Anxiety and insomnia
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is the term to describe a feeling of fear, worry and uneasiness, independent to external events or an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively menacing?
Anxiety
What is an alternative definition of anxiety?
Mood state characterised by strong negative emotion and bodily symptoms of tension in anticipation of future danger or misfortune
What can excessive uncontrollable anxiety cause?
Debilitation
What can moderate amounts of anxiety do?
Helps us think and act more effectively
What are the characteristics of fear?
Fear of immediate threat, increased arousal, sympathetic activation, endocrine activation and increased muscle tone - present-oriented
What are the characteristics of anxiety?
Forseen threat, changes = chronic version of fear - future-orientated
What are pathological causes of fear/anxiety?
No/inadequate cause, interferes with daily living
What is the term to describe a group of physical symptoms of fight/flight response that unexpectedly occur in the absence of obvious danger/threat?
Panic
What are the 3 interrelated anxiety response systems?
Physical, cognitive, behavioural
How does the physical response to anxiety occur?
Brain sends messages to sympathetic nervous system, fight/flight response
How does the cognitive anxiety response occur?
Activation leads to feelings of apprehension, nervousness, panic and difficulty concentrating
How does the behavioural system of anxiety occur?
Aggression coupled with desire to escape threatening situation
What are physical symptoms of anxiety?
Increased HR, Fatigue, increased respiration, nausea, stomach upset, dizziness, blurred vision, dry mouth, muscle tension, heart palpitation, blushing, vomiting, numbness, sweating
What are cognitive symptoms of anxiety?
Thoughts of being scared/hurt, thoughts or images of monsters, self-deprecatory or self-critical thoughts, blanking out, difficulty concentrating, thoughts of inadequeacy, bodily injury, appearing foolish, thoughts of going crazy or contamination
What are behavioural symptoms of anxiety?
Avoidance, crying or screaming, nail biting, trembling voice, stuttering, trembling lip, swallowing, twitching, thumb sucking, avoiding eye contact, physical proximity, clenched jaw, fidgeting
What factors can play a role in causing anxiety?
Genetics, brain biochemistry, overactive fight or flight response, life circumstances, personality - people who have low self-esteem and poor coping skills can be more prone to, certain drugs e.g., recreational or medicinal, tumour of adrenal gland
What is the primary neurotransmitter system implicated in anxiety disorders?
GABA-ergic/y-amnobutyric acidergic system, serotonin and dopamine also linked
What part of the brain is responsible for interpreting inputs and initiating outputs in anxiety?
Amygdala
What part of the brain is responsible for emergency responses that bypass the amygdala and are part of flee, freeze or panic?
Periaqueductal Grey
What part of the brain is part of controlling passive avoidance - caution vs impulsiveness?
Behavioural inhibition system - involving amygdala
What parts of the brain are involved in the limbic system?
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Cingulate gurus
Parahippocampal gyrus
Hypothalamus
Mammillary bodies
Anterior nucleus of thalamus
What is the dysfunction of the neurotransmitters in anxiety?
Decreased 5HT transmission, reduced GABA availability, over-active noradrenergic system, excessive activity in excitatory glutamatergic neurons
What is a diagram showing the Periaqueductal grey area?
