Clinical Anatomy -- Enteric Nervous System and The Peritoneum
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Enteric Nervous System
highly complex system of sensory, motor, and interneurons
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Parietal peritoneum
the outer layer of the peritoneum that lines the interior of the abdominal wall; has nerve for pain, temp, touch, and pressure; well-localized
well-localized, pain, temp, touch, pressure
the parietal peritoneum has ___________ nerves for...
Visceral peritoneum
the inner layer of the peritoneum that surrounds the organs of the abdominal cavity; has nerves for stretch only; insensitive to pain, but sensitive to distention; generalized, non-specific
non-specific, stretch
the visceral peritoneum has ___________ nerves for...
pain, distension
the nerves of the visceral peritoneum are insensitive to ______, but sensitive to ______.
Serous fluid
lubricates the organs and allows them glide without friction
Peritoneal cavity
potential space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum
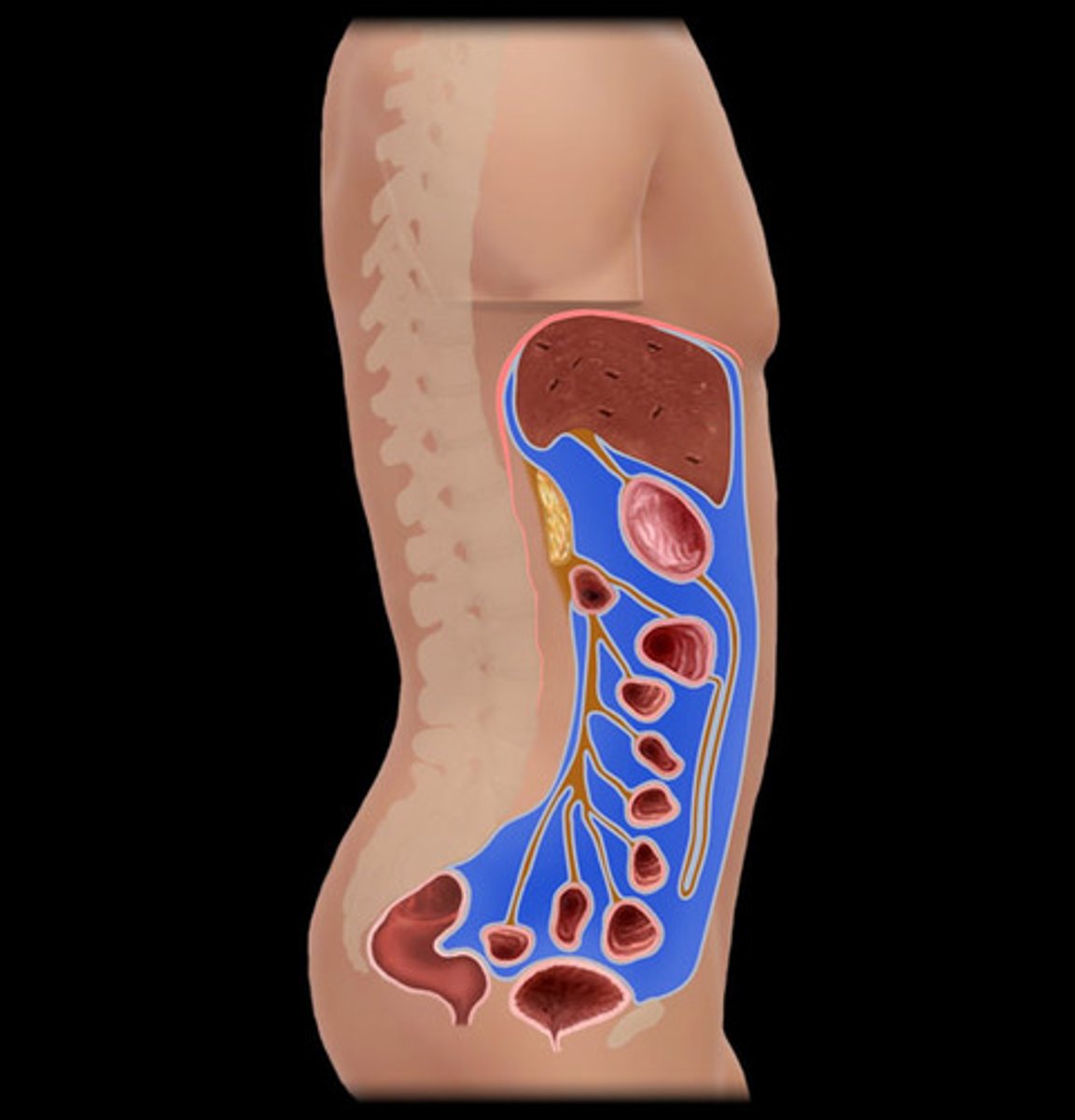
poorly
visceral pain is _______ localized
somatic sensory fibers with same spinal cord segment that receives visceral sensory fibers from viscus concerned (visceral nerve is close to dermatome)
visceral pain radiates to body part supplied by...
