DSA07 - Benign & Malignant Diseases of the Breast
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
B/c a disproportionate amount of the breast glandular/lobular tissue is found here
Why is breast cancer MOST COMMONLY found in the Upper Outer Quadrant of the breast?
At the terminal duct-lobular units (follows duct path)
Where in the breast does cancer start forming?
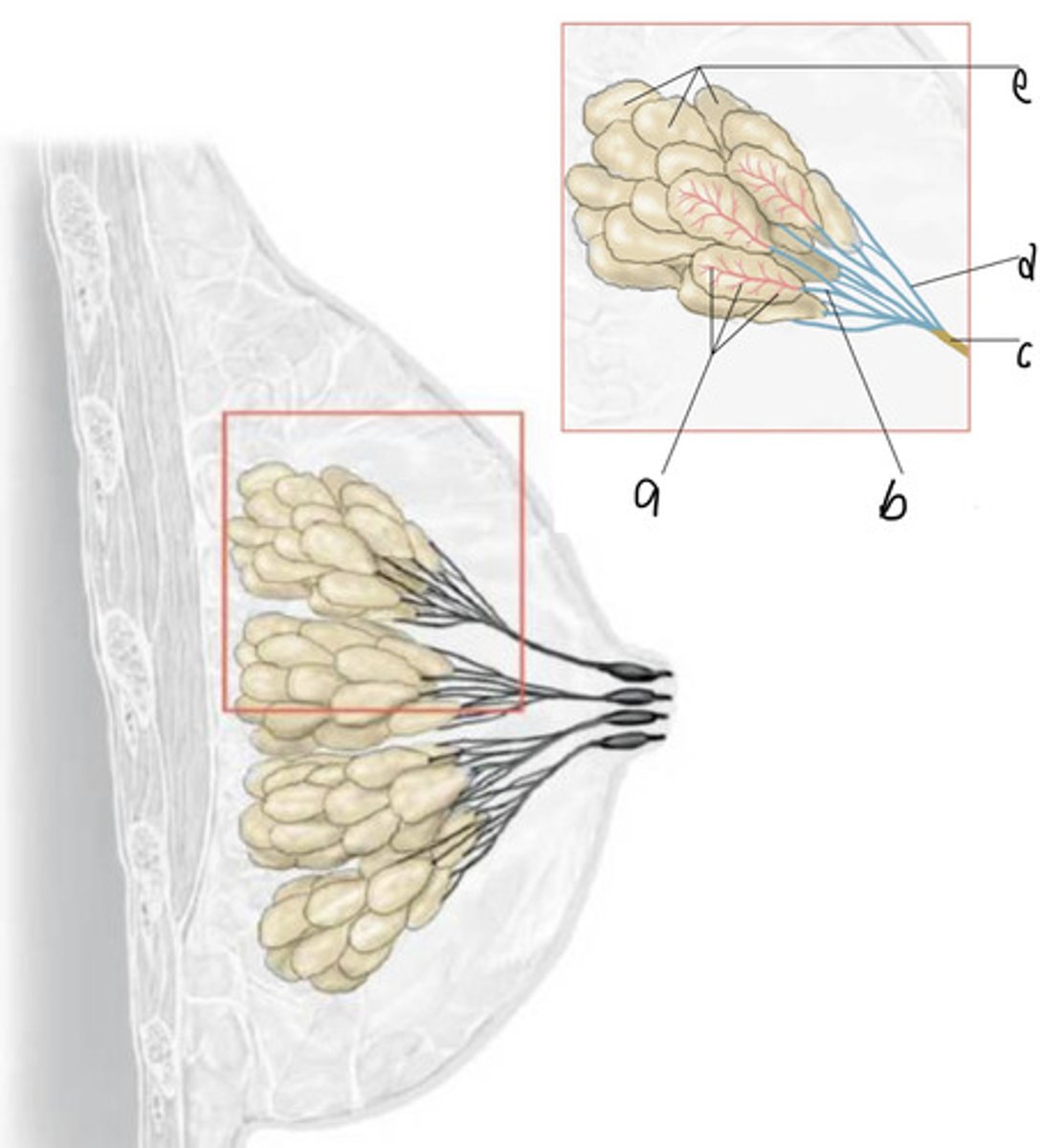
Anywhere along "milk lines" from axilla to groin
Where can congenital anomalies for the breast (ex: Polythelia, or Extra Nipples; Polymastia, or accessory breasts) be found?
-Internal Mammary Artery
-Lateral Thoracic Artery
-Thoracodorsal Artery
-Thoracoacromial Artery
-Intercostal (perforating) Arteries
List the blood supply for the breasts
-Ipsilateral Axillary LN
-Internal Mammary LNs
What are the most common routes of breast cancer metastasis?
Adipose tissue growth + Growth of Lactiferous ducts
Estrogen is responsible for what hormonal changes in the breast?
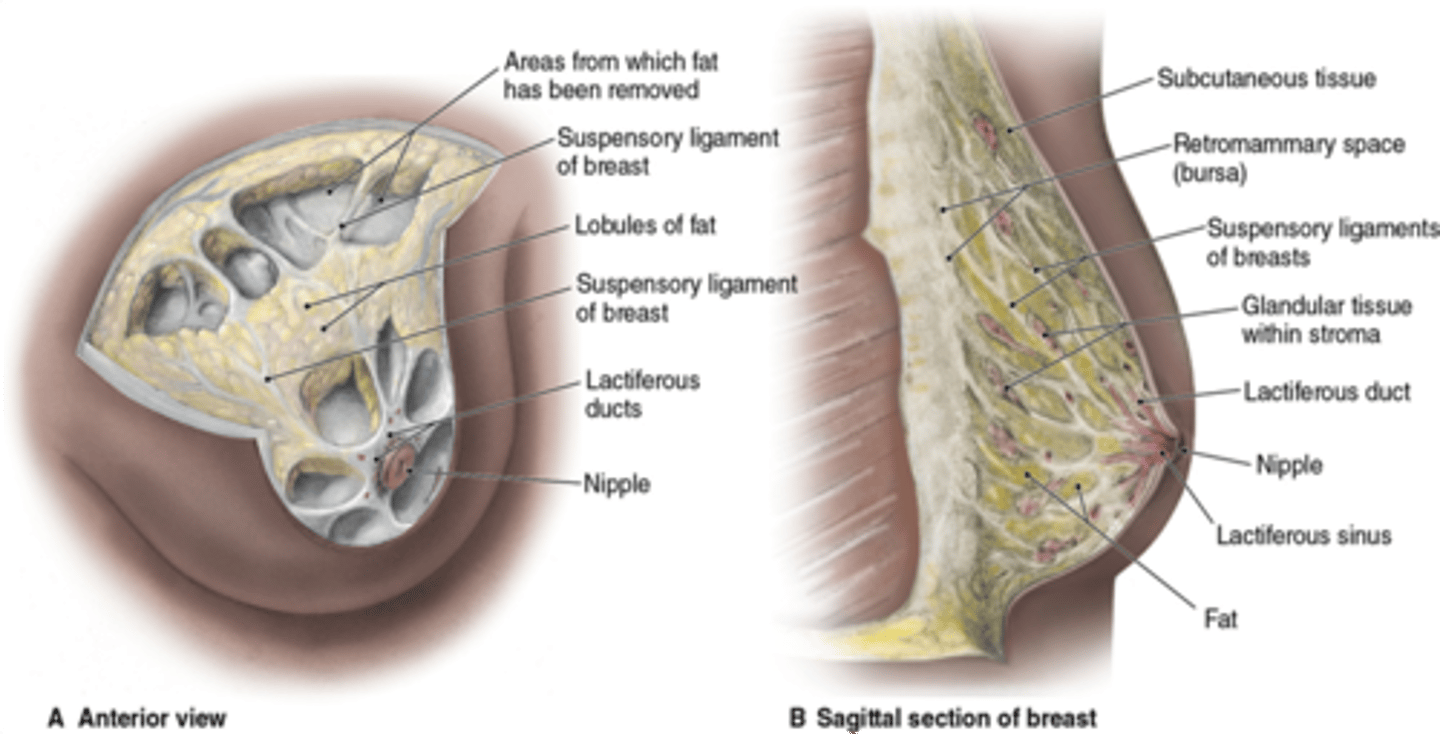
Lobular growth + Alveolar Budding
Progesterone is responsible for what hormonal changes in the breast?
-Self-Examination
-Clinical Breast Exam/CBE (> 35 y/o)
-Mammogram (> 40 y/o)
List the screenings for ASX Breast Disease Pts
-At least every 3 yrs
-YEARLY if high-risk
How often should CBEs be done in females > 35 y/o?
In Follicular Phase AFTER Menstrual Cycle
What is the best TIME to perform CBEs (aka when during the Ovarian Cycle)?
-Pain
-Mass
-Discharge
-Skin changes
What are typical complaints during CBEs of Breast Disease pts w/ Sx?
-New asymmetry/contour changes
-Nipple/skin retraction (tethering to underlying malignancy --> have pt extend arms over head to check)
-Fixed Masses
-Bloody Discharge
What are WARNING signs during CBEs of Breast Disease?
-Yearly w/ normal risk
-BEFORE 40 y/o if HIGH RISK
How often should Mammograms be done in females > 40 y/o?
Fine calcifications and densities
What should you look for on Screening Mammograms?
