Biology and Behavior
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
Biological Psychology
The scientific study of the links between biological and psychological proceses.

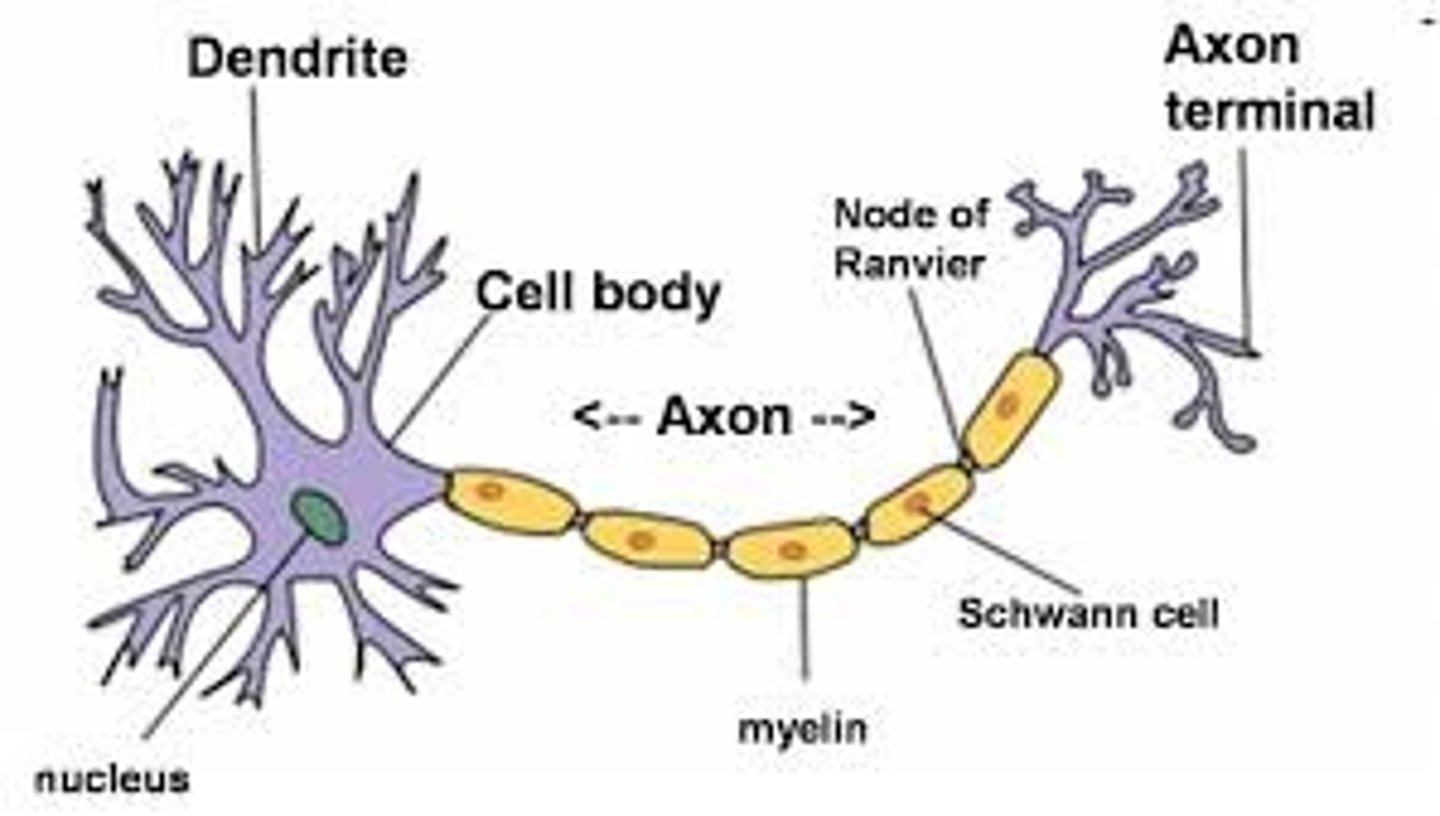
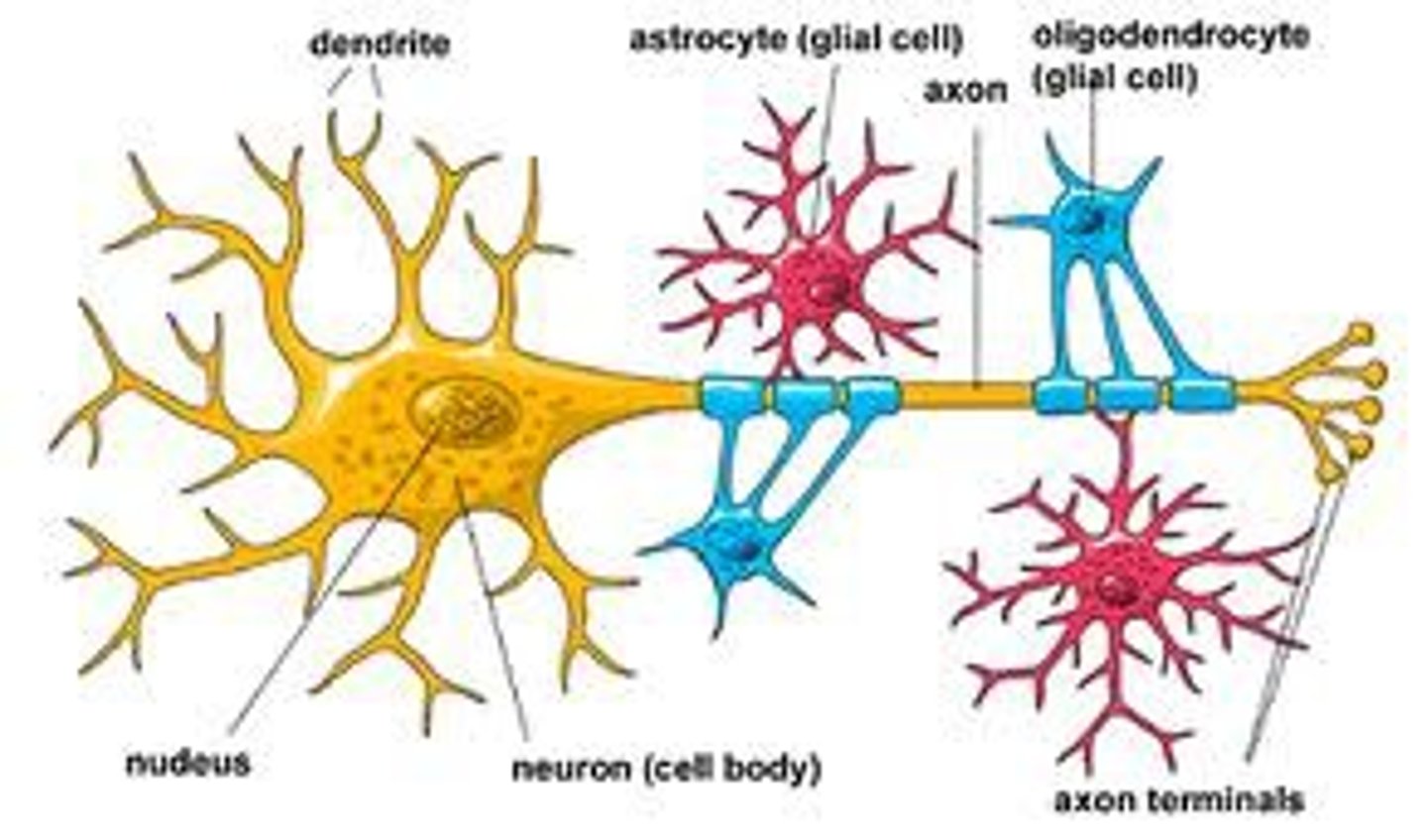
Neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
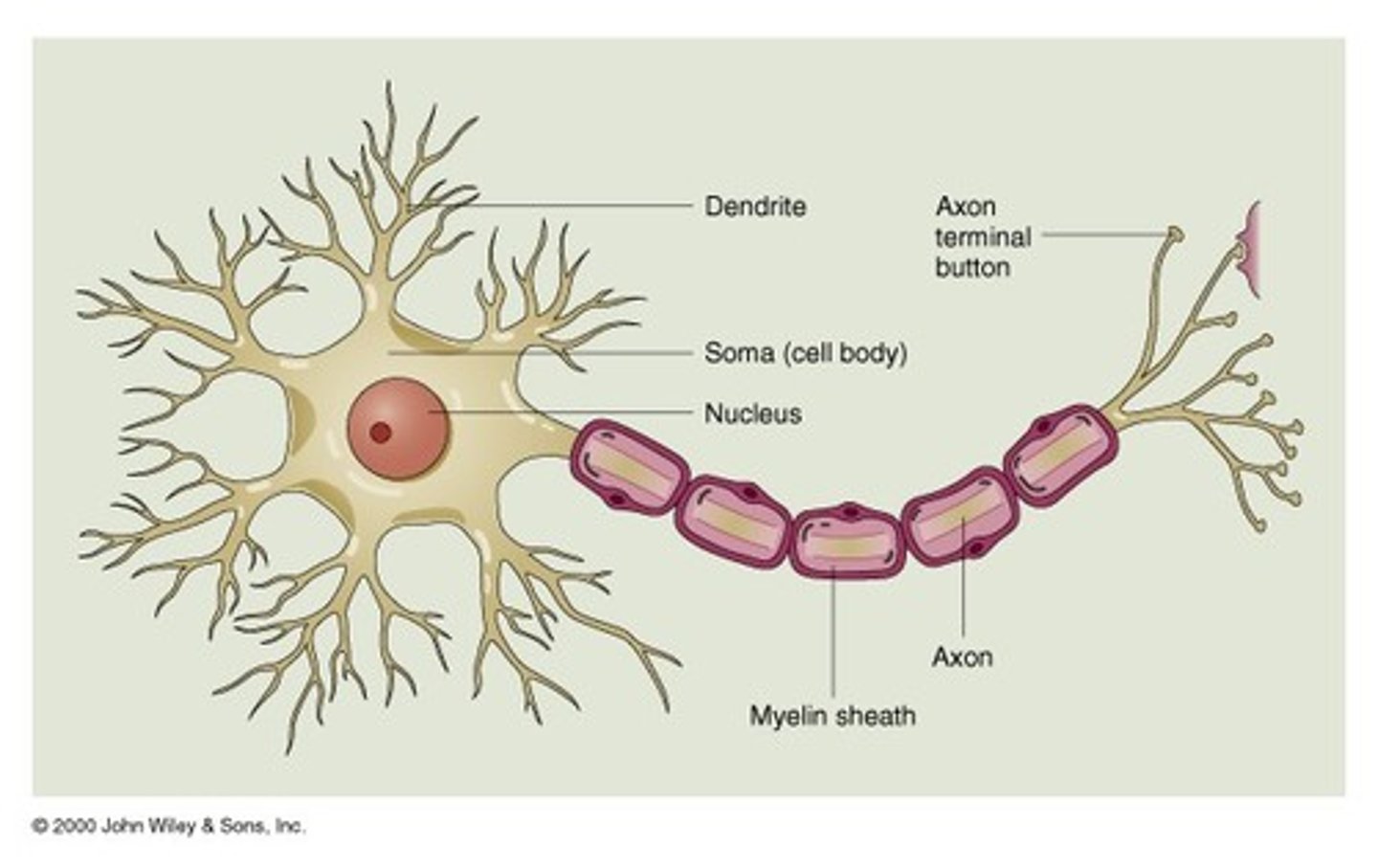
Dendrites
Branching extensions that receive chemical messages from other neurons.
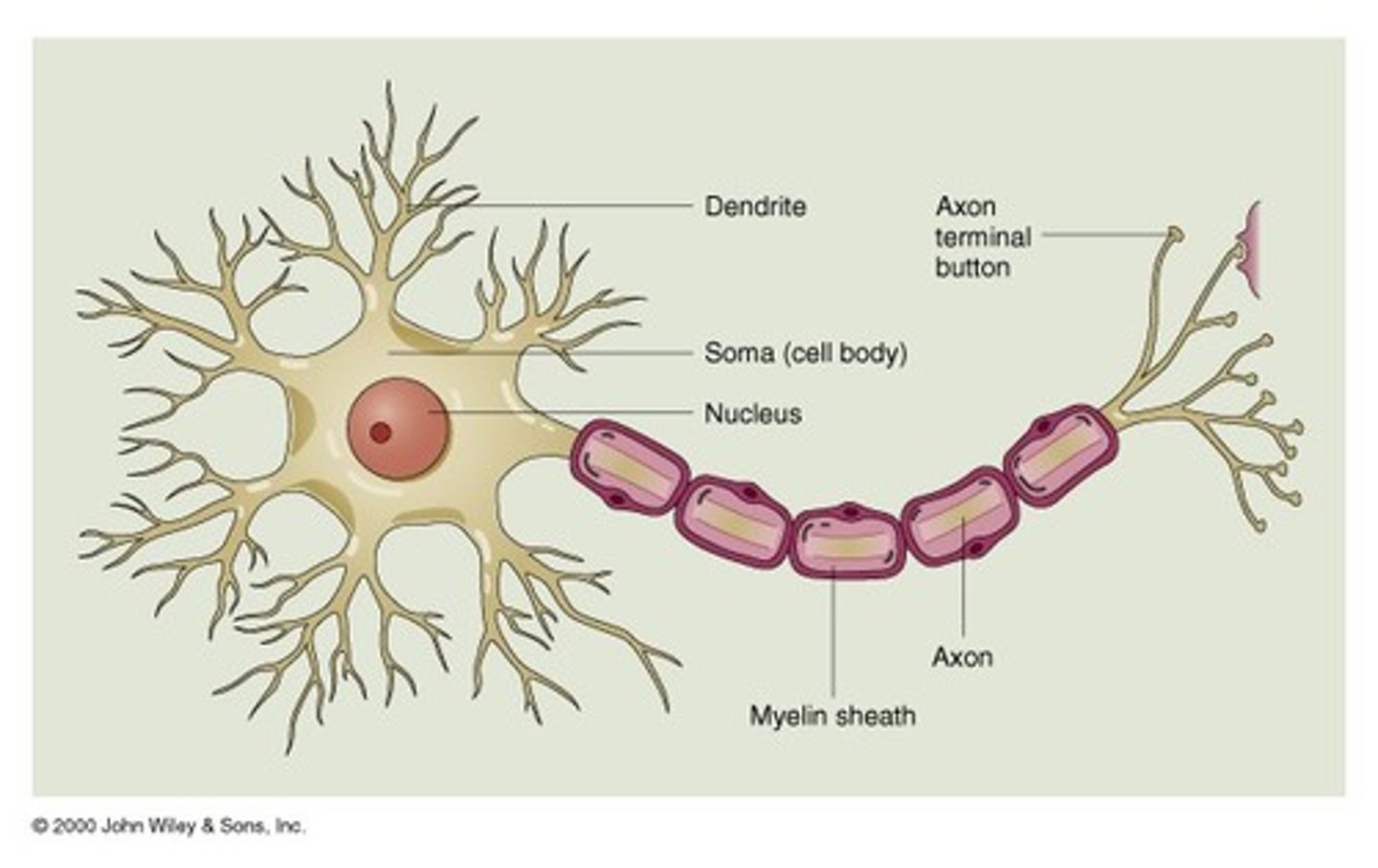
Axon
After threshold level is reached, depolariztion begins down this portion of the neuron.
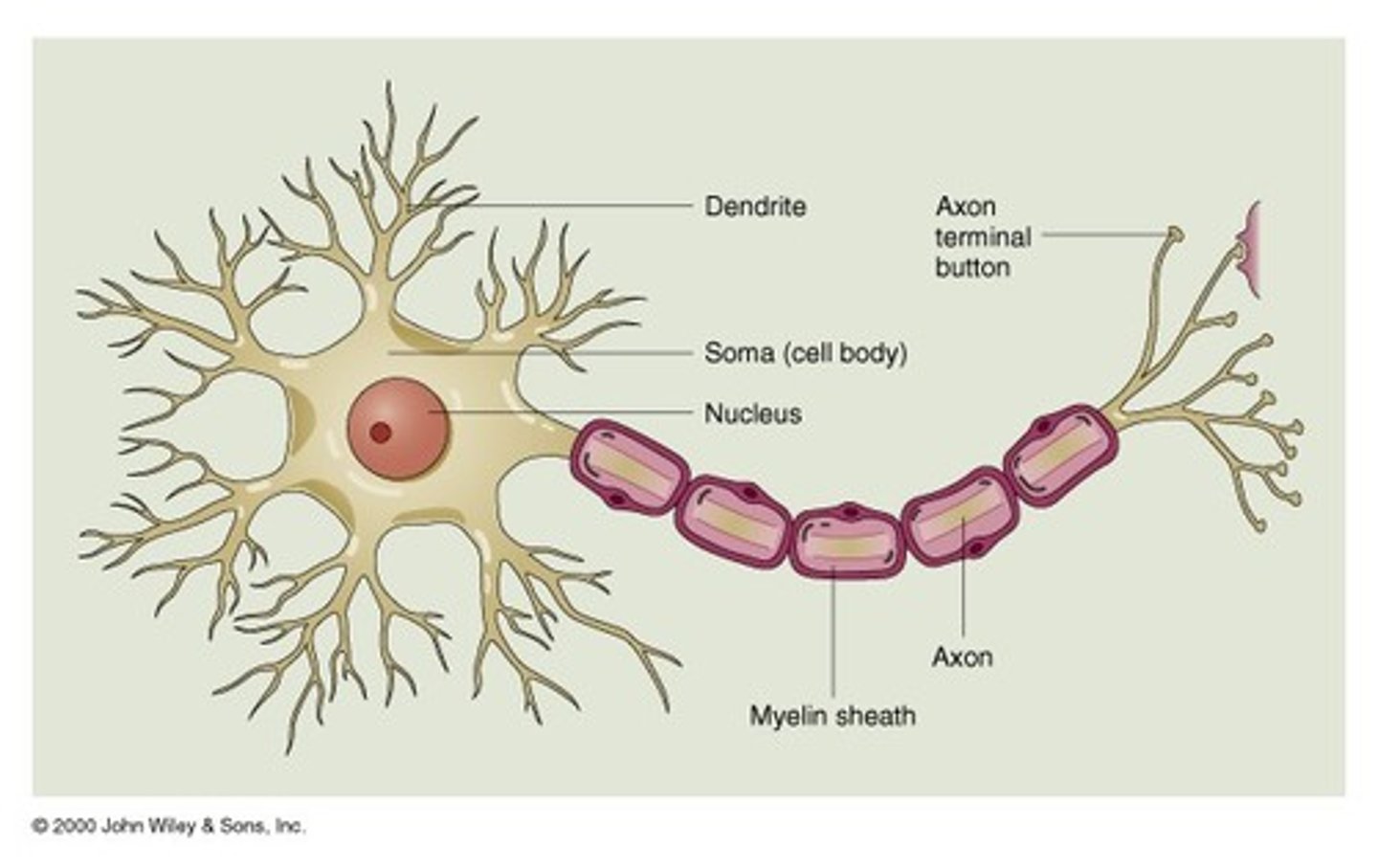
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer of glial cells that encases axon. Allows for speedier communication.
