Neural & Research Foundations and Sensory Systems
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to the neural and research foundations as well as sensory systems, aiding in student's understanding and preparation for their exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
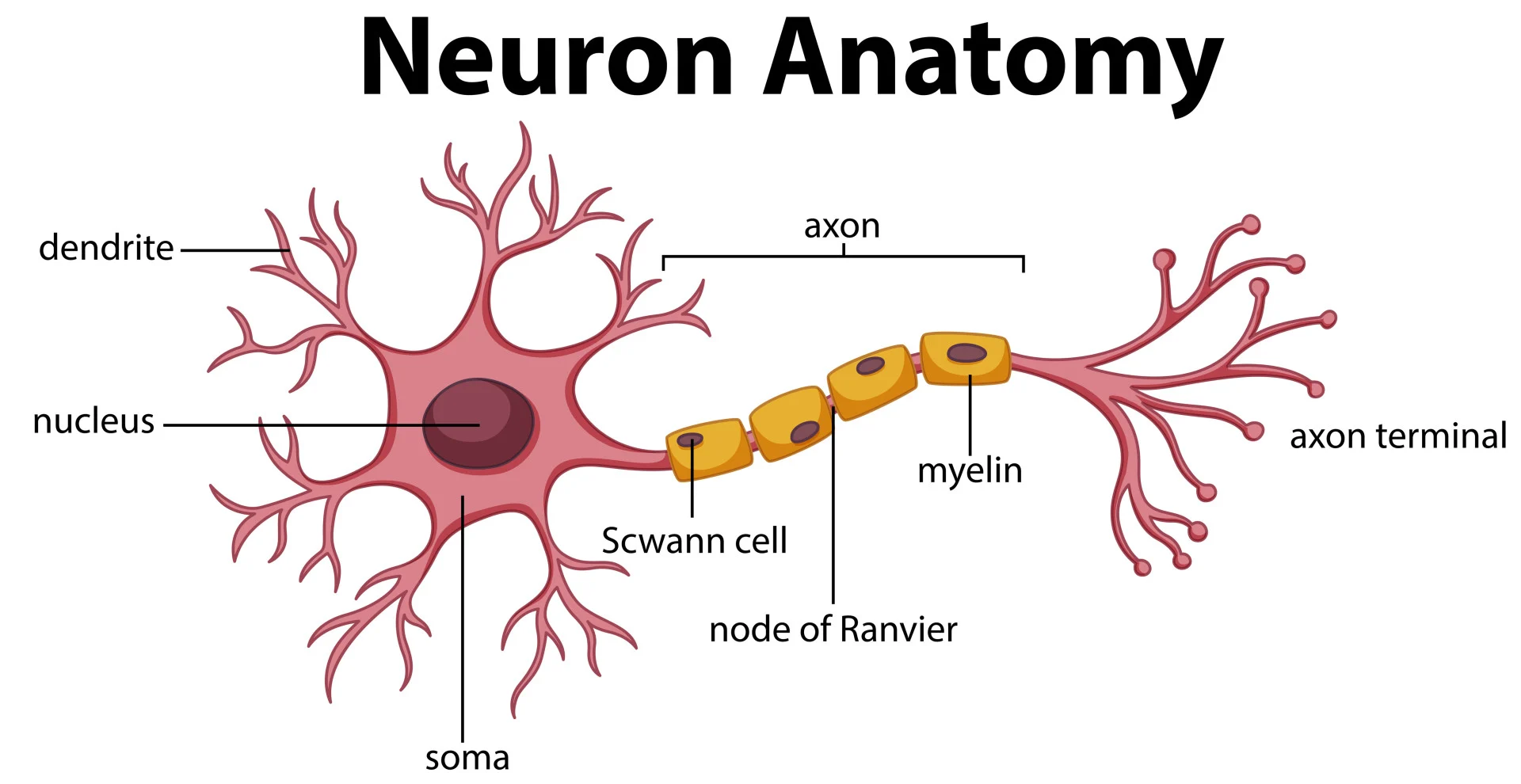
What are the basic units of the brain that communicate via electrical impulses called Action Potentials?
Neurons.
What percentage of brain cells are neurons, and what are the remaining cells called?
Neurons make up about 10% of brain cells; the rest are glial cells.
