Neuro 15 and 16 - Cerebral Hemorrhage and Headaches
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What type of hematoma is lens shaped and is often caused by a temporal bone fracture resulting in a middle meningeal artery rupture?
Epidural Hematomas
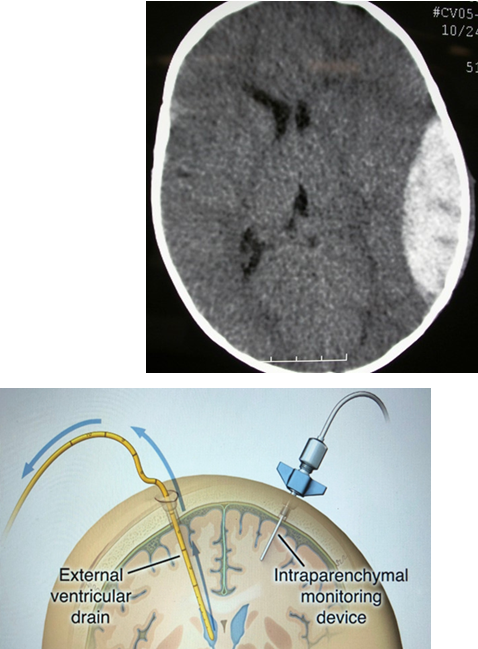
what does a subdural hemorrhage look like on CT scan?
concave, crescent shaped hematoma
what do you use for treatment after a vasospasm- and what is the MOA?
Nimodipine is a calcium channel blocker that is commonly used after a cerebral aneurysm rupture to reduce the risk of a condition called cerebral vasospasm. Here's how it works:
Cerebral Vasospasm: After an aneurysm ruptures and causes subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), blood is released into the subarachnoid space around the brain. This blood can irritate the blood vessels, causing them to constrict or spasm. Vasospasm can lead to reduced blood flow to parts of the brain, which increases the risk of ischemia (lack of oxygen) and further brain damage.
Action of Nimodipine: Nimodipine works by blocking calcium channels in the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels. By doing so, it relaxes and dilates the blood vessels, reducing the risk of vasospasm. This helps to maintain adequate blood flow to the brain and prevent further ischemia after an aneurysm rupture.
Clinical Benefit: By reducing vasospasm, nimodipine improves outcomes for patients who have suffered a subarachnoid hemorrhage due to aneurysm rupture. It helps to prevent secondary brain injury and improves overall recovery.
In short, nimodipine helps manage the dangerous effects of vasospasm following an aneurysm rupture by relaxing the brain's blood vessels, ensuring better blood flow to the brain and reducing the risk of ischemic damage.
What is Cushing’s Triad
signs that indicate increased ICP
increased BP, bradycardia, irregular respirations
describe what you should do for a headache physical exam?
vitals, general, HEENT (include eyes and palpate over sinuses, temporal arteries), neck, neuro
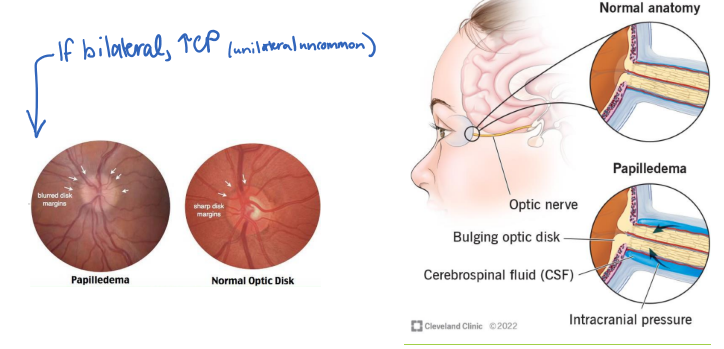
Someone comes in with a headache, and they have bilateral papilledema on fundoscopy. What is this indicative of?
increased ICP
are tension headaches throbbing?
no
What are some prophylactic treatments for migraines?
beta blockers, amitriptyline, anticonvulsants, CGRP
how do you treat cluster headaches (both acutely and prophylactically)?
100% oxygen (avoid in CO2 retention) treatment acutely
prophylactic: verapamil

true or false; in the first episode of a cluster headache, the patient should go to the ER to be imaged
true
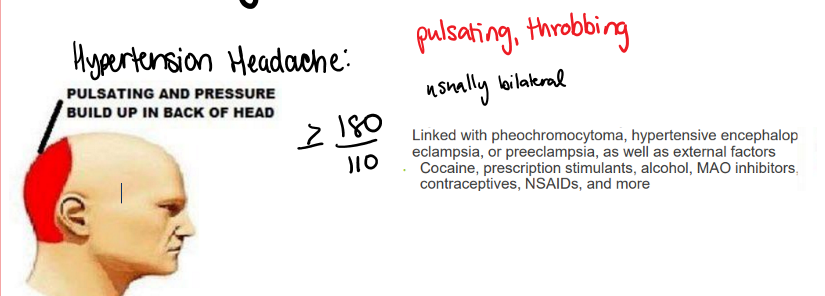
where do hypertension headaches present?
pulsating and pressure build up in back of head
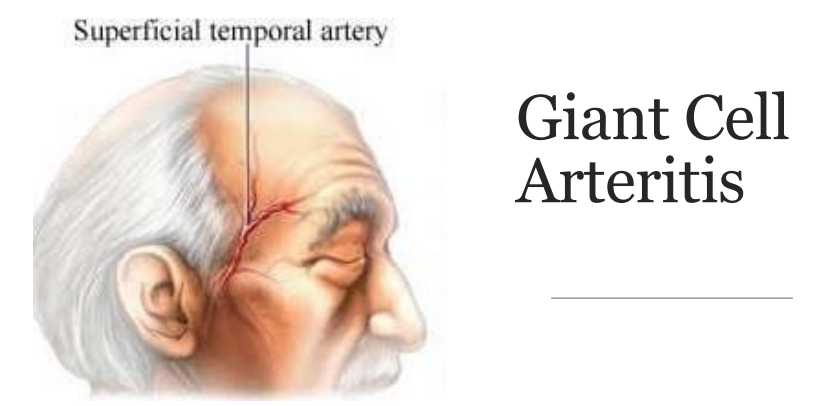
abrupt vision disturbances, tenderness to palpation on temples, and jaw claudication (all unilaterally) are symptoms indicative of…
GCA
treat w steroids
A 28-year-old woman presents with a 2-week history of worsening headaches, particularly in the morning. She reports associated nausea and occasional vomiting. On examination, her fundoscopic exam shows bilateral papilledema. Neurological examination is otherwise unremarkable. MRI of the brain is normal, but lumbar puncture reveals an opening pressure of 30 cm H2O. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Migraine
B) Cluster headache
C) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
D) Acute bacterial meningitis
E) Brain tumor
C - idiopathic intracranial hypertension
NOTE: TREAT WITH ACETAZOLAMIDE DIURETIC; POSSIBLE ROLE FOR FUROSEMIDE. SHORT COURSE OF PREDNISONSE FOR VISUAL symptoms prior to surgery