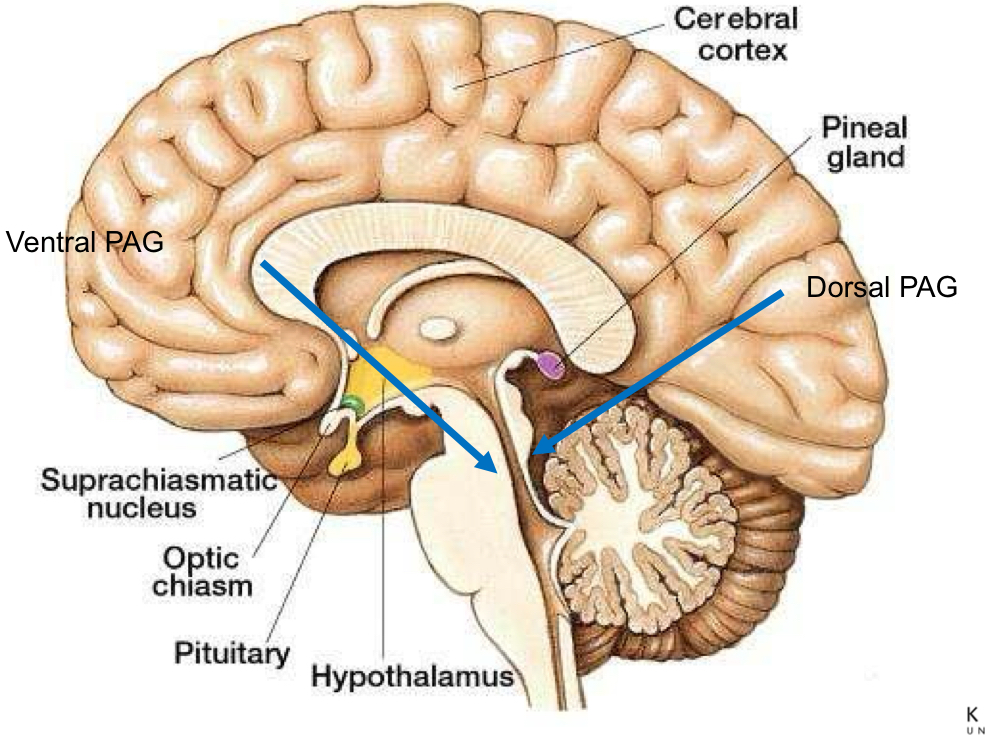
What neurotransmitter inhibits amygdala and in higher doses also PAG?
GABA
What neurotransmitter is pro-anxiety in the amygdala, anti-anxiety in PAG?
5HT
What neurotransmitter is involved in alertness and sympathetic nervous system?
Noradrenaline
What peptides are involved in anxiety?
CCK, NPY
What is the type of anxiety disorder which describes excessive anxiety lacking any clear reason or focus?
Generalised anxiety disorder
What brain areas are involved in generalised anxiety disorder?
Amygdala, cortex and lateral habenula
What are the transmitter paths in GAD?
GABA, serotonin
What is the type of anxiety disorder describing compulsive ritualistic behaviour driven by irrational anxiety resulting in distress?
OCD - obsessive compulsive disorder
What is the anxiety disorder which describes sudden episodic attacks of overwhelming fear with somatic symptoms?
Panic disorder
What somatic symptoms may be present in panic disorder?
Sweating, tachycardia, chest pains, trembling, choking
What is the type of anxiety that describes strong anxiety/fear of a specific object/situation?
Phobias
What is the name of the response that reacts to extreme physical/psychological stress?
Acute stress reactions
What is the type of anxiety triggered by a recall of past stressful experience?
Post-traumatic stress disorder
What part of the brain does PTSD and panic attacks include?
Periaqueductal grey area inputs LH, outputs - amygdala, hypothalamus and motor outputs
What is a diagram showing the dorsal periaqueductual areas role in PTSD/Panic attacks?
Persistent neuroplastic changes may occur in dPAG that outlast the initial aversive situation
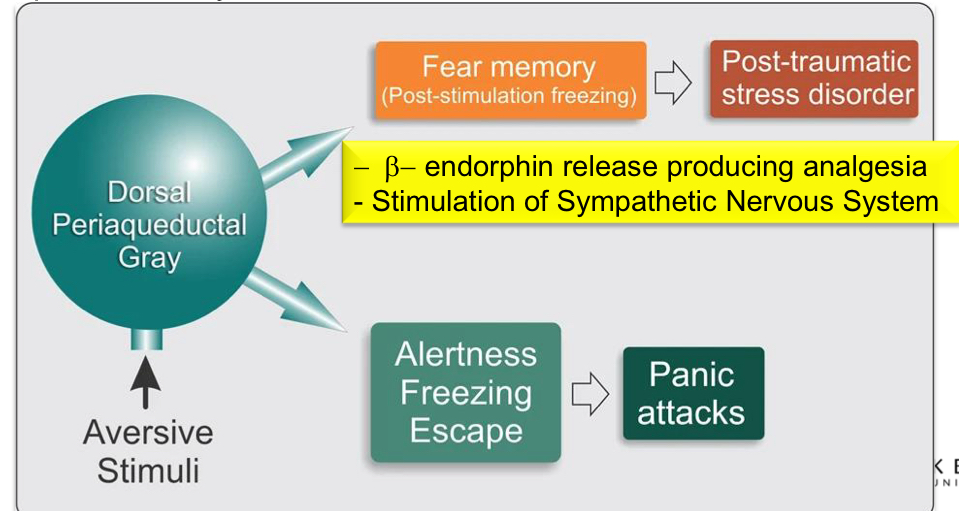
What are the 3 treatment types for anxiety?