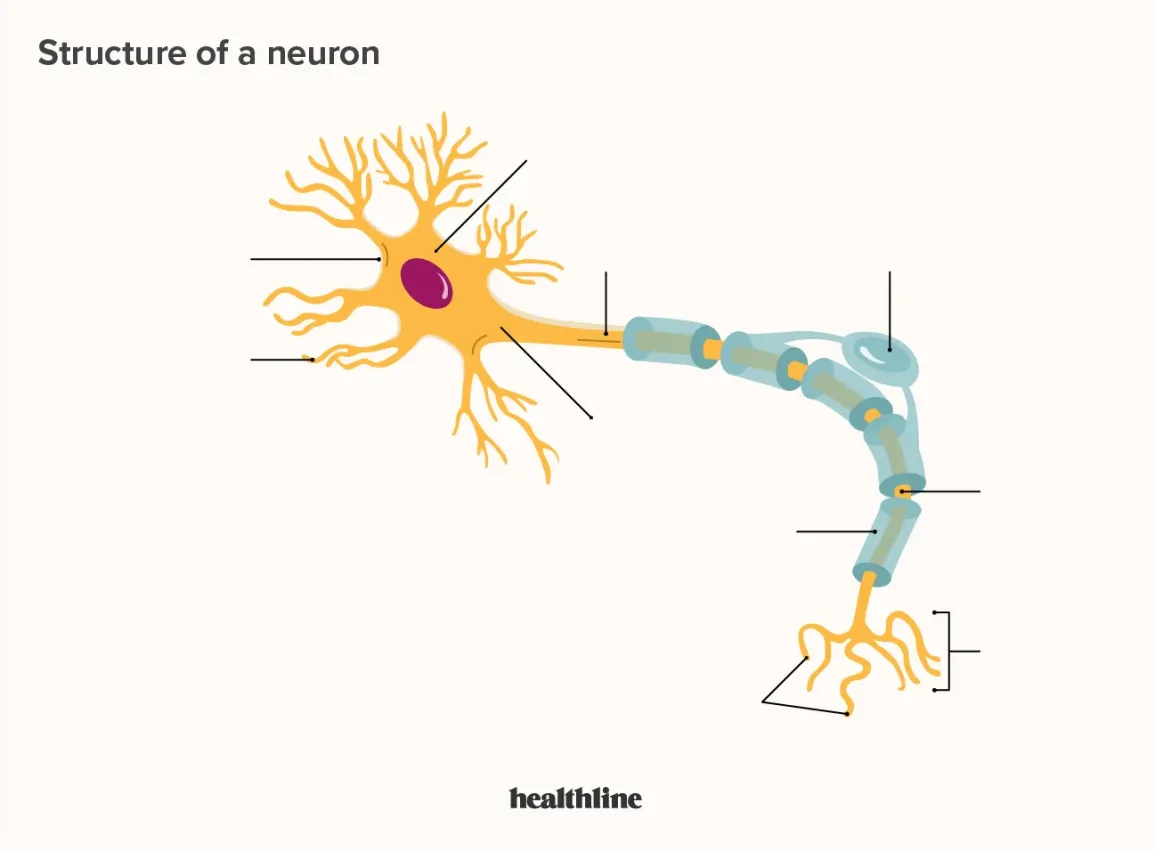
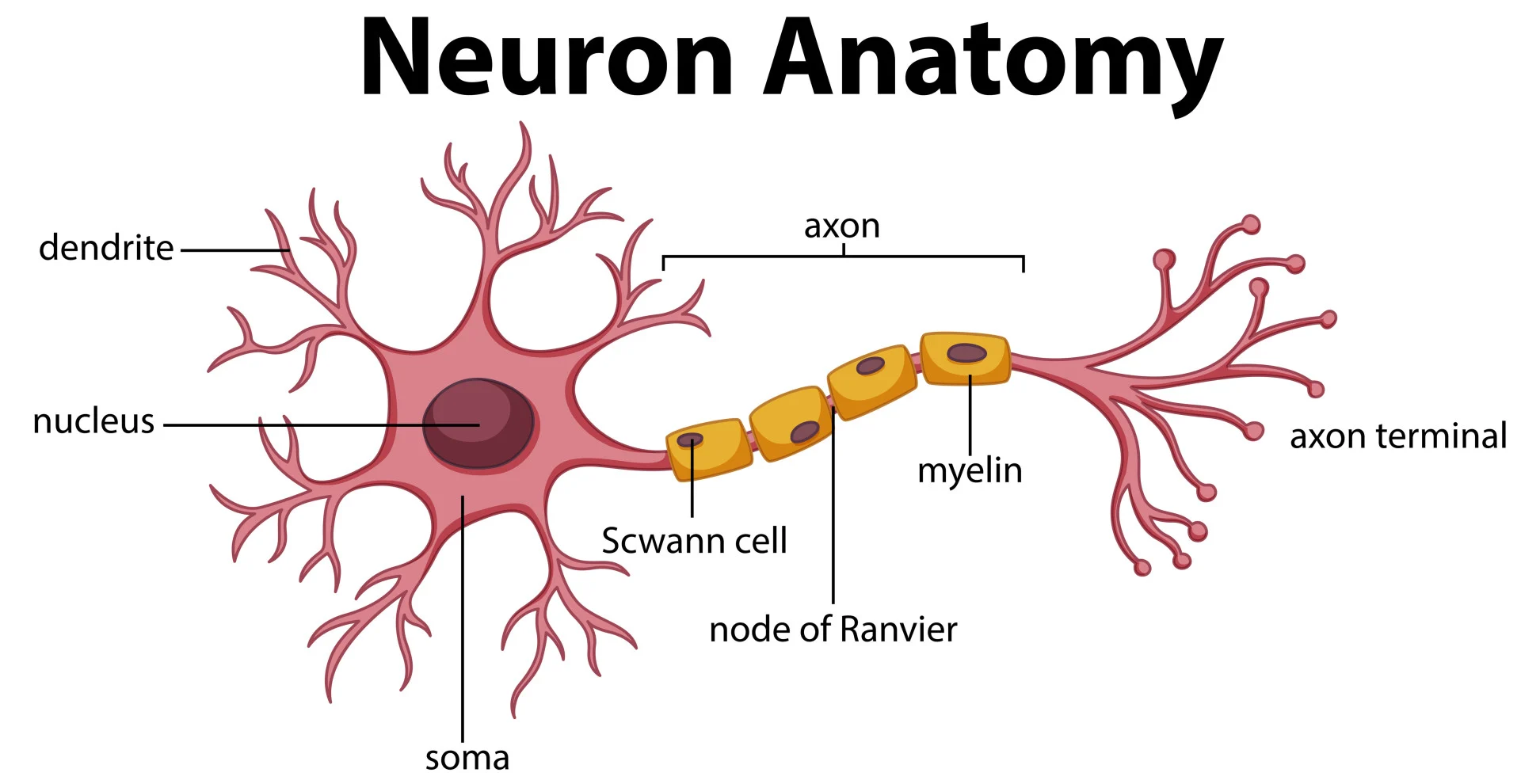
What is the primary role of the Dendrites in a neuron?
Dendrites receive signals, which are then sent down the Axon.
