min 2030 final exam: Part 2 - Lec 1 - optical microscope
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
light waves
electromagnetic radiation that have both electrical and magnetic properties
frequency
V/λ
brightness of the light
is proportional to the amplitude (A)
distance for 1 wave cycle=
wavelength (λ), in nm
wave front
Surface over which the phase of the wave is constant
wave normal
Line perpendicular to the wave front, and parallel to the propagation direction
plane wave front
Plane (2D) surface where phases of parallel wave rays are aligned.
plane polarized light (PPL)
light passed through a polarizing filter which constrains the light to oscillate in a single plane
cross polarized light (XPL)
two polarizers in which the polarizing directions are perpendicular
if nothing changes the orientation of light between the two crossed polarizers, what do you see transmitted on the other side?
nothing
the velocity of light depends on…
the nature of the material it travels through and the wavelength of light
velocity decreases when changing from a less to more dense material
when velocity of light decreases…
wavelength must also decrease
optically isotrophic
Material in which the velocity of light is the same in all directions. • Isotropic materials: Isometric minerals, glass (i.e., volcanic glass, opal)
Optically Anisotropic
The velocity of light is different in different directions. Anisotropic materials: Non-isometric minerals.
for reflected light
the angle of incidence and of reflection are identical. Mineral luster depends on these reflections, and are affected by the mineral’s refractive index.
a bent (refracted) light path occurs…
when the incident light angle is not 90 degrees
refractive index (RI)
based on the difference between the speed of light in a vacuum vs. in the material
n= Vv / Vm = velocity of light in vacuum / velocity of light in material
denser materials have higher RI (slow light velocity)
angle of refraction
is proportional ton the difference in RI between the two materials
snells law
critical angle (CA)
he minimum angle of incidence inside the mineral at which the refracted light angle in the lower-index medium reaches 90°, grazing along the interface. Beyond this angle, light cannot escape the mineral and is totally internally reflected.
important when cutting gemstones (so they the most sparkle)
petrographic microscope
•Relatively inexpensive
Provides a very large amount of information
•Mineral ID in rock samples
•Estimating composition of some solid solution series
•Mineral abundances, morphology (2D), size range, abundance
•Rock textures / micro-structure
•Genetic information!
polished thick section
A thicker type of polished section (100+ micrometers) typically prepared for sulphide ore samples
• Used for reflected light polarized light microscopy.
grain mount slide
individual grains immersed in oil and covered with glass
useful to study asbestiform minerals, zeolites
round epoxy grain/ sample mount
sample mounted in epoxy puck and polished
used for small individual grains such as zircons for U-Pb dating, or minerals for EPMA work
used for sulphide-bearing samples for examination by reflected light microscopy, and EPMA work
anisotropic materials
different light velocity in different directions- change when stage is rotated in XPL
show double refraction
non-isometric
have birefringence
uniaxial and biaxial
isotrophic materials
identical light velocity in all directions- stays black when the stage is rotated in XPL
isometric minerals
materials with no internal structure- glass
uniaxial minerals
have two different refractive indices
crystal systems where a = b ≠ c
tetragonal, trigonal, hexagonal
biaxial minerals
have three different refractive indices
monoclinic, orthorhombic, triclinic
birefringence
Double refraction of light in a transparent ordered material resulting in orientation-dependent differences in refractive index.
parallel extinction
extinction parallel to cleavage planes
only occurs in minerals with 90 degree crystal axis angles (trigonal, hexagonal, tetragonal)
retardation
Phase shift between the polarization component projected along the fast axis and the component projected along the slow axis.
the amount by which the slow wave falls behind the fast wave during passage through an isotropic crystal
= thickness x birefringence
optic sign
birefringence (B) = |nε-nω|
is positive or negative depending on which is more
uniaxial negative
ε<ω
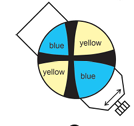
uniaxial positive
ε>ω
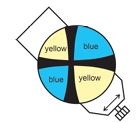
biaxial negative
γ-β<β-α
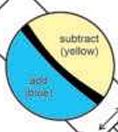
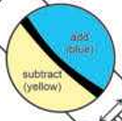
biaxial positive
γ-β>β-α
melatope
Point in an interference figure corresponding to direction of an optic axis in the crystal section ( middle of cross)
isogyre
Dark shadow in an interference figure, usually as a cross (uniaxial) or bands (biaxial)
isochromes
Curve in an interference pattern where colour is identical (rings around the cross/ coloured sections)
Mineral ID in thin section
Hand sample and thin section broadly: What type of rock? Can you visually ID the mineral?
2. Examination in plane polarized light
• If opaque, use reflected light
• Color, Pleochroism
• Crystal shape, habit
• Cleavage
• Relief
Examination in cross-polarized light
• Isotropic vs Anisotropic (if the latter, continue)
•Maximum birefringence
• Extinction angle
• Twinning
4. Interference figure (Bertrand lens)
• Uniaxial or Biaxial
• Optic sign (+ or -)
• If biaxial, estimate 2V angle