Psychological, pharmacological, psychosurgery
What are examples of psychological anxiety treatments?
Relaxation e.g., desensitisation therapy
What pharmacological treatment can be recommended for anxiety?
Anxiolytic drugs e.g., benzodiazepines, anti-depressant drugs e.g., SSRIs, MAOIs, antipsychotic drugs, B antagonists e.g. propranolol
When is psychosurgery considered for anxiety?
Extreme cases of non-responsive OCD
What does CBT focus on?
Development of personal coping strategies that target solving current problems and changing unhelpful patterns in cognitions, behaviours and emotional regulation
What can be taught in CBT?
Teaching pt to react differently to situations and bodily sensations that trigger anxiety, teaches pt to understand how thinking patterns that contribute to symptoms and change how they perceive anxiety feelings
What are the benefits of exercise for anxiety?
Symbolic meaning, distraction from worries, mastery of a sport, effects on self image, biochemical and physiological changes associated with changes - expels negative emotions and adrenaline out of the body to enter a more relaxed state
What is the MOA of benzodiazepines?
Selective agonist on GABA A receptors, benzodiazepines modulate GABA A receptors opening frequency by changing/exposing GABA binding site and enhance responses to GABA by facilitating the opening of GABA-activated chloride channels as it binds more readily and inhibits neuronal excitability
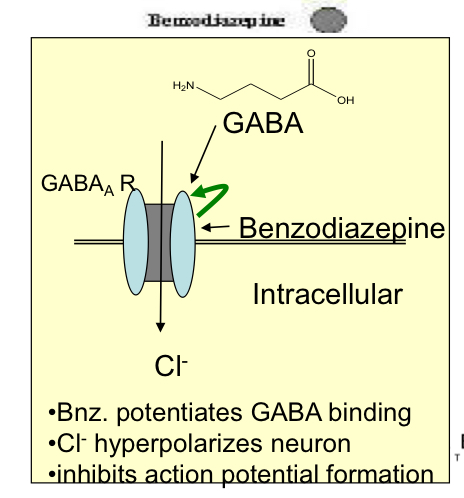
What are the pharmacological effects of benzodiazepines?
Reduce anxiety/aggression, all are sedative, some are hypnotic at high dose or muscle relaxants, some are anticonvulsant, anterograde amnesia
What are some indications for benzodiazepines?
Significant anxiety disorders, transient disabling insomnia, acute seizures, pre-medication and sedation, muscle spasm, alcohol withdrawal
What is an antagonist of GABA?
Flumazenil
What are some ADRs of benzodiazepines?
Respiratory distress and arrest - life-threatening with other CNS depressants (alcohol), CNS side effects such as sedation, drowsiness, ataxia, confusion, amnesia, tolerance and dependance!!
What are benzodiazepines cautioned in?
Liver disease, avoid with alcohol and in pregnancy, elderly, respiratory disorders
What are the contraindications of benzodiazepines?
Respiratory depression and myasthenia gravies
What can drug interactions of benzodiazepines be?