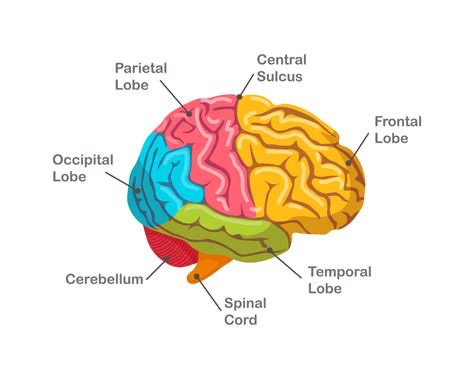
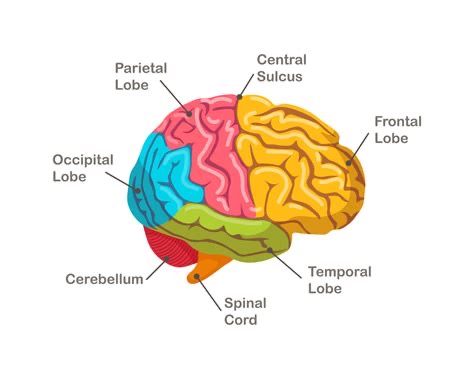
Which part of the brain is responsible for higher cognitive functions like thinking and decision-making?