epigastric region
pain arising from the foregut derivatives localizes to the...
esophagus, stomach, pancreas, first portion of the duodenum, liver, biliary tree
what are the foregut derivatives?
periumbilical region
pain arising from the midgut derivatives localizes to the...
small intestine, distal to bile duct, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, most of transverse colon
what are the midgut derivatives?
hypogastric region (below the umbilicus)
pain arising from the hindgut derivatives localizes to the...
distal transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum
what are the hindgut derivatives?
well
somatic pain is ____ localized
the site of pain origin (because PP is supplied by somatic sensory fibers through the thoracic nerve)
somatic parietal peritoneum pain occurs at...
thoracic nerve
the parietal peritoneum is supplied by somatic sensory fibers through the...
stretching
inflamed parietal peritoneum is extremely sensitive to...
Rebound tenderness
a sign of inflammation of the peritoneum in which increased pain is elicited by the sudden release of the fingertips pressing on the abdomen.
Peritoneal ligaments
two-layered folds of peritoneum that connect solid viscera to the abdominal walls, usually containing remnants of fetal vessels
falciform, coronary, and triangular ligaments
what are the ligaments responsible for connecting the liver to the diaphragm?
Omentum
two-layered folds of peritoneum that connect the stomach to other viscera
stomach
the omentum is responsible for connecting the ______ to other viscera
Greater omentum
connects the stomach to the transverse colon; helps to prevent viscera from adhering to abdominal wall; walls off inflamed organs (prevents spread); cushions organs and insulates against loss of body heat
stomach to transverse colon
the greater omentum connects...
Lesser omentum
connects lesser curvature of stomach to liver
Hepatoduodenal ligament
encloses the portal triad and marks opening (epiploic foramen of Winslow) to the omental bursa)
proper hepatic artery, portal vein, common bile duct
what makes up the portal triad?
Gastrosplenic omentum
ligament that connects the stomach to the spleen
Mesenteries
two-layered folds of peritoneum connecting parts of the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall
connecting parts of the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall
function of mesenteries
more mobility
organs with mesentery have...
mesentery of small intestines, transverse mesocolon, sigmoid mesocolon
examples of mesenteries
closed, open
the peritoneal cavity is a _______ system in males, and _____ in females
greater sac, lesser sac
two divisions of the peritoneal cavity
behind the lesser omentum
the lesser sac of the peritoneal cavity is found...
The Greater Sac
peritoneal compartment of the abdominal cavity that extends from the diaphragm to the pelvis and covers the width of the abdomen
transverse colon (transverse mesocolon)
the greater sac is divided by the mesentery of the...
Supracolic compartment
Lies above the transverse mesocolon and contains the stomach, liver and spleen.
liver, spleen, and stomach
what is contained within the supracolic compartment?
Infracolic compartment
lies below the transverse mesocolon and contains the small intestine, ascending and descending colon
small intestine, and sometimes the ascending and descending portions of the colon
what is contained within the infracolic compartment?
