
around the ileal ostium
where are lymphatic nodules concentrated in the cecum of horses and cats?
near the apex of the cecum
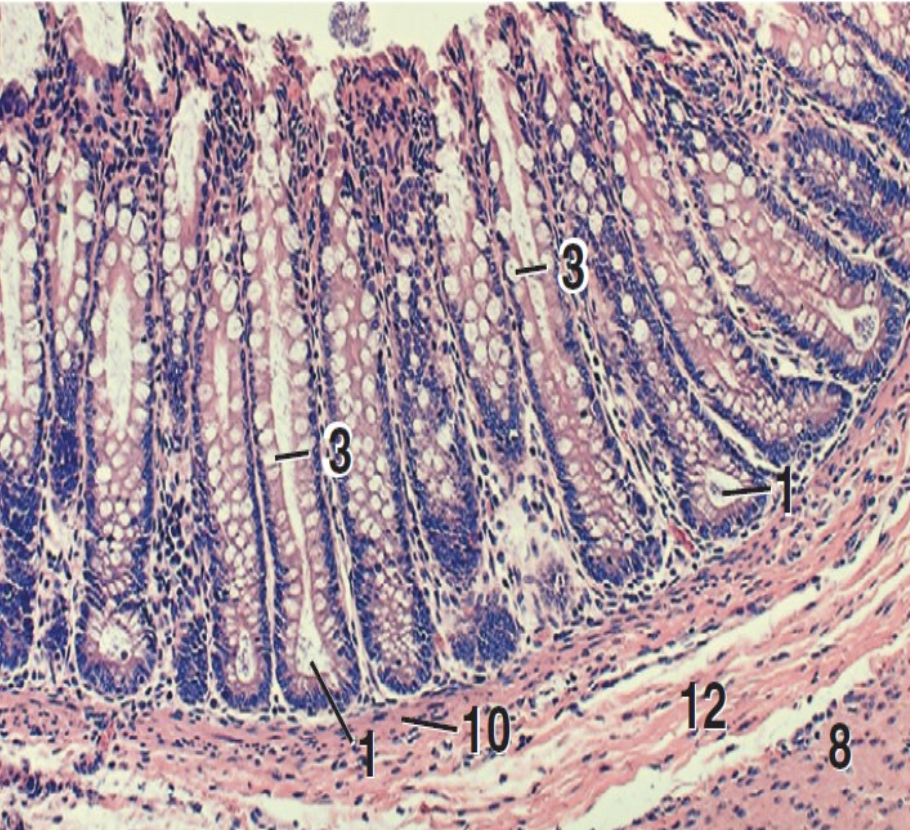
what is 1?
intestinal crypts
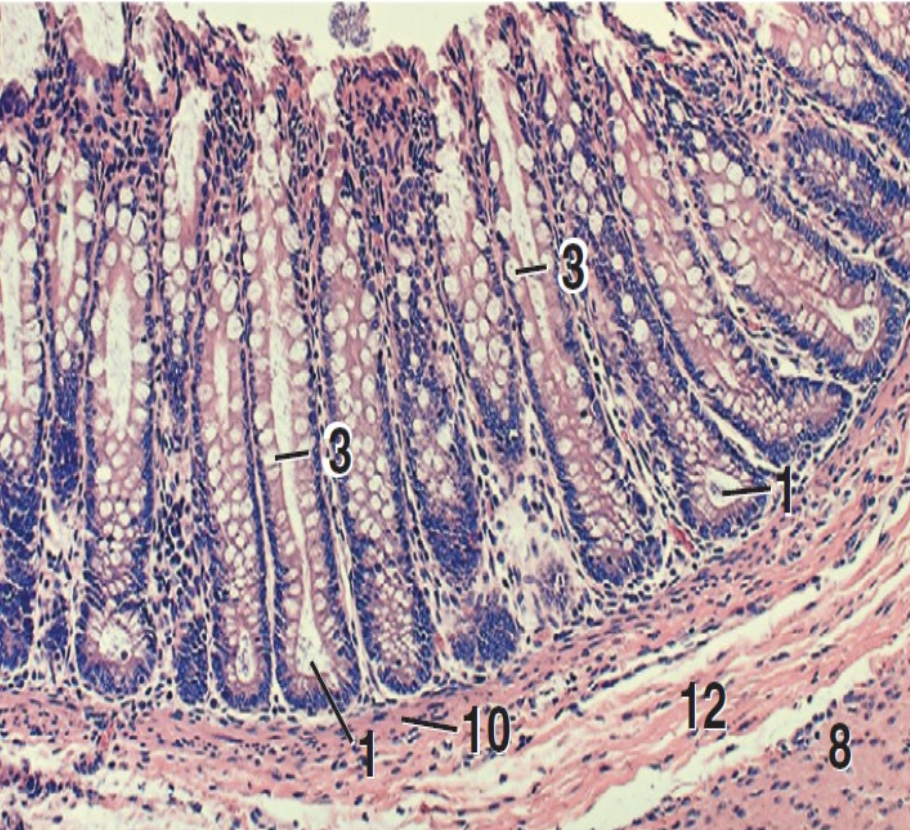
what is 3?