Cerebral Cortex.
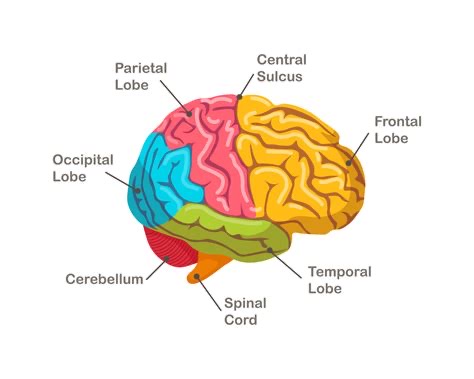
What structure is composed of myelinated axons and connects different brain regions?
White Matter.
What is the function of the Cerebellum?
It is crucial for motor coordination, balance, and fine-tuned movements, and also plays a role in cognitive functions.
What does Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) allow researchers to determine?
TMS allows scientists to determine if a specific brain region is necessary for a certain function.
What is the difference between Single Dissociation and Double Dissociation in cognitive psychology?
Single Dissociation: A patient is impaired in Task A but normal in Task B. Double Dissociation: Two patients demonstrate the opposite impairments, indicating distinct cognitive systems.
What are the three dimensions of color perception?
Hue, saturation, and brightness.
What is the process called in which light is converted into neural signals by photoreceptors?
Phototransduction.
What visual phenomenon occurs in the area on the retina where the optic nerve exits?
Blind Spot.
What are the primary types of receptors for color vision?
Rods and cones.
What is the key role of the Cochlea in auditory processing?
It performs transduction of sound vibrations into neural signals.
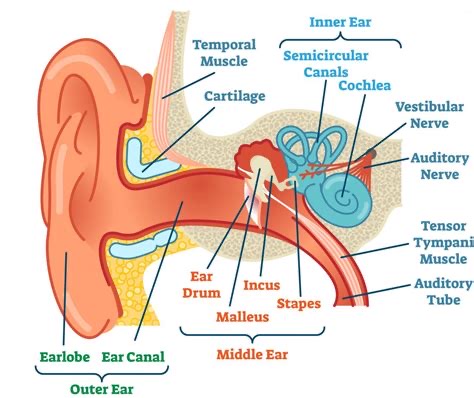
What term describes the organization of sound frequency sensitivity along the cochlea?
Tonotopic Map.
What does the term 'Haptic Perception' refer to?
Active exploration that integrates touch, movement, and cognition to recognize object shape and material.
What are the five major tastes identified in gustation?
Sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
What does the Neuronal Recycling Hypothesis suggest about culturally acquired skills?
Culturally acquired skills reuse or 'recycle' older brain circuits that are plastic and suited for new functions.
What happens to visual acuity as age increases, specifically in adults over 85?
Good visual acuity drops significantly, down to about half.
What is the primary cause of cataracts?
Caused by proteins in the lens clumping together, leading to clouding.
What is the difference between congenital and acquired conditions in sensory systems?
Congenital conditions are present at or shortly after birth, while acquired conditions develop later in life due to injury or disease.
What are the primary signaling units of the nervous system that transmit information via electrical impulses?
Neurons.