Potentiate other CNS depressants, erythromycin, Ketoconazole, fluconazole all inhibit its metabolism
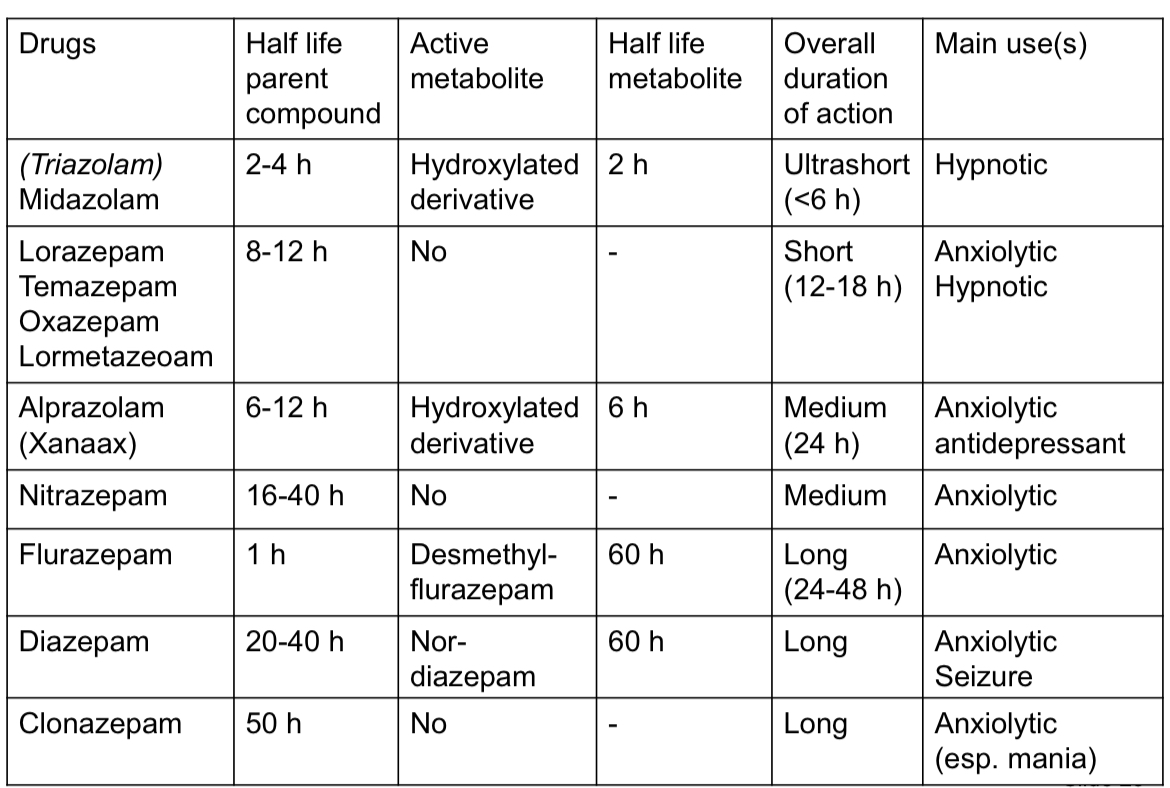
What is a table showing benzodiazepines properties and their uses?
Half life can determine clinical use
What are effects of benzodiazepine toxicity?
Excessive sedation, respiratory depression and coma
What is the risk of driving with benzodiazepines?
Significant crash risk
What is the antidote for benzodiazepine toxicity?
Flumazenil - short duration so dosing may be needed
What symptoms can abrupt withdrawal of benzodiazepines cause?
Insomnia, anxiety, disturbed sleep, vivid dreams - severe can be confusion, convulsion and psychosis, can occur within hours
What can be advice for benzodiazepine withdrawal?
Avoid prolonged treatment, restrict use to less than 4 weeks
Gradual withdrawal over 4-8 weeks
First switch to longer acting benzodiazepine
Dose reduce 2mg diazepam every 2 weeks
May take months or years
What type of drug is buspirone?
Partial 5HT1A agonist
What is the MOA of buspirone?
Inhibits serotonin neuronal firing - anxiolytic action is delayed due to desensitisation, also blocks D3 receptors in striatum
What is an advantage of buspirone?
No dependence, sedation or cognitive impairment
What are the indications of buspirone?
GAD, anxiolytic with slow onset, NOT FOR PANIC ATTACKS
What are the ADRs of buspirone?
Nausea, dizziness, headache, restlessness - NO ataxia, sedation or withdrawal
What is the use of beta blockers e.g., propranolol oxprenolol?
peripheral action - Prominent somatic signs/performance anxiety
What is the MOA of pregabalin?
Blocks Ca+ N channel in neural membranes responsible for linking the action potential to transmitter release so decreased release of many transmitters, increases GABA availability for release by increasing glutamate to GABA
What are positives of pregabalin?
Low abuse potential, less sedative than benzodiazepines, continued effectiveness and well tolerated
What are downsides of pregabalin?
Possible adverse effects wide - regarded as 3rd line
When are benzodiazepines as anxiolytics most effective?
GAD
What affect do antidepressants e.g., SSRIs have on anxiety?
