Lecture 27: Cnidarians, placozoans and ctenophores
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
● List and describe key features of cnidarians
● Compare the development and body plan of cnidarians to other animals
● Describe the functions of cnidocytes
● Contrast the role of the polyp and medusa stages in the life cycle of cnidarians
● Explain the use of muscles and nerves in cnidarians in comparison to other animals
● Explain the symbiosis between coral and dinoflagellates, and its role in coral reefs and their sensitivity to perturbations
● Describe main features of Ctenophores and Placozoans
● Cnidarians Form.
● Most are dimorphic. What does this mean?
● What are key features of these morphs?
● Are both morphs always present?
Dimorphic: Alternate bw two stages
Asexual Polyp Stage: oral ends up w/ stalk attaching to surface, usually small; can form colonies. Produce medusa asexually
Sexual Medusa Stage: motile, free-swimming, “sea jelly”, oral end down, sexually reproductive stage
● Cnidarians Form.
● Do cnidarians have muscles?
form from a mix of endoderm and ectoderm
appear to be a seperate origin from those of other animals
● Do cnidarians have nerves? If yes, what type of system? If yes, does their system have a common origin to that in other animals?
have nervous net: decentralized systems (no brain) used to sense and respond to stimuli (eg prey capture movement)
evolved independently
● Do cnidarians have symmetry? If yes, what type?
radial symmetry
● Which cnidarians have eyes?
○ What are cnidocytes?
single-use cells triggered by touch or chemistry found in cnidarians
○ What are nematocysts?
stinging organelles inside cnidocytes that contain toxins
○ What do nematocysts and cnidocytes have to do with feeding?
most cnidarians are carnivorous
used to capture prey
○ How do some organisms protect themselves from cnidocytes?
clownfish have protecting coating that prevents nematocysts from firing (form of mutualism)
● Cnidarians Life cycle
○ Sketch out the general life cycle
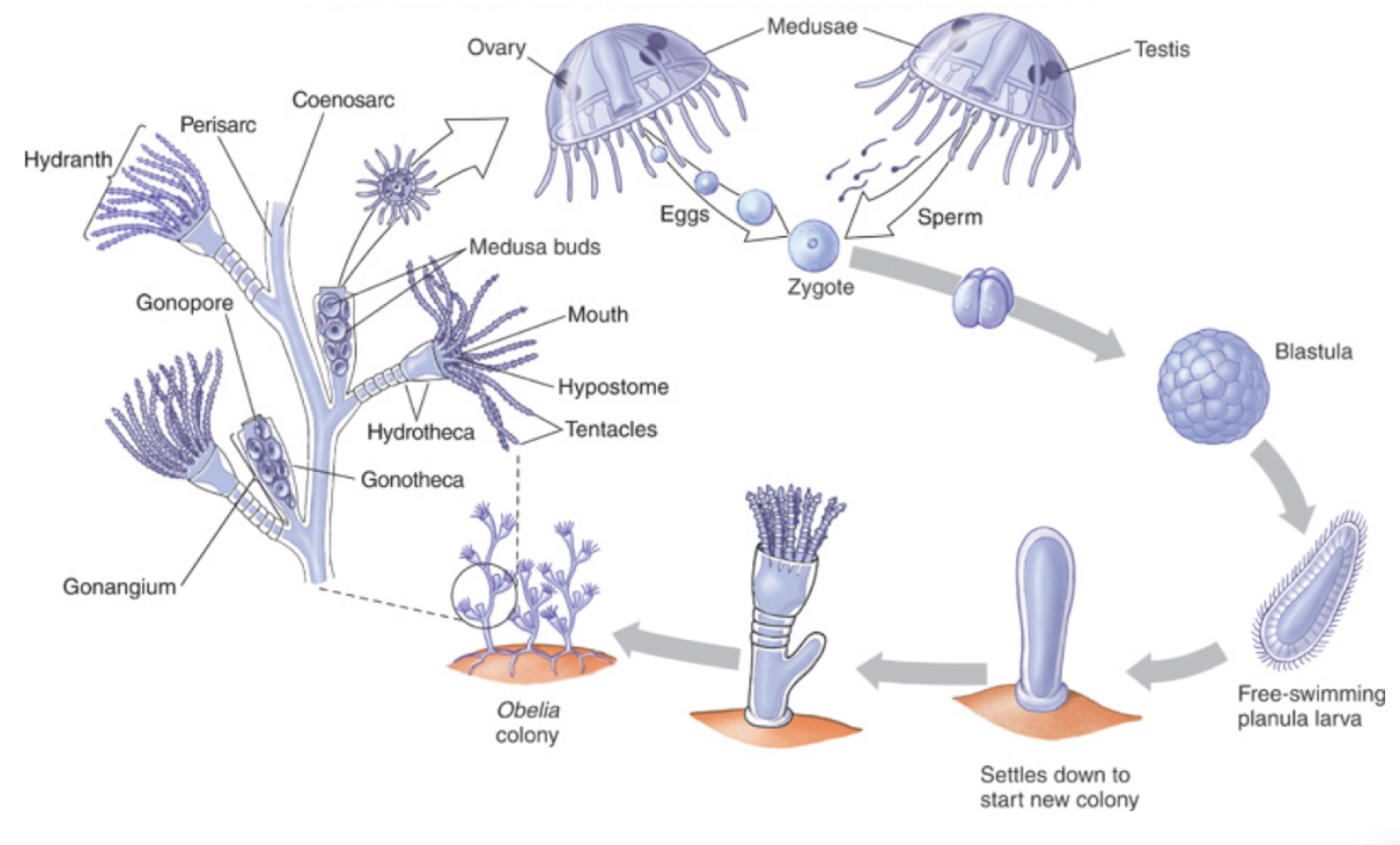
○ What is coral?
are sessile and colonial Anthozoans (no medusa stage)
polyps secrete organic molecules on which they deposit calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which form a “skeleton”
living polyps form a layer on top of skeletal remains which forms coral reefs and islands
○ What are coral reefs? Why are they important?
major marine foundational habitat
habtat 25% of world’s fish species
major food source for humans
structurally buffer shorelines
○ How can some coral supplement the energy they get from predation?
many corals supplement diet via mutualistic symbiosis with dinoflagellates
these dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, unicell eukaryotes that live endosymbiotically w/ in coral cells
dinoflagellates provide sugar to their hosts
most reef-forming corals are restricted to clear surface waters w/ enough light to support photosynthesis by dinoflagellates
● Where does ctenophores name come from?
named for their “ctenes” (or combs)
● How do ctenophores move?
their “combs” which are stacks of cilia used for locomotion
● How do ctenophores feed? Do ctenophores have stingers?
cells on feeding tentacles discharge adhesive material to capture prey
● Do ctenophores have nerves? If yes, what type of system? If yes, does their system have a common origin to that in other animals?
have nerve nets like cnidarians
● Do ctenophores have muscles?
have muscles made up of endo/ectoderm
● Do ctenophores have symmetry? If yes, what type?
radial symmetry
● How many cell layers do ctenophores have?
are diploblastic (2 layers)
● What is mesoglea?
is gelatinous and the 2 cell layers are separated by it
do ctenaphores have a complete gut
yes
● How many species are there of placozoans?
only 4
● Do placozoans have a nervous system? Muscles? gut? mouth?
do not have any
how do they move
with cilia
● What type of symmetry do Placozoans have?
asymmetrical
● Are placozoans primitive? Ancient?
yes
● How many cell layers do placozoans have?
only a few cell types; diploblastic; are small
● Is placozoan simplicity an ancestral or derived state?
likely due to loss of features