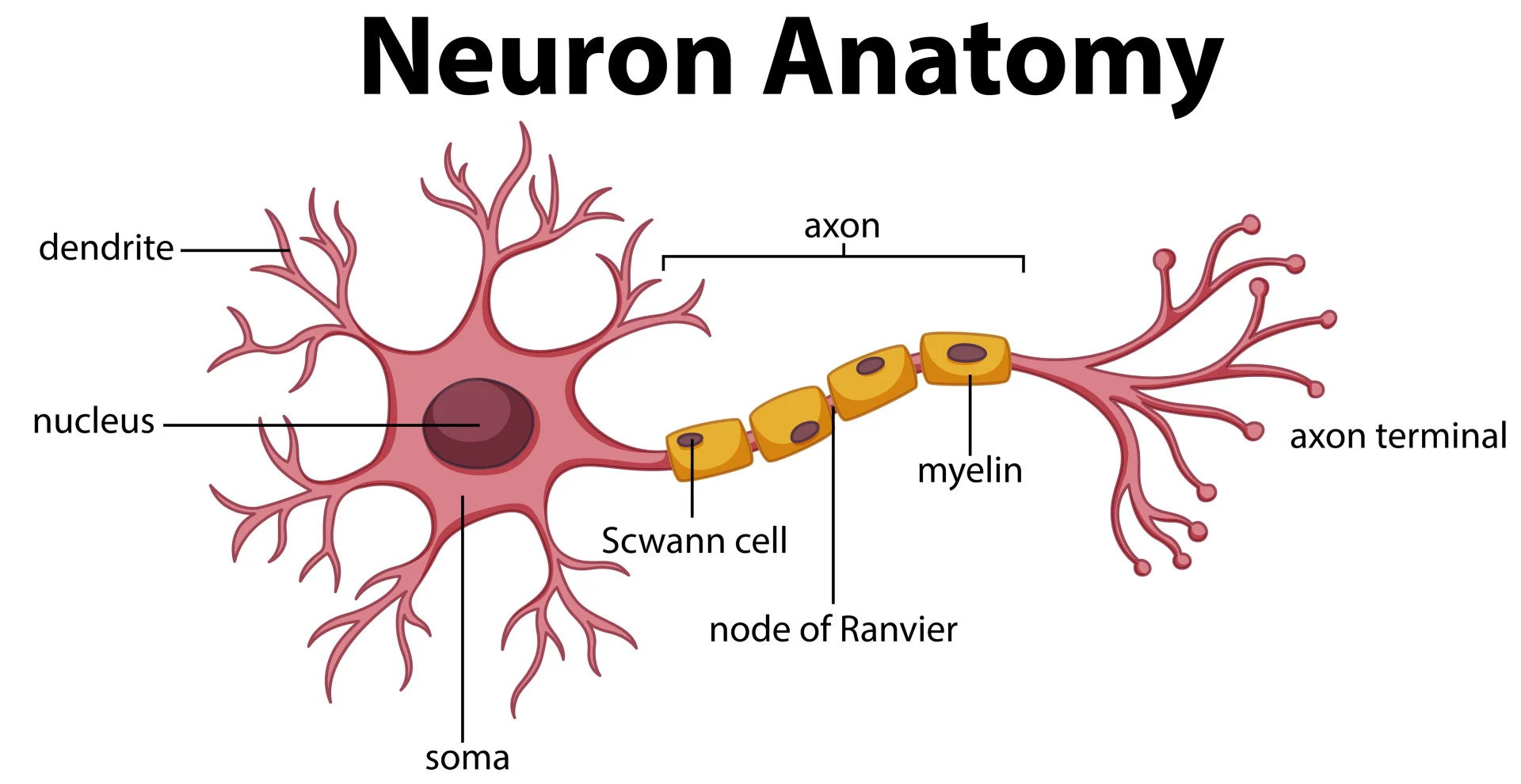
What specific electrical signal is used by neurons to communicate over long distances?
Action Potentials.
Quantitatively, what percentage of the total number of cells in the brain are neurons?
10%
Which group of brain cells makes up approximately 90\% of the total cell population and provides support to neurons?
Glial cells (Glia).
