PSK4U - kinesiology exam flashcards
1/228
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 1, 5-7, 9-11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
3 main energy nutrients
carbohydrates, fats & proteins
What does carbohydrates break down into
glucose
Where is glucose stored & in what form
stored in skeletal muscles & liver
form of glycogen
Metabolism
chemical processes which break down food & convert it into energy
ATP
full form
what is it
what does it turn into
Adenosine triphosphate
3 phosphates attached to 1 adenosine by a ribose sugar molecule
Energy stored inside the tight bonds & is released when ATP is metabolized (phosphate is removed)
When a ATPase breaks apart bonds, ADP is created
2 energy systems
(which is w/ oxygen, which is w/ out), (where does it occur), (classify the twitch)
Anaerobic Systems (w/ out O2)
1st
occurs in CYTOPLASM of muscle fibres
quick & powerful movements, doesn’t last long
Fast Twitch
Aerobic Systems (w/ O2)
once Anaerobic runs out
occurs in MITOCHONDRIA
Slow twitch
Anaerobic System
w/ out oxygen
fast twitch
CYTOPLASM
doesn’t last long
lactic acid buildup due to lack of oxygen
Aerobic
w/ oxygen
slow twitch
MITOCHONDRIA
3 Metabolic Pathways
ATP-PC pathway (Anaerobic Alactic)
Glycolysis (Anerobic lactic)
Cellular Respiration (Aerobic)
ATP-PC System
classification
location
energy source
oxygen or no
# of ATP produced
Duration
Muscle fibre type
Advantage / Disadvantage
(Anaerobic Alactic Sys.)
Cyptoplasm
ADP & PC (phosphocreatine)
ADP + PC —> ATP + creatine
w/out oxygen
1 ATP
10-15 sec
Fast twitch
Adv: available automatically
Dis: runs out quickly
ATP-PC energy source
ADP + PC (phosphocreatine) —> ATP + creatine
Glycolysis
classification
location
energy source
oxygen or no
# of ATP produced
Duration
Muscle fibre type
Advantage / Disadvantage
(Anaerobic lactic)
Cytoplasm
Glucose (glycogen)
w/out oxygen
Lactic acid burn → no oxygen
2 ATP per glucose
15 sec - 3mins
Fast twitch
Adv: produces double ATP
Dis: burns due to lactic acid since no oxygen/recovery is 30-60 MINs
Glycolysis recovery time
30-60 mins
Glycolysis duration
15 sec - 3 min
Glycolysis energy source
Glucose (glycogen)
Cellular Respiration
classification
location
energy source
oxygen or no
# of ATP produced
Duration
Muscle fibre type
Advantage / Disadvantage
(Aerobic)
Mitochondria
Fats, Protein, Glucose
HAS oxygen
Glucose + oxygen + ADP + phosphate → Co2 + 36ATP + h20
36 ATP produced
1 min
Slow twitch
Adv: LOTS of ATP
Dis: 1 day to recover, takes a long time to kick in, muscle fatigue
Cellular Respiration duration kick in
1 min
Cellular Respiration #ATP produced
36 ATPs produced
Cellular Respiration # of rxns
20 rxns
ATP-PC enzyme
creatine kinase
Cellular Respiration Energy Sources
fats, proteins
Aerobic Systems (cellular respiration pathways)
glycolysis w/ oxygen (pyruvate)
Kreb’s cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Does fast twist need oxygen or does slow twitch need O2
Slow twitch needs O2
Myoglobin
a protein that stores and delivers oxygen to muscles
having more myoglobin lets you perform for longer
Hemoglobin
protein in red blood cells that delivers oxygen to tissues
Slow-Twitch Muscles
classification
myoglobin
colour
myosin ATPase
glycolytic enzyme
oxidative enzyme
relative size
cellular respiration (aerobic)
aka: slow-oxidative
MORE myoglobin, OXYGEN delivery
darker red in colour
maintain low-level activity for long time (walking) → fatigue resistant
LOW myosin ATPase, instant energy
LOW glycolytic enzymes (have o2 instead)
HIGH oxidative enzymes
small, weaker contractions (take longer time)
Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibres
classification
myoglobin
colour
myosin ATPase
glycolytic enzyme
oxidative enzyme
relative size
Anaerobic
pale
larger diameter
HIGH myosin ATPase (instant energy), glycolytic enzymes (glucose)
2-3 times faster than slow-twitch
2 major components of nervous system
Central Nervous Syst.