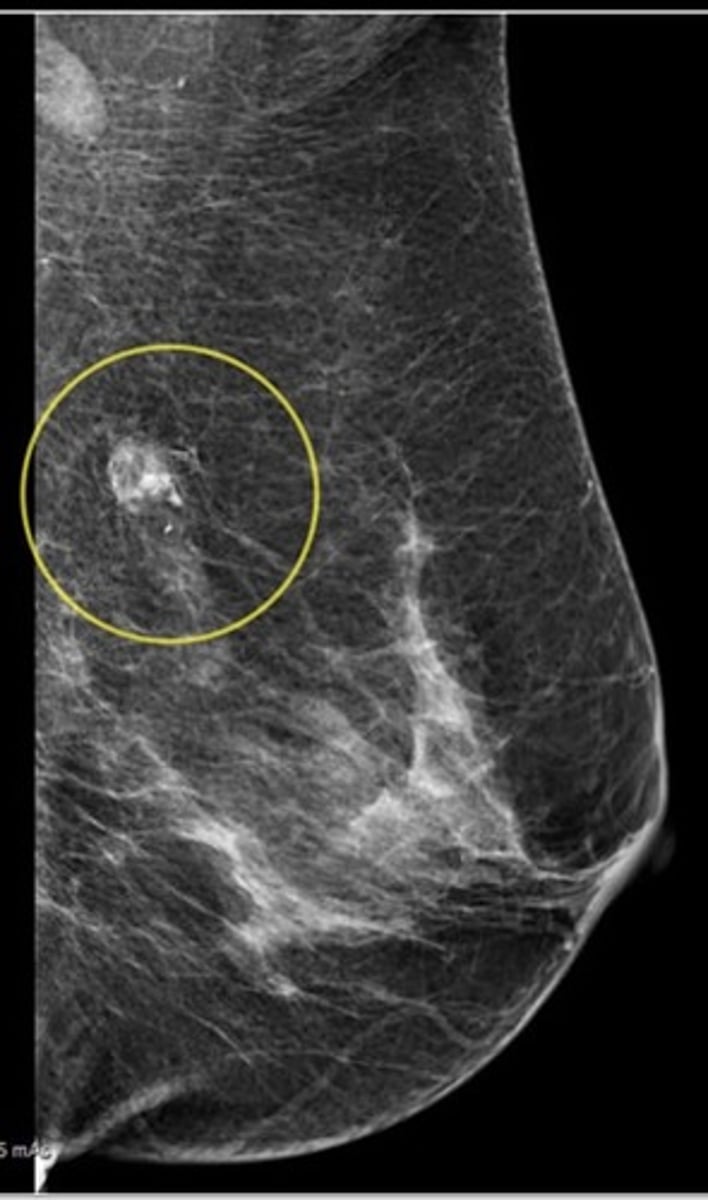
Able to detect lesions approximately 2 yrs before they become palpable
What is a benefit of Mammograms?
-To evaluate PALPABLE MASSES (differentiate cyst from solid mass)
-For Females < 40 y/o OR pregnant Pts (GREAT FOR ADOLESCENTS w/ mainly GLANDULAR tissue)
When might Breast U/S be done instead of Mammograms?
-Augmented Breasts
-Detecting Recurrence
-Improved screening if High Risk (ex: BRCA)
When might Breast MRIs be done instead of Mammograms?
-If Abn/Lesion found either CLINICALLY or on SCREENING MAMMOGRAM
-Takes MULTIPLE VIEWS w/ Radiologist present
-Use BI-RADS report
When might a DIAGNOSTIC Mammogram be done instead of a Screening Mammogram?
Describe what is done
Standardizes reporting of mammogram results
What is the purpose of the BI-RADS (Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System)?

Use a 22 gauge needle to aspirate a small, palpable suspicious lump (esp for CYSTIC LESIONS)
When is a Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) performed and how is it done?
Discard the smear prepped for cytology evaluation
If a post-FNA lesion disappears, the fluid is NOT bloody, and the pt is < 50 y/o, what should you do?
Send prep for cytology
If a post-FNA lesion is BLOODY or DOESN'T DISAPPEAR what should you do?
Core/Open Biopsy
If there are clinical/imaging signs of suspicion (REGARDLESS of POSITIVE or NEGATIVE CYTOLOGY), what should be done after cytology?
-Clinically suspicious findings
-(+) FNA
-Non-collapsing/Recurrent mass after FNA
-Benign Mass BUT Positive PMHx or FHx of Breast/Ovarian Ca, Hx of Atypical Hyperplasia, Equivocal findings on mammogram/cytology