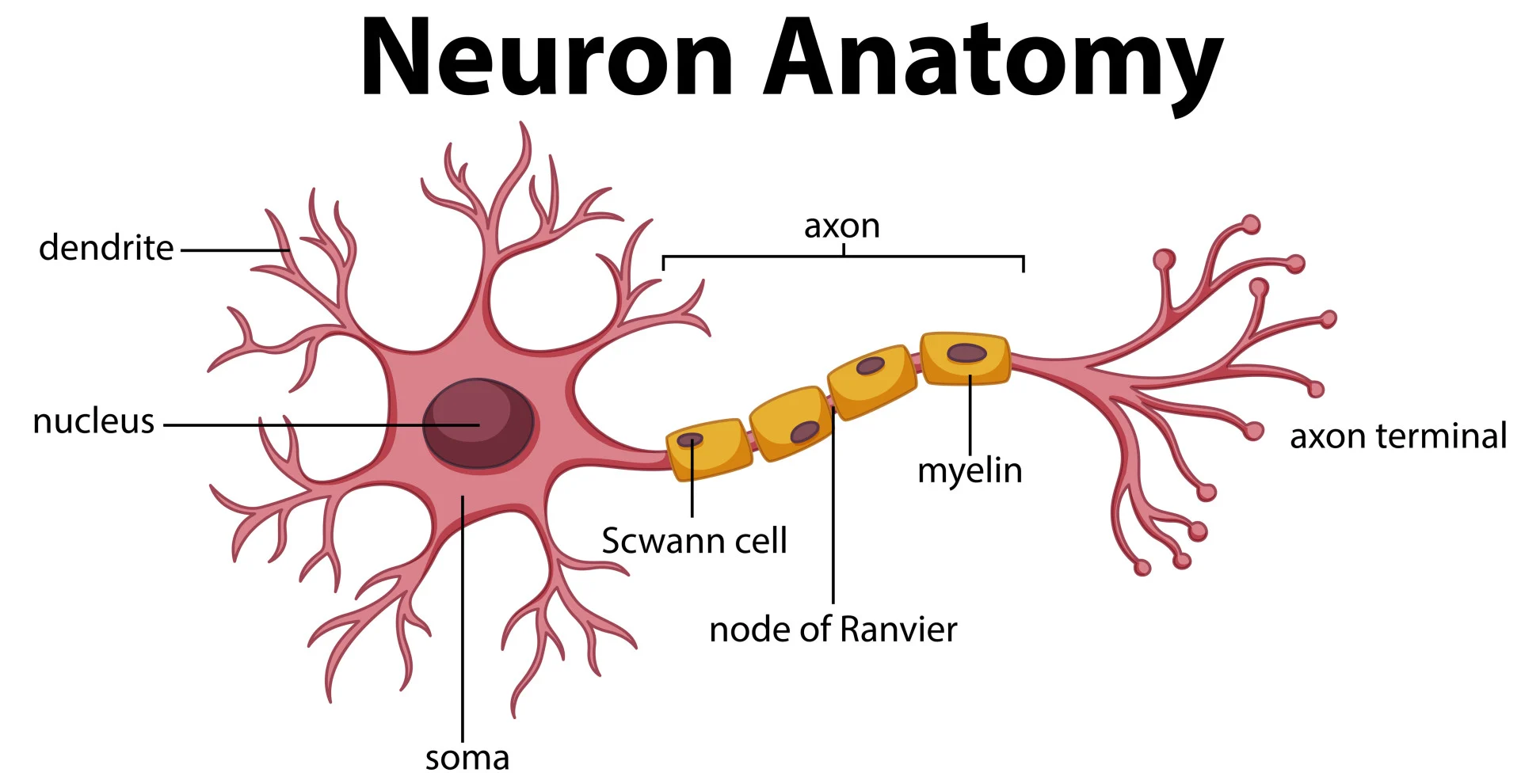
In the anatomy of a neuron, which branching structures are specialized for receiving signals?
Dendrites.
Which part of the neuron is responsible for conducting the electrical impulse away from the cell body toward other neurons?
The Axon.
Which specific layer of the brain is dedicated to complex processing, including thinking and executive decision-making?
The Cerebral Cortex.
What type of brain tissue consists of bundles of myelinated axons, facilitating communication between different regions?
White Matter.
What is the function of the Cerebellum regarding physical movement?
It is essential for motor coordination, balance, and the execution of fine-tuned movements.
Expanding on the Cerebellum, what non-motor role does it play in the brain?
It facilitates various cognitive functions.
What non-invasive technique uses magnetic fields to establish if a specific brain area is causally necessary for a function?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS).
Why is TMS preferred over fMRI when trying to determine if a brain region is required for a task?
fMRI only shows correlation (activity during a task), whereas TMS can demonstrate causality by temporarily 'disabling' the region.
Define 'Single Dissociation' in cognitive neuropsychology.
A situation where a patient is impaired on Task A but performs normally on Task B.
Define 'Double Dissociation' and describe its significance.
A situation where Patient 1 is impaired on Task A (but not B) and Patient 2 is impaired on Task B (but not A); it proves that the two tasks rely on distinct cognitive and neural systems.
What are the three subjective dimensions of color perception?
Hue, Saturation and Brightness
What is 'Phototransduction'?
The biological process of converting light energy into neural electrical signals within the retina's photoreceptors.
Where is the 'Blind Spot' anatomically located on the retina?
