Chapter 8: The Competitive Firm - Market Structure, Profit Maximization, and Supply Decisions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is the primary goal of Chapter 8?
To explain how businesses make price and production decisions.
What are the learning objectives of this chapter?
1. How profits are computed. 2. Characteristics of perfectly competitive firms. 3. How a competitive firm maximizes profit. 4. When a firm will shut down. 5. Difference between production and investment decisions. 6. What shapes or shifts a firm's supply curve.
How does the degree of competition affect profits?
Less competition makes it easier to be profitable, while more competition makes it more difficult.
What is the profit motive?
The expectation of profit is the basic incentive to produce, defined as the difference between total revenue and total cost.
What are explicit and implicit costs?
Explicit costs are payments made for the use of a resource, while implicit costs are the value of resources used for which no payment is made.
How do economists and accountants differ in calculating profit?
Economists include both implicit and explicit costs, while accountants include only explicit costs.

What is economic profit?
Economic profit equals total revenue minus explicit costs and implicit costs.
What is normal profit?
Normal profit is the opportunity cost of capital; it is earned if economic profit is zero.
What motivates an entrepreneur to start a business?
The prospect of earning more than the normal profit and the potential for economic profit.
What defines market structure?
The number and relative size of firms in an industry, ranging from monopoly to perfect competition.
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
Many firms compete, products are identical, low entry barriers, no market power, and firms are price takers.
What is the nature of firm demand in a perfectly competitive market?
The firm's demand curve is perceived as horizontal because it is a price taker.
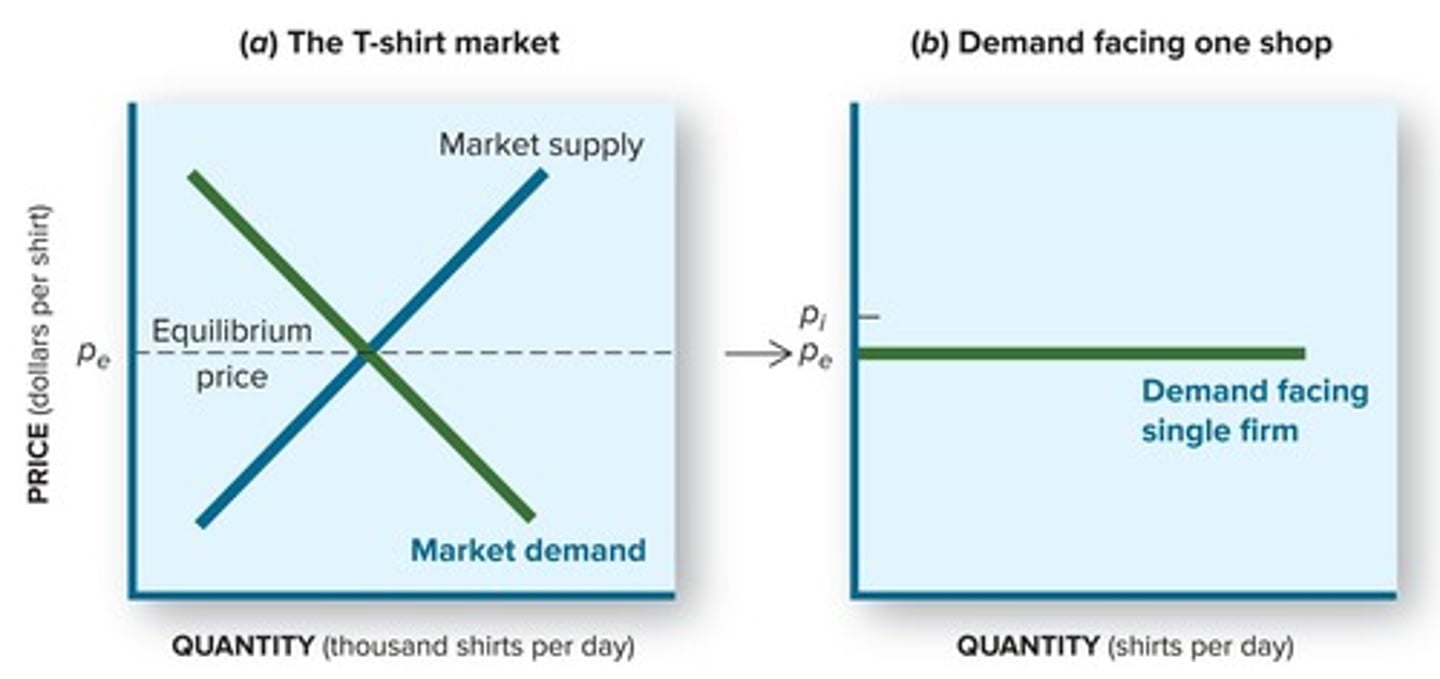
Why do firms in perfect competition have no pricing decisions?