List ALL the indications for Core or Open Breast Biospy
Luteal Phase in Outer Breast Quadrants
When and where does CYCLIC Breast Pain usually occur?
Drop in Progesterone (more so DELTA of Progesterone) + Increase in Estrogen in Latter half of menstrual cycle
What physiologically causes Breast Hyperplasia?
If it's a/w cellular atypia (increases risk for malignancy)
Given that Breast Hyperplasia is very common, when does it start to become concerning?
-Multiple/Bilateral lesions
-Pain & Tenderness
If Breast Hyperplasia is accompanied by Sx (often Sx and is found in imaging), what are those Sx/Signs?
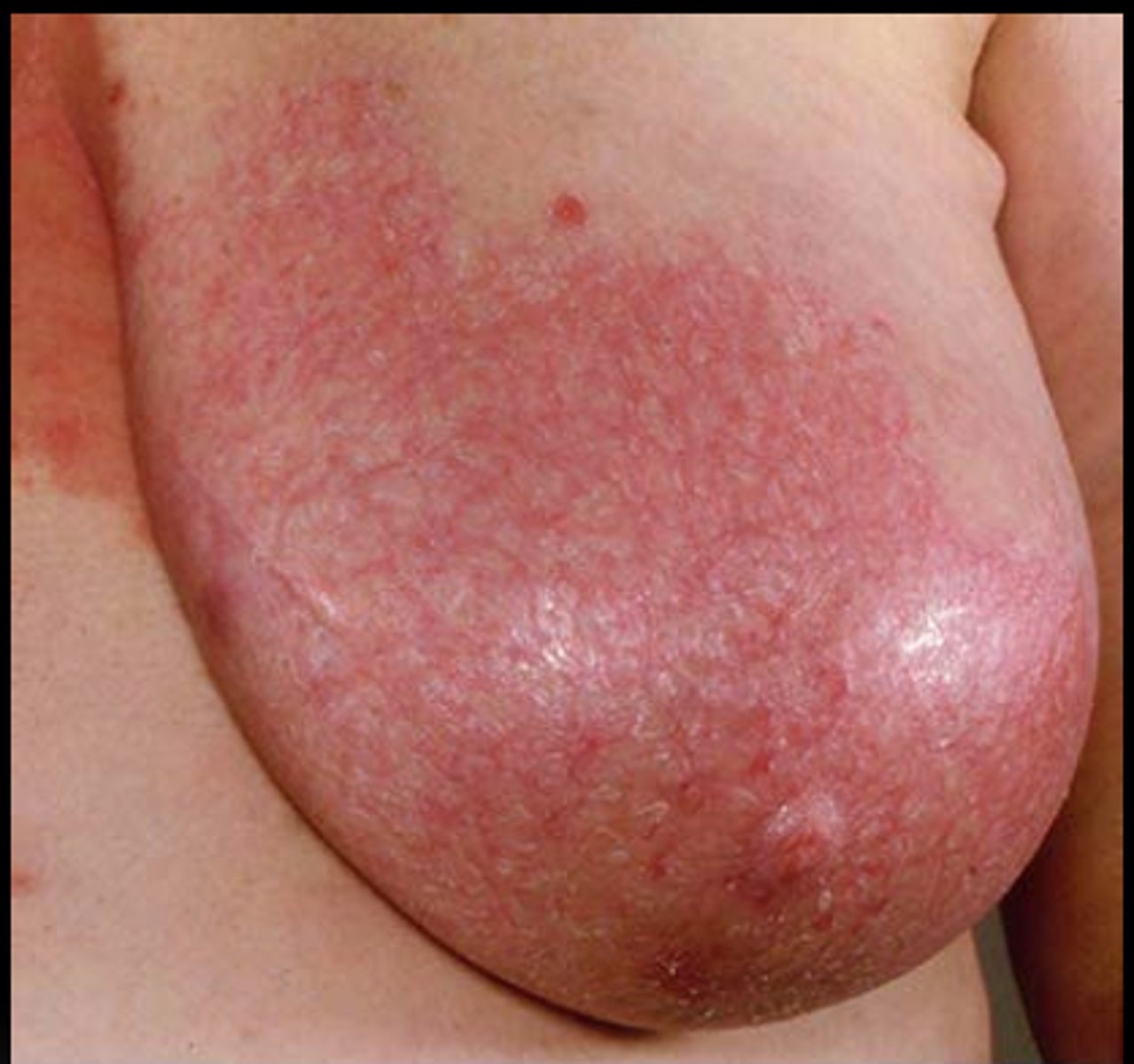
Mastitis
Define Condition:
Infex of Breast Tissue
-Path: Usually lactational (d/t blocked duct/cracks in nipple) + bacterial Infex (MCC = S. aureus)
-Sx/PE:
> Breast pain
> Breast Edema
> Erythema around breast
> Fever
> Chills
> Generalized Malaise
-Tx:
> Abx (Dicloxacillin) + Supportive Care
> NSAIDs
> CONTINUE BREAST BEEDING/Pumping
> Ice Packs/Cold Compress
Breast Abscess
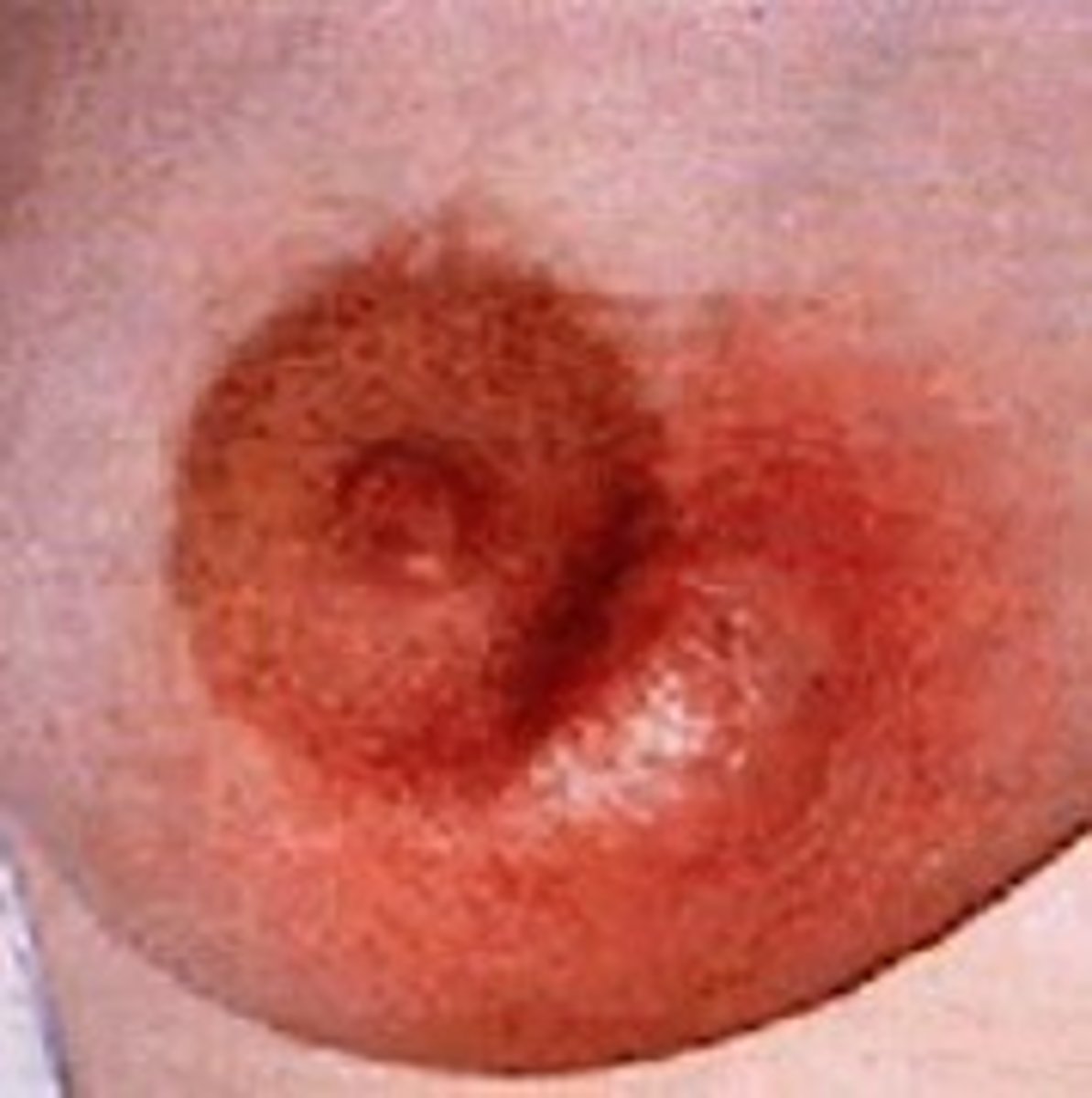
Define Condition:
Mastitis that developed into infected pocket of pus
-Sx:
> Erythema
> Tender, Indurated mass
> Fever
> Chills
> Malaise
-Dx:
> Smaller = Small FNA
> Larger = I&D and Packing (Surgeon)
-Tx: Abx
Simple Fibroadenomas
Define Condition:
Common BENIGN breast tumor
-Hx: Teens to early 20s
-Sx:
> Breast Pain
> Breast "Lumps" (bilateral & multifocal)
-PE: Solid, Firm, Round, Rubbery, Mobile; May enlarge in pregnancy (discomfort)
-Prog: Subtypes w/ more malignancy potential
> Sclerosing adenosis
> Epithelial hyperplasia
-Chest wall trauma
-Rib fracture
-Costochondritis
-Shingles
-Fibromyalgia