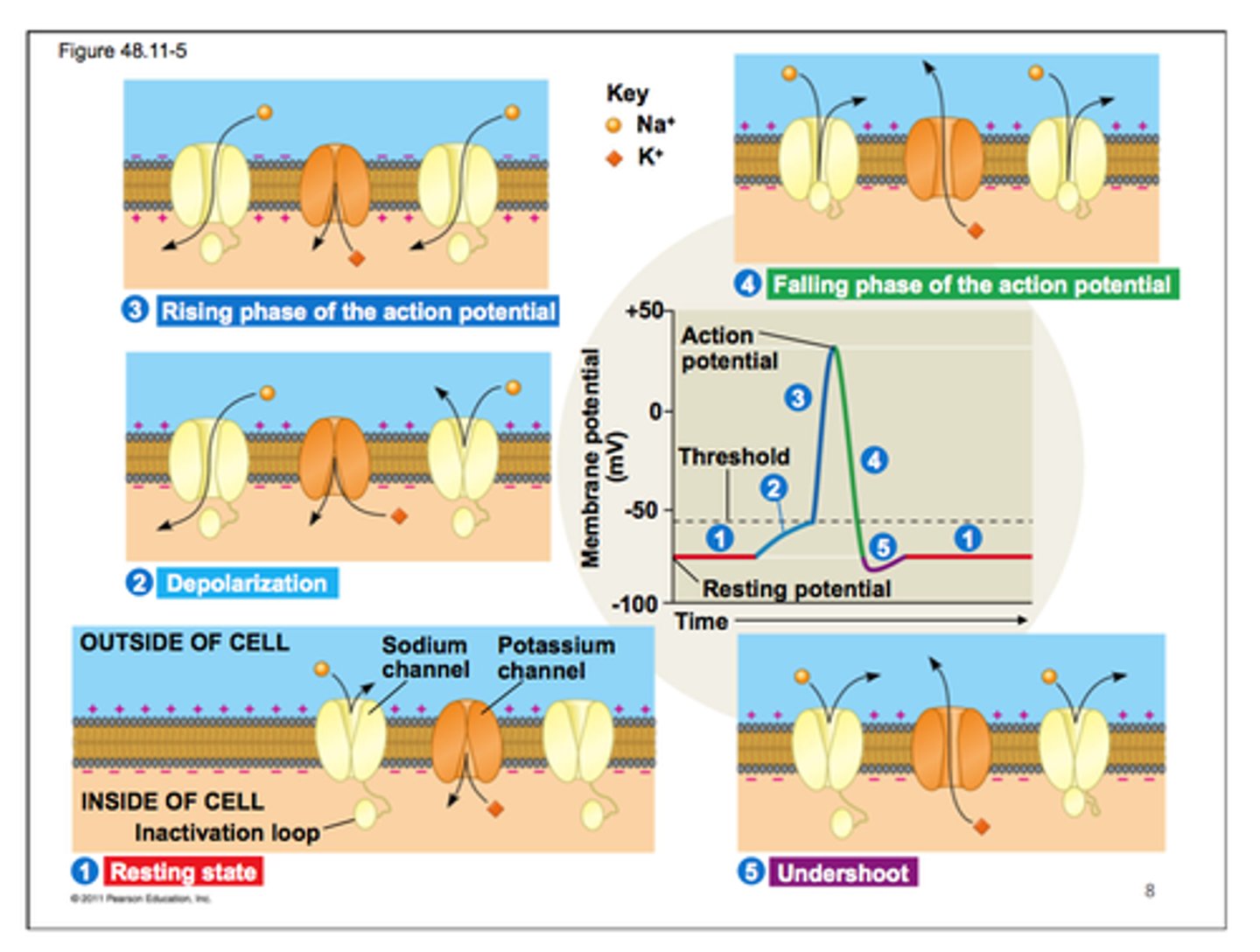
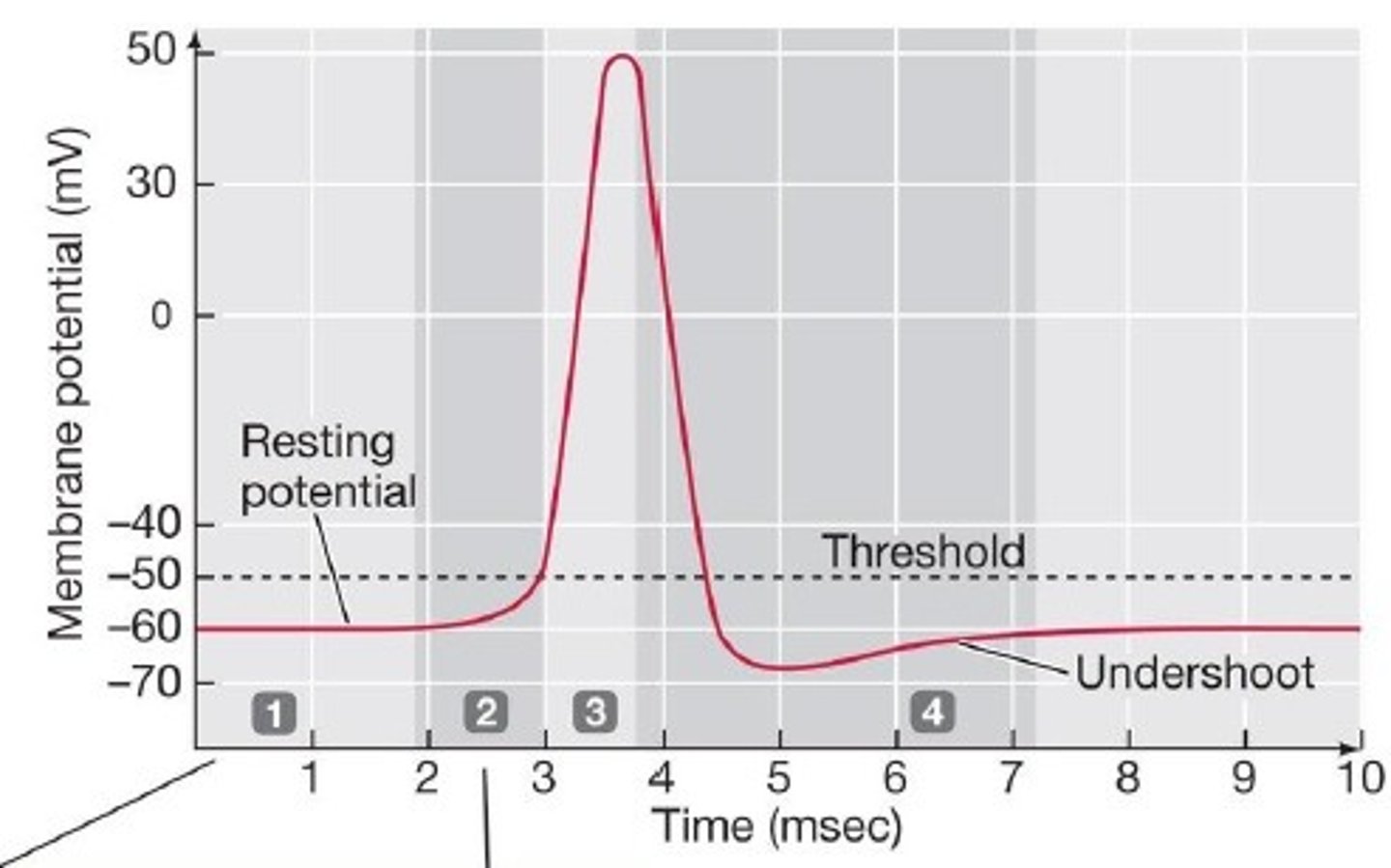
Action Potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
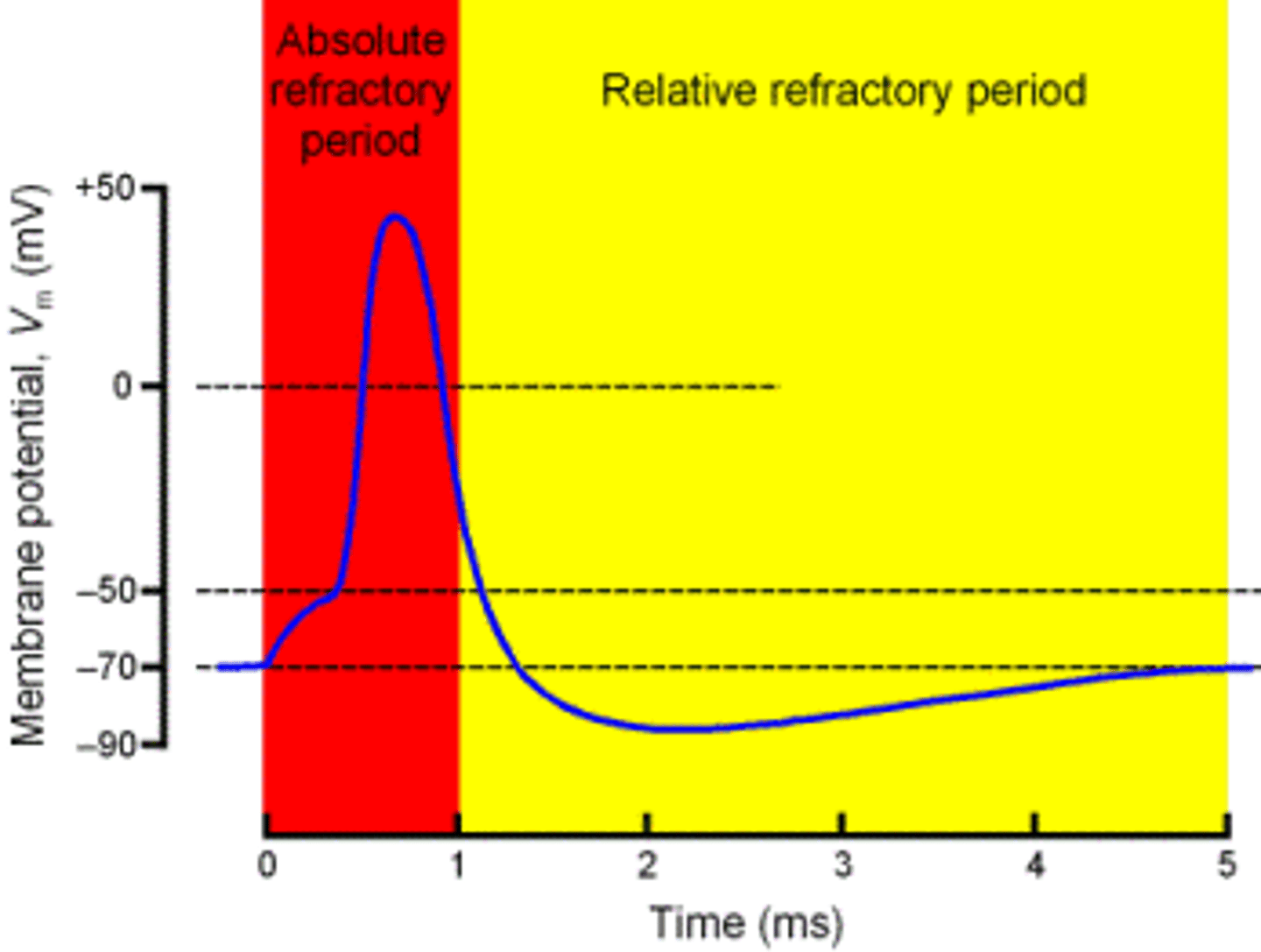
Refractory Period
A period of inactivity after a neuron has fired. The neuron can't fire until it pushes the positive ions back out and "resets" itself.
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse-excitatory signals outweigh inhibitory.
All-Or-None Response
Neuron either fires or doesn't fire.

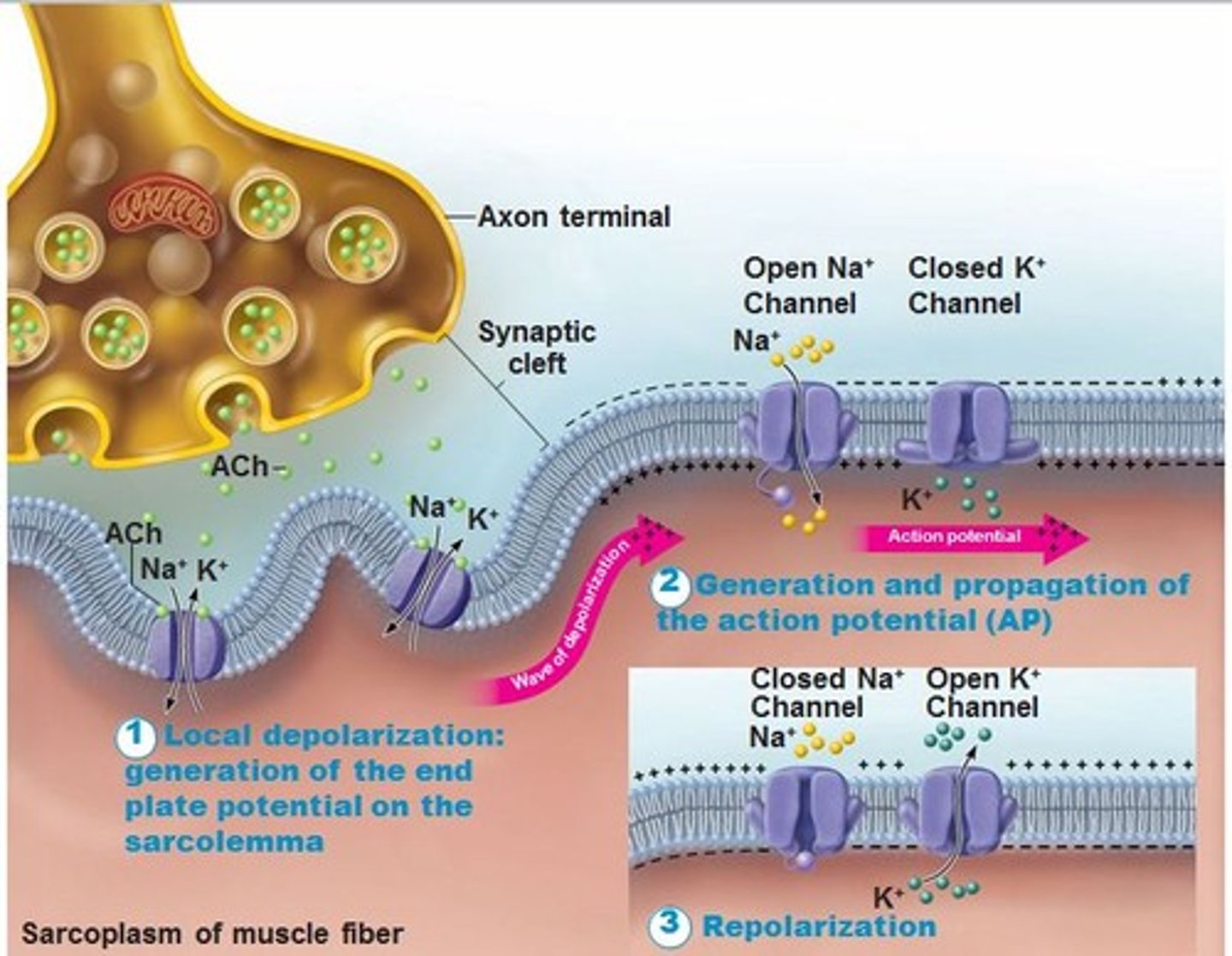
Synapse
Place where chemical communication happens-sending neuron releases neurotransmitters & some connect to dendrite of receiving neuron.
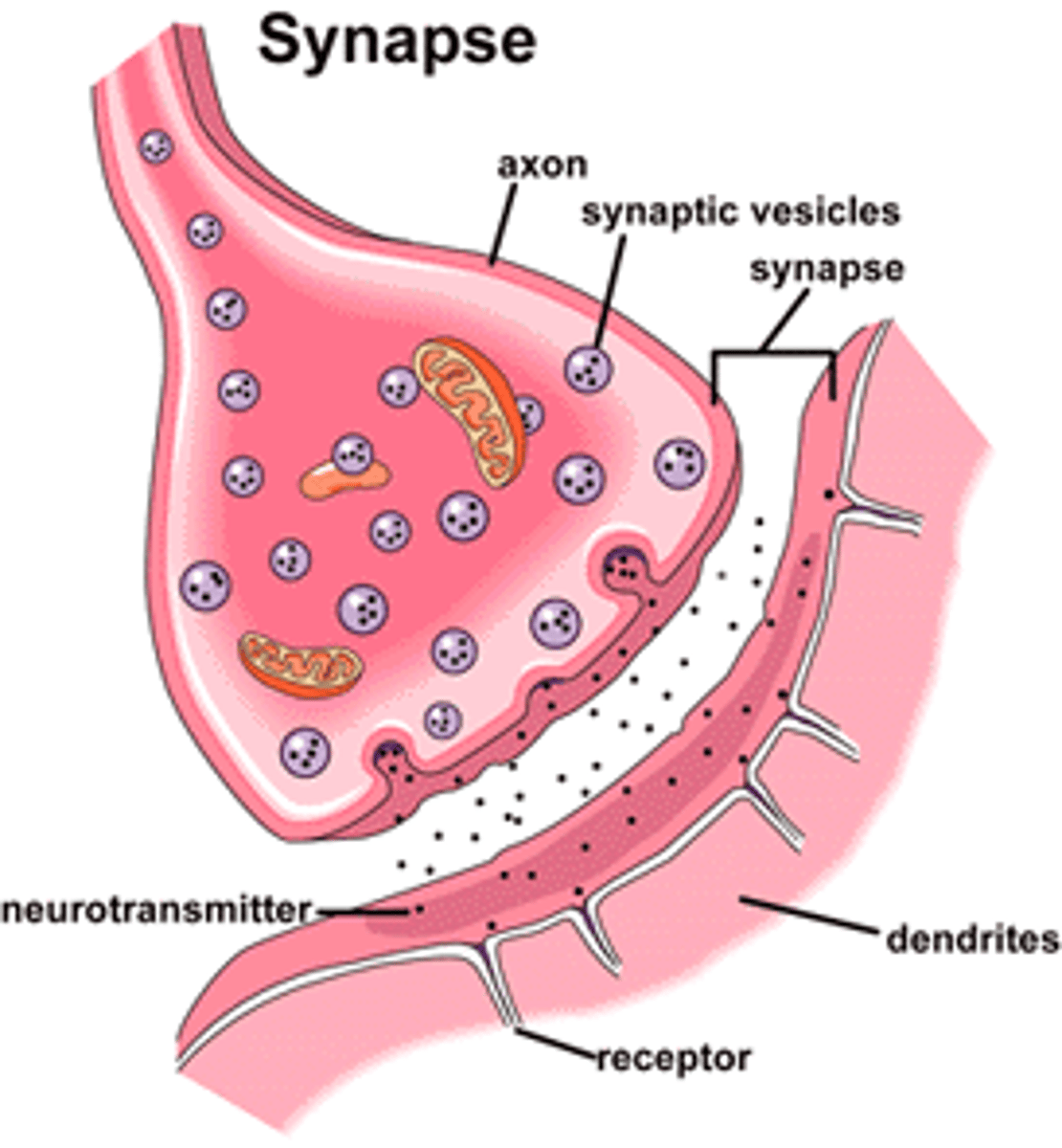
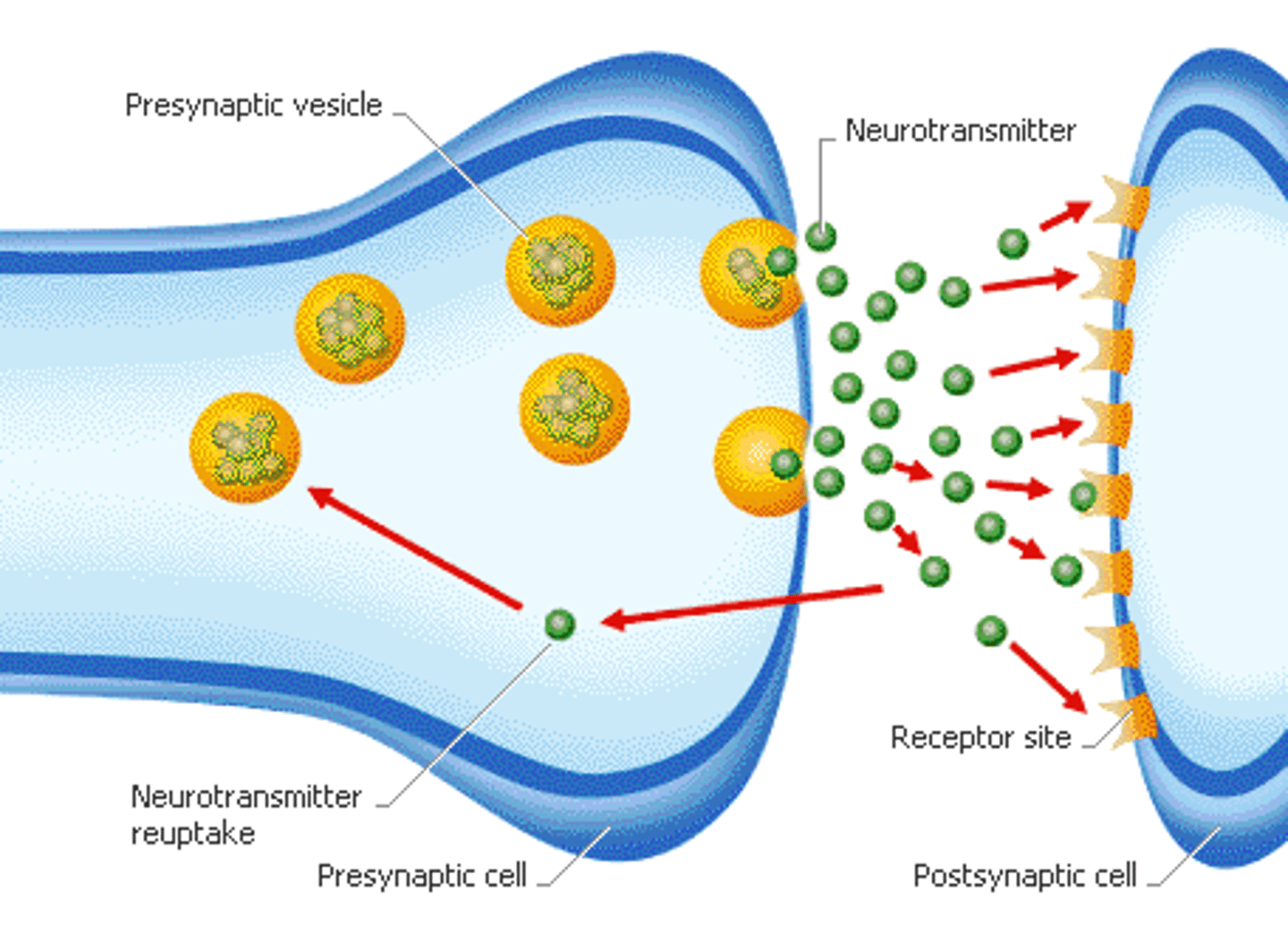
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Enables muscle action, learning, memory. If transmission is blocked, muscles won't contract and paralysis ensues. Also plays a role in Alzheimer's disease.
Dopamine
Influences movement, rewarded learning, attention, emotion. Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply is linked to Parkinson's.