goblet cells
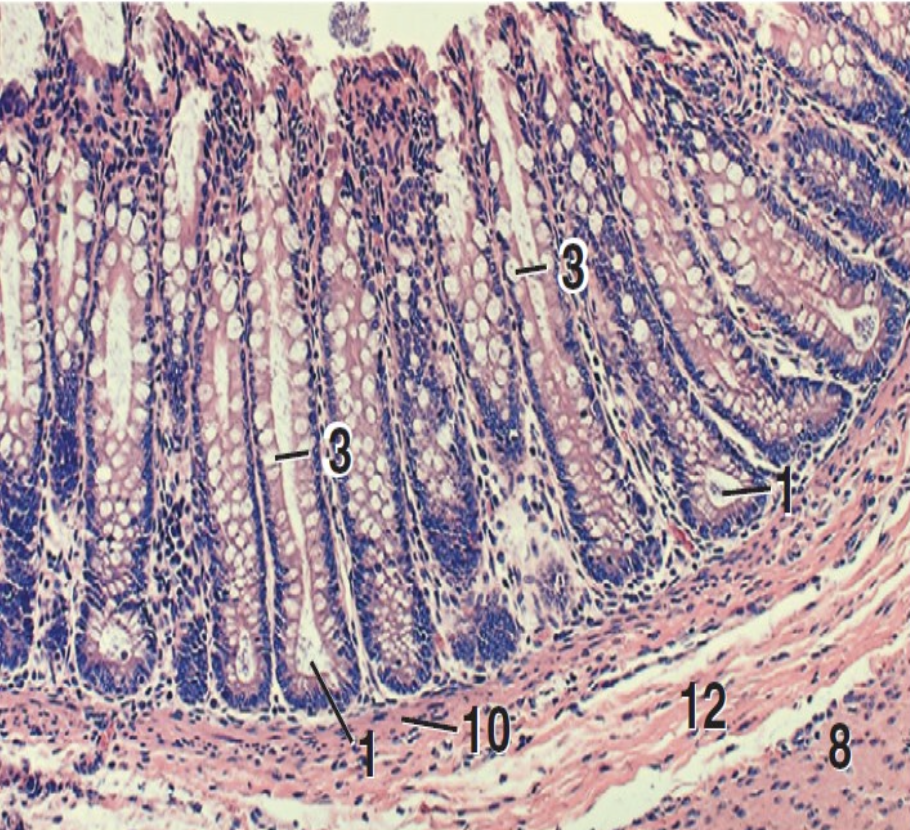
what is 8?