-Cardiac or pulmonary diseases
List what conditions might cause pain in breast region that does NOT originate from breast tissue
-NON-Spontaneous
-NON-Bloody
-Bilateral
Describe Breast Discharge that would be considered "Benign"
-Bloody
-UNI-lateral w/ associated mass
Describe Breast Discharge that would be considered "Suspicious"
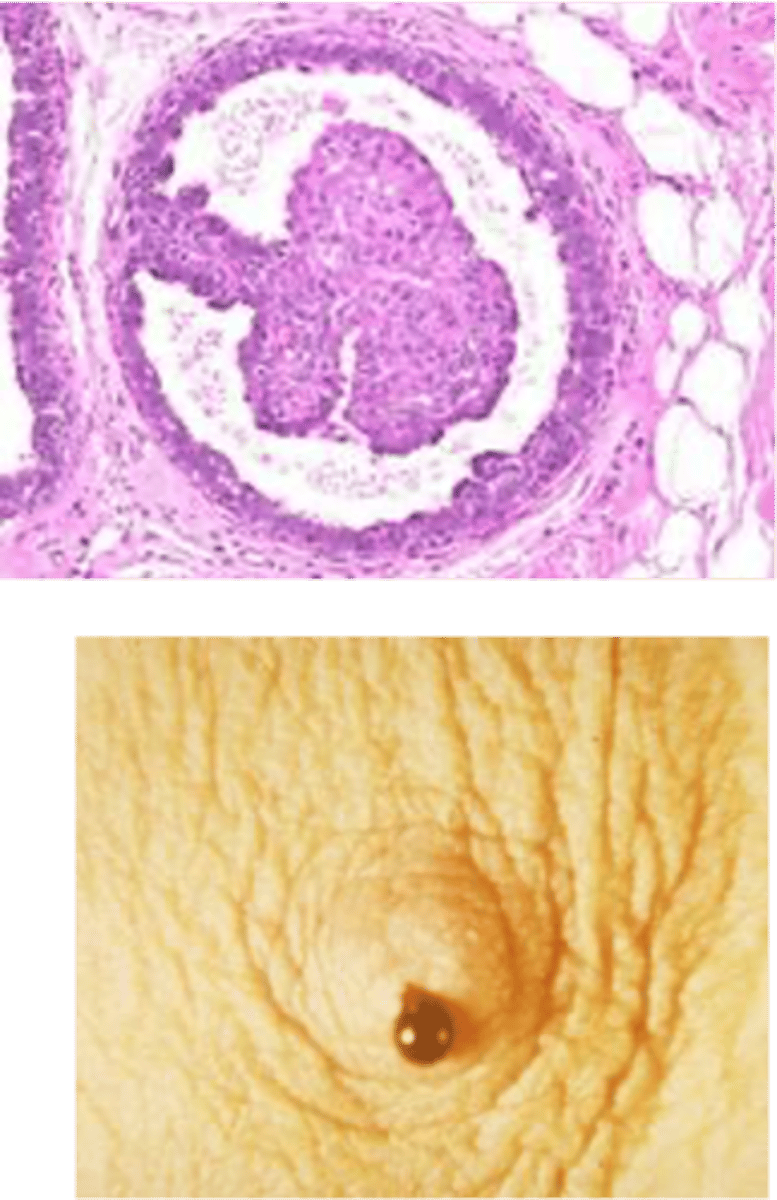
Intraductal Papilloma
Define Condition:
Small fibroepithelial tumor w/in lactiferous ducts, typically beneath areola
-Hx:
> MCC of Nipple Discharge
> Close to or at Menopause (> 45 y/o)
> Usually NOT a/w cancer (slight inc risk)
-Sx/PE:
> Serous, Bloody Nipple discharge
> Rarely Palpable
-Dx:
> Mammography
> Fluid Cytology
-Tx: EXCISION of lesion & involved duct
Ductal Ectasia
Define Condition:
Mammary duct beneath the nipple becomes dilated and obstructed with fluid, often causing nipple discharge
-Hx: PERIMenopausal Women (45 - 55 y/o)
-Sx/PE:
> Thick, GREEN Nipple discharge
> Tenderness/Erythema of nipple and surrounding area
> Can be Asx
-Tx: SELF-LIMITING (Tx w/ Abx if Bacterial Superinfection)
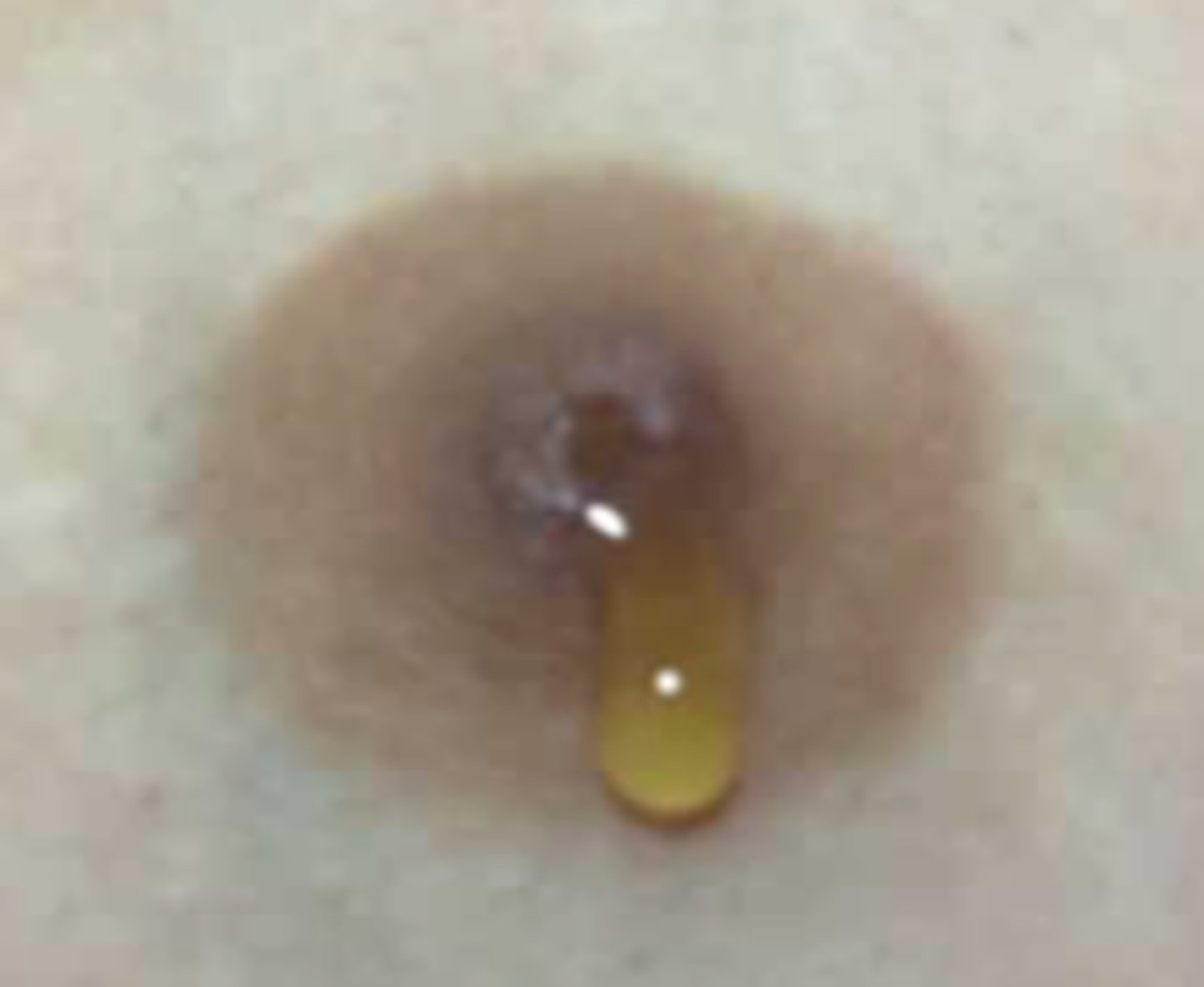
Galactorrhea
Define Condition:
Milky Bilateral Discharge
-Hx:
> IDIOPATHIC in 50%
> Stress
> Nipple Stimulation
> Pregnancy
> MC HORMONAL = Hyperprolactinemia, Thyroid Conditions
> Meds:
>> Antipsychotics
>> SSRIs
>> Opioids
>> PPIs
-Sx: (Optic Chiasm compression from pituitary adenoma)
> Headaches
> Bitemporal Hemianopsia
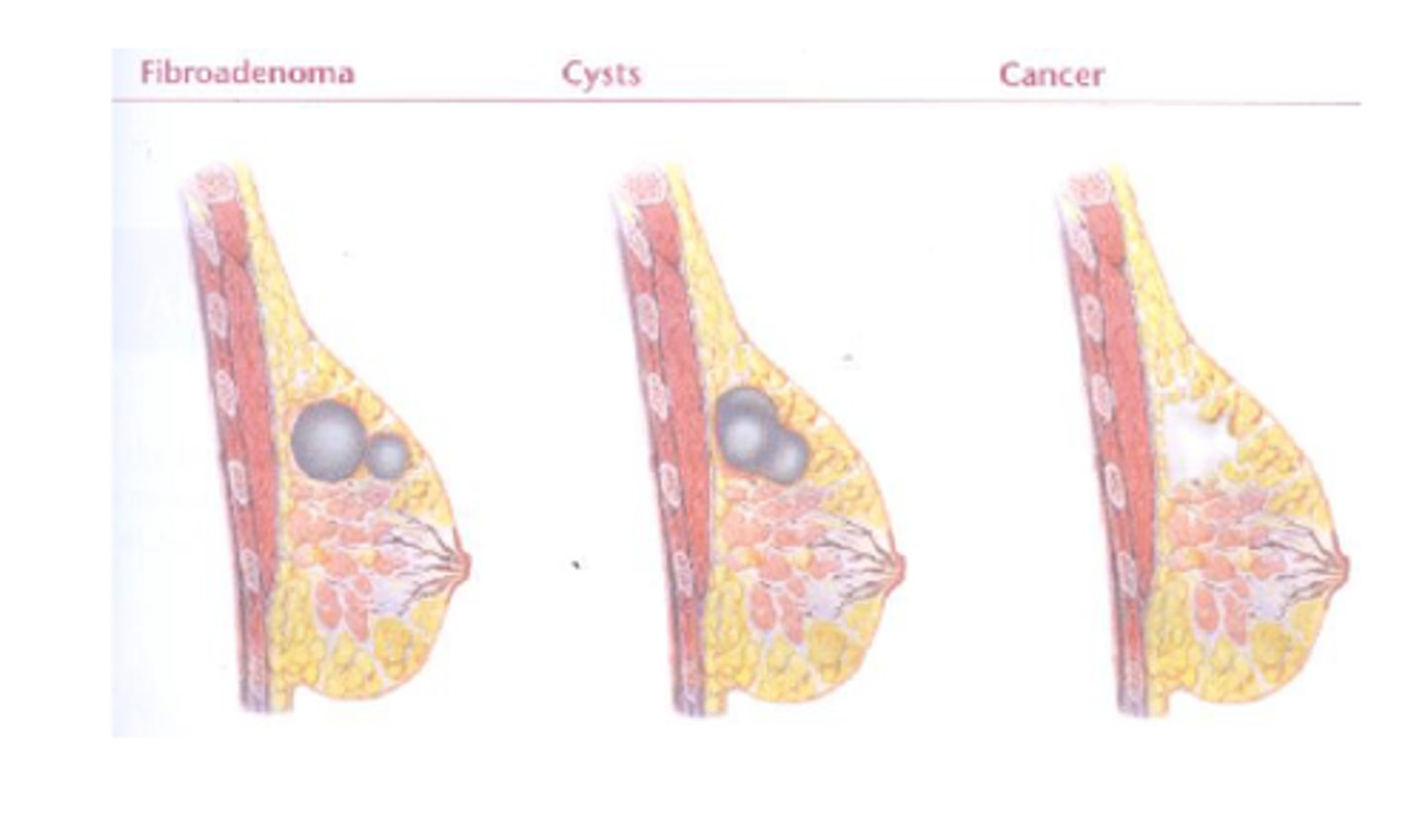
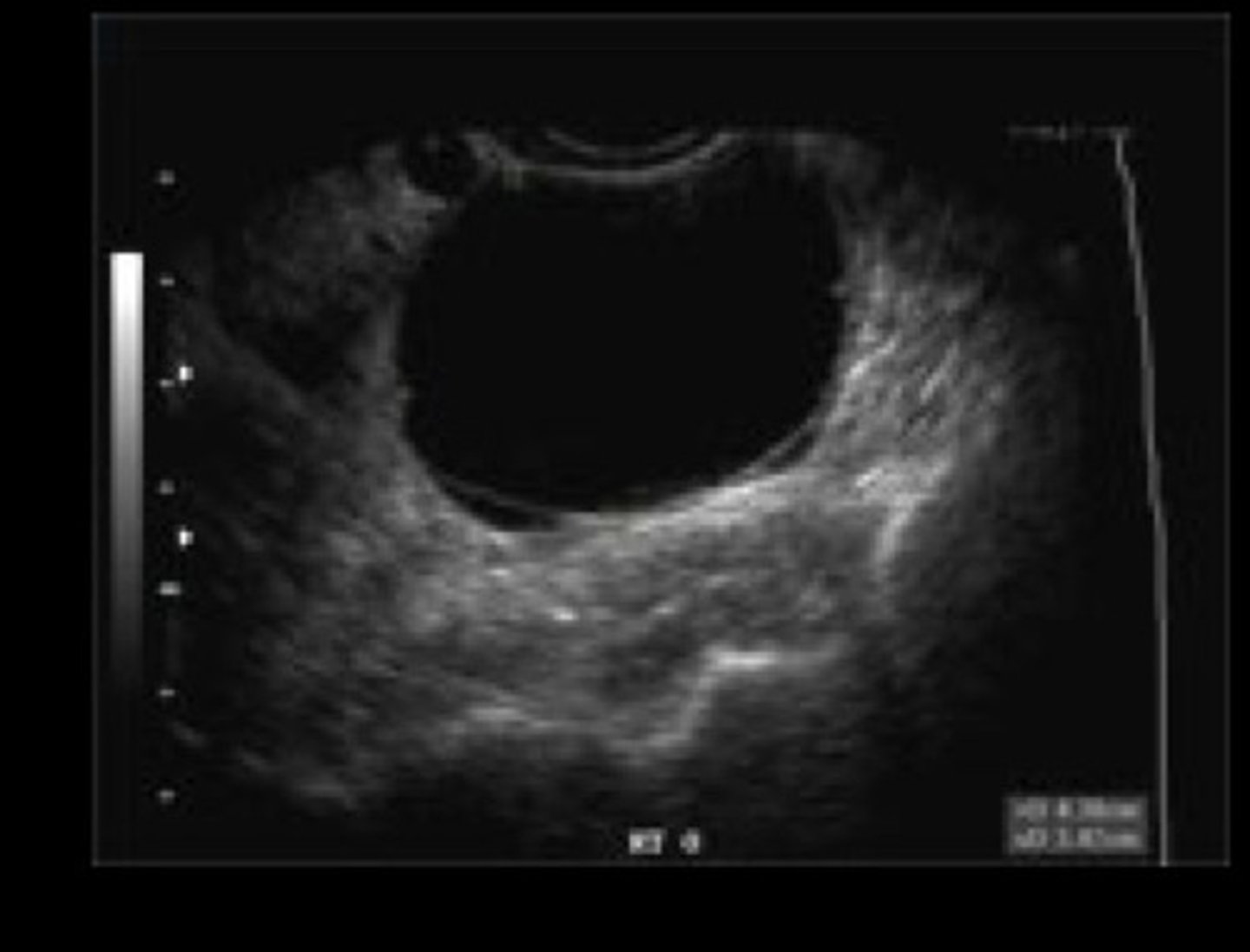
Cyst
Define Condition:
-Hx: YOUNGER Age
-Path: Benign if simple (if complex - aka w/ solid components OR persists --> WORRISOME)
-Dx:
> US!