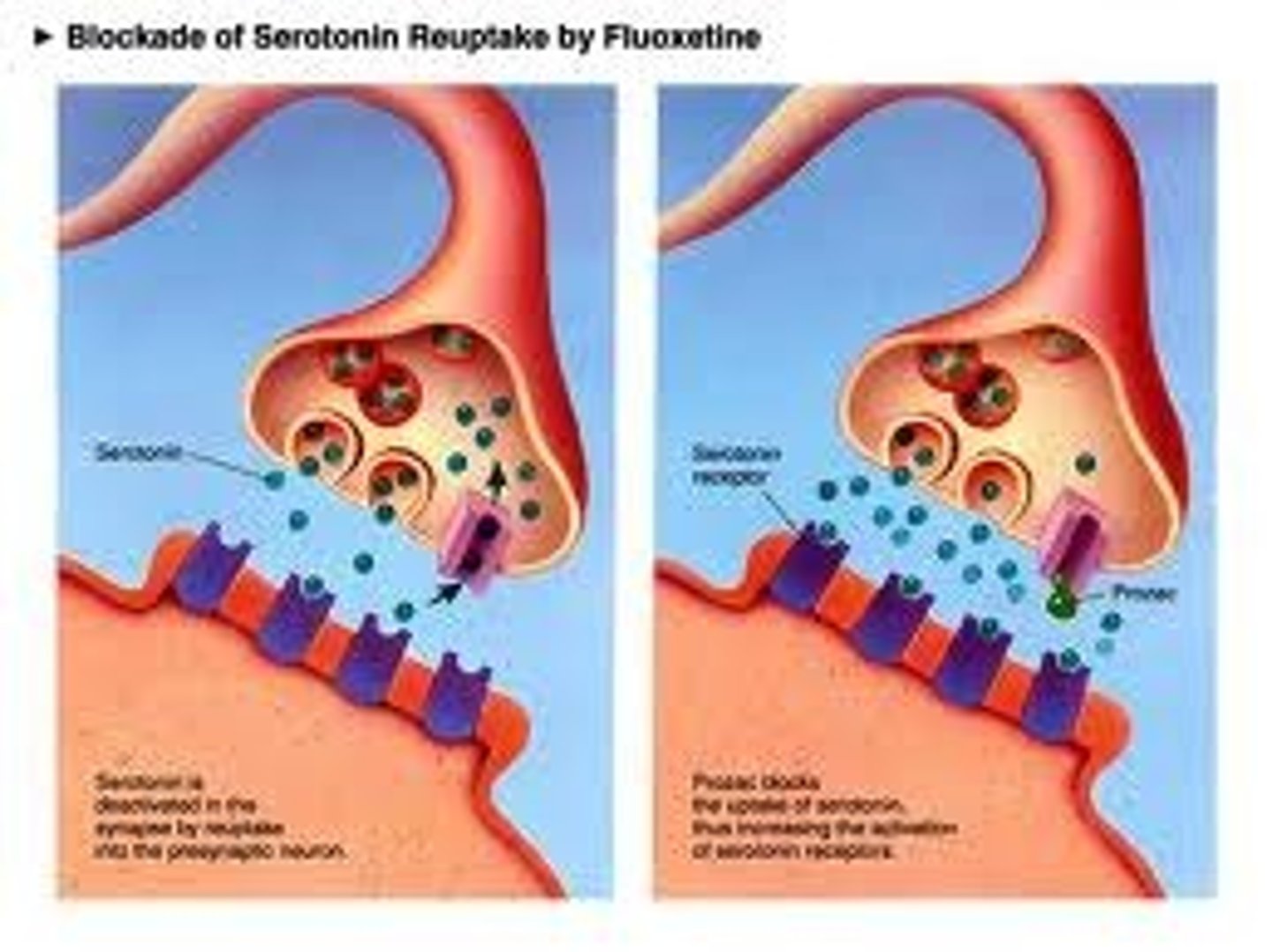
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, arousal. Undersupply linked to depression. Many antidepressant drugs raise its level.
Norepinephrine
Helps control alertness, arousal, fight or flight. Undersupply can depress mood (like serotonin)..
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Inhibitory neurotransmitter-nature's Valium.. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia.
Glutamate
Excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures.
Reuptake
Extra neurotransmitters return to sending neuron-sucked backed up into synaptic vesicles.
Endorphins
Natural morphine linked to pain control and to pleasure-
"runner's high"
Agonist
Drug that mimics neurotransmitter. Fits receptor well and neural firing ensues. Ex: Opiate drugs produce a "high". Black widow spider poison produces muscle spasms.
Antagonist
Drug that inhibits/blocks neural transmission. Fits receptor site poorly. Ex: Botox blocks ACh.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal chord.
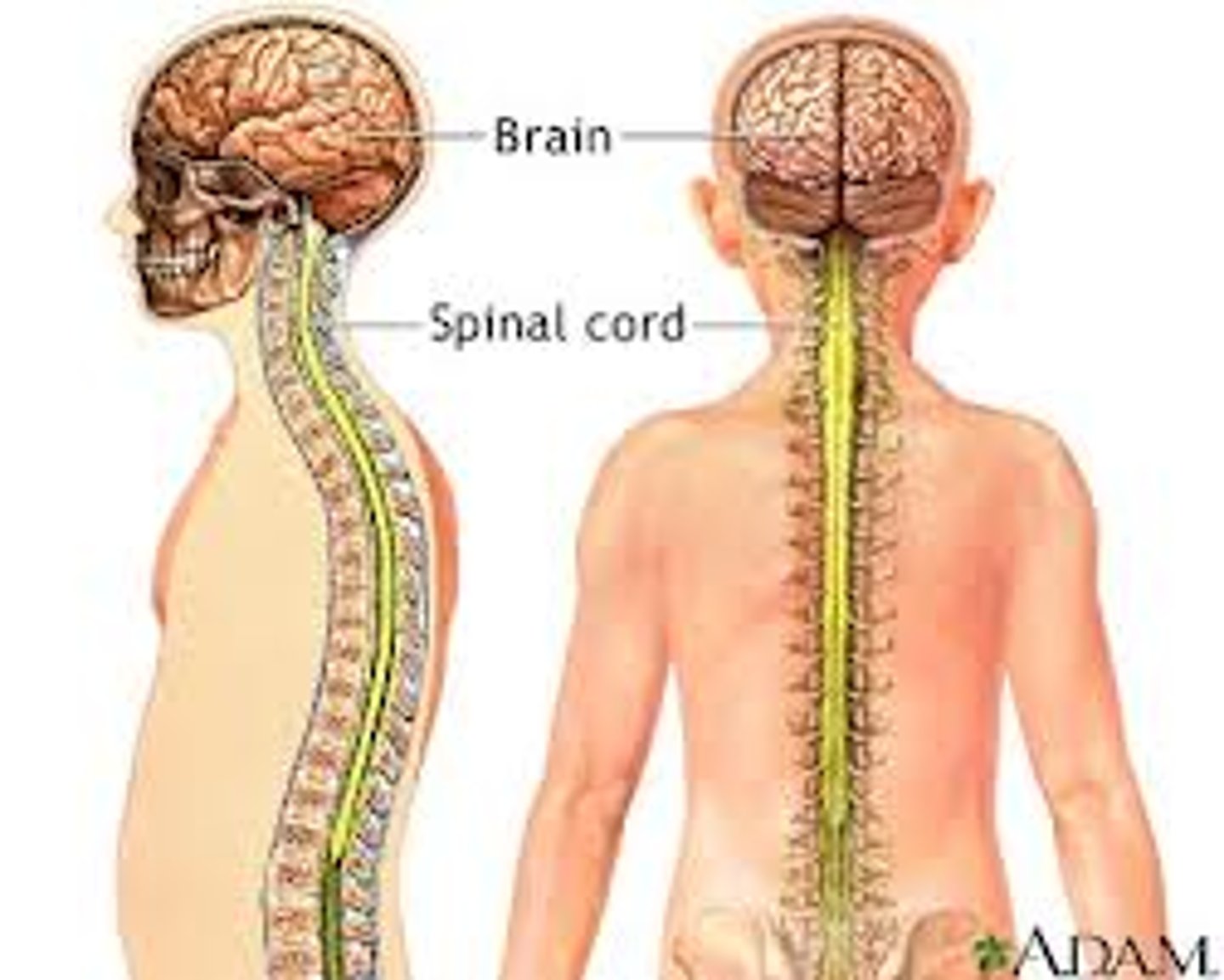
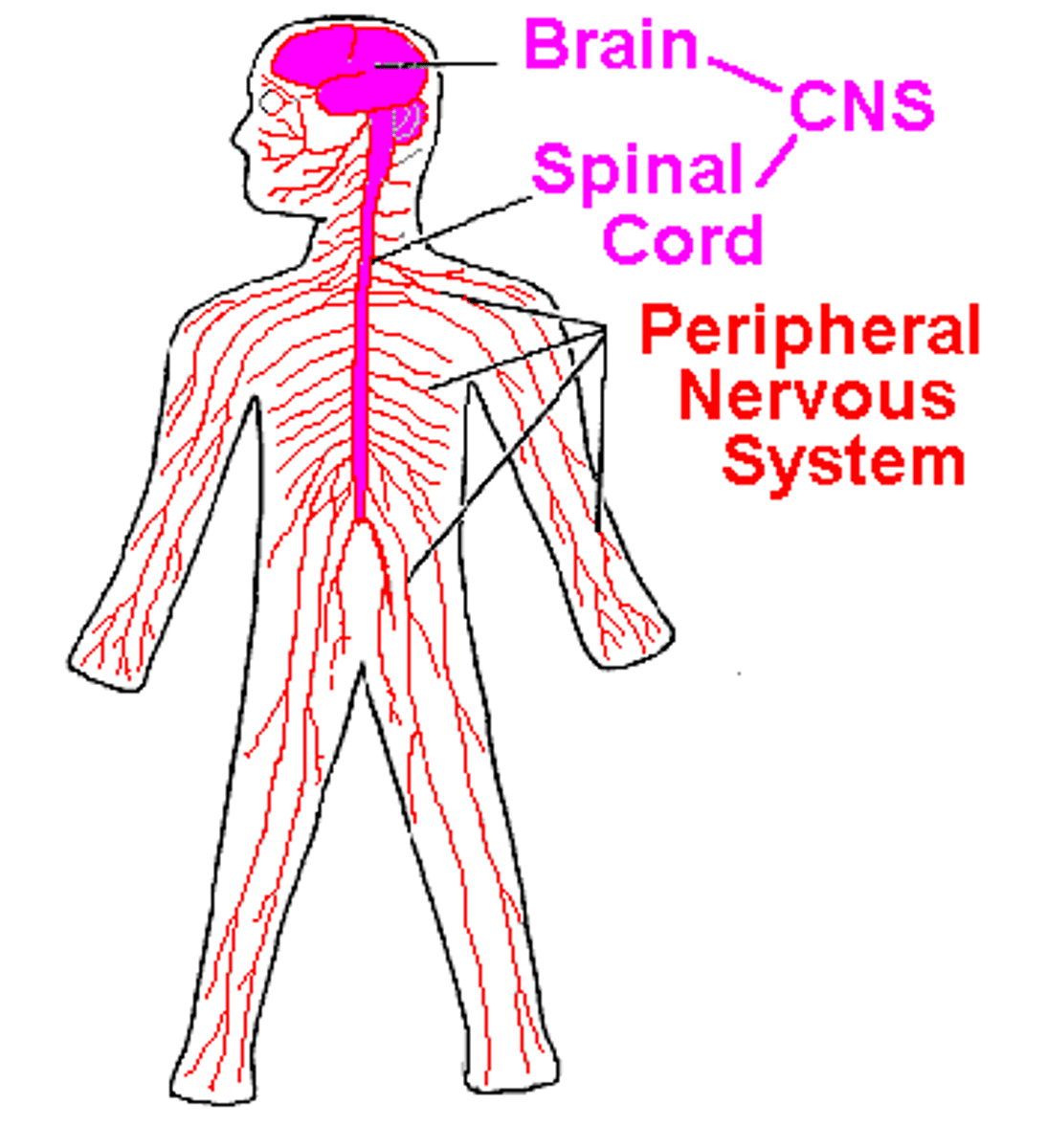
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
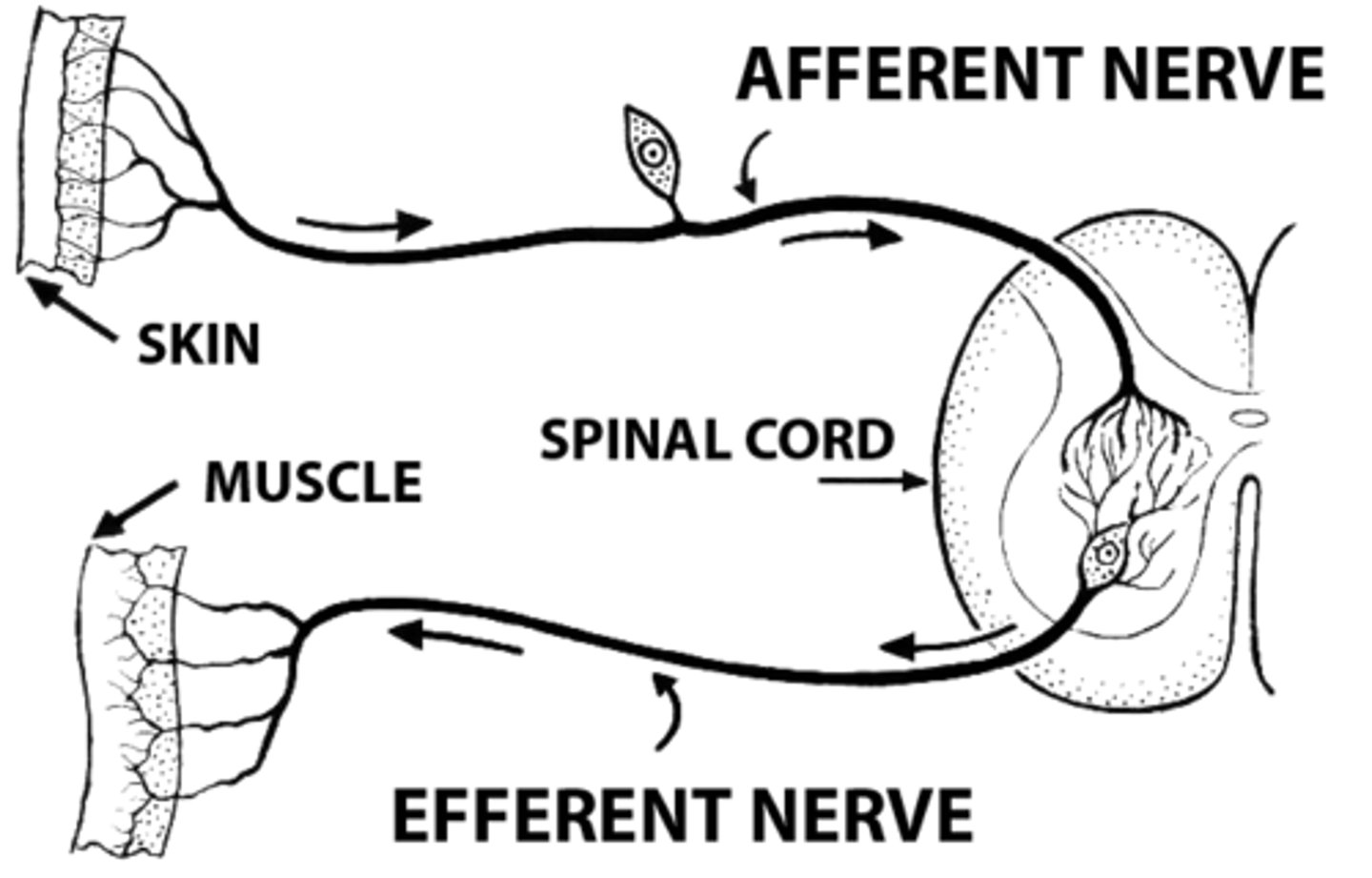
Sensory (afferent) Neurons
Neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
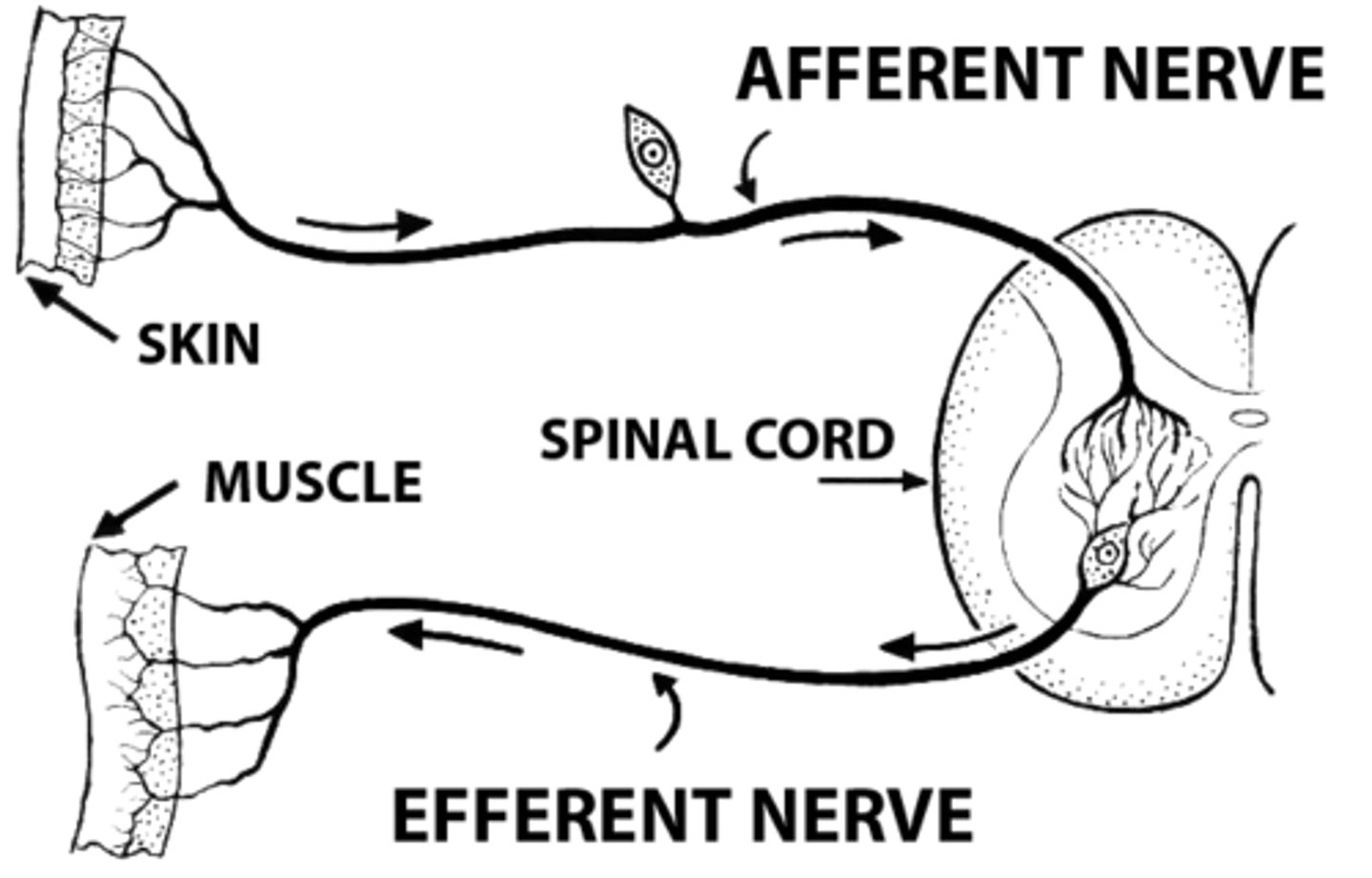
Motor (efferent) Neurons
Neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands.