brain, spinal cord
INVOLUNTARY
Peripheral Nervous Sys.
rest of body
involuntary & voluntary
(Autonomic & Somatic)
Central nervous system
brain is in control
controls necessities (movement, sleep, hunger, thirst)
emotions
vertebral column provides passway for nerves to travel to organs & tissues
VC carries sensory info towards brain & motor info towards body
Vertebal column
what is it, two types of information & their pathways
passway for nerves to travel to organs & tissues
Sensory: info to brain
Motor: info to body
Sensory info goes to the…
brain
Motor info goes to the…
body
Peripheral Nervous Sys.
two types of nerves, two types of components
pt of system that lies outside of central nervous sys.
12 cranial nervers & 31 pairs of spinal nerves
EFFERENT (motor) nerves: signals away from central nerv. sys. to body
AFFERENT (sensory) nerves: signals from sensory recept. to central nerv. sys. (brain)
Autonomic (involuntary) & Somatic (voluntary) components
Autonomic Nervous System
Voluntary or Involuntary?
function, two subcategories
involuntary contractions
prepares body for emergencies/regular functioning
SYMPATHETIC syst: preps body for emergencies
releases adrenaline, increase heart rate, dilate blood vessels
PARASYMPATHETIC Sys: returns body to normal once threat is over
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary & purposeful movements
Allows us to cope w/ changing environment & react
AFFERENT nerves: info to brain (central nerv. sys)
EFFERENT nerves: info to body (skeletal muscles)
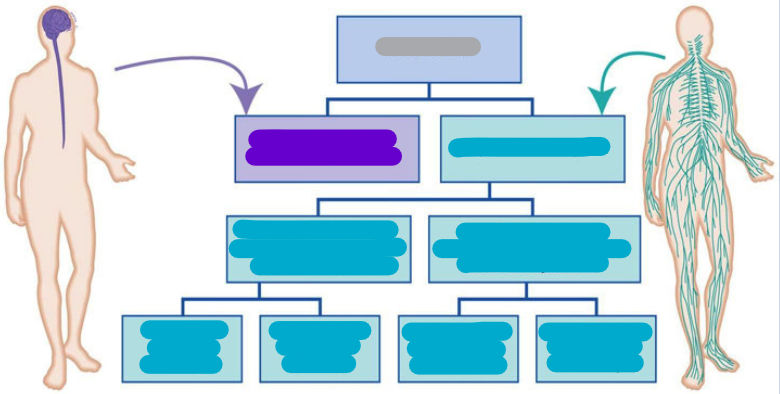
Diagram
Name of system, purpose/location
Diagram answers:
Nervous System:
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic (communicates with internal organs - involuntary)
Sympathetic (emergency response)
Parasympathetic (calming response)
Somatic (communicates with voluntary muscles - voluntary)
Efferent (motor) - signals to body (skeletal muscles)
Afferent (sensory) - signals to brain (central nervous sys.)
Reflex Arc
description and 2 catagories
The 5 parts
automatic & rapid responses
AUTONOMIC SYS.: smooth & cardiac muscles (digestion, elimination, BP, sweating)
SOMATIC SYS.: skeletal muscles - no brain involved because it’s so quick
5 parts
RECEPTOR: receives stimulus
SENSORY (afferent) NERVE: carries impulse to spinal cord
INTERMEDIATE NERVE FIBER (interneuron): interprets & issues response
MOTOR (efferent) NERVE: carries response to muscle/organ
EFFECTOR ORGAN: skeletal muscle that carries out response
** THE REFLEX ARC PARTS
RECEPTOR: receives stimulus
SENSORY (afferent) NERVE: carries impulse to spinal cord
INTERMEDIATE NERVE FIBER (interneuron): interprets and issues response
MOTOR (efferent) NERVE: carries response to skeletal muscles/organs
EFFECTOR ORGAN: skeletal muscle that carries out response
Tension reflex
golgi tendon organs sense change in tension & cause muscle to relax to prevent injury
Crossed-Exterior reflex
when arm or leg automatically compensates for reflex of another arm/leg (Polysynaptic reflex)
Three parts to the cardiovascular system
Blood vessels
Blood
Heart
Main functions of the cardiovascular system
Delivery of O2 and other nutrients to tissues in body
Removal of CO2 & other waste from tissues
Maintenance of constant body temp
Prevention of Infection (immune sys.)