Firms take the market price as given and cannot influence it.
What happens if a firm raises its price in a competitive market?
No one will buy from the firm, as consumers will purchase at the market price.
What is the relationship between market demand curves and firm demand curves?
The market has a downward-sloping demand curve, while individual firms have a horizontal demand curve.
What is the implication of being a price taker for a firm?
Firms can sell increased quantities only at the market price.
What is the significance of the profit motive in a competitive market?
It encourages firms to produce goods that consumers desire at prices they are willing to pay.
What are some criticisms of the profit motive?
it leads to inferior products, pollution, restricted competition, and unsafe workplaces.
What is the typical case for economic profit in a firm?
A firm can earn a positive economic profit if it earns more than its opportunity cost.
What is the role of competition in shaping a firm's supply curve?
Competition influences the prices and quantities that firms are willing to supply in the market.
When will a firm decide to shut down?
A firm will shut down if it cannot cover its variable costs in the short run.
What is the difference between production and investment decisions?
Production decisions involve current output levels, while investment decisions relate to future capital expenditures.
What is the impact of low entry barriers in a competitive market?
Low entry barriers allow new firms to enter the market easily, increasing competition.
What is oligopoly?
A market structure characterized by a few firms, each having considerable market power.
What is monopolistic competition?
A market structure with many firms and very little market power.
What is the primary goal of firms in a competitive market?
To maximize profits, not revenues.
How is profit calculated?
Profit equals total revenue minus total costs.
What does marginal cost (MC) represent?
The increase in total cost associated with a one-unit increase in production.
What is the Profit-Maximizing Rule?
Never produce a unit of output that yields less revenue than it costs.
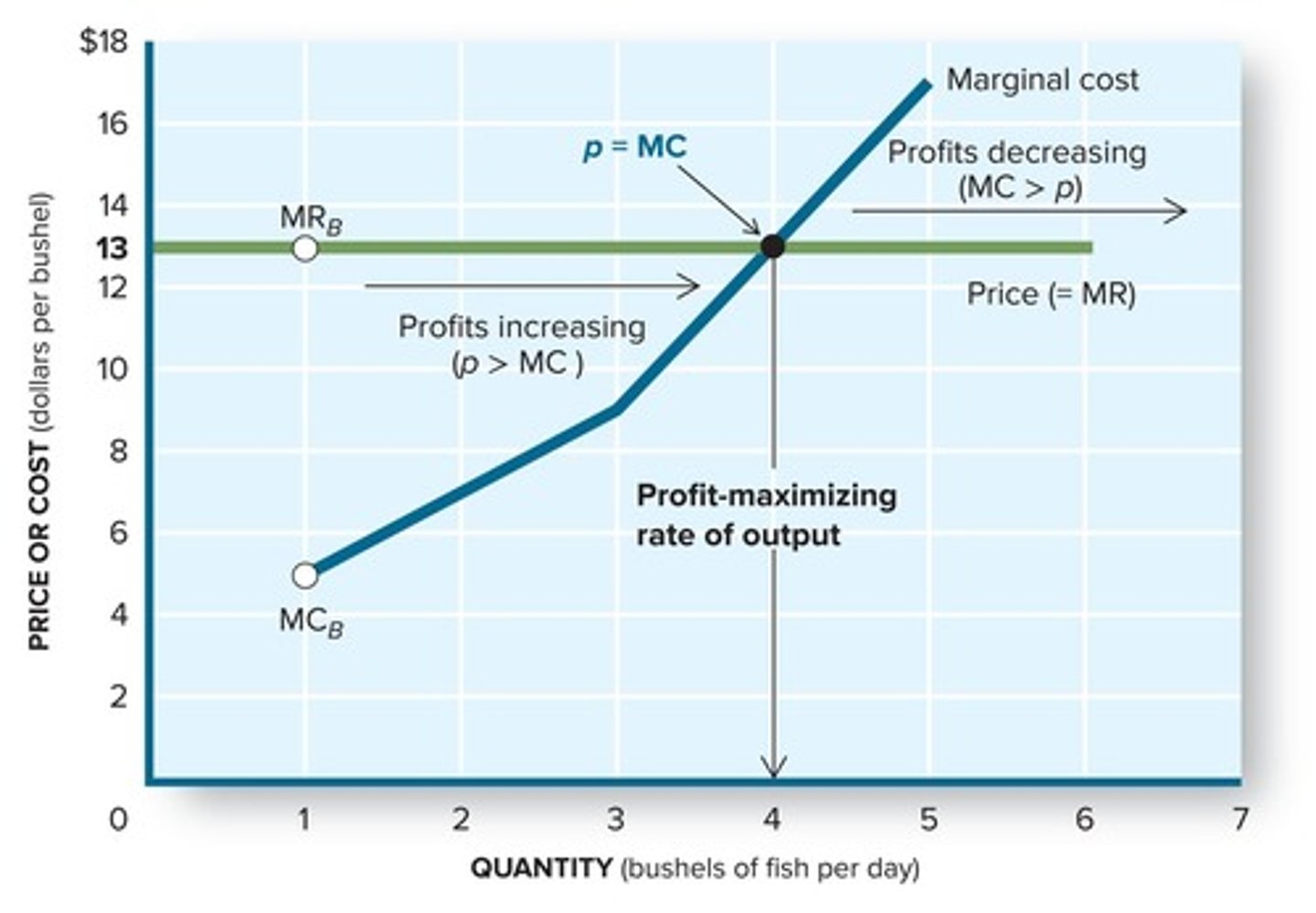
