Test 1 General Nuc Med Fall 2024
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Which of the following is not considered a route by which a nuclear medicine drugs can be administered:
Topically applied (rubbed on to) to the skin
Which of the following are reasons why PET is considered better/superior when compared to SPECT imaging?
The patients receive much less radiation from the radiopharmaceuticals
The images have much better resolution
Which of the following are reasons why SPECT imaging is considered better/superior when compared to planar imaging?
-It has better resolution than Planar images
-It has better diagnostic sensitivity than Planar imaging for most exams
-It has better contrast between normal and abnormal regions than a Planar image
Static/Planar Image
Image of a single view acquired for a set period of time or counts
Dynamic/Planar image
A series of images of a single view aquired for a set period of time or counts which when viewed together forms a movie
Whole Body Image
An image involving scanning/moving the camera from the top of a patient down to their feet
SPECT Image
A 3 dimensional image of a patient produced by rotating the camera around the patient and then reconstructing the data into a model which can be cut into slices
PET Image
A 3 dimensional image of a patient using a ring of detectors surrounding the patient which detect coincident photons being emitted by positons anhilating
Select all of the answers that will impact how well (how efficient) a radiopharmaceutical will be deposited at a desired site
- the efficiency of the mechanism of localization
- the concentration of the radiopharmaceutical in the bloodstream
- how much blood flow is going to the organ being imaged
Your clinic has started performing a new nuclear medicine exam which evaluates patients for the presence of damage to the mid brain in an attempt to diagnose Parkinson's disease. Unfortunately, because the drug is similar in structure to cocaine, a very small percentage (approximately 1%) of patients will develop confusion and migraine headaches upon administering the radiopharmaceutical. Luckily the symptoms pass quickly and typically do not cause long term effects. This risk of developing confusion and migraines would be considered a:
Clinical warning for the exam
A patient has been experiencing intense abdomen pain followed by nausea and vomiting every time they eat hamburgers and french fries. After establishing that the patient isn't allergic to the food in question and that the food is actually tasty as well as safe to eat for other patrons, a nuclear medicine exam has been ordered to evaluate the cause of the patients abdomen pain. In this particular case the abdomen pain would be considered a:
Clinical indication for the exam
A patient scheduled for a nuclear medicine exam to evaluate their heart (because of chest pain) was just diagnosed with a large blood clot in their lung (a pulmonary embolism). If the exam proceeds, the patient may experienced significant adverse effects, even death. The condition could be considered a:
Contrindication for the exam
These substances are designed to be used in conjunction with radiographic exams and they help visualize organs better. They typically are made from metals like iodine or gadolinium that readily absorb radiation. Although they are used for diagnostic purposes, they often have a direct effect on the patients physiology and they may cause symptoms in a patient.
A contrast agent
These substances are designed to ablate or destroy tissues using isotopes emitting high energy particles.
A therapy radiopharmaceutical
These substances are designed so that they have no direct effect on the patients physiology but instead allow biologic processes to be imaged, measured, or monitored using isotopes.
Diagnostic radiopharmaceutical
When setting up an imaging exam to look at a patients bones you have been asked to optimize the imaging parameters. Your choices are to adjust the matrix size, the pixel depth, and the length of time you will take for each view. Assuming that the patient has enough radioactivity in them to produce a quality image, Answer the following True/False questions:
Using a 64 x 64 matrix image will have far better resolution than a 512 x 512 matrix
False
When setting up an imaging exam to look at a patients bones you have been asked to optimize the imaging parameters. Your choices are to adjust the matrix size, the pixel depth, and the length of time you will take for each view. In the event that the patient has very little radioactivity in them such that there are very few photons coming out of the patient, answer the following True/False questions:
Using a 512 x 512 matrix image will have far better image quality than a 64 x 64 matrix, as long as you only image for a short period of time
False
When setting up an imaging exam to look at a patients bones you have been asked to optimize the imaging parameters. Your choices are to adjust the matrix size, the pixel depth, and the length of time you will take for each view. Assuming that the patient has enough radioactivity in them to produce a quality image, Answer the following True/False questions:
When acquiring the image around the bladder area, you notice that the bladder is extremely hot (radioactive) and there are large areas of artifact within the bladder that appear to have no count's at all. One way to fix this is to increase the pixel depth from 8 bits to 16 bits.
True
Upon completing an image for an exam you notice that the picture looks terrible. It's very pixelated, has lots of background "noise" and it is hard to see any anatomy at all. Which of the following approaches could be used to improve the image quality on future exams?