3 main blood vessels
Arteries
oxygenated blood
thick walls (high pressure flow)
bright red blood
AWAY from heart
Veins
deoxygenated blood
thin walls (low pressure)
contain valves to prevent backflow
dark red
TOWARDS heart
Capillaries
thin vessels
deliver O2 & nutrients to cells
remove CO2 & waste
link veins & arteries
Exception: pulmonary arteries/veins
Arteries
(5 details)
oxygenated blood
AWAY from heart
thick walls
high pressure
bright red blood
Veins
(6 pts)
deoxygenated blood
TOWARDS heart
thin walls
low pressure
contains valves to prevent backflow
dark red blood
Capillaries
(4 pts)
links arteries & veins
thin vessels
deliver O2 & nutrients
remove CO2 & waste
The components of blood
PLASMA (liquid, mostly water + proteins & ions)
RED BLOOD CELLS (erythrocytes, TRANSPORT O2 & CO2 w/ help of hemoglobin proteins, gives colour red)
WHITE BLOOD CELLS (leukocytes, important in IMMUNE response)
PLATELETS (formation of blood clots)
Plasma
large component of blood
mostly water
has proteins & other ions
Red Blood Cells
2nd largest component of blood
transports O2 & CO2 w/ help of hemoglobin proteins
gives blood red colour
erythrocytes
White Blood Cells
3rd largest component of blood
important in IMMUNE RESPONSE
leukocytes
Platelets
cell fragments
BLOOD CLOTS
Human Heart
composed of specialized tissue called cardiac tissue/myocardium
double pump
LEFT side:
oxygenated to body
Systemic Circulation
RIGHT side:
deoxygenated to lungs
PULMONARY syst.
protective layer: PERICARDIUM
Specialized tissue in heart
myocardium
Left Side of Heart
oxygenated
brings blood to the body (aorta)
systemic circulation
Right Side of Heart
deoxygenated
brings blood to lungs
pulmonary system
pericardium
protective layer around heart
6 principles of training
(OPSIRD)
Overload
Progression
Specificity
Individual Differences
Reversibility
Diminishing Returns
Macronutrients
function
what they are
direct sources of energy for daily life, physical exercise & work
carbohydrates, proteins, fats
Micronutrients
what they are
main function
not direct energy
required for aiding in body processes
minerals & vitamins
Proteins
function
types
breaks down into
growth & repair, key comp. of hormones, enzymes, immune response, source of energy when others are low
Complete proteins: contains all 20 amino acids from animal products
Incomplete proteins: from vegetables (limited amino acids)
Breaks into amino acids (20 types, 9 essential)
Carbohydrates
function
types
breaks down into
main energy source for body
Complex carbohydrates: take longer to absorb (potatoes, fruits, vegetables, whole grain pasta)
Simple carbohydrates: quick energy sources (sugar)
breaks down into glucose, stored as glycogen in muscles & liver
Fats
function
types
breaks down into
examples
source of energy, insulates & protects vital parts of the body