inner circular layer of tunica muscularis
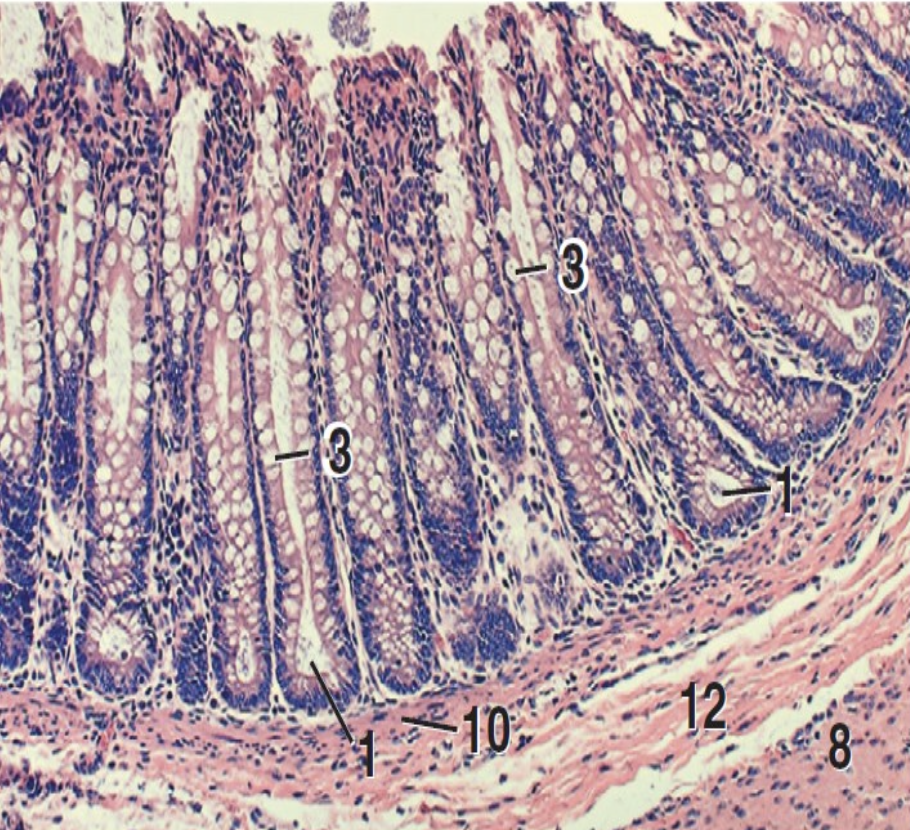
what is 10?
lamina muscularis
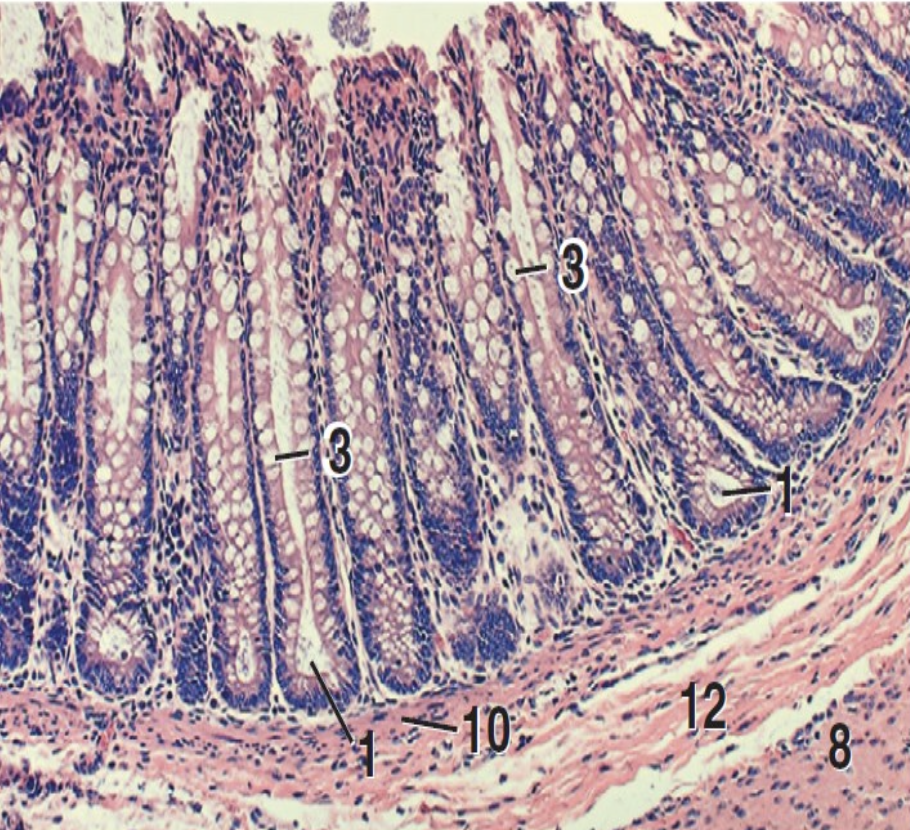
what is 12?