All of the above
Which of the following is a primary advantage of using hybrid SPECT/CT imaging?
Improved anatomical localization and attenuation correction
Which mechanism of localization is is occurring:
When doing a lung scan looking for pulmonary embolisms, the patient is injected with 99mTc-MAA (small particles of macroaggregated albumin) which lodge in the lungs capillaries.
Capillary Blockade
Which mechanism of localization is is occurring:
When doing a liver scan, particle of 99mTc-Sulfur Colloid are captured by the livers Kupfer cells and eaten.
Phagocytosis
Which of the following is the most appropriate description of "grayscale" when describing a Nuclear Medicine image
The number of shades of grey there are between the darkest and brightest pixel
Which planar imaging technique produces time-stamped data streams that allow flexible post-acquisition binning, but can result in very large data files?
List mode imaging
Which planar imaging technique involves acquiring a single image at one point in time, sometimes with multiple energy windows?
Static imaging
Which planar imaging technique synchronizes image acquisition with the cardiac cycle to evaluate heart motion?
Gated imaging
Why does patient motion reduce diagnostic accuracy in imaging?
It causes streaks, ghosting, or blurring that obscure fine details
When choosing isotopes to perform imaging with on a gamma camera, the isotopes that work best have primary energies >250 kEv, emit multiple gamma ray energies with each decay, and have half lives between 10 days and 30 days.
False
Capillary blockage:
The intentional microembolization of a capillary bed with radiolabeled particles
Active transport/metabolism:
The cell exerts energy to actively move a material from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration as part of a metabolic processes
Phagocytosis:
The mechanism that uses the body’s process for removing waste to entrap the pharmaceutical
Cellular sequestration:
Using the body's process of eliminating damaged red blood cells to image the spleen
Compartmental localization:
The radiopharmaceutical is contained with in a confined space where it diffuses and fills the space
Simple / passive diffusion:
The radiopharmaceutical diffuse and redistribute from areas of high concentration to low concentration
Chemical bonding / adsorption / chemisorption:
The adhesion of atoms, ions, or molecules from a gas or liquid to the surface of a solid or crystal
Antigen / antibody binding:
Using a radiopharmaceutical designed to attach to surface antigens on the targeted cells
Receptor binding:
Targeting membrane proteins that are critical to a cells function
Chemotaxis:
Using leukocyte's ability to migrate to cites of infection
Which of the following are reasons why SPECT imaging is considered better/superior when compared to planar imaging?
It has better contrast between normal and abnormal regions than a Planar image
It has better diagnostic sensitivity than Planar imaging for most exams
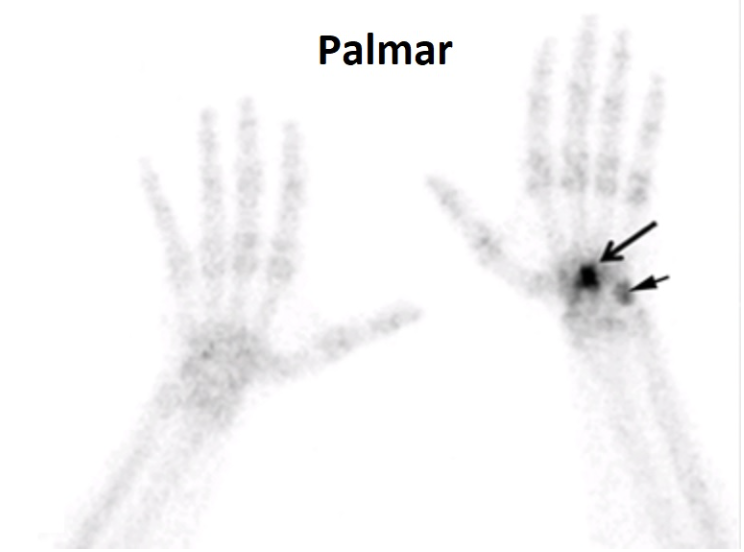
Below is a bone scan image. The patient has a fracture on one of their wrists as indicated by the arrows.
Which wrist is the one with the fracture?