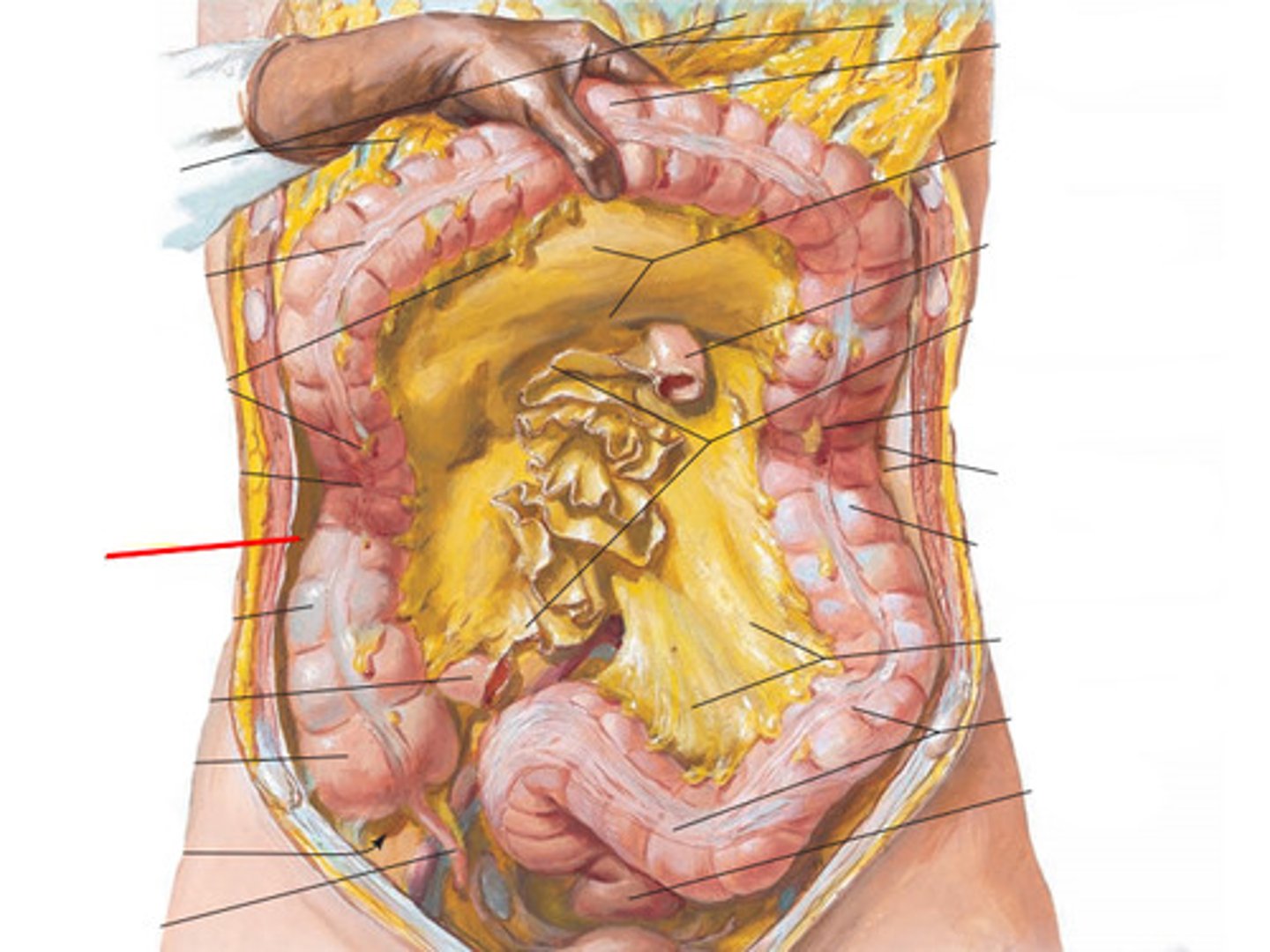
Paracolic gutters
spaces between the ascending/descending colon and the abdominal wall
The Lesser Sac
peritoneal pouch located behind the lesser omentum and stomach
Foramen of Winslow (epiploic foramen)
the opening in the lesser sac/omental bursa connects to the greater sac through the...
hepatoduodenal ligament
the lesser sac lies posterior to the free edge of the...
Foramen of Winslow (epiploic foramen)
Allows communication between the lesser and greater sacs
area of potential herniation of small bowel
if cystic artery is cut during a cholecystectomy, hemorrhage is controlled by compressing the proper hepatic artery in this foramen (within hepatoduodenal ligament)
what is the clinical relevance of the Foramen of Winslow?
Pringle maneuver
occulsion of the portal triad aka hepatoduodenal ligament.
proper hepatic artery
if the cystic artery is cut during cholecystectomy, hemorrhage is controlled by compressing the ______________.
Peritoneal fossae
depressions or pouches formed between various peritoneal folds
internal hernias
Peritoneal fossae may be the sites of...
Subphrenic spaces
small spaces between the diaphragm and the liver, on each side of the Falciform Ligament
potential spaces for pus/blood/ascites to collect
why are subphrenic spaces clinically important?
hepatorenal recess (Morrison's pouch)
the right subphrenic space is continuous with the...
fluid
the right subphrenic space/hepatorenal recess should be assessed for ____ after trauma, suspected peritonitis, abscess, etc.
provide channels for accumulation and movement of fluid in peritoneal cavity
clinical relevance of parabolic gutters