tunica submucosa
why is the mucosa of the colon thicker than that of the small intestine?
due to the increased length of the intestinal glands
what happens to the submucosa of the colon?
often distended by lymphatic tissue which disrupts the lamina muscularis and can extend gland into submucosa
what is unique about the colon in pigs and horses?
outer longitudinal layer of tunica muscularis of cecum and colon form taenia ceci and taenia coli
what does the cecum and ventral colon of the horse have more of?
more elastic fibers than smooth muscle
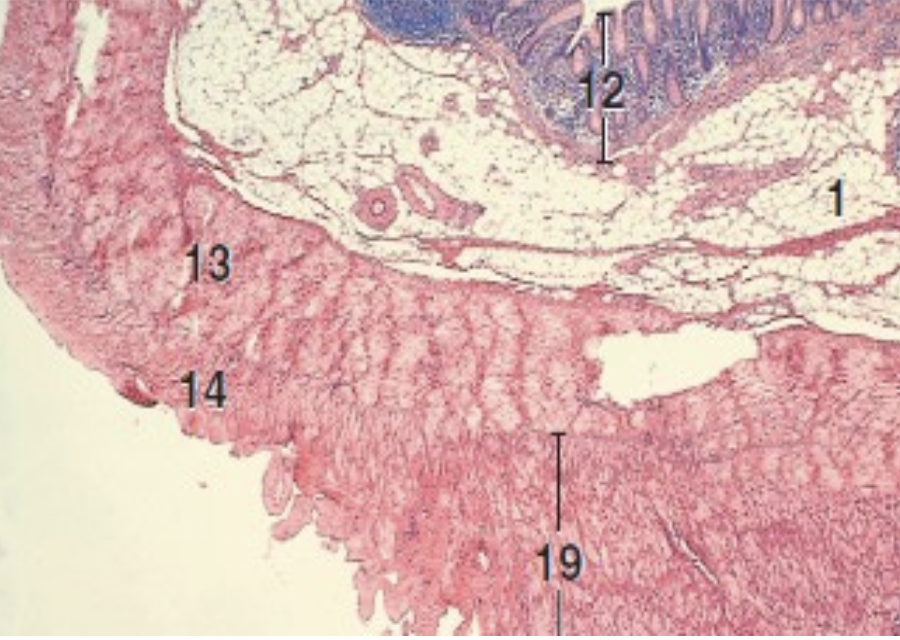
what is 19?
taenia coli in colon of pig
what layer of the rectum is thickened in carnivores?
outer longitudinal layer of tunica muscularis
in which animals are elastic fibers most prominent in the rectum?
horses and cattle
in which animals are elastic fibers the least prominent in the rectum?
sheep and goats
which layer of the tunica muscularis contains more elastic fibers?
outer longitudinal layer
what covers the cranial portion of the rectum?
serosa
what surrounds the retroperiotoneal portion of the rectum?