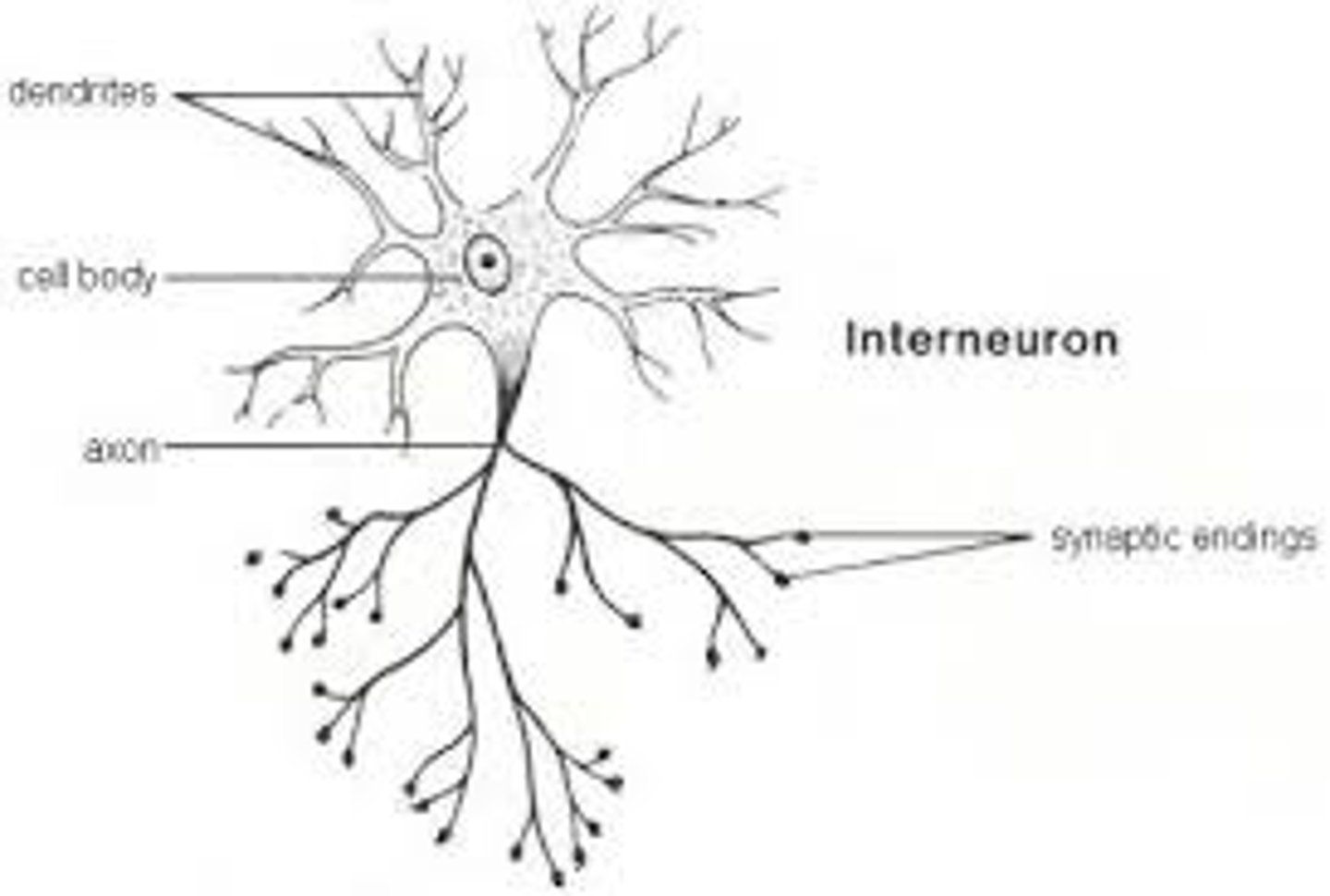
Interneurons
Neurons within brain and spinal cord.
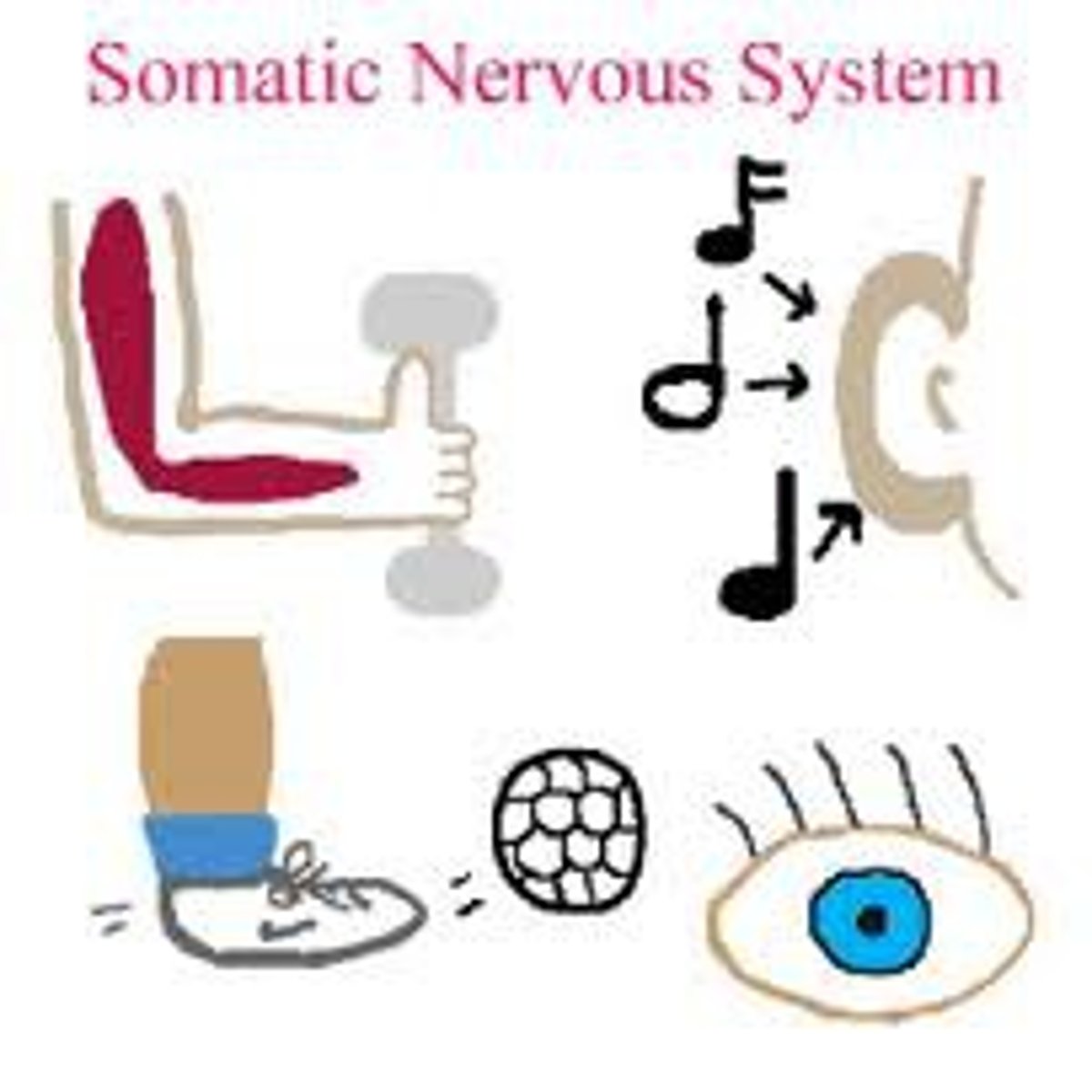
Somatic Nervous System
Division of the peripheral nervous system-controls the body's skeletal muscles. It can be voluntarily manipulated.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
"Automatic" part of peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Division of autonomic nervous system. Arouses body, prepares one to run away or to fight
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Division of autonomic nervous system. Calms body, conserving energy. Decreases heartbeat and lowers your blood sugar.
Reflex
Simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, processed by spinal cord.
Endocrine System
Body's "slow" chemical communication system; set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
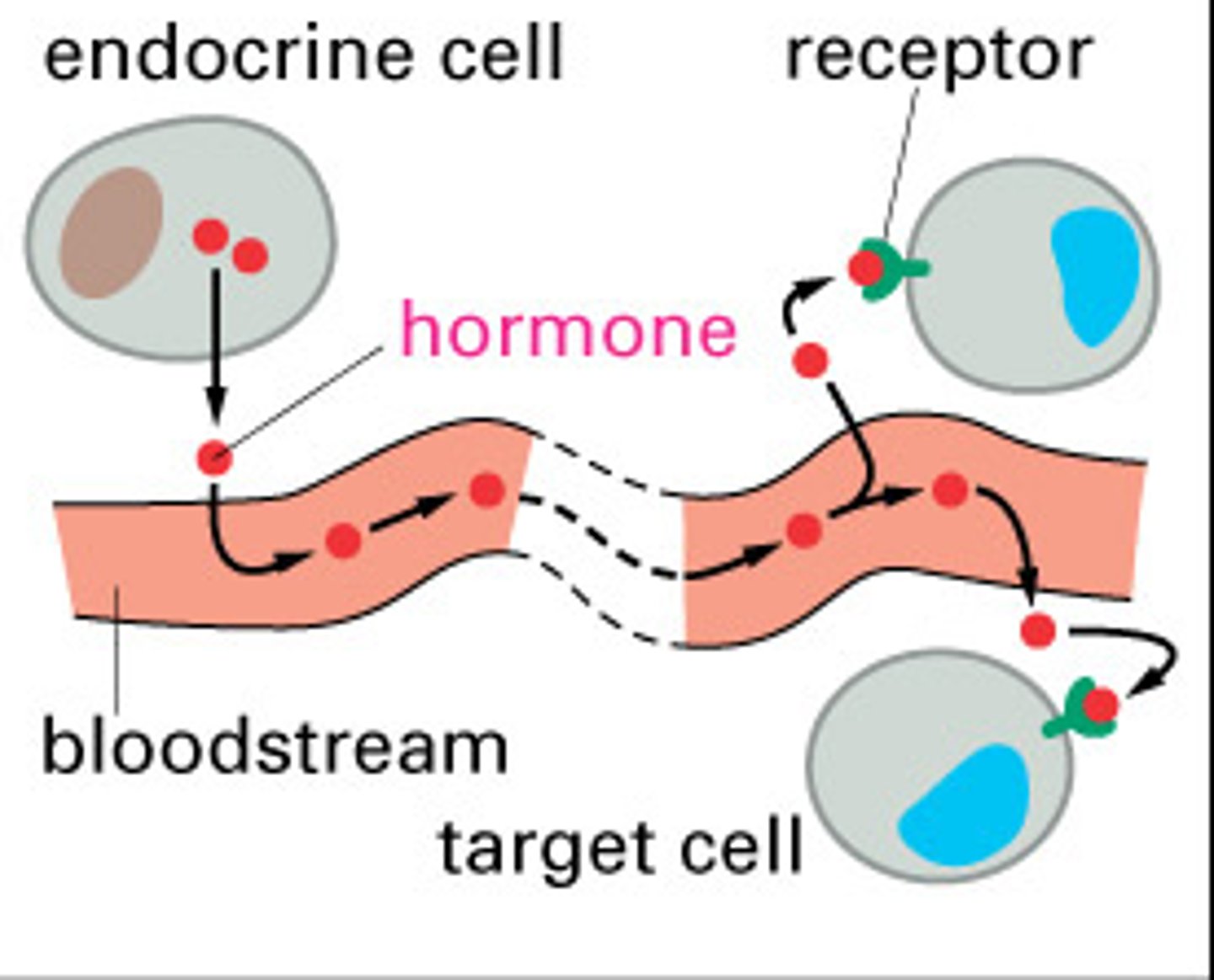
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream.
Adrenal Gland
Pair of endocrine glands that sit just above kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress.
Pituitary Gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
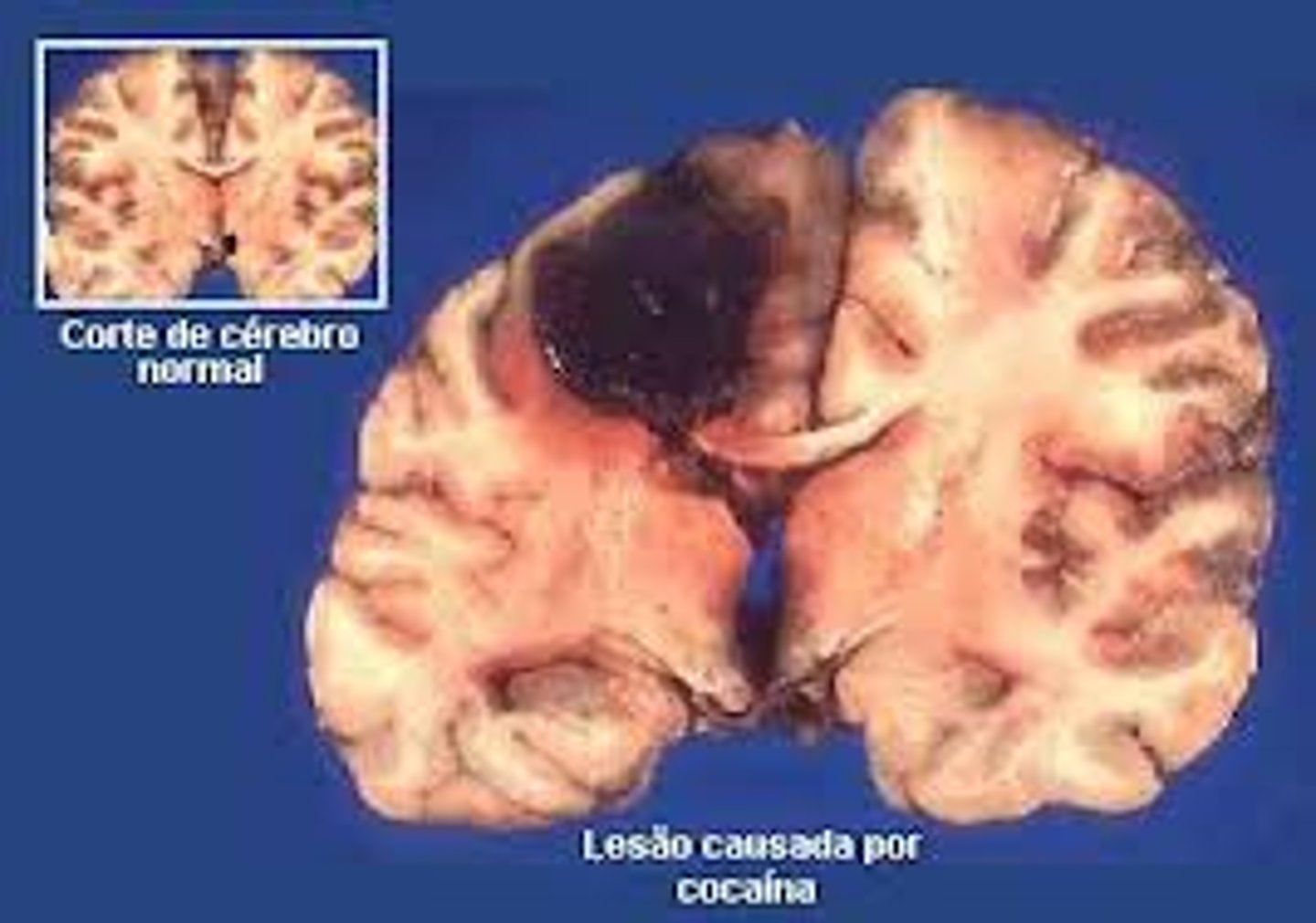
Lesion
Brain tissue destruction- naturally or experimentally caused.
EEG
Amplified recording of brain's electrical waves. Helpful in diagnosing seizures.
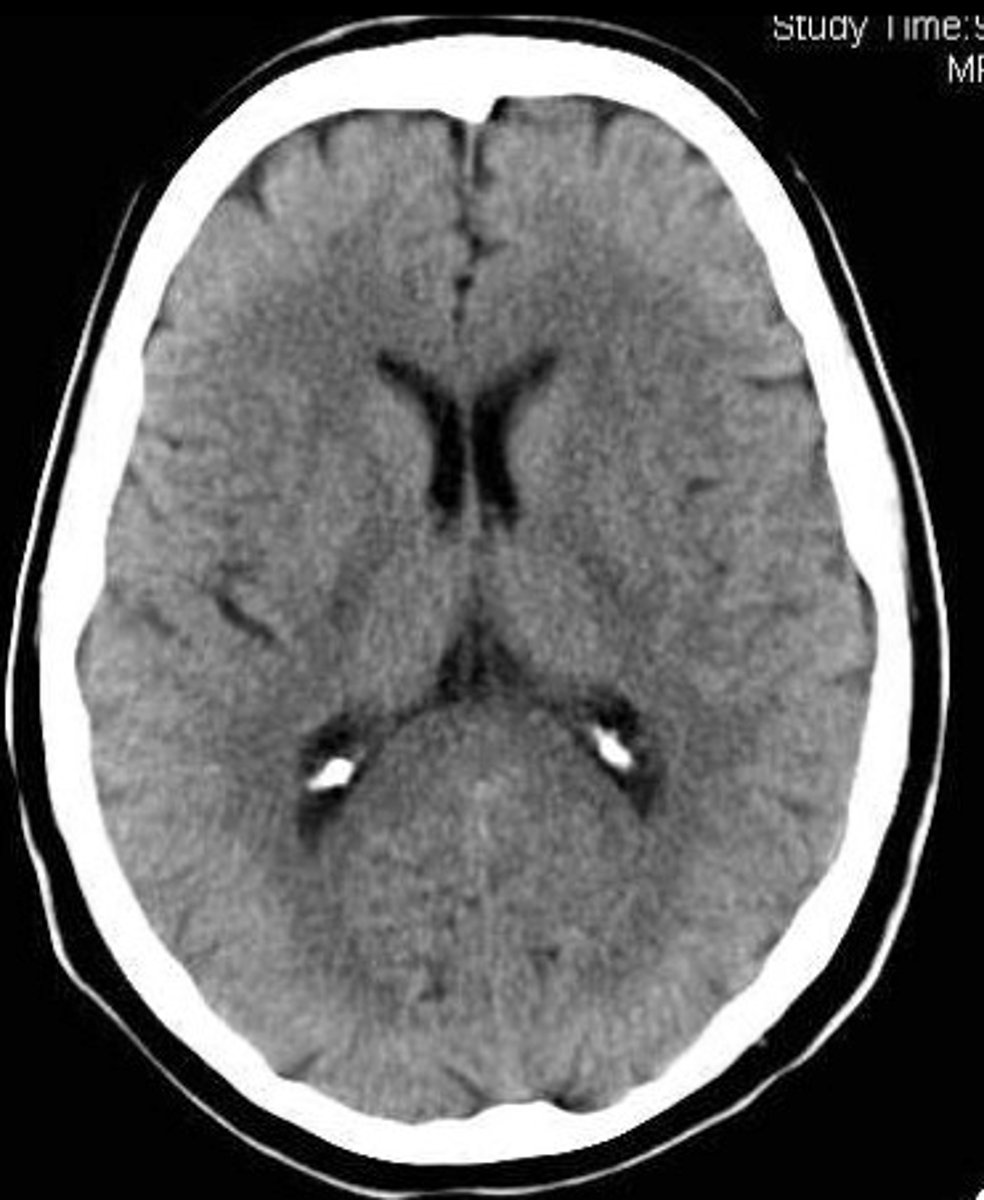
CT Scan
X-ray photographs of brain illustrating structure. Can show brain tumors.
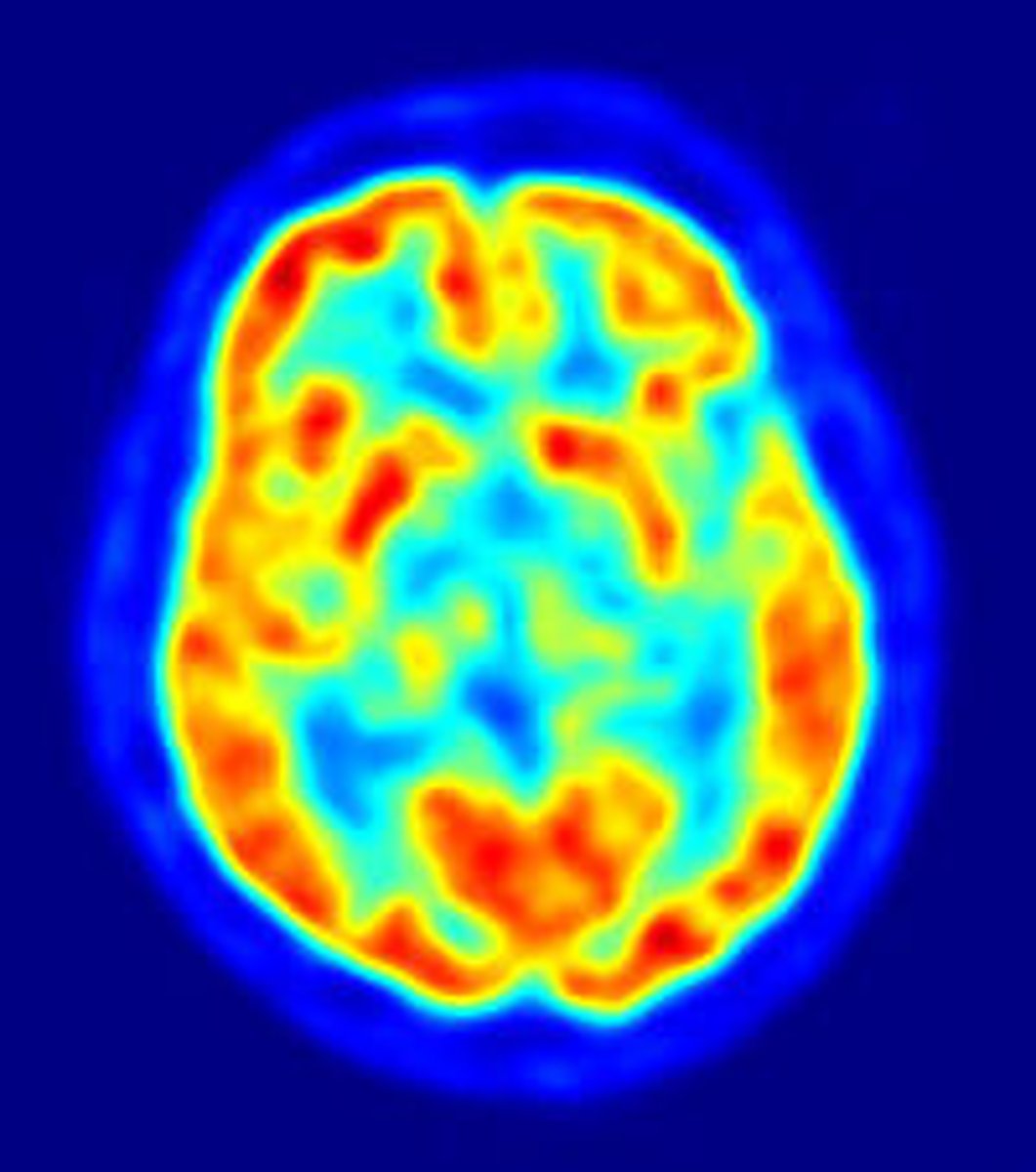
PET Scan
Visual display of brain function shown by injection of radioactive glucose..