The area where the optic nerve exits the eyeball.
Why is there no visual data at the Blind Spot?
Because that specific area lacks photoreceptors (rods and cones).
Contrast: What is the primary functional difference between Rods and Cones?
Rods are highly sensitive to low light levels (scotopic vision), while Cones are responsible for high-acuity color vision in brighter light (photopic vision).
What is the primary sensory function of the Cochlea in the ear?
It performs the transduction of mechanical sound vibrations into electrical neural signals.
Describe the 'Tonotopic Map' found in the auditory system.
The spatial organization where different frequencies of sound are processed in specific, orderly locations along the cochlea and auditory cortex.
What does the term 'Haptic Perception' encompass?
The active exploration of objects through touch and movement to identify their shape, texture, and material.
Identify the five primary tastes recognized in human gustation.
Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter, and Umami.
What is the core claim of the Neuronal Recycling Hypothesis?
Cultural inventions (like reading or arithmetic) repurpose existing neural circuits that are evolutionarily designed for similar functions but possess high plasticity.
In the geriatric population (over age 85), what quantitative change is seen in visual acuity?
High visual acuity typically drops by around 50% (half).
What is the physiological mechanism behind the development of Cataracts?
Proteins within the lens of the eye clump together, leading to clouding and impaired light transmission.
Distinguish between Congenital and Acquired sensory conditions.
Congenital conditions are present at or near birth; acquired conditions develop later in life due to trauma, disease, or aging.
What are the three dimensions of color perception?
Hue (color name), saturation (purity), brightness (intensity)
What does Trichromatic Theory explain?
Receptoral stage: three cone types (S, M, L) sensitive to different wavelengths.
Why do afterimages occur?
Opponent channels fatigue and rebound
What causes color blindness?
Opponent channels fatigue and rebound.
Common test for color blindness?
Ishihara plates.
What determines pitch?
Frequency (Hz).
What determines loudness?
Amplitude; perceived on a non-linear dB scale.
How is sound localised?
Binaural cues (time/intensity) + spectral cues (ear/head shape).
Evidence for pathway separation?
Double dissociation with temporal lobe damage.
What is the cutaneous system?
Skin system for touch, temperature, protection.
Rapid vs slow adapting receptors?
Rapid = change/movement; Slow = sustained pressure.
Where is flavor integrated?
Orbitofrontal cortex (OFC).
What is flavor?
Multisensory integration of taste + smell.
What is blindsight?
Visual processing without awareness.
What are functional modules?
Specialized, domain-specific processing systems.
What is cultural evolution?
Rapid transmission of skills beyond genetics.
When did reading/writing emerge?
6,000 years ago.
Neuronal recycling hypothesis?
New skills reuse older, plastic circuits.
Why cross-cultural psychology matters?
Reveals non-universality in cognition.
Example of neuronal recycling?
VWFA for reading.
Who was Galton?
Pioneer of quantification; intelligence testing.
Key problem with Galton’s theories?
Biased, socially prejudiced evidence.
What is quantification?
Numerical measurement of psychological traits.
What is pupillary miosis?
Smaller pupils → less light intake.
What is AMD?
Macular degeneration → central vision loss.
PCA (Benson’s syndrome)?
Visual dementia; early perception deficits.
Parkinson’s disease dementia hallucinations?
40% visual/auditory.
Why remove congenital cataracts early?
Prevent amblyopia (<12 weeks).
Congenital vs acquired nystagmus difference?
Acquired = oscillopsia; congenital = adaptation
What do mechanoreceptors detect?
Skin deformation/pressure
Meissner corpuscles?
Superficial, rapid; light touch & vibration
Merkel disks?
Superficial, slow; fine details & texture.
Ruffini endings?
Deep, slow; skin stretch & finger position
Pacinian corpuscles?
Deep, rapid; high-frequency vibration
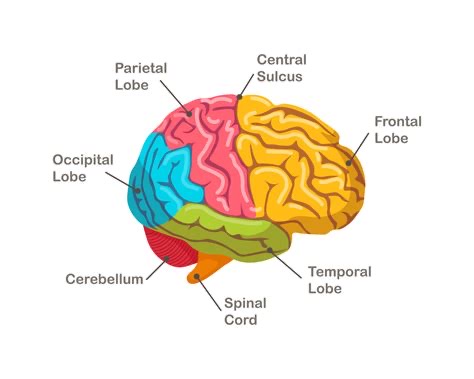
Where is the somatosensory cortex?