In perfect competition, how does marginal revenue (MR) relate to price?
Marginal revenue is equal to price (MR = P).
What should a firm do if price (P) is greater than marginal cost (MC)?
Increase output to add to profit.
What should a firm do if price (P) is less than marginal cost (MC)?
Decrease output to avoid losses.
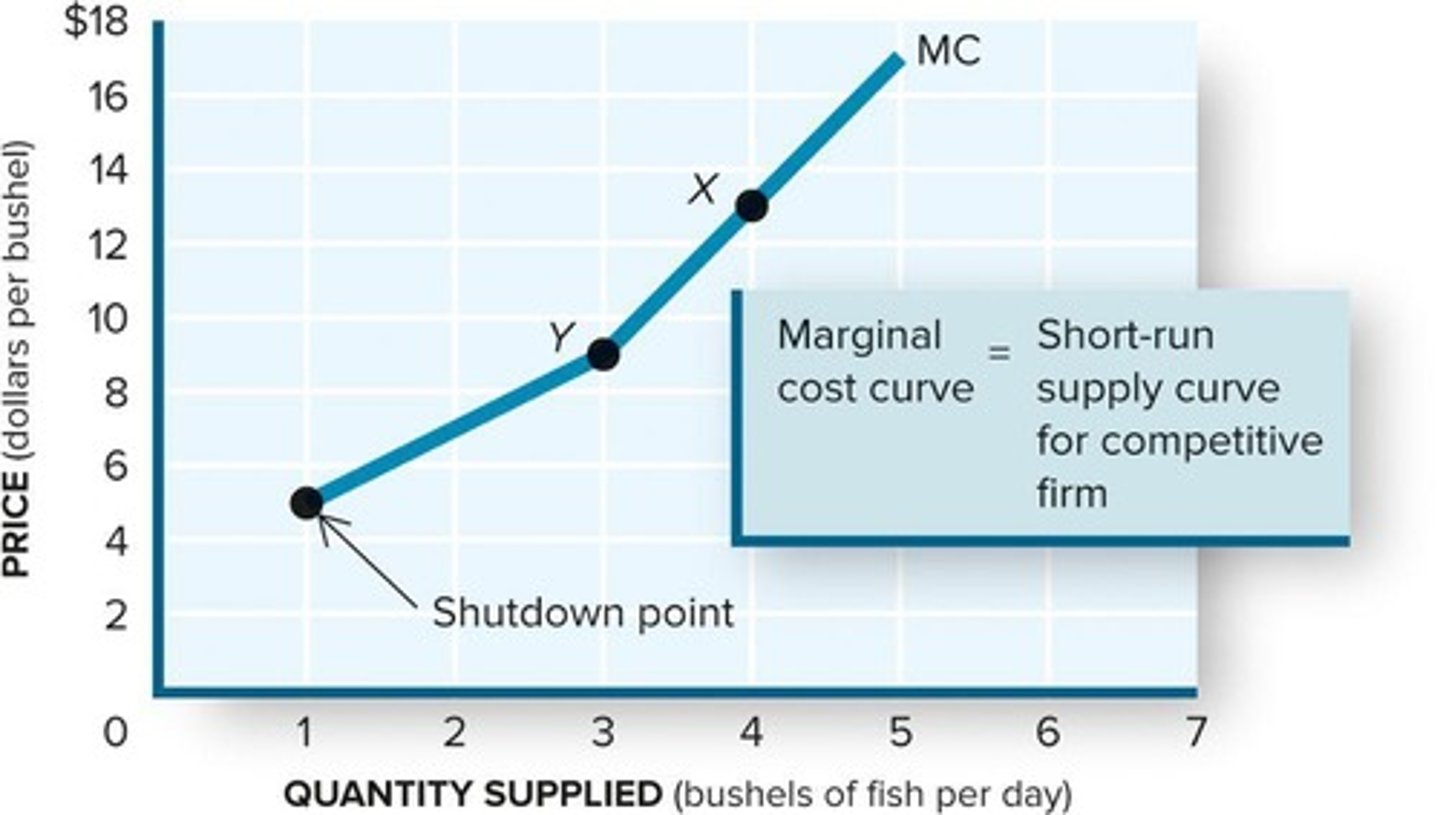
What is the shutdown decision in economics?
A decision to cease production when losses exceed fixed costs.
What is the shutdown point?
The output level where price equals minimum average variable cost (AVC).
What factors influence a firm's investment decision?
The anticipated profits must be large enough to compensate for effort and risk.
What are the determinants of supply?
Factors include the price of inputs, technology, expectations, taxes, and subsidies.
What does the short-run supply curve represent?
The quantity a firm is willing to supply at each price, determined by where P = MR = MC.
What happens to the supply curve if costs decrease?
The supply curve shifts to the right.
What happens to the supply curve if costs increase?
The supply curve shifts to the left.