> FNA for Sx relief and/or diagnosis
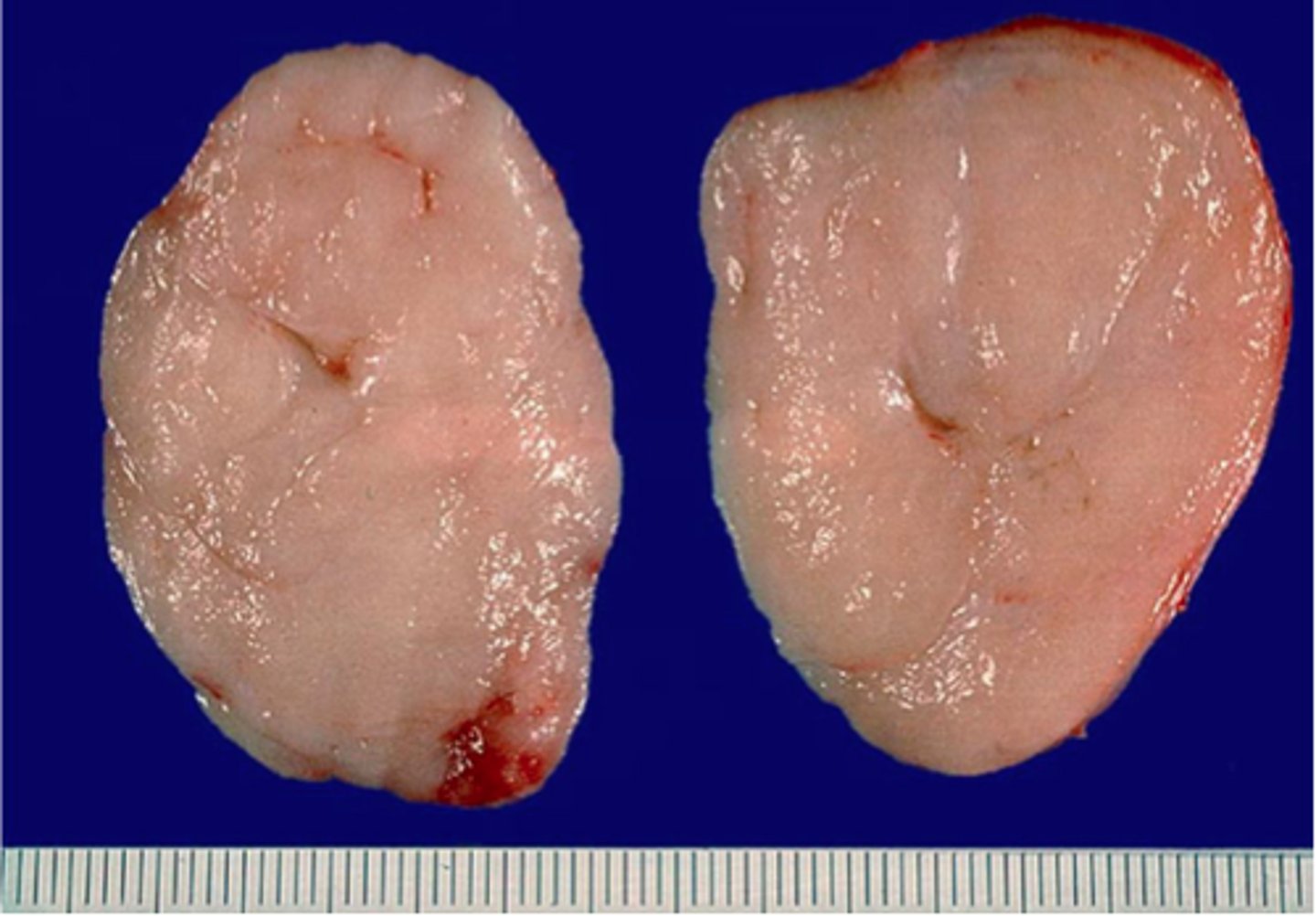
Fibroadenoma
Define Condition:
MC BENIGN Tumor of Female Breast
-Hx:
> ANY AGE, but usually before 30 y/o
-Dx:
> Gross =
>> Mobile, firm, sharply circumscribed
>> SOLITARY and 2-4 cm
> Micro = Fibrous & Glandular Tissue
-Prog:
> MORE ESTROGEN (Pregnancy, PMS) --> Bigger & More Tender
> Giant Form (up to 15 cm) = Malignant Potential
-Tx: Surgical Excision!
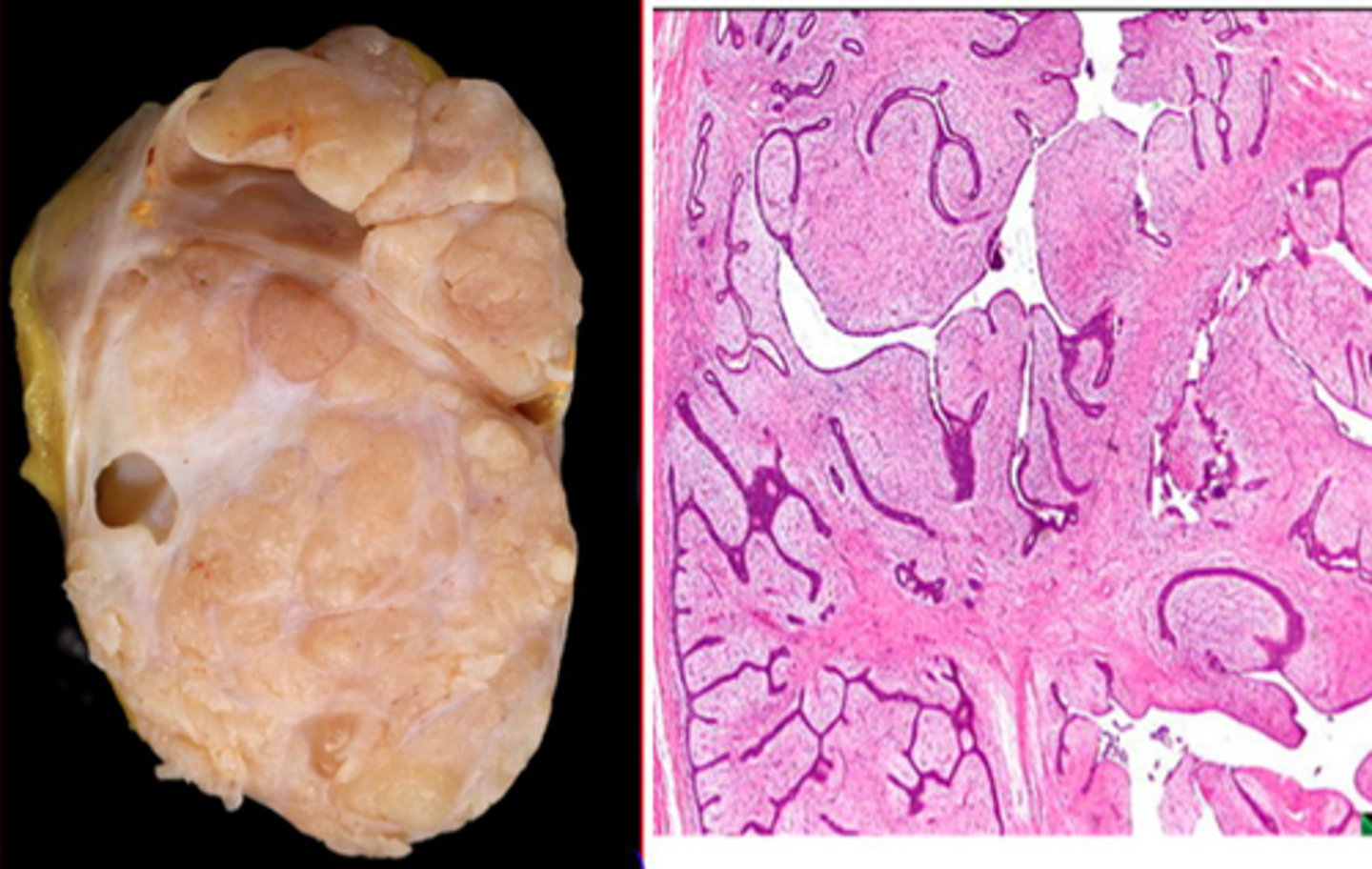
Phyllodes Tumor
Define Condition:
Large, fast-growing masses of connective tissue and cysts - rare variant of Fibroadenoma
-Hx:
> Perimenopausal (MC = 50s)
> RARE (less than 1% of breast tumors)
-Path: Can be benign, borderline, malignant (all forms have malignant potential)
-Tx: Surgery with or w/o radiation
Fat Necrosis
Define Condition:
Area of fatty breast tissue is damaged, usually as a result of trauma but can also occur after surgery or radiation, resulting in scar tissue
-PE: Palpable lump that can be difficult to differentiate from cancer
> Benign
> PAINLESS
-Dx:
> Need Imaging & BIOPSY!