MRI
Technique that uses magnetic fields/radio waves to produce detailed computer-generated images of brain tissue structure. Useful for showing enlarged ventricles in schizophrenia.
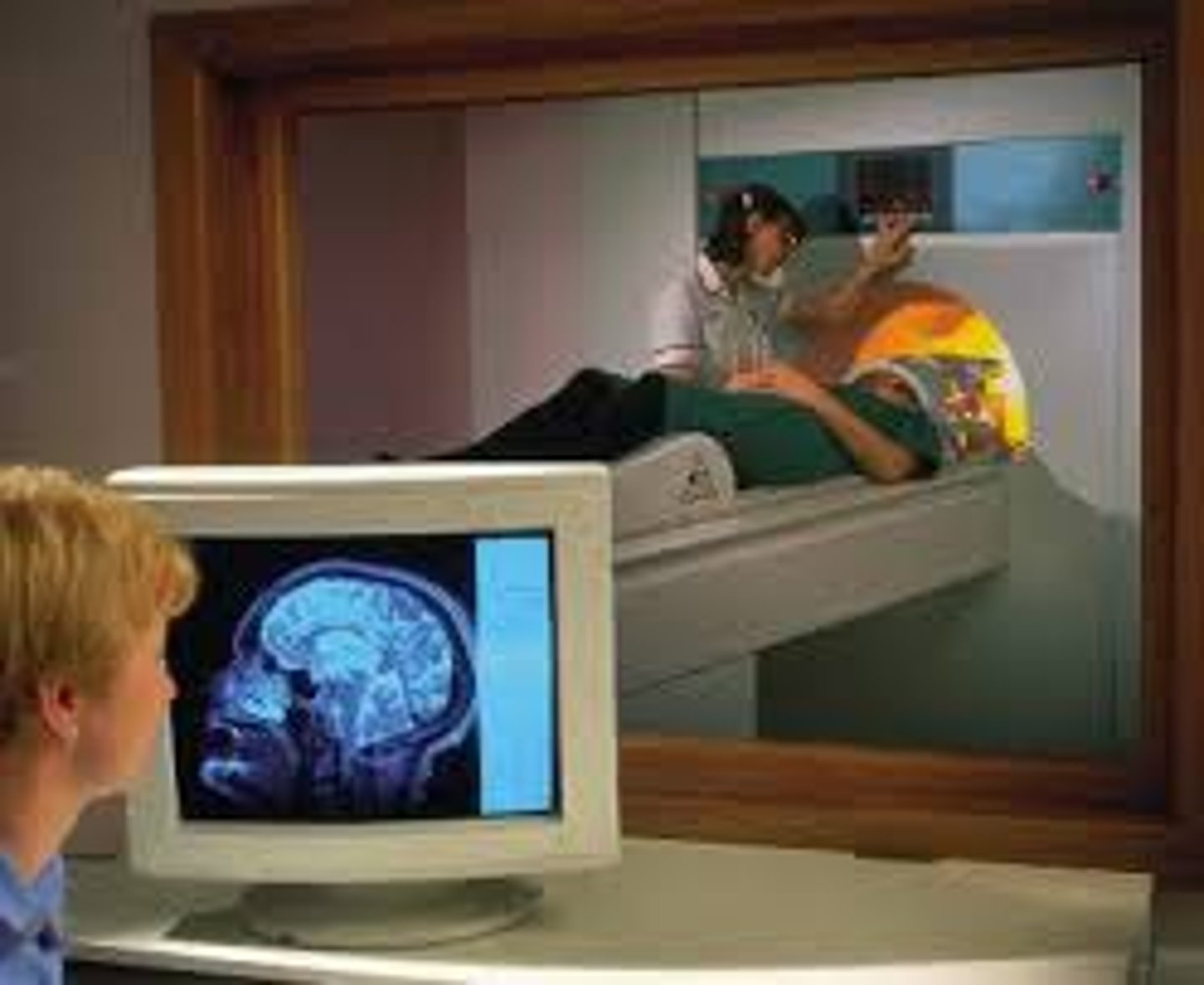
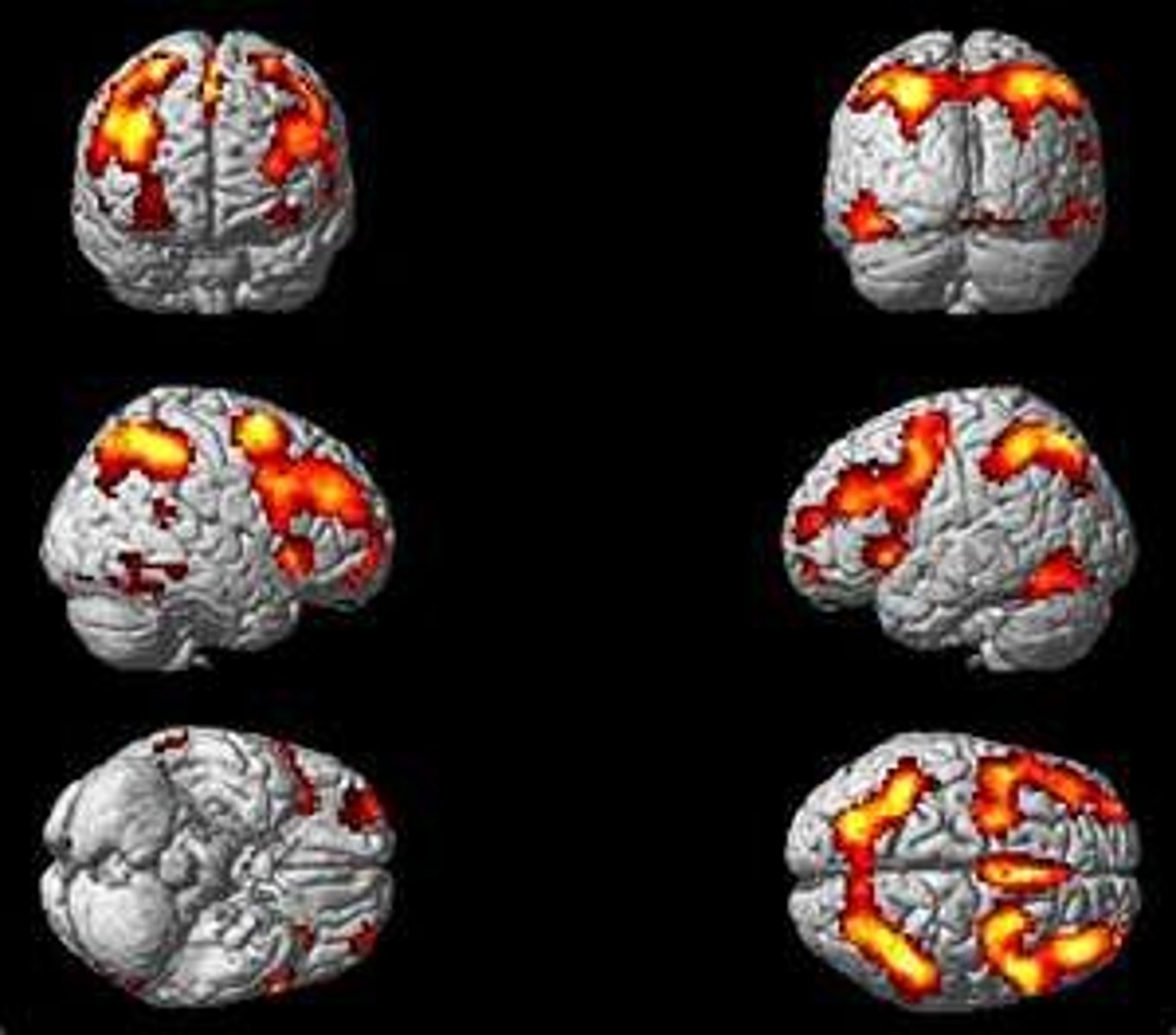
fMRI
Research technique used to highlight both brain function and structure. Used in mirror neuron video to illustrate areas of brain that are active when both seeing and mimicking a face.
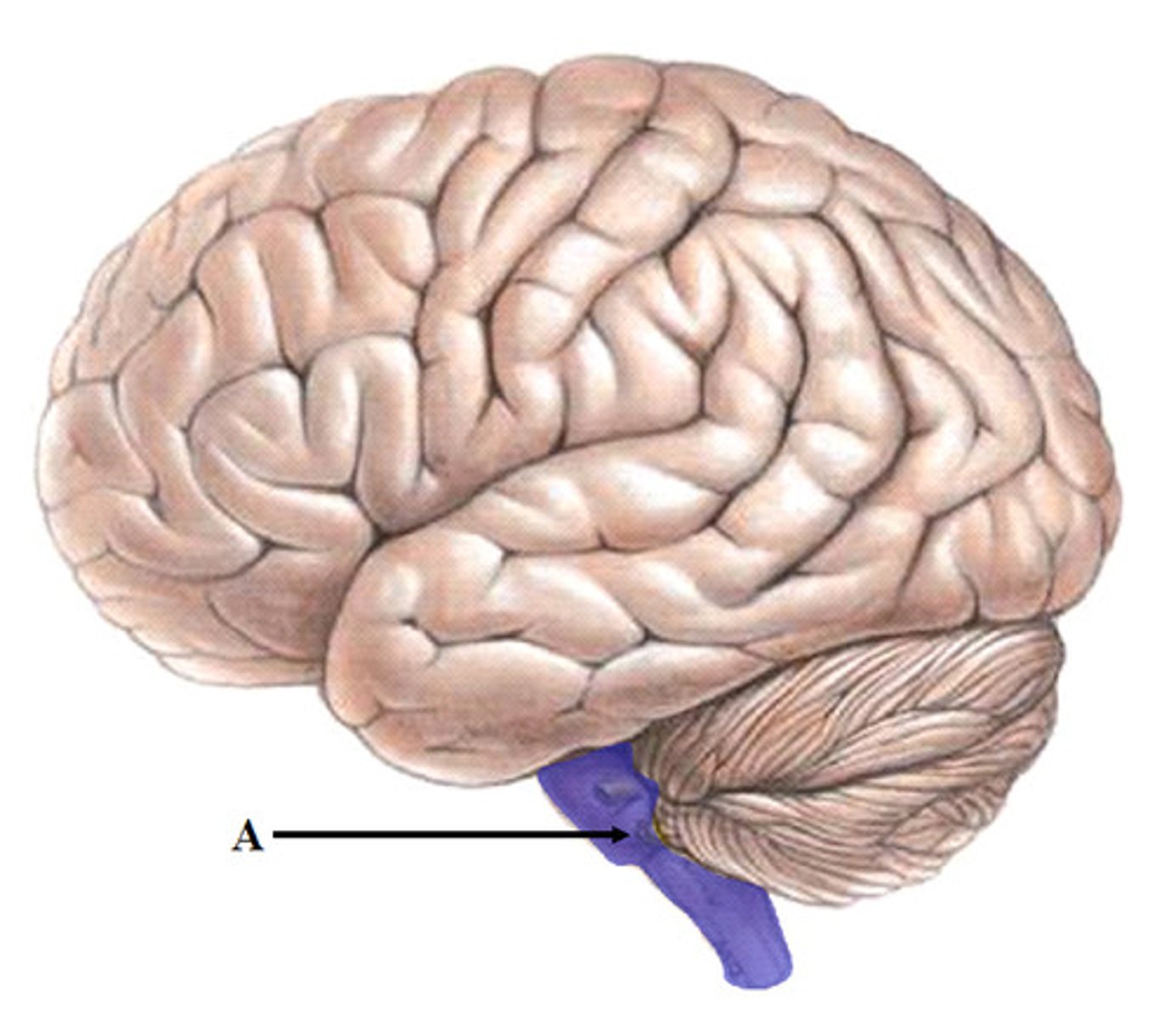
Brainstem
The oldest part of brain-composed of medulla, pons, and RAS.
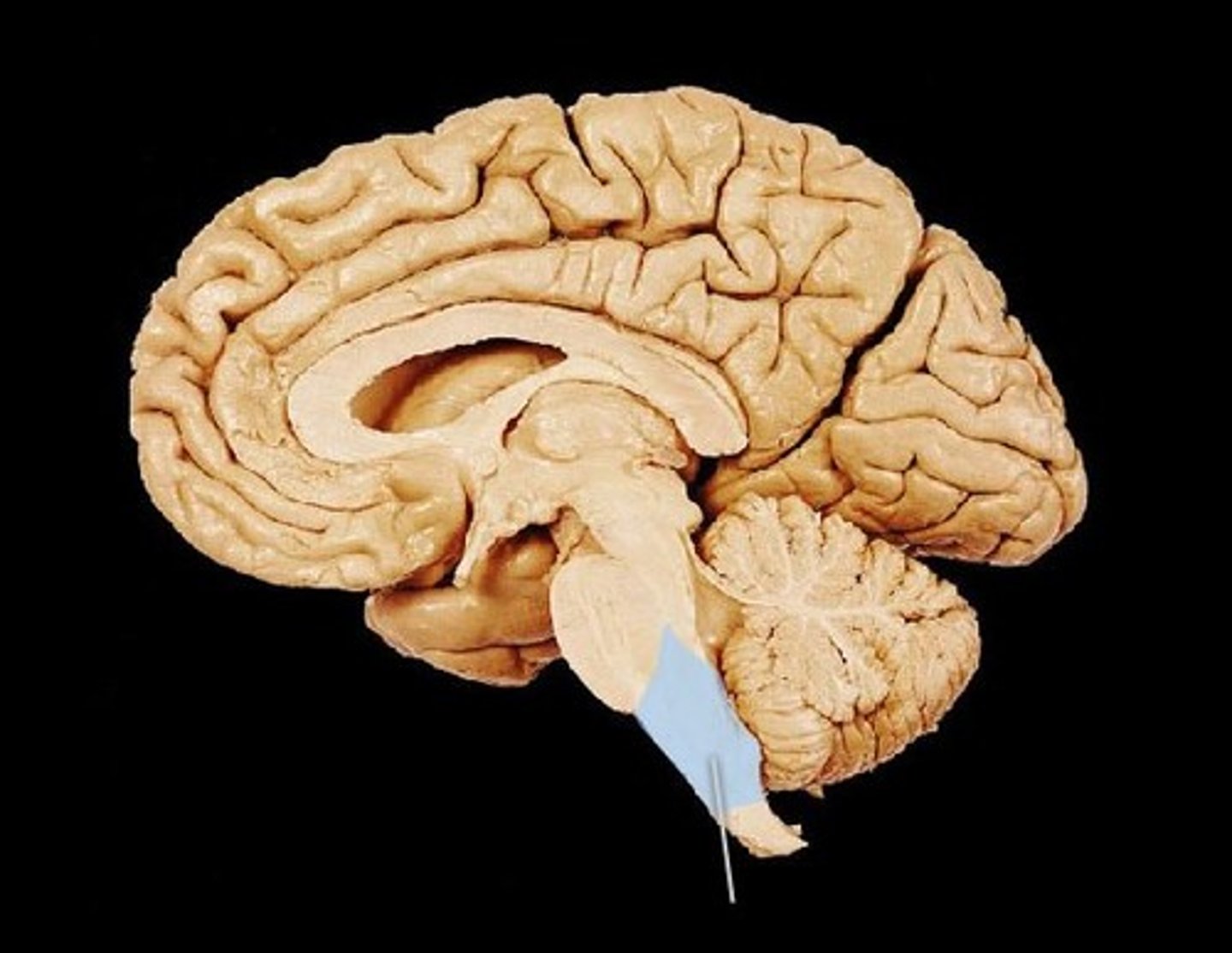
Medulla
The base of the brainstem. Controls heartbeat and breathing.
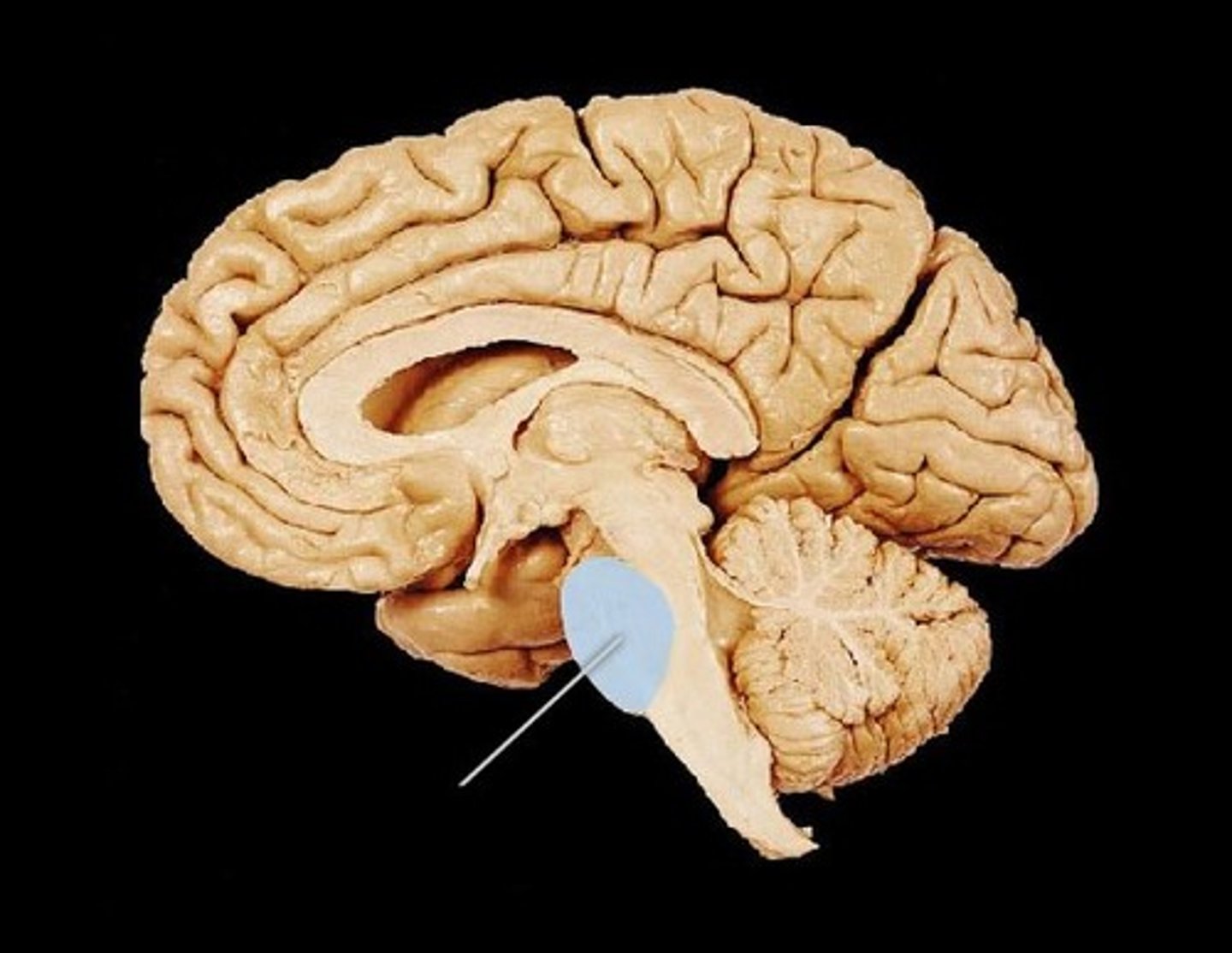
Pons
Part of the brainstem involved in REM sleep.