Left
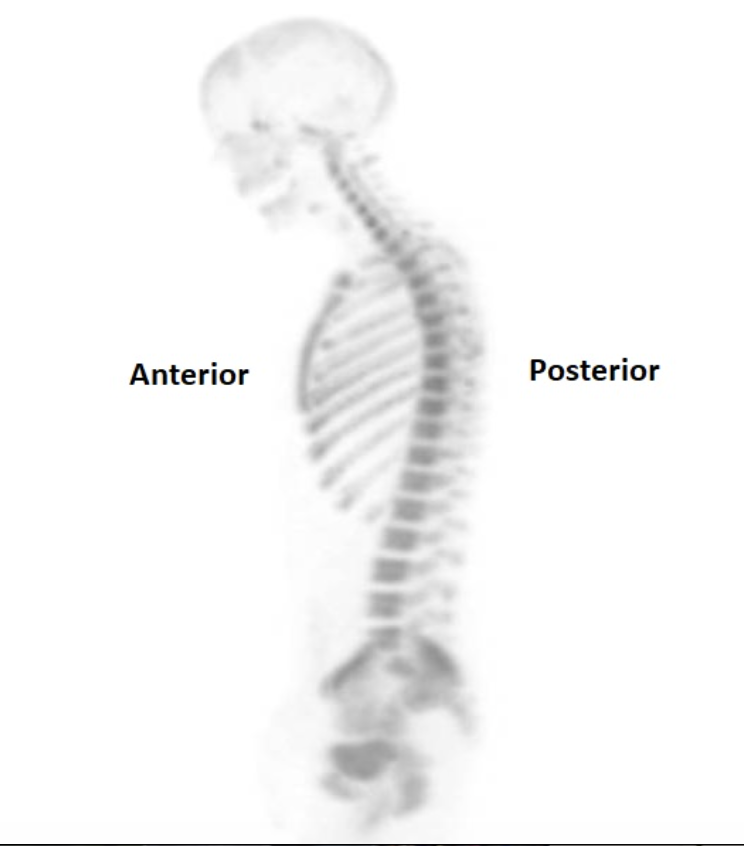
What view does the image below demonstrate?
Left lateral
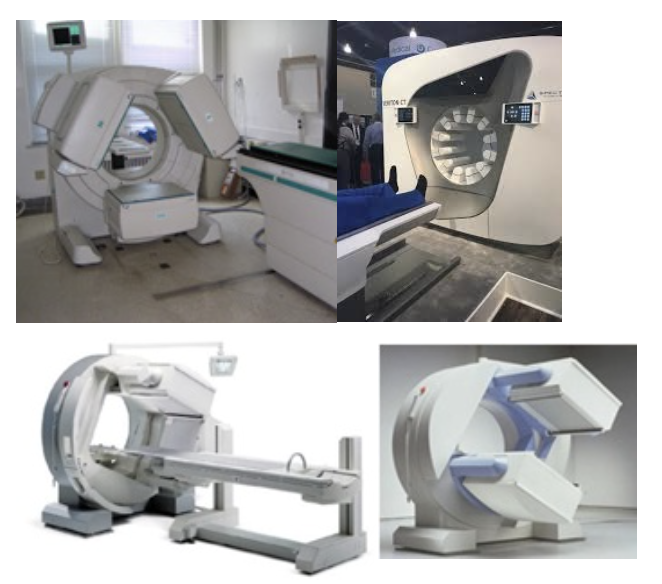
Which gamma camera would be considered the fastest for performing a 360 degree SPECT image?
12 headed gamma camera
Planar Image:
A 2D image of the subject
SPECT Image:
A 3D image produced from taking multiple 2D images from different angles around the subject
PET Image:
A 3D image produced from a ring of detectors around the subject detecting positron annihilation
Dynamic Image:
A series of 2D images displayed in succesion creating an movie
As the amount of scattered photons in a patient increases __________
the resolution of the image decreases
the amount of radiation absorbed by the patient increases
Which mechanism of localization is is occurring:
When looking for a neuroendocrine tumor, the patient is injected with a radiopharmaceutical that looks the the body's protein called somatostatin. Because these tumors, unlike other cells in the body, absorb a lot of somatostatin, we are able to image them.
Receptor binding
Pharmaceutical:
A substance or combination of substances which may be used to restore, correct or modify physiological functions
Diagnostic Radiopharmaceutical:
A radioactive substance which may be used to evaluate physiological functions without altering them
Therapeutic Radiopharmaceutical:
A radioactive substance using a physiologic process to destroy targeted cells
Radiochemical:
A radioactive compound that has not yet gone through the FDA approval process
Scintillation:
Process of capturing photons from an isotope and converting them into electrical signals
How does a smaller number of pixels affect an image?
Larger pixel sizes, less noise, and lower resolution