> Micro = Oil Cysts (Fat Cell Necrose)
-Tx:
> Self Limiting
> FNA/Lumpectomy
-Prog: NO INCREASE in breast cancer risk
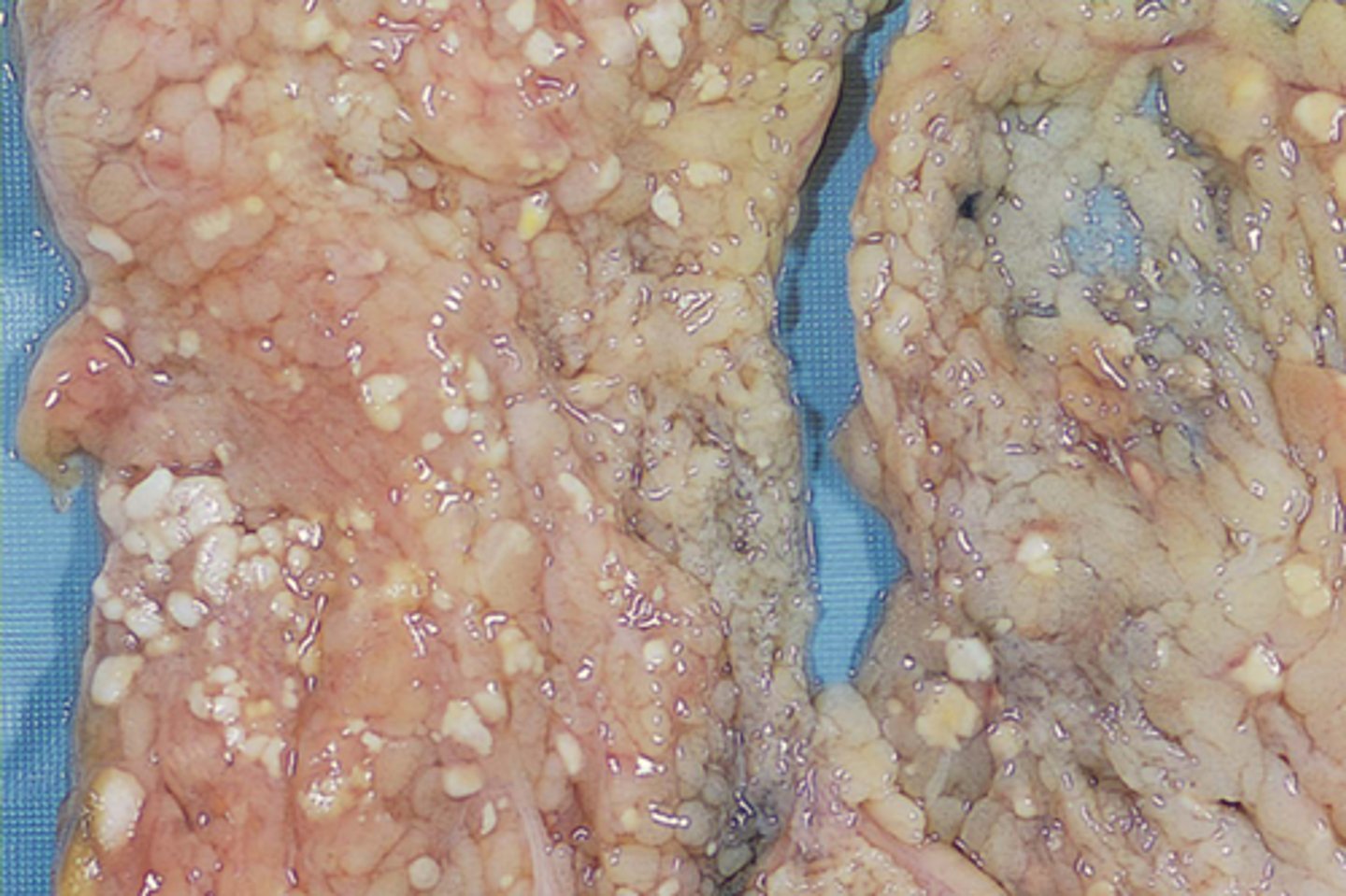
Galactocele
Define Condition:
Cystic dilation of a duct filled with thick, milky fluid due to ductal obstruction (inflammation, hyperplasia, or neoplasia)
-Hx: During or After Lactation
-Sx/PE: Multiple Cysts present
-Prog: Secondary Infex (Mastitis/Abscess)
-Tx: FNA (CURATIVE)
> If bloody/residual mass ==> Excisional Biopsy
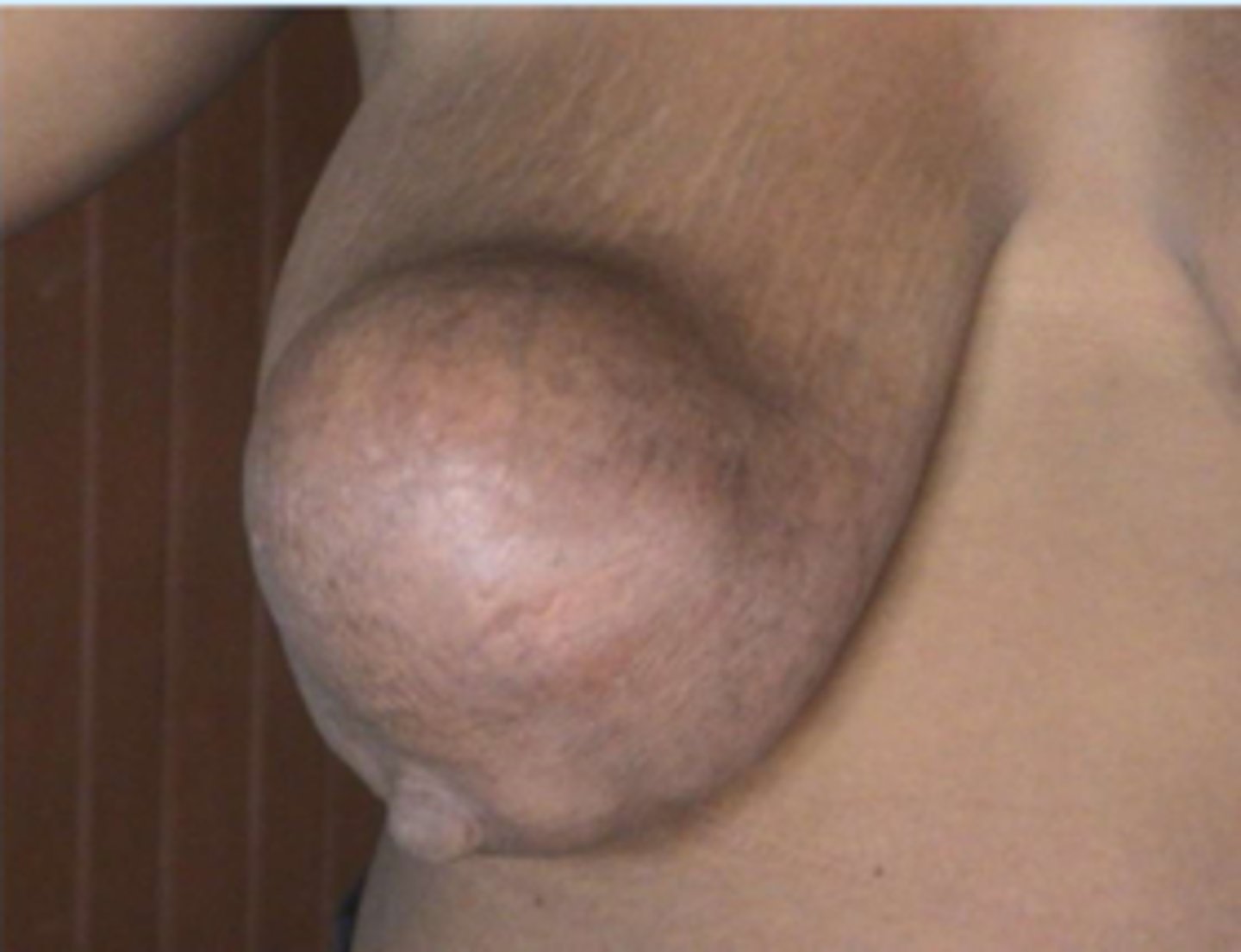
-Size > 2 cm
-Immobility
-Poorly defined margins
-Can be PAINLESS
-Firmness
-Skin dimpling/color changes
-Retraction/nipple changes
-Bloody nipple discharge
-Ipsilateral lymphadenopathy
List the characteristics that are concerning for MALIGNANCY
Breast Cancer
Define Condition:
Most common female malignancy (1/4); Second leading cause of cancer death in women
-Hx:
> 1 in 8 change of developing (40,000 die each year)
> 5x higher in North America and Northern Europe
> Age > 50 y/o
> 5-10% HEREDITARY
>> BRCA gene:
>>> Inc risk of Ovarian Cancer (also higher incidence of prostate, pancreatic, gastric cancers)
>>> If Hereditary = More in PRE-menopausal women
>>> Up to 70% risk developing by age 65
>> Lynch Syndrome
> Nongenetic Factors (MORE ESTROGEN):
>> Early menarche
>> Late menopause
>> Late first pregnancy (after 30)
>> Nulliparity
>> No breast feeding
>> Combination Hormone replacement therapy >5 yrs
>> Obesity
>> Chest radiation
>> Benign breast disease (atypical hyperplasia)
-Prog:
> Depends on AXILLARY NODE INVOLVEMENT (No nodes = 83% 5 yr; > 4 nodes = 45% 5 yr)
> Better If Diagnosed OLDER
-Start mammography screening or MRI at Age 25
-Screen person w/ known breast cancer FIRST (if possible)
What should be done diagnostically if pt has FHx of BRCA mutation?
BRCA1
Which BRCA mutation is described?
> Chromosome 17
> AD (High Penentrance)
> Breast Cancer Risk = 55-85%
> Ovarian Cancer Risk = 15-40%
BRCA2
Which BRCA mutation is described?