adventitia which blends with the pelvic fascia
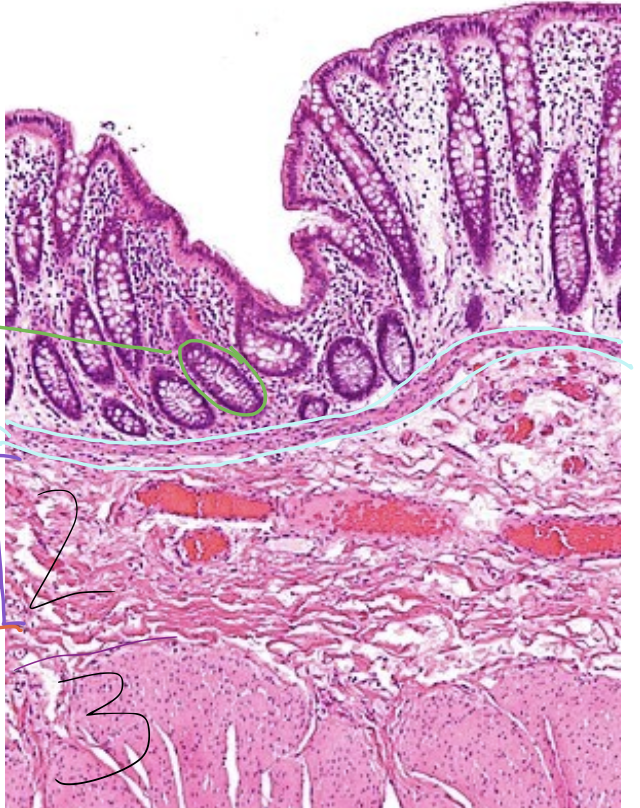
green circle
gland
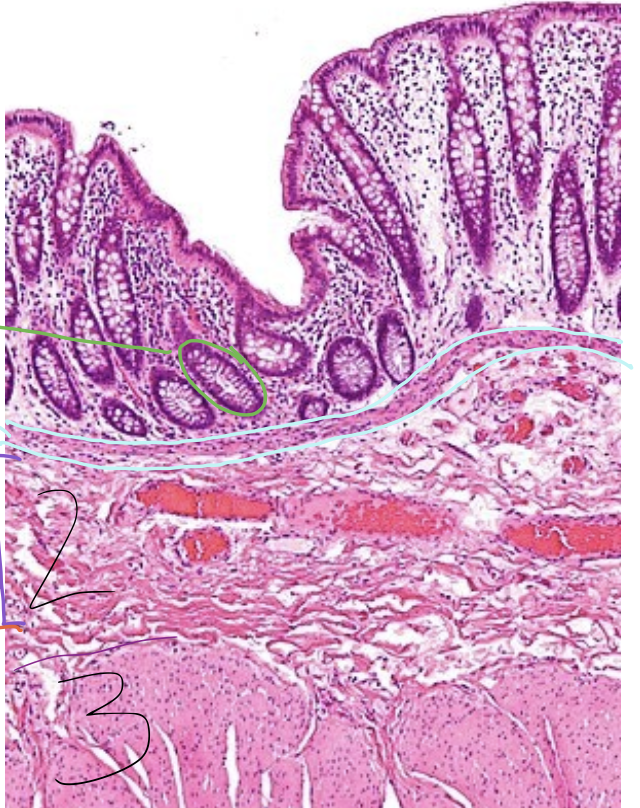
blue lining
lamina muscularis
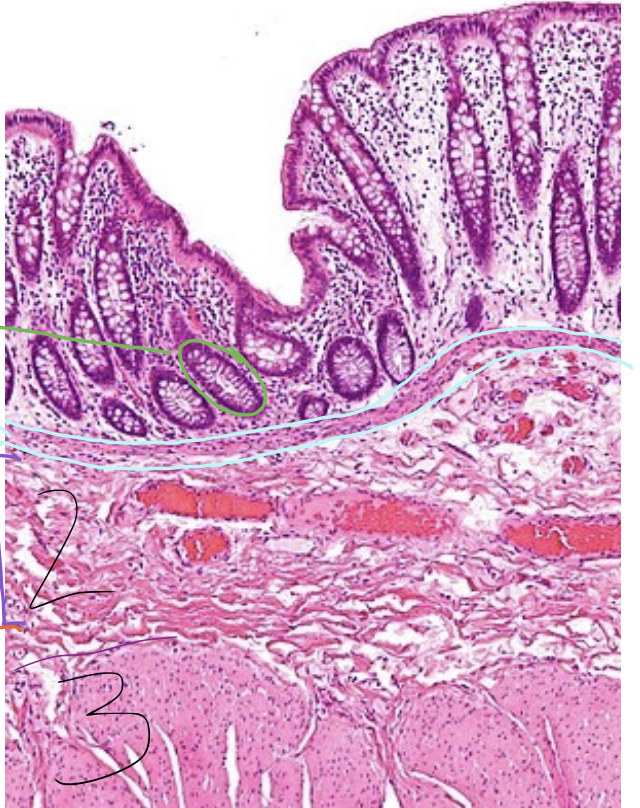
2
tunica submucosa
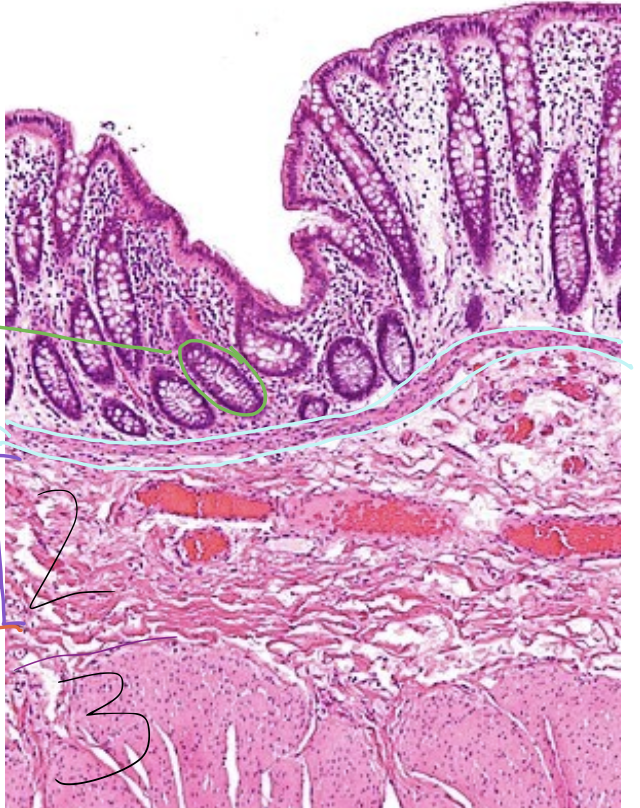
3
tunica muscularis
rectal columns
longitudinal folds of rectal mucosa to allow for stretch and facilitate passage of fecal matter
where does the outer longitudinal layer of the tunica muscularis of the rectum terminate?
at the anorectal junction
where does the inner circular layer of the anal canal terminate?
internal anal sphincter muscle
external anal sphincter
composed of skeletal muscle, covers the internal anal sphincter muscle
what happens at the anorectal line of the anal canal?
simple columnar epithelum of rectum changes abruptly to non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
which species lack glands in teh mucosa of the anal canal?
ruminants and horses
which species is the anal mucosa divided into three zones?
pigs and carnivores
columnar zone of anal canal
contains longitudinal folds, anal columns, and anal sinuses
MCQ: the taenia coli of the large intestine is an organ-specific specialization of what layer of the intestinal wall?
tunica muscularis
what lines the mucosa of both the columnar and intermediate zones?
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, and modified tubuloalveolar sweat gland
where is the intermediate zone of the anal canal?
between the columnar zone and cutaneous zone
where do anal glands occupy in the anal canal?
propria-submucosa of intermediate zone
which animals is the secretion of the anal glands a lipid secretion?
dogs and cats
which animals is the secretion of the anal glands mucuous?
pigs
where does the cutaneous zone of the anal canal begin?
acutaneous line
what lines the cutaneous zone of the anal canal?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
where do the ducts of the anal sacs open at in carnivores?
at the junction of the intermediate and cutaneous zones
what does teh mucosa of the outermost part of the cutaneous zone contain in dogs?
large modified sebaceous glands
circumanal glands