Parietal lobe.
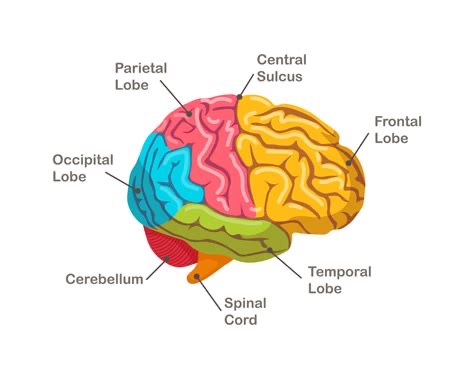
What is cortical plasticity?
Cortex can reorganize/expand with use.
Where are taste receptors located?
Taste buds in tongue papillae.
Where is taste processed?
Gustatory cortex
What is olfaction?
Smell; detects airborne molecules.
Orthonasal vs retronasal olfaction?
Orthonasal = through nose; Retronasal = from mouth during eating
Other influences on flavor?
Vision, touch, context
Ventral pathway function
“What” pathway; object recognition
Dorsal pathway function?
“How/Where” pathway; spatial action guidance
Who was Sir Francis Galton?
Pioneer of intelligence testing; emphasized numerical measurement of traits.
Why is Galton called the “apostle of quantification”?
He promoted measuring mental traits statistically
What theory influenced Galton’s ideas?
Darwin’s natural selection.
What is Hereditary Genius (1869)?
Galton’s book arguing intelligence is largely inherited.
Major criticism of Galton’s work?
Biased evidence shaped by social prejudice.
What is the first structure light enters?
Cornea
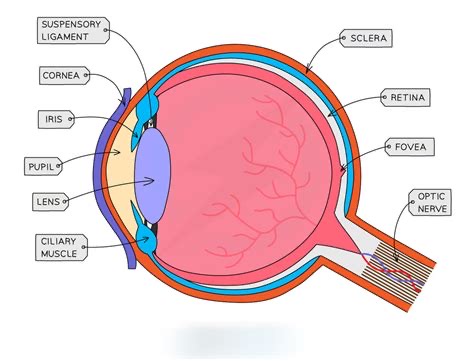
What does the pupil do?
Allows light in; size controlled by the iris.
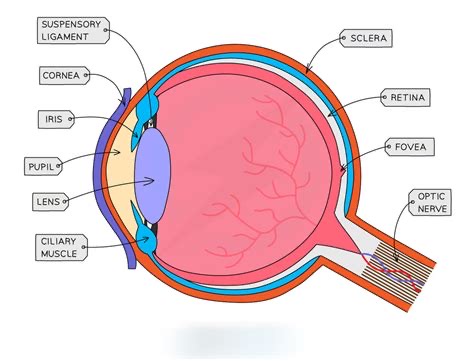
Function of the iris?
Regulates pupil size.
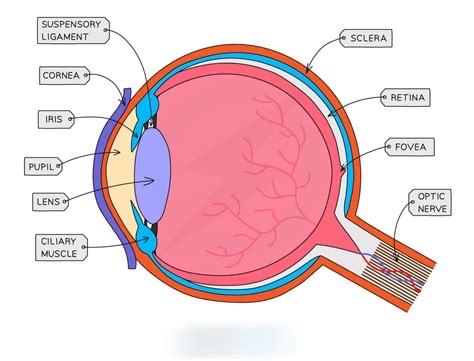
Role of the lens?
Focuses light onto the retina.
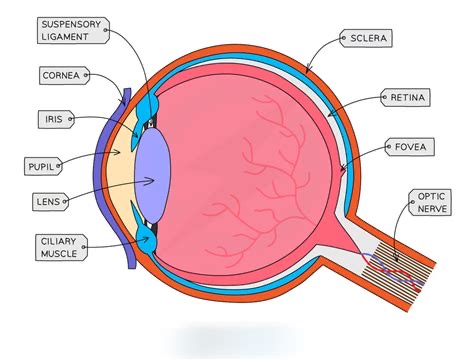
What is accommodation?
Lens changing shape to focus.