> Chromosome 13
> AD (High Penentrance)
> Breast Cancer Risk = 30-50%
> Ovarian Cancer Risk = 25-30%
> Male Breast Cancer = 6%
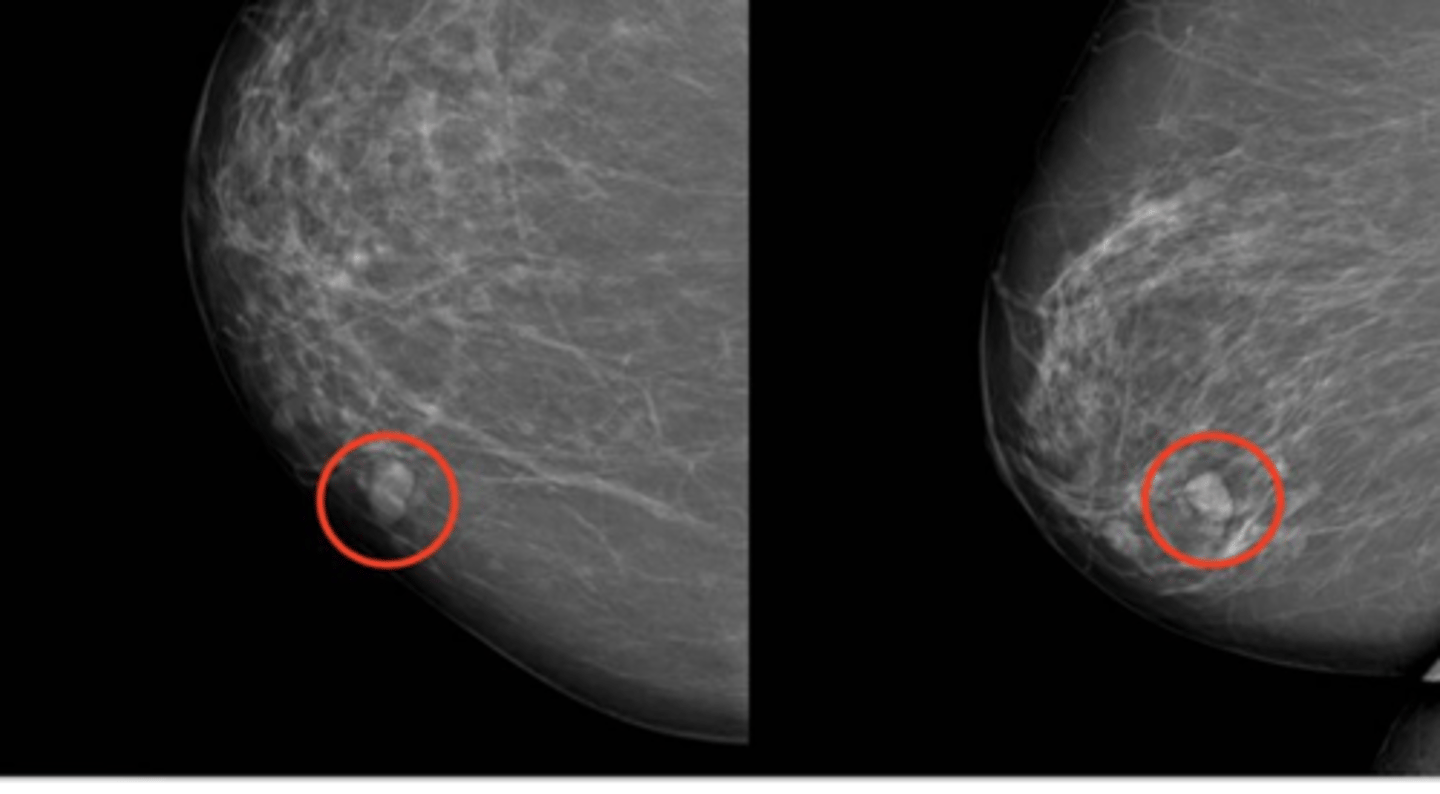
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
Define Breast Cancer:
Breast cancer at its earliest stage before the cancer has broken through the wall of the milk duct
-Hx:
-Path: NONInvasive
> Fills ductal lumen (arises from DUCTAL ATYPIA)
> Early malignancy WITHOUT basement membrane penetration
-Sx/PE: Not usually palpable
-Dx: Mamm = Micro-calcifications
-Prog: Inc risk of cancer in same breast/quadrant
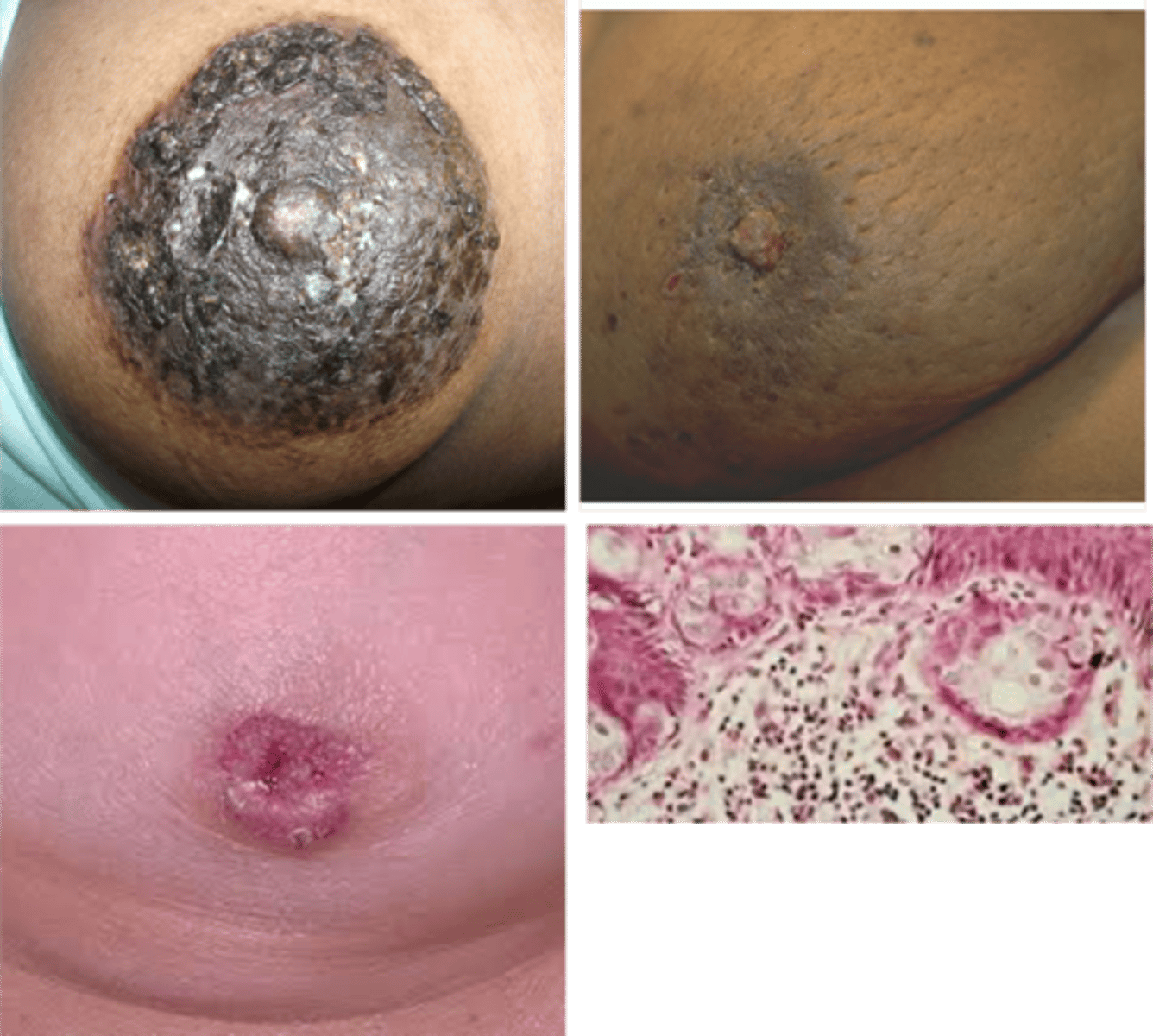
Paget Disease
Define Breast Cancer:
Extension of DCIS/invasive breast cancer up the laciferous ducts and into contiguous skin of nipple --> eczematous patches over nipple/areolar skin
-Hx: 3% of breast cancer
-Path: NONInvasive
-Sx/PE: 2/3 of PALPABLE mass
-Dx: Intraepithelial adenocarcinoma cells
Lobular Carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
Define Breast Cancer:
-Hx: INCIDENTAL finding on biopsy
-Path: NONInvasive
> Decreased E-cadherin expression
-Sx/PE:
-Dx: NO MASS OR CALCIFICATIONS on Mammogram
-Prog: Inc risk of breast cancer in EITHER breast
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Define Breast Cancer:
-Hx: 80% of all breast cancer
-Path: INVASIVE
> Significant fibrotic response
-Sx/PE: STONY HARD (Firm, fibrous, "rock hard" mass with sharp margins)
-Dx: Histo = Small, glandular, duct-like cells in desmoplastic stroma
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Define Breast Cancer:
-Path: INVASIVE
> Decrease E-cadherin
-Sx/PE: Bilateral w/ multiple lesions in same location
-Dx: Histo
> Orderly row of cells ("single file") and NO duct formation
> LACKS desmoplastic response (pervasive growth of dense fibrous tissue around the tumor)
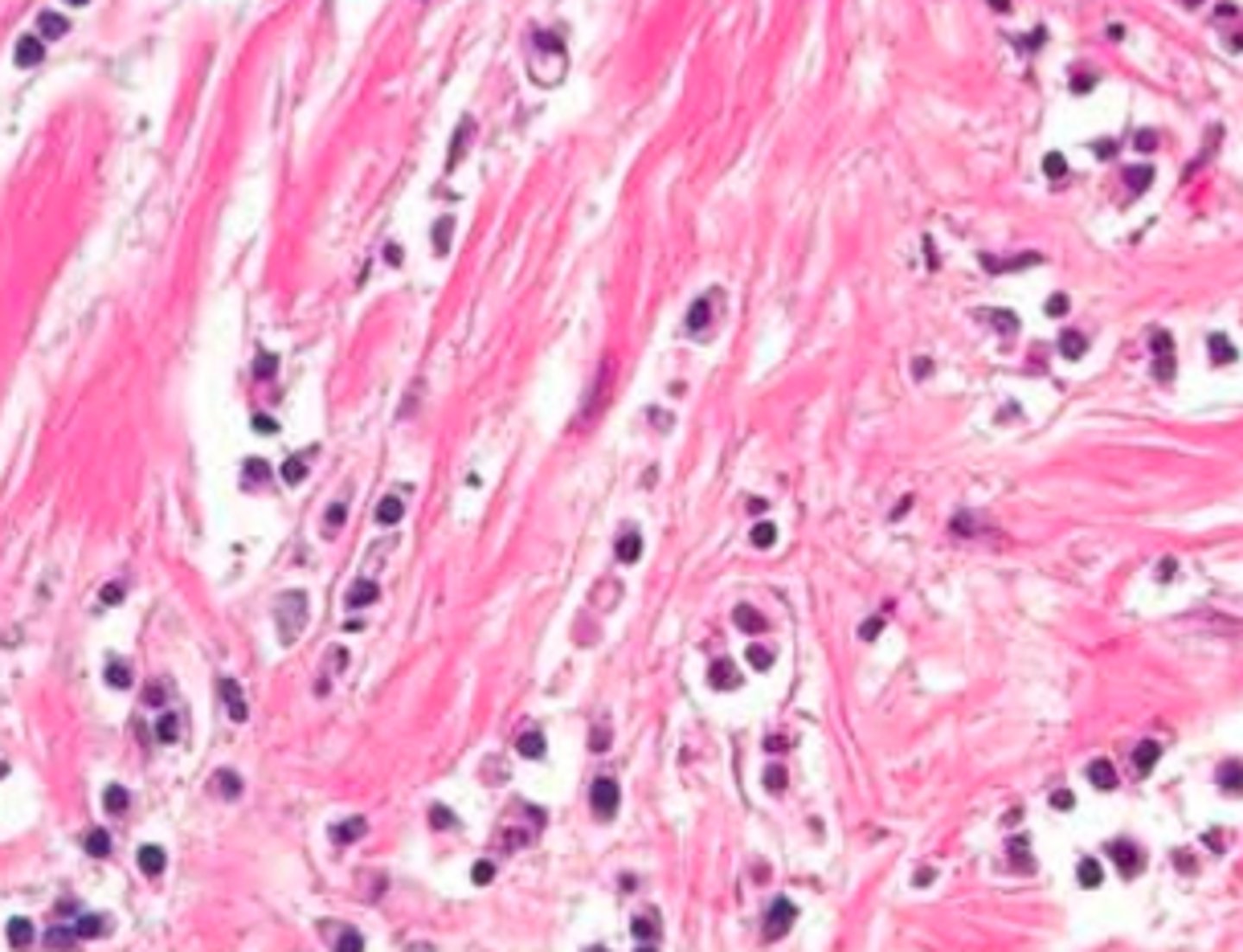
Medullary Carcinoma
Define Breast Cancer:
-Path: INVASIVE
-Dx: Histo/Gross
> Well-circumscribed tumor (mimics fibroadenoma)
> LARGE, ANAPLASTIC cells in sheets (a/w plasma cells & lymphocytes)
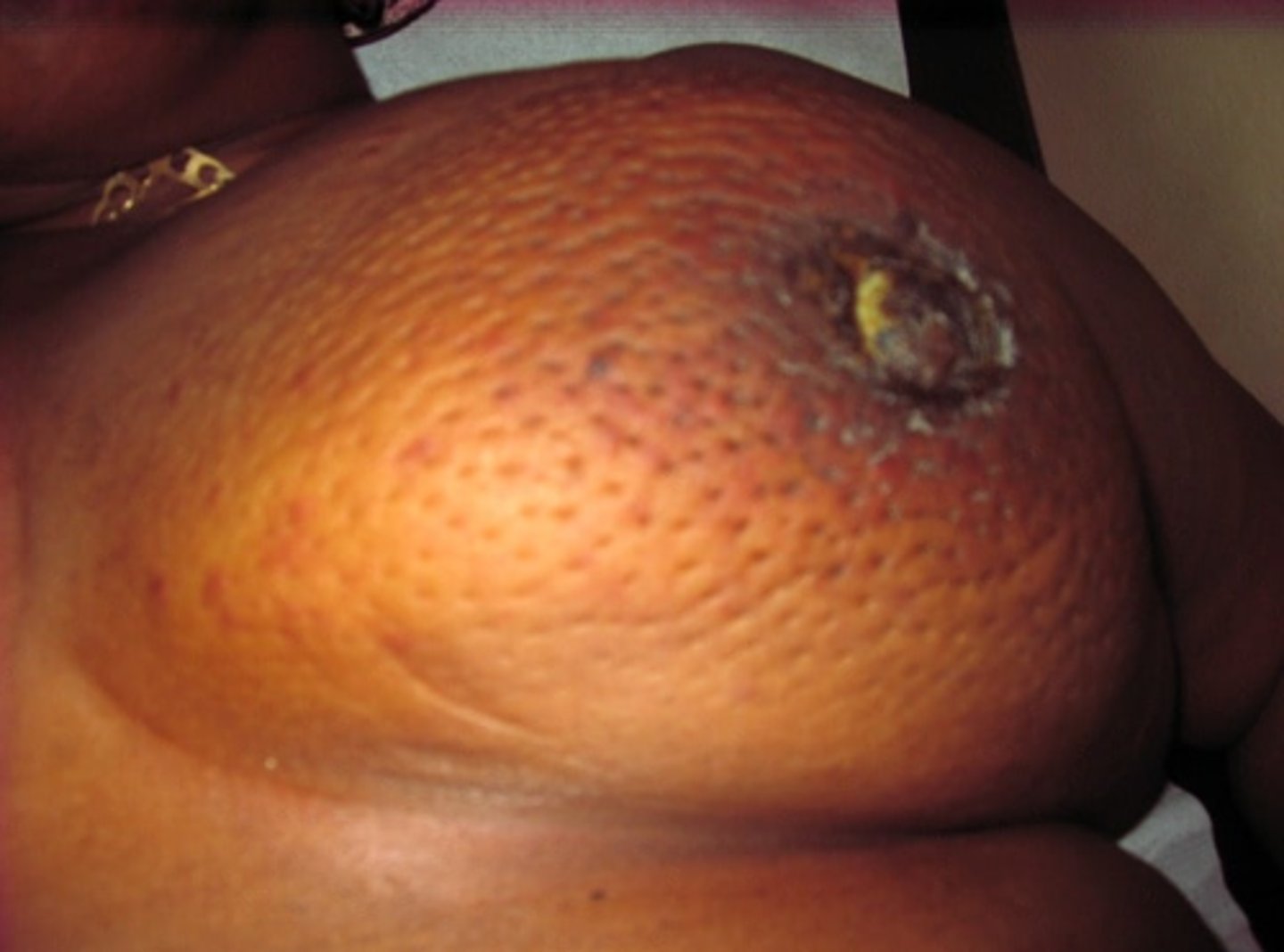
Inflammatory Carcinoma
Define Breast Cancer:
Info
-Hx:
> 1-4% of breast cancers
> Often in Pregnancy or Younger Women
-Path: INVASIVE & AGGRESSIVE
-Sx/PE:
> Warm & red
> Indurated & painful
> Peau d'orange (d/t dermal lymphatic space invasion --> lymphedema and skin thickening)
> Lacks palpable mass
> Palpable LAD at initial presentation