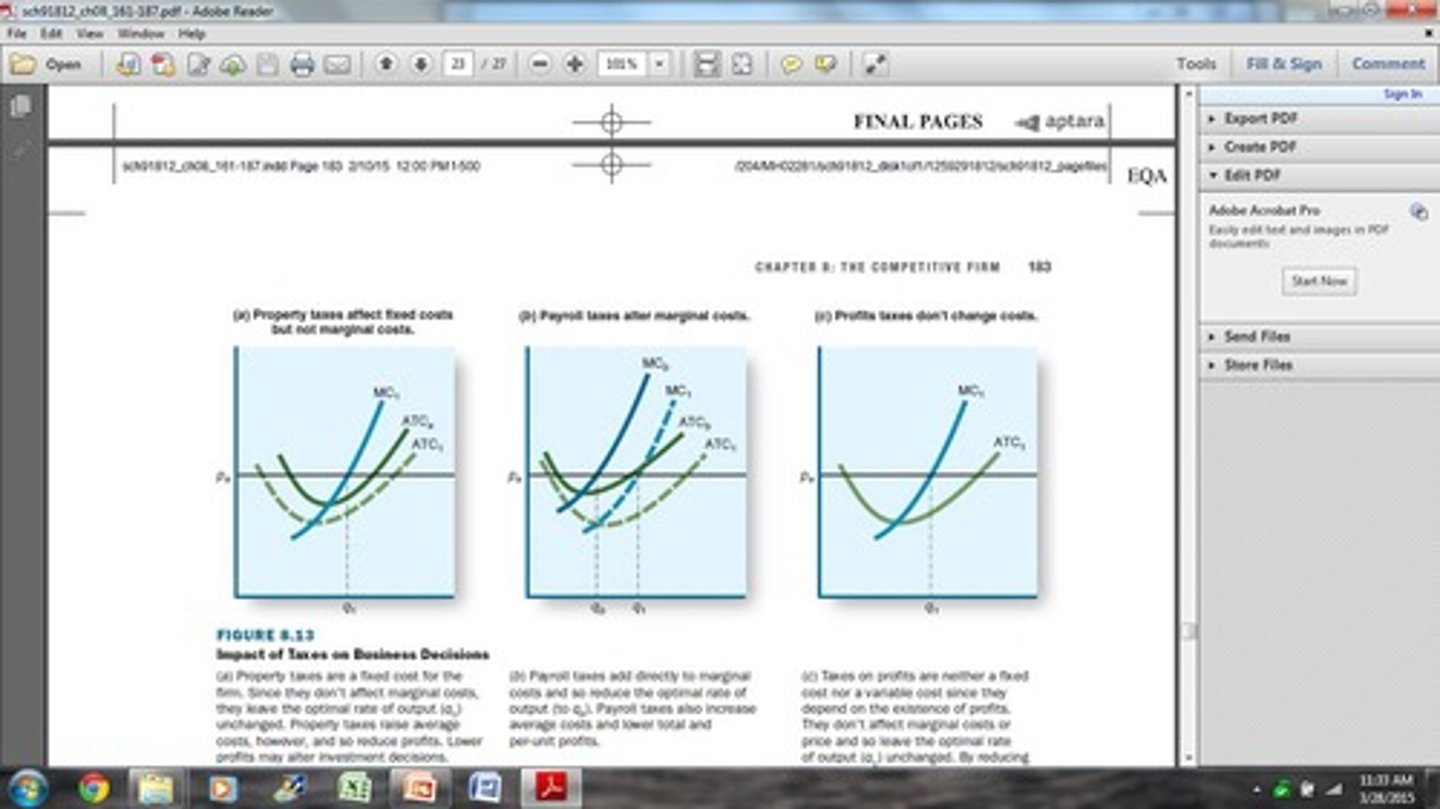
How do property taxes affect business decisions?
They are a fixed cost that increases average total cost.
How do payroll taxes impact a firm's costs?
They are variable costs tied to wages, increasing both marginal and average total costs.
What is the effect of profit taxes on a business?
They reduce after-tax profits and may decrease investments in new businesses.
What is the relationship between marginal cost and the firm's short-run supply curve?
The marginal cost curve is the firm's short-run supply curve.
What should a firm do if price equals average total cost (ATC)?
The firm breaks even, making no profit or loss.
What is the significance of point b in profit maximization?
It is where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC), maximizing profits.
What occurs when the price exceeds average variable cost (AVC) but not ATC?
The firm minimizes losses but may still incur losses.
What is the long-run investment decision for a firm?
It involves building, buying, or leasing plants and equipment based on anticipated profits.
How does an increase in input prices affect the supply curve?
It shifts the marginal cost curve upward, reducing desired output.