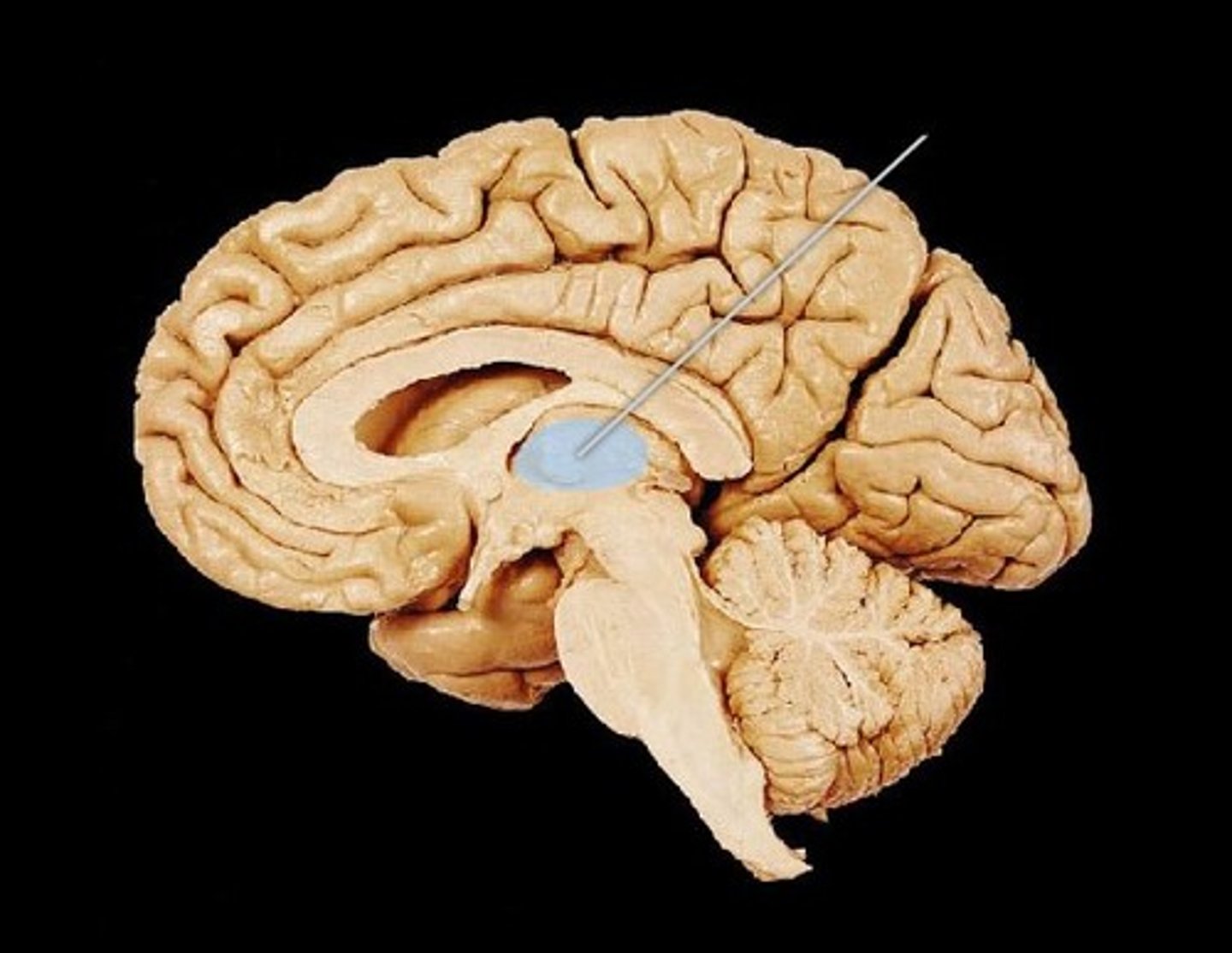
Thalamus
The brain's sensory control center, located at the top of the brainstem. Receives information for all the senses except smell.
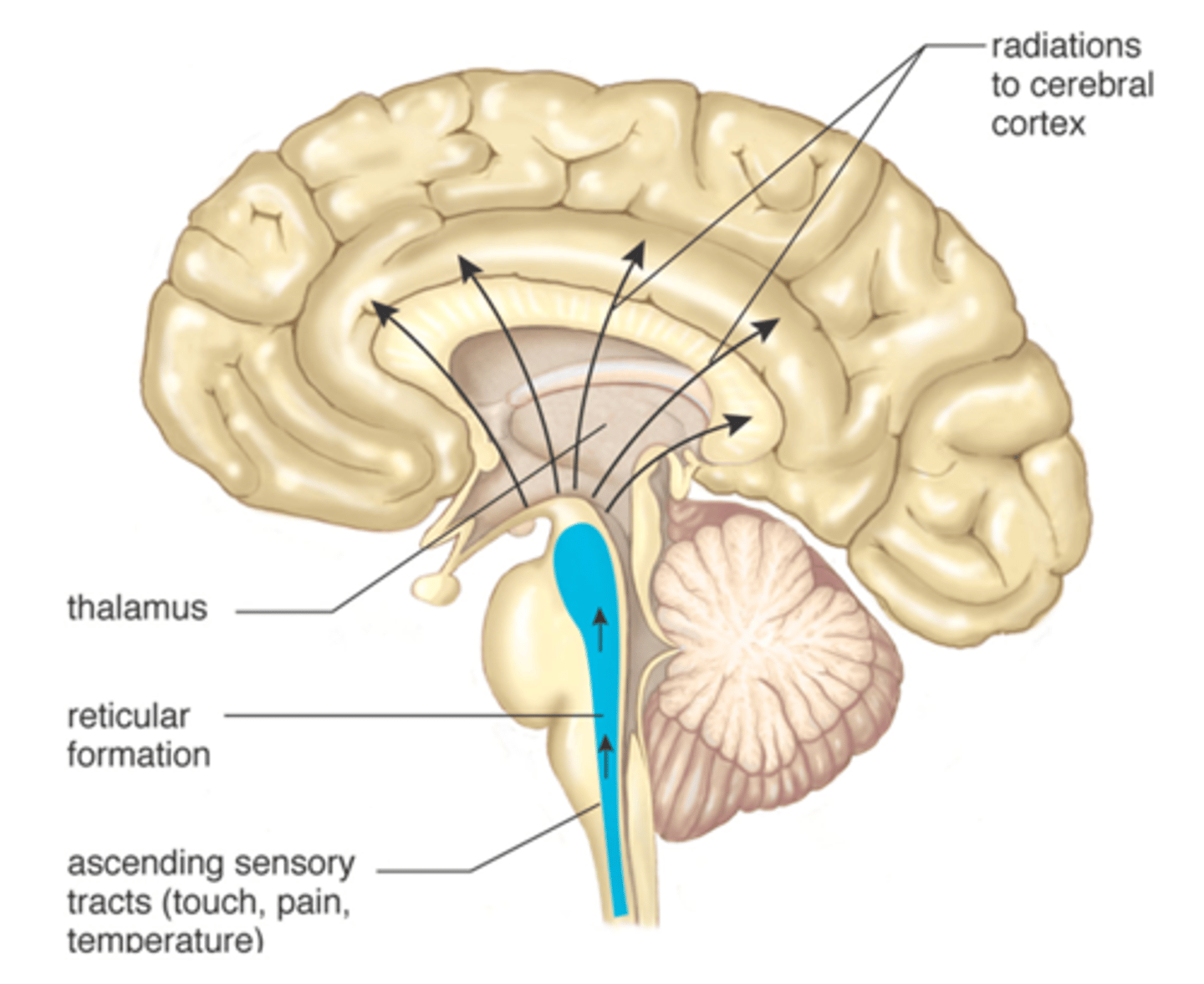
Reticular Formation
Neural network located in both hindbrain and midbrain. Plays an important role in arousal.
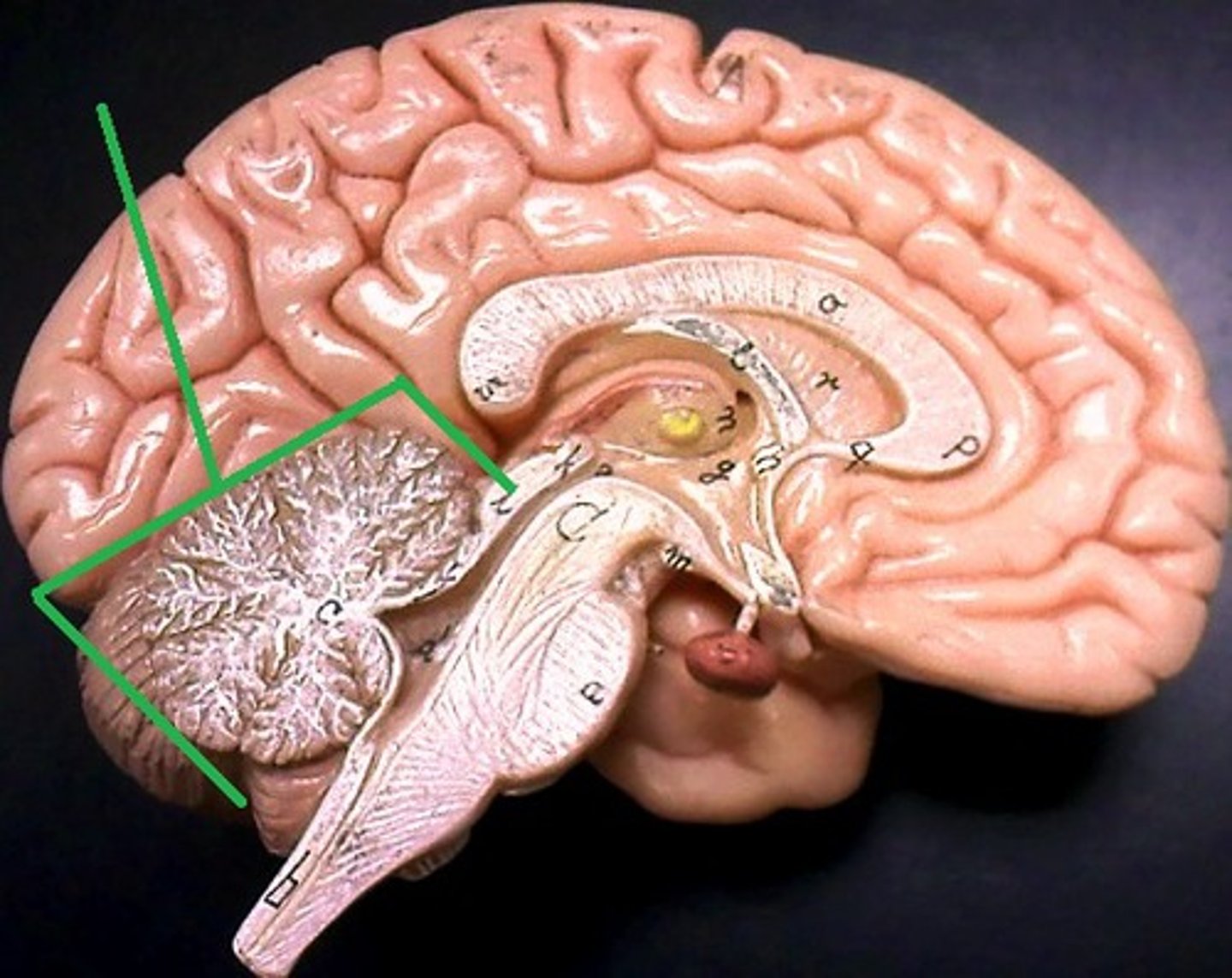
Cerebellum
"Little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include coordinating movement and balance, and processing implicit memory.
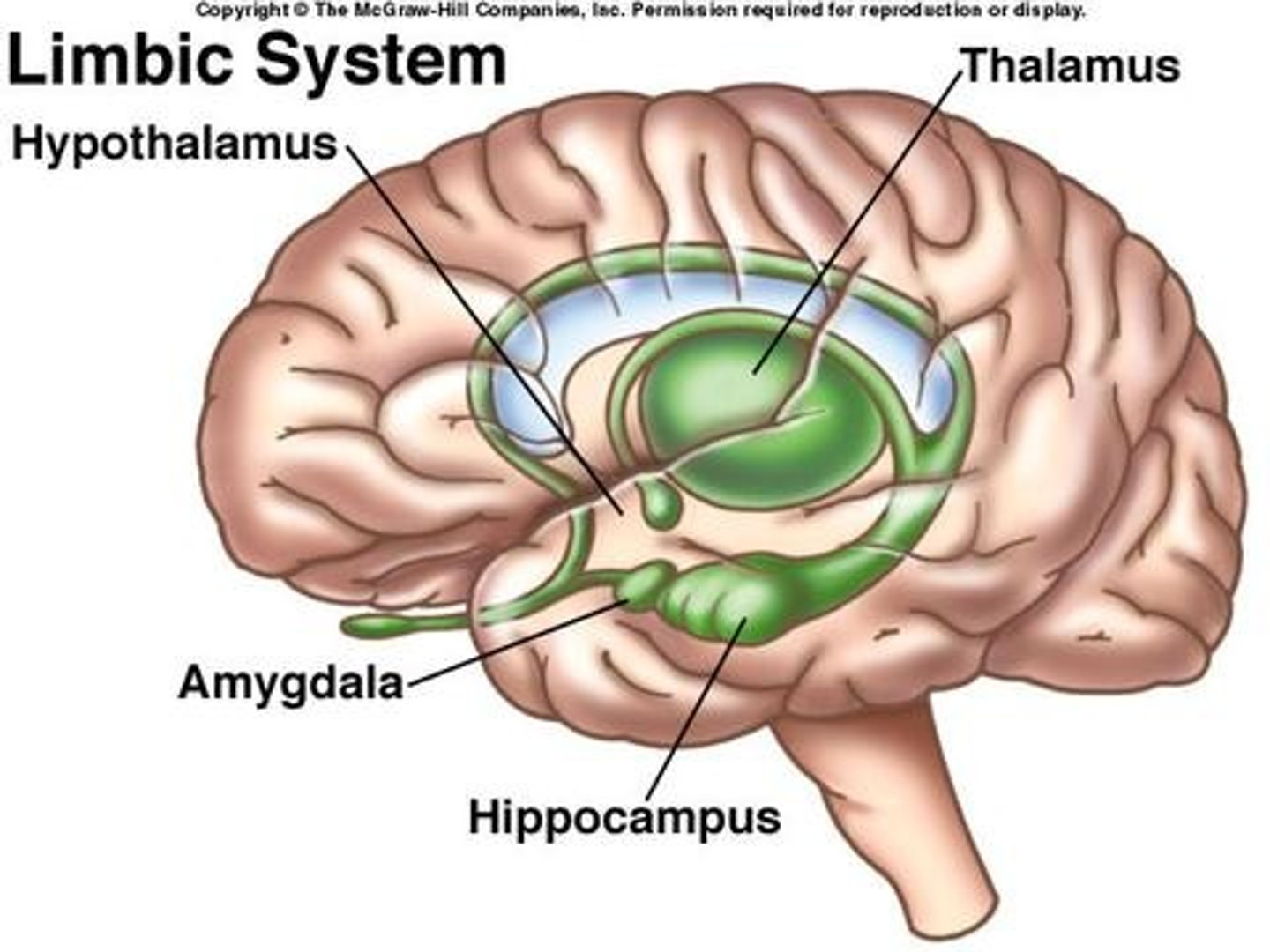
Limbic System
Neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with motivated survival functions. Contains hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus.
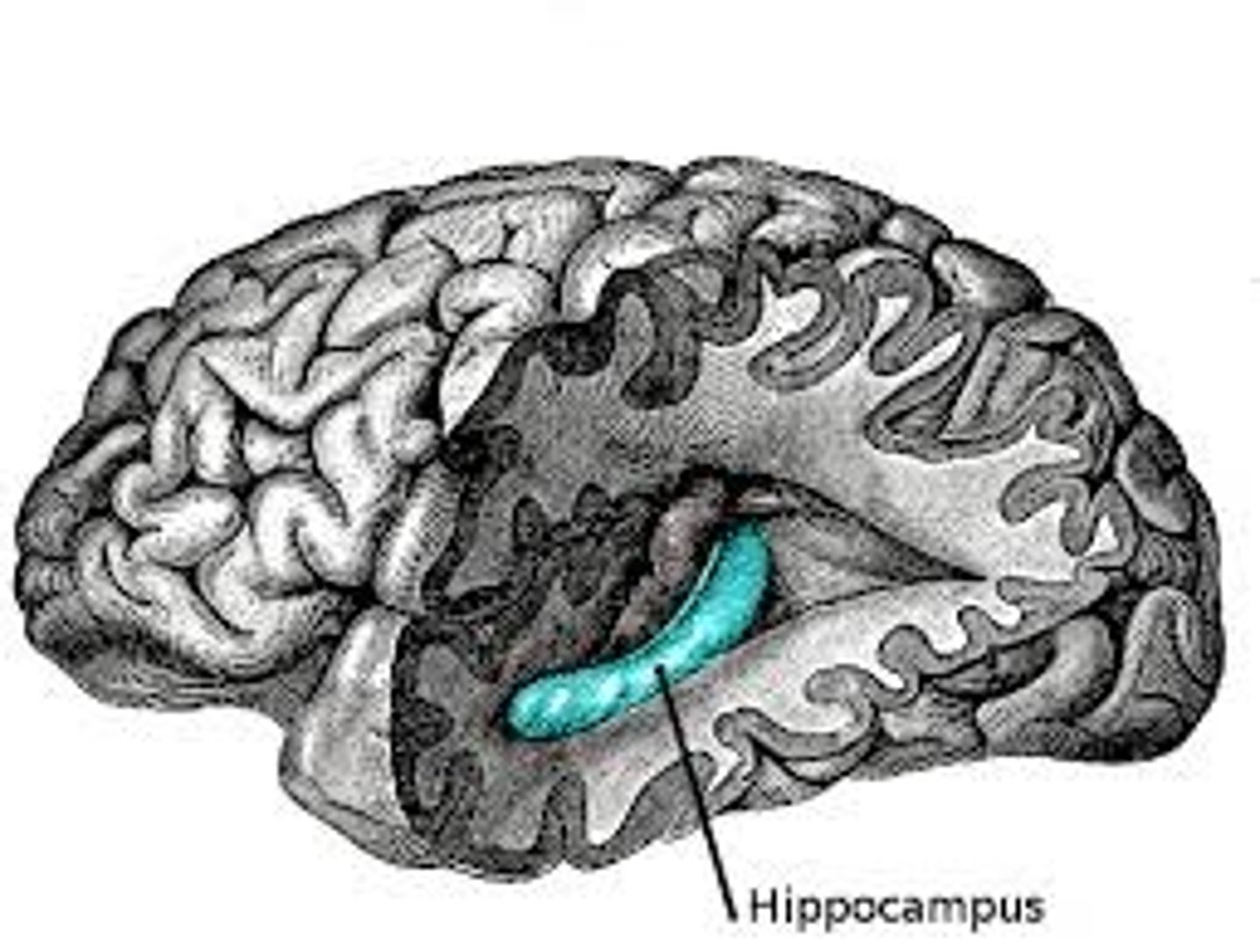
Hippocampus
Processes explicit memories.
Amygdala
Two bean-sized nerve clusters in the limbic system linked to emotion such as anger and fear.
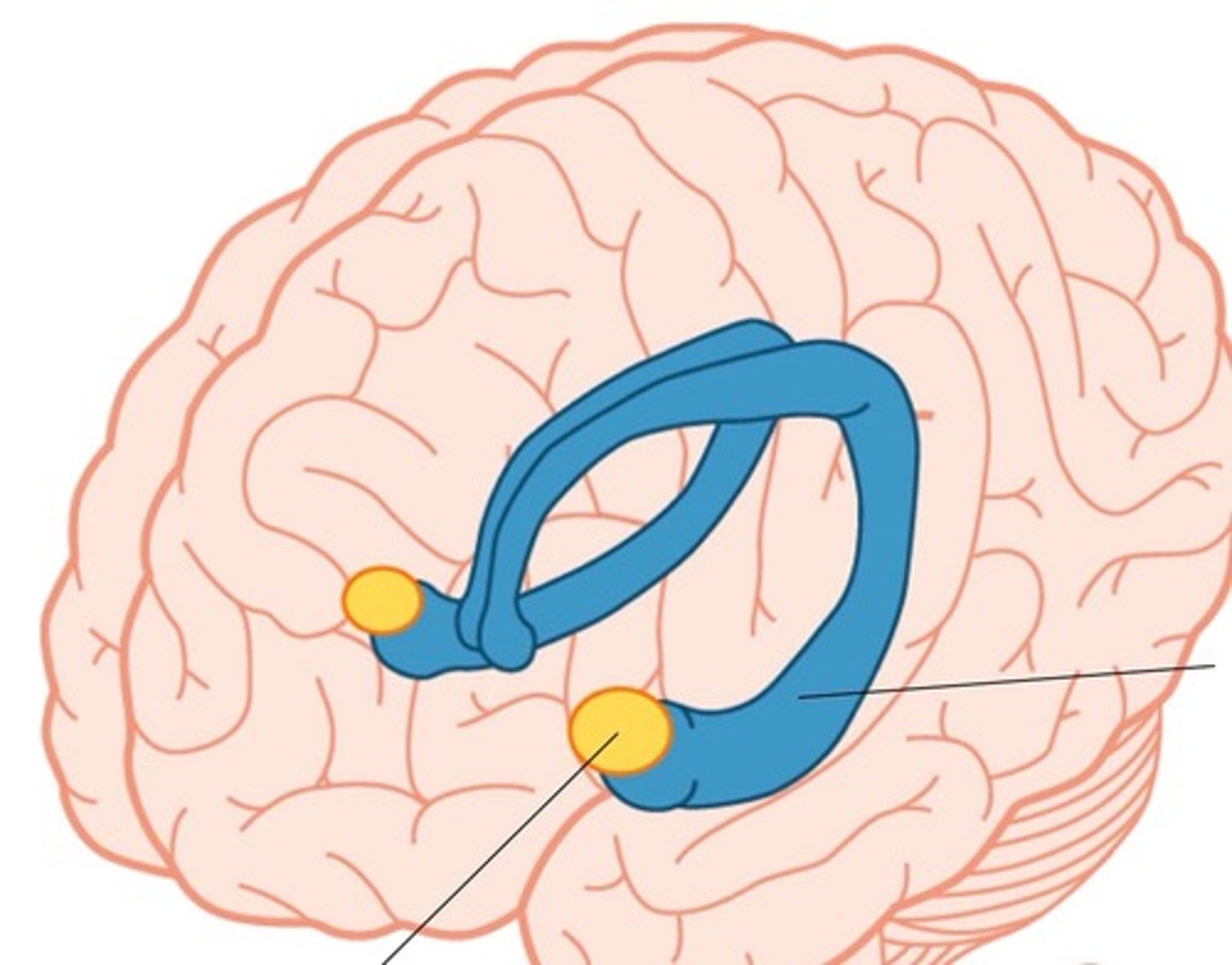
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities such as eating, drinking, sexual behavior and body temperature. It help govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is liked to emotion and reward.