All relieve anxiety disorders
What anxiety disorders is SSRI effective in?
GAD, panic disorders, social phobia, OCD, PTSD
What can be an issue with using SSRIs for depression/anxiety?
Lag-phase - initial anxiety at increase
What are the main medications for GAD?
Benzodiazepines NOT advised
Antidepressants - mostly SSRIs
Pregabalin
What are the main medications for PTSD and panic attacks?
Mainly SSRIs
Pregabalin not licensed, benzodiazepines not prescribed
What are the main medication treatments of OCD?
Strong 5HT reuptake inhibition work - SSRI and venlafaxine, longer to reach full effect
What is the term to describe an inadequate/poor quality sleep accompanied by significant distress or impaired function?
Insomnia
What can be criteria for insomnia?
Takes more than 30-45 mins to sleep
Wake up during the night and cannot sleep again
Wake up feeling unrefreshed
Can only sleep with aid of sleeping aids or alcohol
What is the type of insomnia occurring for less than 4 weeks, triggered by excitement/stress and occurs when away from home?
Transient insomnia
What is the type of insomnia lasting 4-6 weeks, ongoing stress at home/work, medical problems, psychiatric illness, lasts from a few nights to few weeks, caused by worry?
Short term insomnia
What is the type of insomnia categorised by poor sleep every night or most nights for 6 weeks or more, psychological factors, lasts months or years, caused by general anxiety, medications, chronic pain?
Chronic insomnia
What are some possible causes of insomnia?
Changes in sleep pattern due to work/travel
Medical conditions - anxiety, depression, stress,, hyperthyroidism, arthritis, chronic pain, benign prostatic hyper trophy, headaches, sleep apnoea, sleep related periodic leg movement
Using caffeine or stimulants
Using alcohol or other sedatives that can alter normal sleeping patterns
Sleep/nap during day
Death of a loved one, job loss, failing in school
What does treatment of insomnia include?
Alleviates any physical/emotional problems that are contributing to the condition and exploring changes in lifestyle that will improve the situation
What is the main recommended behavioural and environmental practice intended to promote better quality sleep?
Sleep hygiene
What can be some sleep hygiene tips?
Go to bed when sleepy
Only sleep in bedroom
Get up same time every morning
Get up when sleep onset doesnt occur within 20 mind and go to another room
NO daytime naps
What is the aim of CBT in insomnia?
strengthen association between sleep behaviours and stimuli such as bed, bedtime and bedroom surroundings
Consolidate sleep over shorter periods of time spent in bed
What hypnotics can be used for insomnia?
Benzodiazepines
Non benzodiazepines include lipophilic antihistamines, older hypnotics such as chloral hydrate, triclofos, chlomethiazole
When are benzodiazepines used for insomnia?
Used as needed, reduce length of time to fall asleep, used for transient insomnia
What are the issues related to benzodiazepine use in insomnia?
Poor functional day time status, cognitive impairment, daytime sleepiness, falls and accidents, depression and dependence
What is the MOA of Z drugs for insomnia?
Bind GABA A receptor increase and cause Cl- influx
What are the indications for Z drugs?
Short term for insomnia - only for a week
What are the ADRs of Z drugs?
Drowsiness, headache, weakness, dizziness, little/no tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, no muscle relaxation or anti-convulsants
What are the cautions of Z drugs?
Confusion in elderly - half the dose, possible dependence if used long term
What is Z drugs contraindicated in?
Respiratory insufficiency, sleep apnoea, myasthenia gravis
What is a diagram showing action of Z hypnotics related to their half lives?
Indication can depend on half life

What can residual effects of hypnotics be?
Daytime sleepiness - elderly confusion, falls, short half life no guarantee, next-day effects in driving
What is the hormone produced in the pineal gland increase the brains and secreted in dim light and darkness, promoting sleep?
Melatonin
What is the goal with melatonin dosing?
Lowest dose that will help you fall asleep
What is a common side effect of antihistamines that can be used in insomnia?
Sedation e.g., from diphenhydramine, doxylamine
What antidepressants can have sedating effects and can improve quality of sleep?
Serotonin antagonists e.g., trazodone, TCAs e.g., Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine
What is a type of complementary and alternative medicine in which the mind is used in an attempt to help with a variety of problems?
Hypnotherapy