-Dx: Histo = malignant cells invade dermal lymphatic space causing obstructive lymphangitis; inflammatory cells are rarely present
-Prog: POOR (50% survival in 5 yrs)
Parenchyma --> Skin/Deep Pect Fascia ==> AXILLARY NODE FIRST --> Internal Mammary Chain (1st if medial/central) --> Supraclavicular Node
What is the order of breast cancer spreading LYMPHATICALLY?
MAINLY to LUNGS and LIVER (later = brain, bone, pleura, ovaries)
How does breast cancer spread HEMATOGENOUSLY?
True
T/F - Results of wide local excision/lumpectomy in selected patients are comparable to that of modified radical mastectomy
If the sentinel node is negative, then axillary node will be negative 95% of the time
Why is LN mapping and sentinel node biopsy preferred over axillary LN dissection for surgical treatment options?
-Had equivalent outcomes to modified radical or simple mastectomy
-Improved functional and cosmetic results
Why should radiation ALWAYS be performed in conjunction w/ conservative surgery?
Risk of Lymphedema
Why should radiation to axilla POST-DISECTION be avoided?
Tamoxifen (Aromatase inhibitor follows)
Estrogen/Progesterone Receptor (+)/ER + Breast Cancer pts should receive what adjuvant therapy?
None - just chemo
Estrogen/Progesterone Receptor (-)/ER - Breast Cancer pts should receive what adjuvant therapy?
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
Human Epidermal Growth Factor 2 (+)/HER2 + Breast Cancer pts should receive what adjuvant therapy?
-Receptor ANTAGONISTS in BREAST
-Receptor AGONISTS in BONE
-Block binding of estrogen to ER+ cells
What is MoA for Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERMs?
Breast Cancer treatment and prevention (in ER/PR + cases)
What is Clinical Use for the Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERM, Tamoxifen?
Partial AGONIST in endometrium => increased risk of endometrial cancer; Can use up to 5 years & may increase BMD
What are the S/Es for the Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERM, Tamoxifen?
Prevent Osteoporosis (increased BMD) & breast cancer prevention
*NO TIME LIMIT + NO RISK OF ENDOMETRIAL CANCER*
What is Clinical Use for the Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERM, Raloxifene?
ANTAGONIST in endometrium => NO increased risk of endometrial cancer
What are the S/Es for the Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERM, Raloxifene?
Increased risk of thromboembolic events (DVT, PE) and "hot flashes"
What are the S/Es for BOTH Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators/SERMs?