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.

Glial Cells
Cells that help neurons by providing nutrients, creating myelin, and mopping up ions and neurotransmitters.
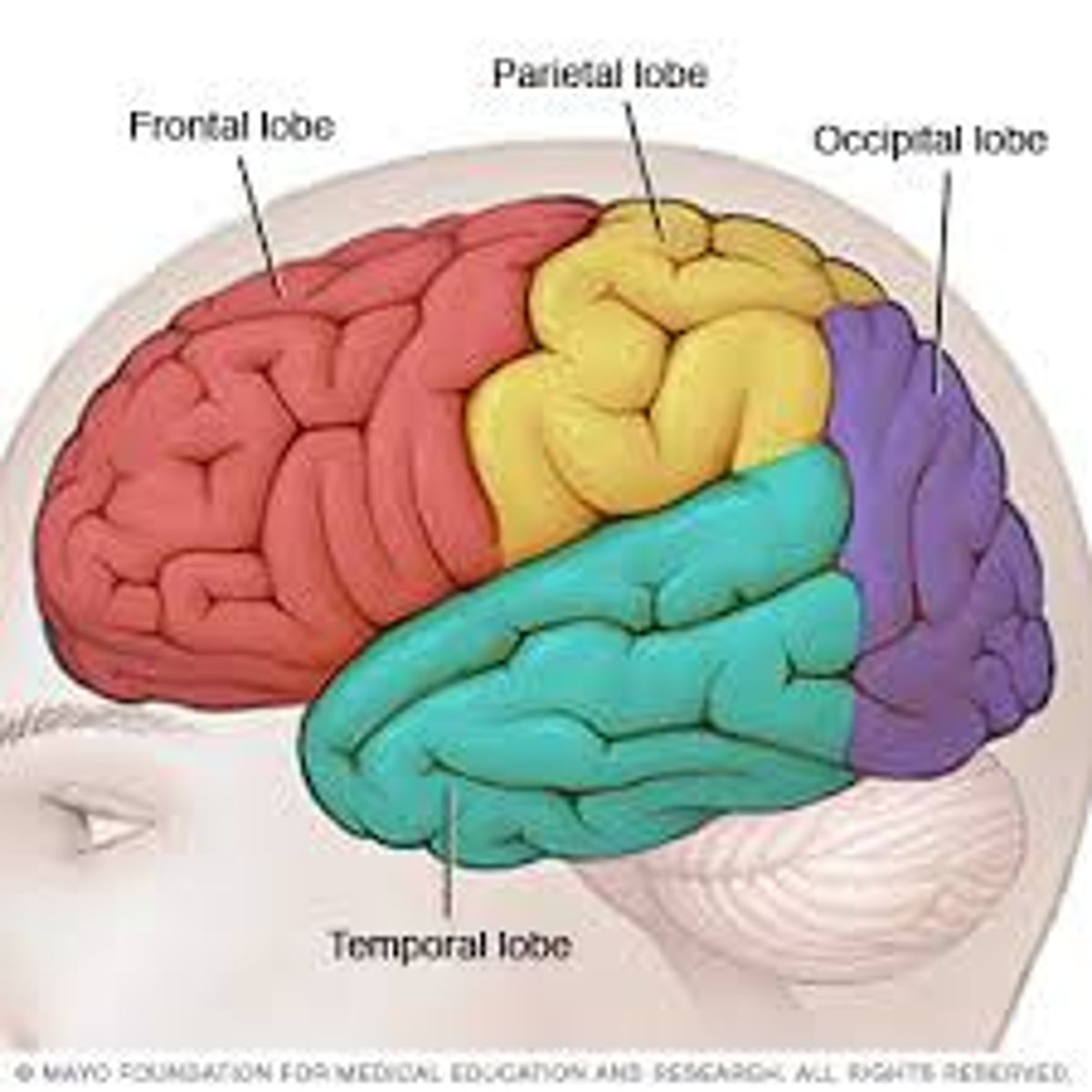
Frontal Lobes
Portion of the cerebral cortex lying in the front, behind the forehead. It is involved with speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgements. It aso impacts personality.
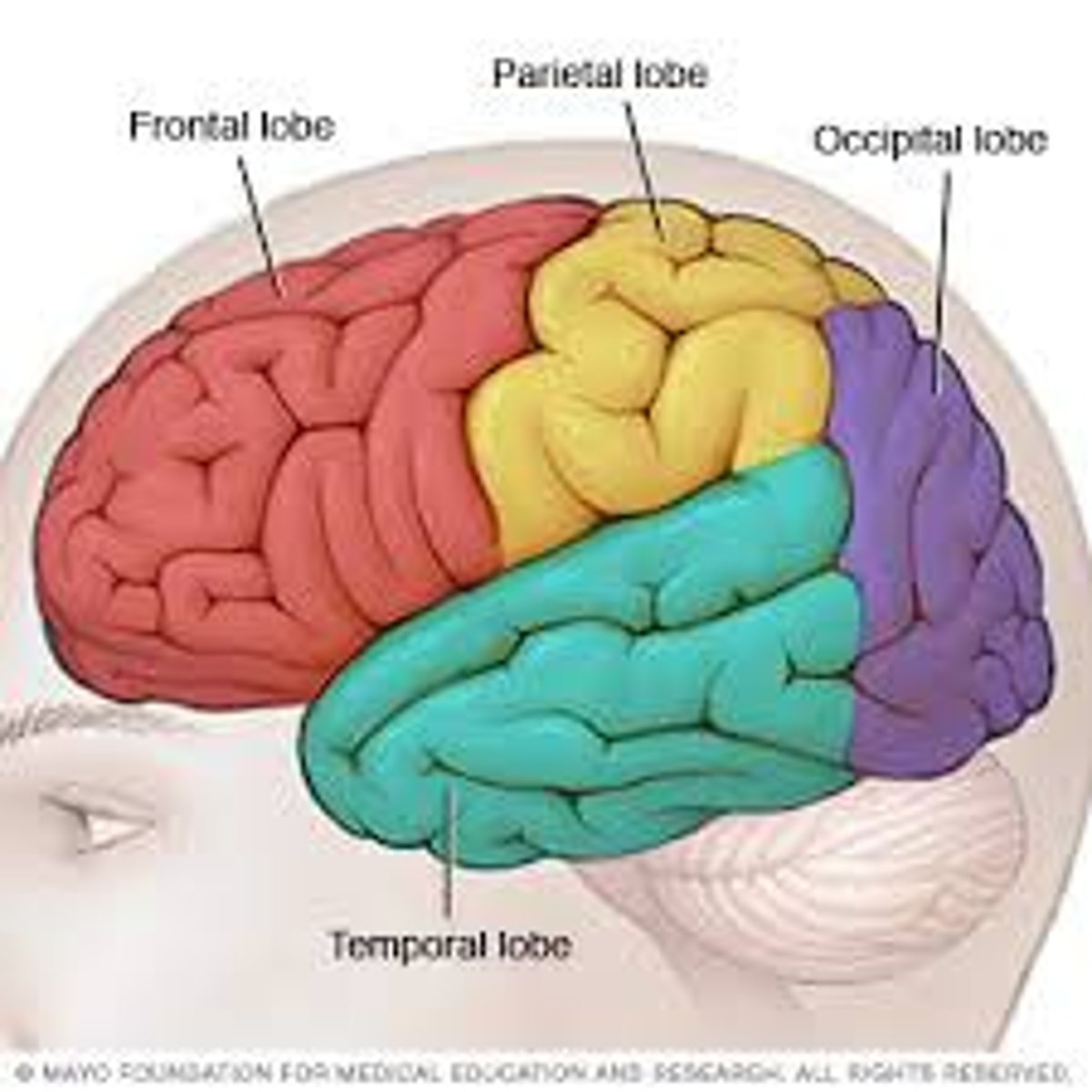
Parietal Lobes
Portion of the cerebral cortex which is at the top to the back of the head. Receives sensory input for touch and body position. Handles math and spatial reasoning.
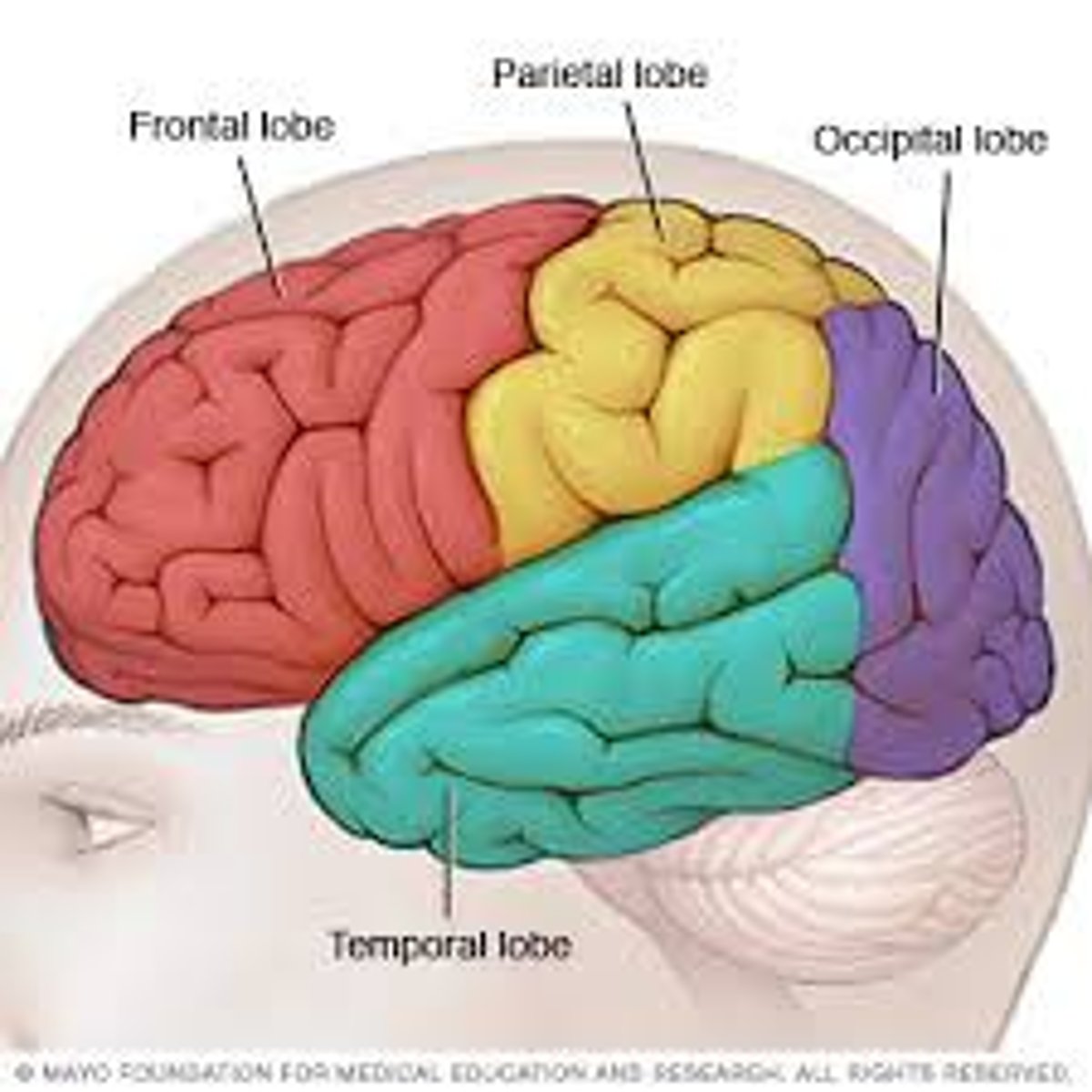
Occipital Lobes
Portion of the cerebral cortex located at the back and bottom of the head. It includes areas that receive information from the visual fields. It processes vision.
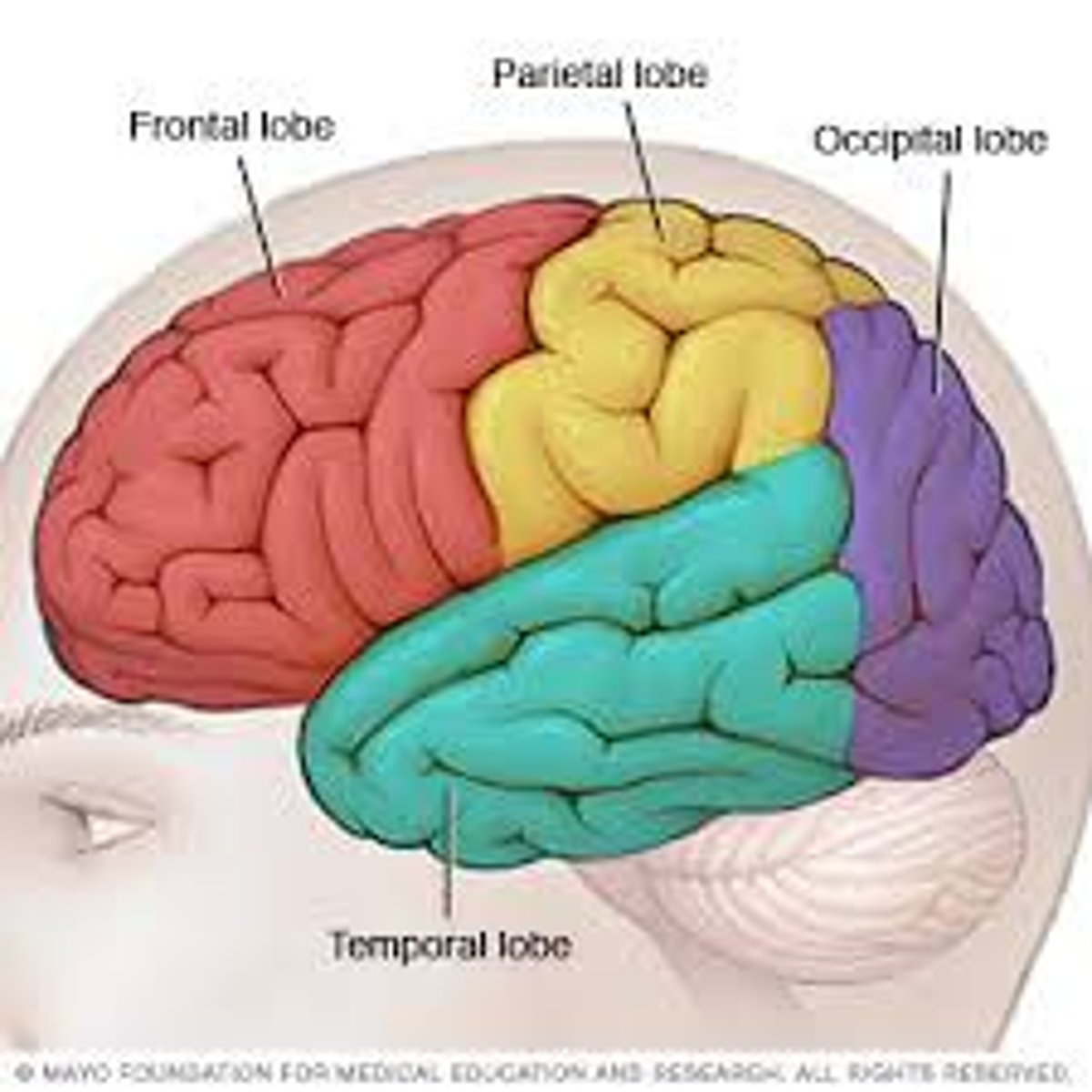
Temporal Lobes
Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears and near the temples, on the side. Includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear.
Motor Cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movement and motions by sending impulses from the brain to the body.
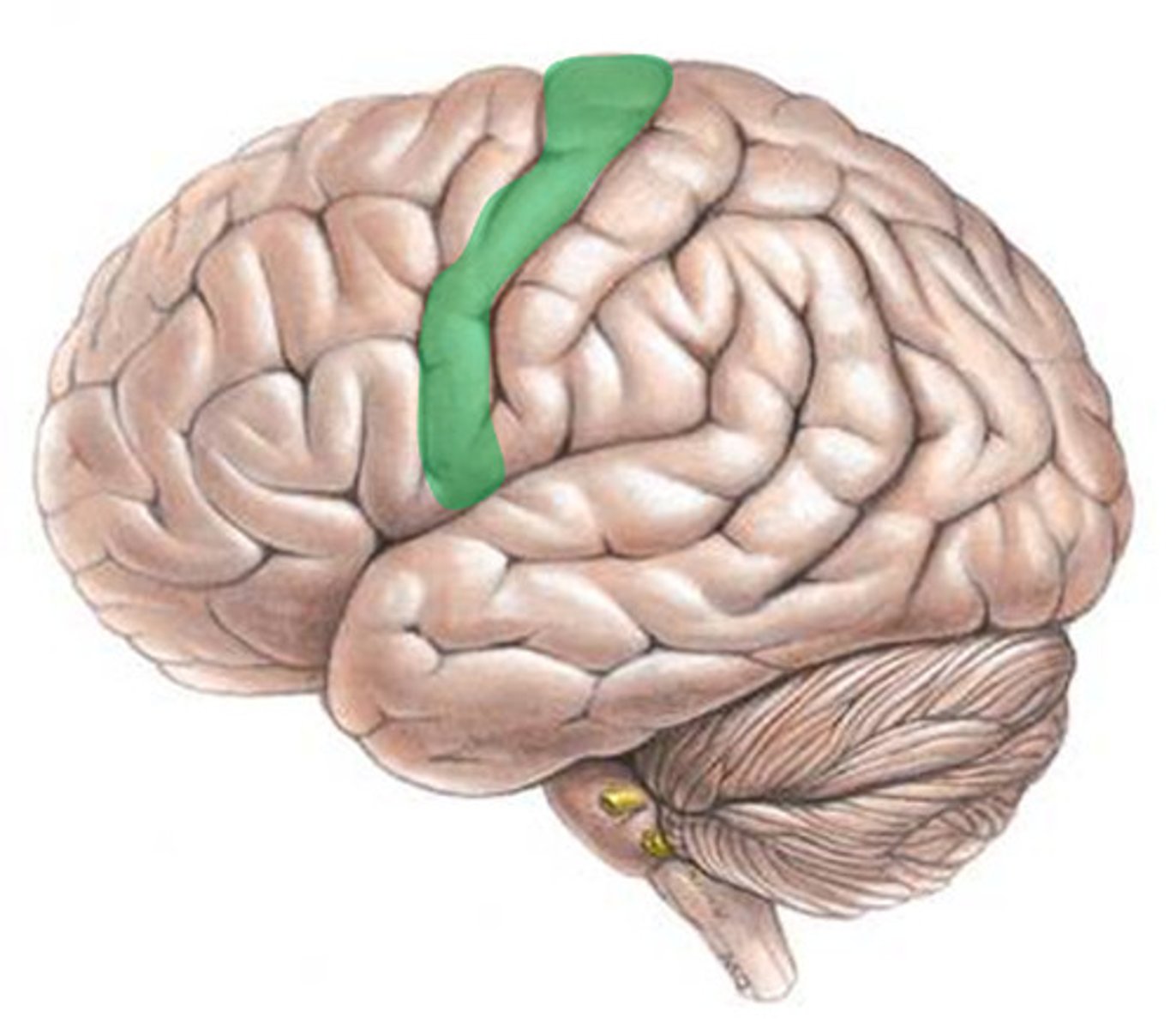
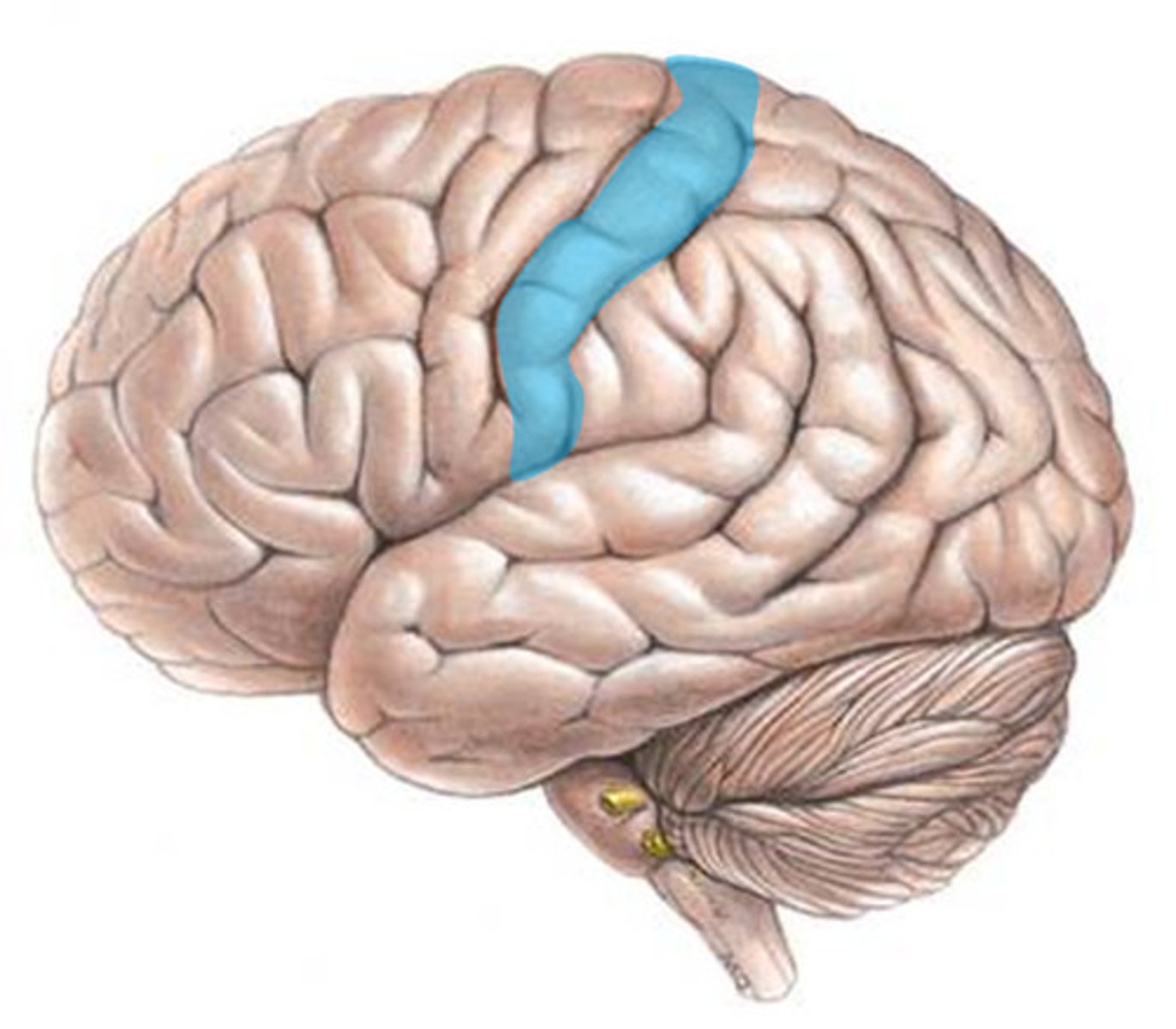
Somatosensory Cortex
An area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations.