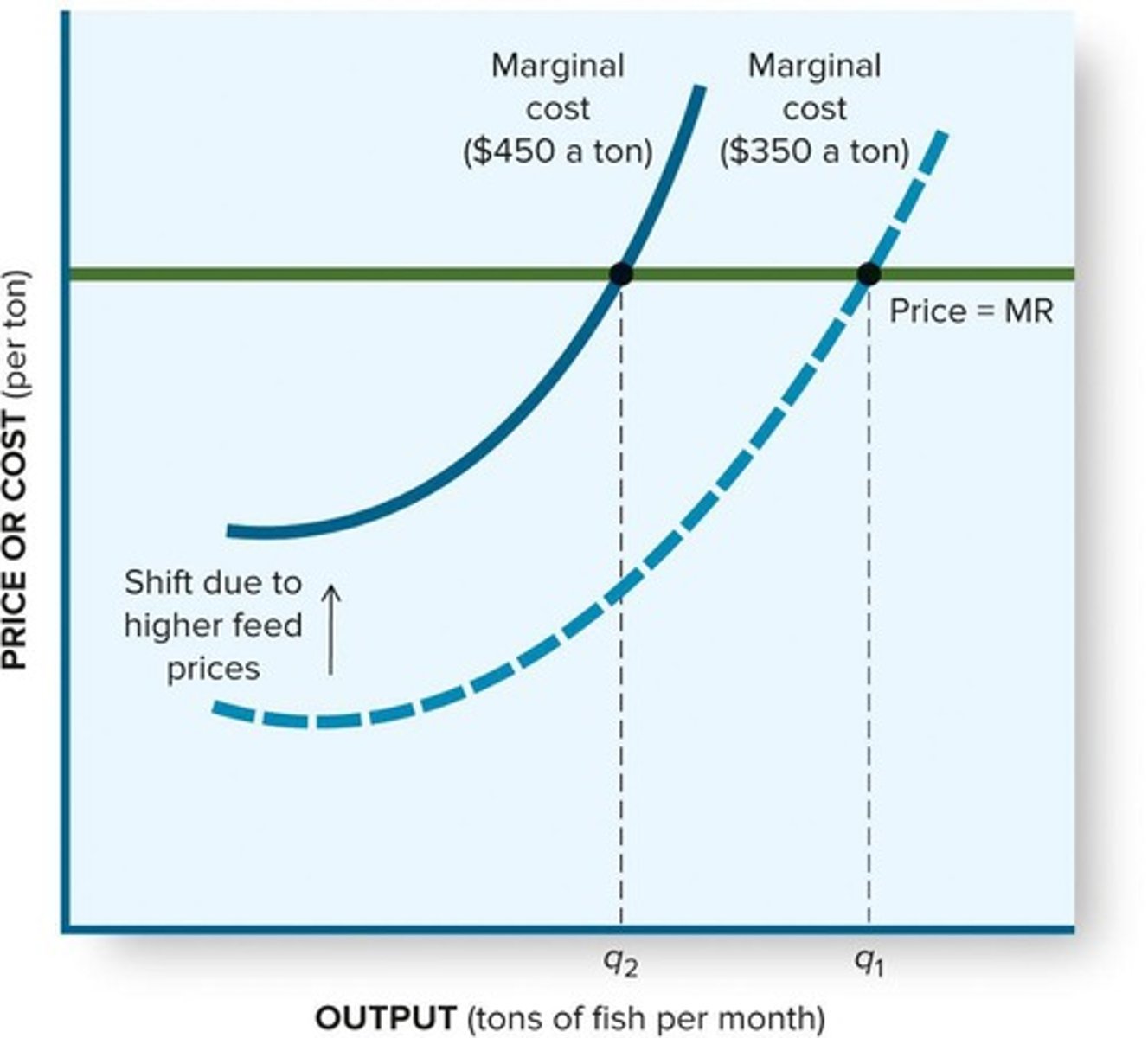
What is the impact of taxes on business decisions?
Taxes can increase costs and affect output decisions.