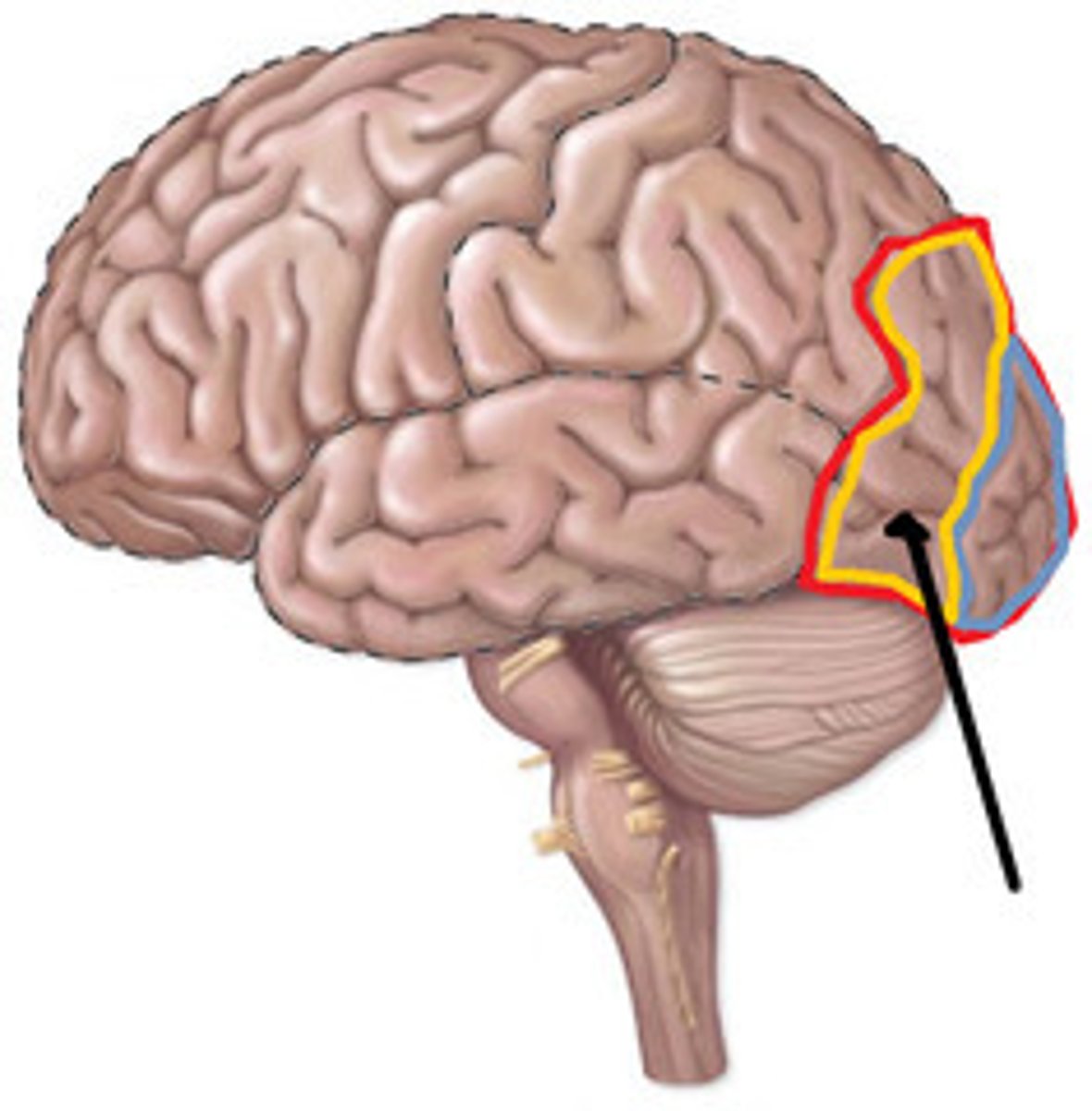
Association Areas
Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
Plasticity
Brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience.
Neurogenesis
The formation of new neurons.
Corpus Callosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
Split Brain
A condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers connecting them.
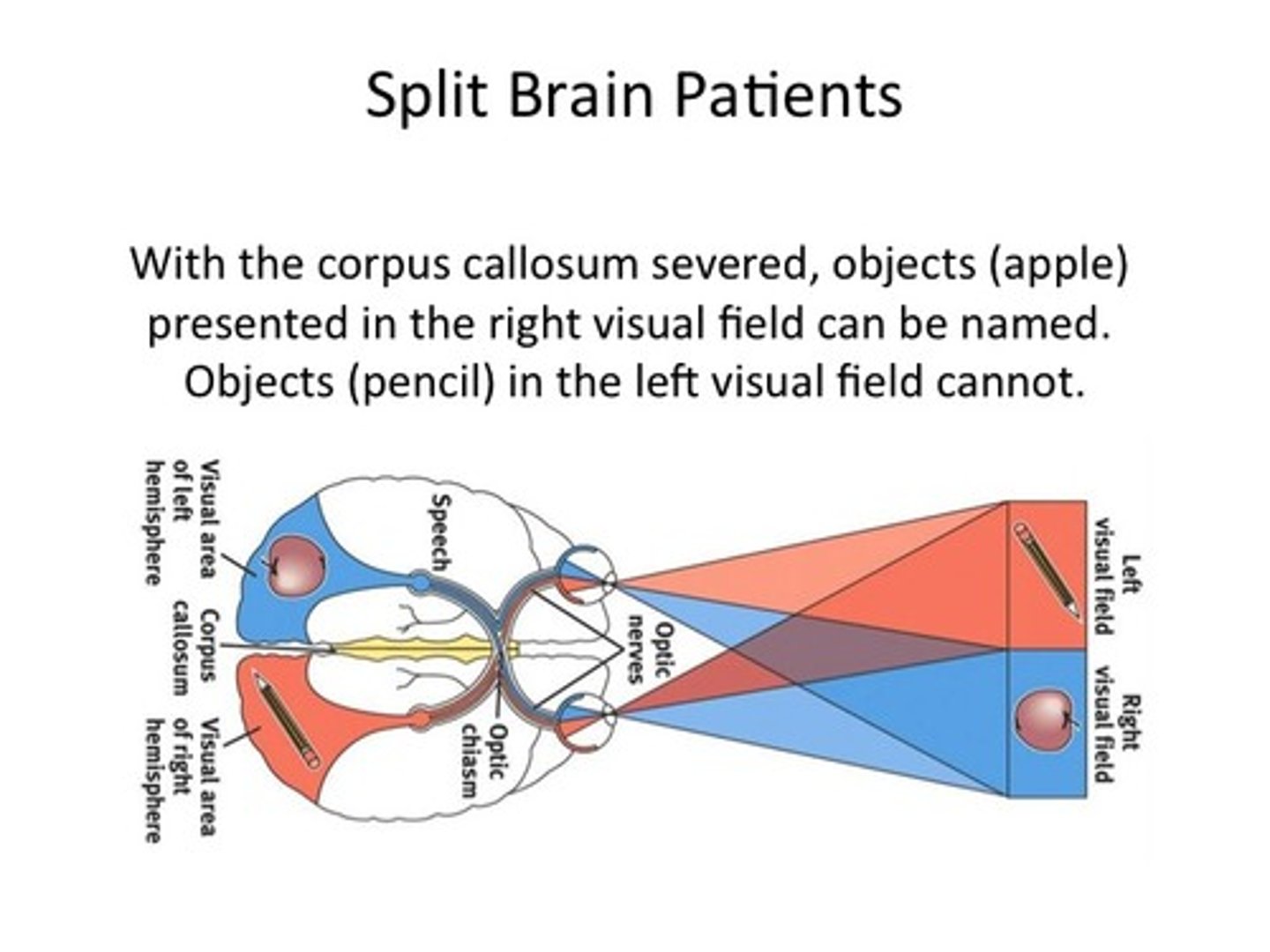
Left Brain
Handles rational, logical thought, and language.
Right Brain
Handles images, emotions, intuition, and drawing inferences.
Cognitive Neuroscience
The interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition; including perception, thinking, memory, and language.

Dual Processing
Information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks. Ex: Blindsight
Behavior Genetics
The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior.
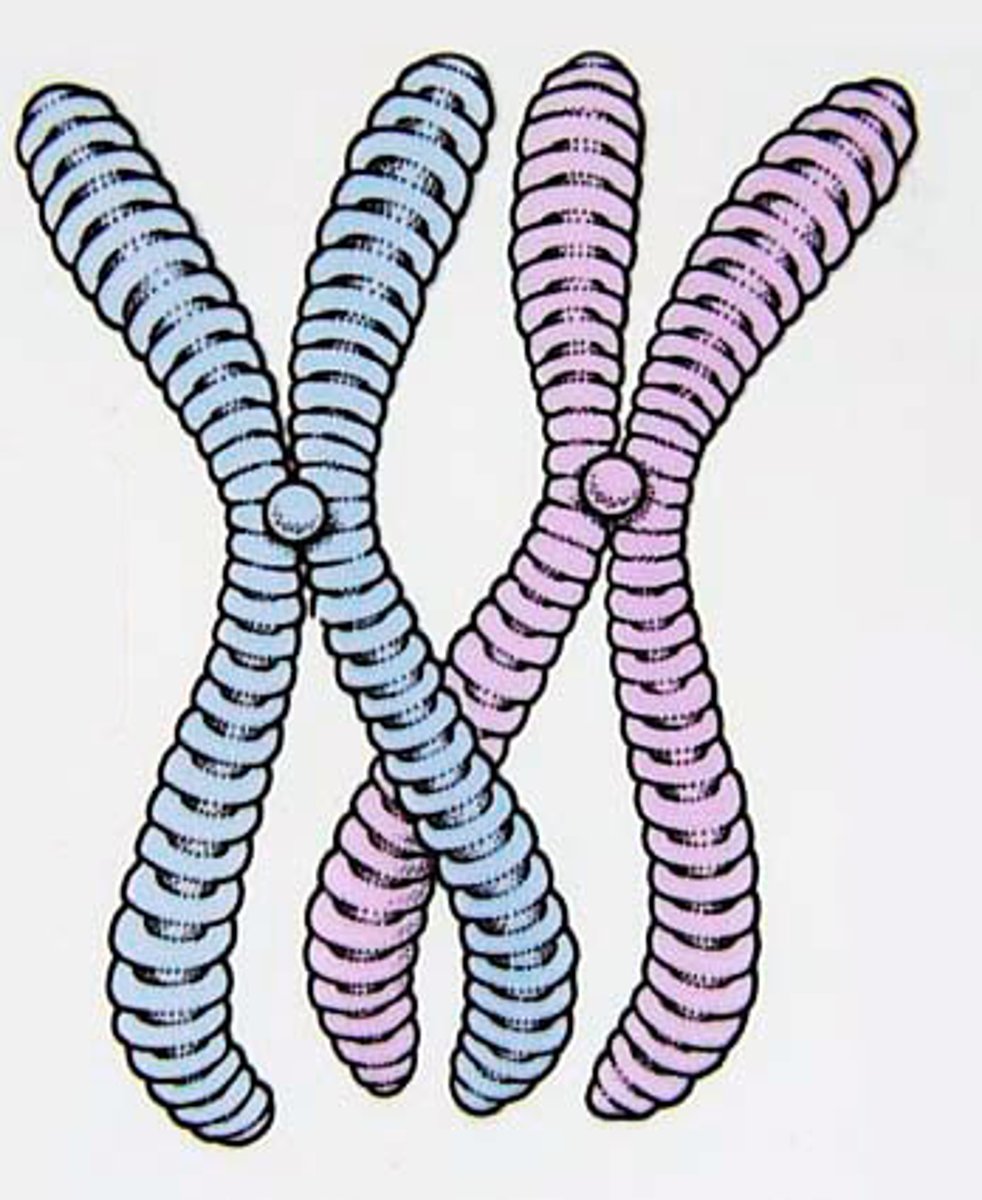
Chromosomes
Threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes.
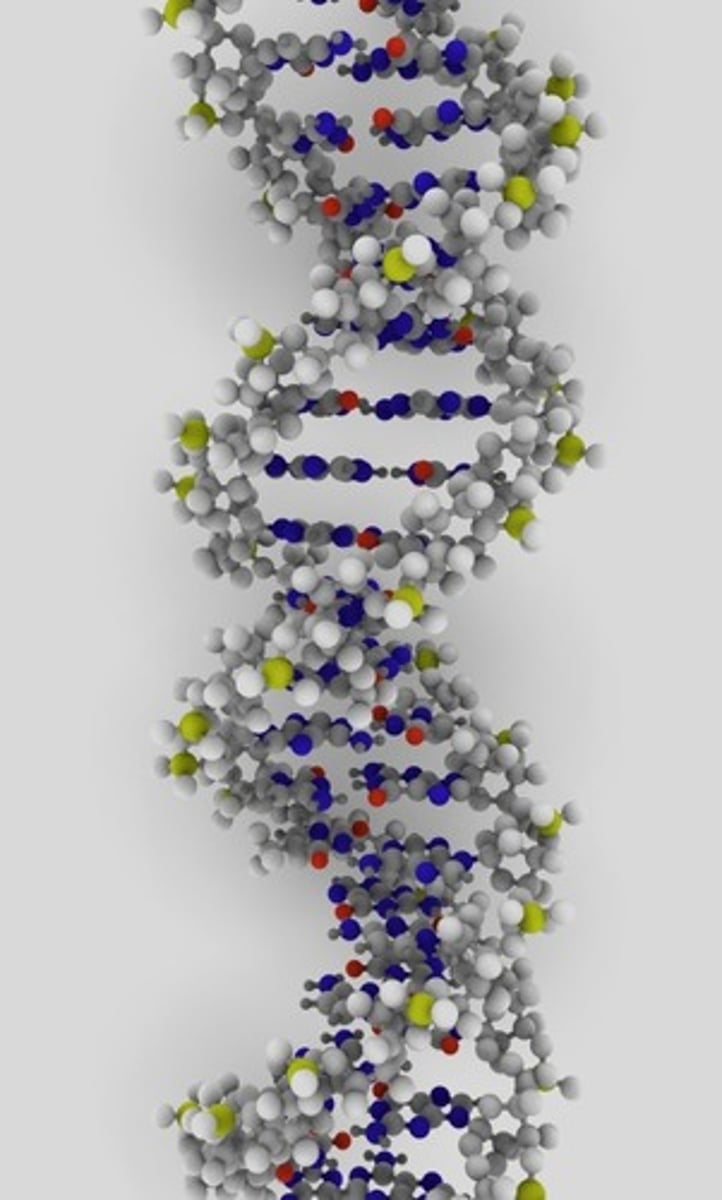
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
Genes
The biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins.
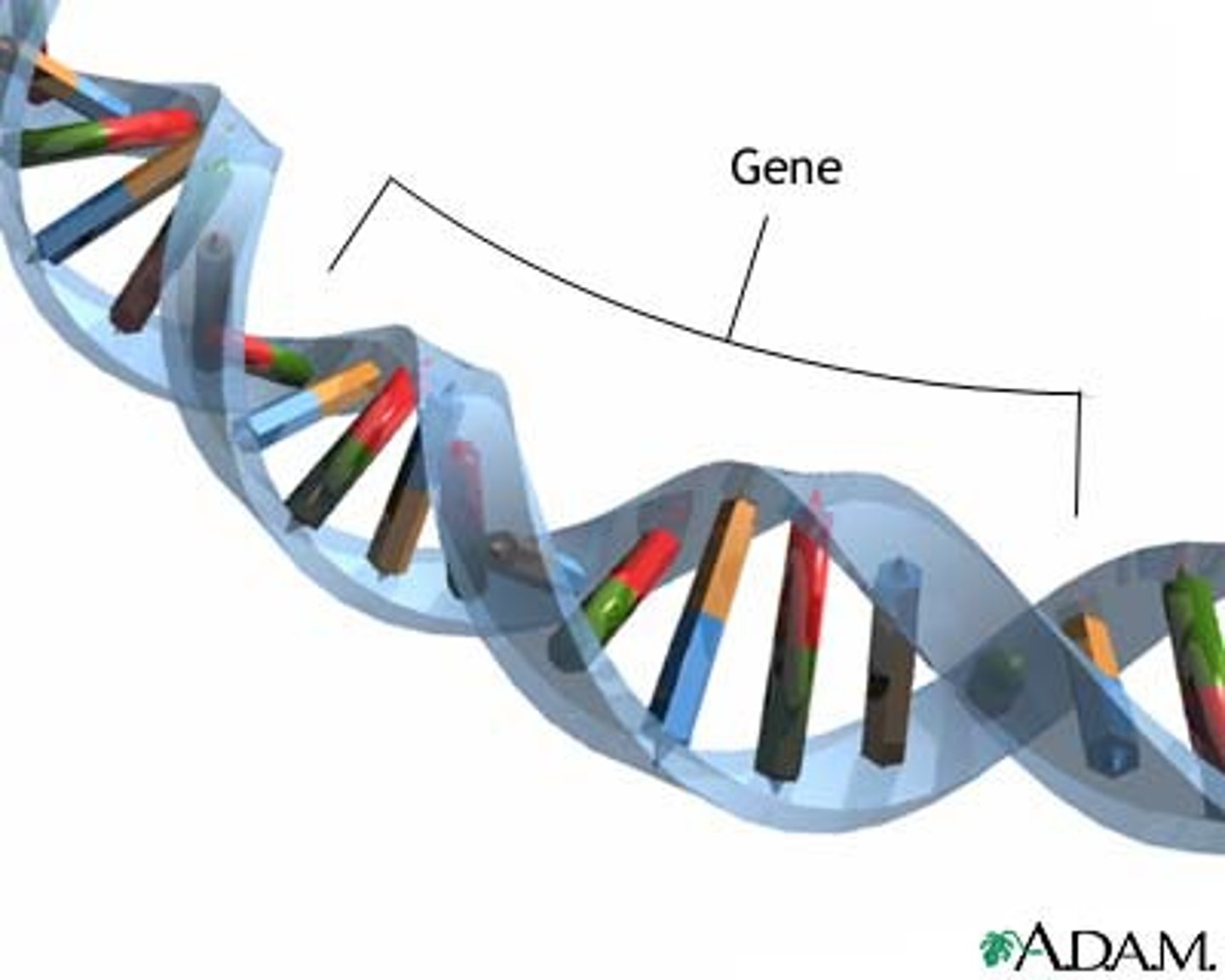
Genome
The complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes.
Identical Twins (monozygotic)
Twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms. Similar temperaments, personality, interests, intelligence.
Fraternal Twins (dizygotic)
Twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment.
Heritability
Proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. If people grow up in similar environments, heritability is high. This is because any differences are likely due to genes.
Molecular Genetics
Tries to single out how specific genes influence the body or behavior.
Epigenetics
Study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without DNA change.
Mutation
A random error in gene replication that leads to a change.
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.