Saturated Fats: (bad fats) from animal products, solids
Unsaturated Fats: (good fats) come from plant sources & take on form of oils, liquids
breaks down into triglycerides (fatty acids)
Eg) saturated: meats, butter, dairy
Eg) unsaturated: vegetable oils, good cholesterol
Physiology
studies the funct of systems and processes (growth & metabolism)
Anatomical Position
1) standing upright, feet flat on floor
2) arms to side
3) facing observer
4) palms facing forward
The three planes of the body
1- Frontal Plane (into front/back)
2- Sagittal Plane (into left/right)
3- Transverse Plane (into up/down)
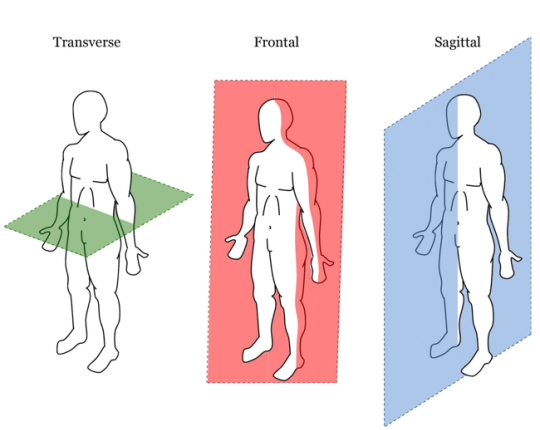
Frontal Plane
divides body into front & back sections
antero-posterior axis
Sagittal Plane
divides body into left & right
horizontal axis
Transverse Plane
divides body into top & bottom
longitudinal axis
3 Axis of the Body
1- Longitudinal (extends from head to toe)
2- Horizontal (extends from side to side)
3- Anterior-Posterior (extends from bellybutton to back)
Longitudinal Axis
extends from head to toes
paired with transverse plane
Anterior-Posterior Axis
extends through bellybutton
paired with FRONTAL plane
Horizontal Axis
extends from side to side
paired with SAGITTAL
Movement (axes and planes)
movement occurs ON the plane
SAGITTAL: can perform in NARROW hallway
FRONTAL: HIT NARROW hallway
TRANSVERSE: rotation
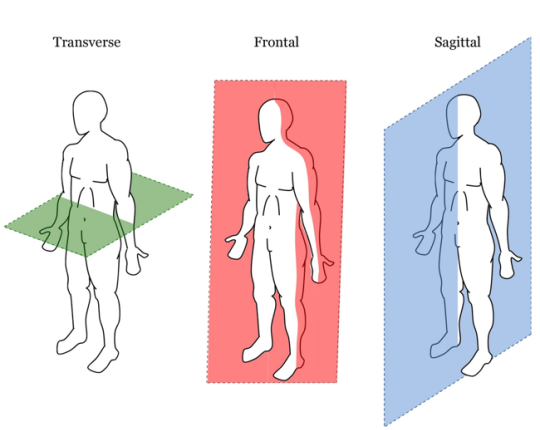
Plane & Axis of basketball free throw
Plane: sagittal
Axis: horizontal
Plane & Axis of shaking head no
Plane: transverse
Axis: longitudinal
Plane & Axis of shrugging shoulders
Plane: sagittal
Axis: horizontal
Plane & Axis of cartwheel
plane: frontal
axis: anterior-posterior
Anterior
front
eg) nose
opp: posterior
Posterior
back
eg) latissimus dorsi
opp: anterior
superior
above waist
eg) eyes
opp: inferior
inferior
below waist
eg) inferior vena cava
opp: superior
medial
towards midline
eg) bellybutton, pinkie finger
opp: lateral
lateral
away from midline
eg) arms, thumb
opp: medial
proximal
towards point of attachment
eg) shoulders
opp: distal
distal
away from point of attachment
eg) phalanges
opp: proximal
superfical
closer to surface
eg) skin
opp: deep
deep
inside/within surface
eg) heart
opp: superfical
flexion
movement of 2 bones, DECREASING the angle @ joint
eg) bicep curls
opp: extension
extension
movement of 2 bones, INCREASING the angle @ joint
eg) bicep curls
opp: flexion
abduction
movement AWAY from midline
eg) lat raises
opp: adduction
adduction
movement TOWARDS midline (ADDING)
eg) lat raises
opp: abduction
Internal rotation
rotating limb TOWARDS midline
eg) close the gate
External rotation
rotating limb AWAY from midline
eg) open the gate
Circumduction
circular motion combining flexion, extension, abduction, adduction
non-stop, circular
eg) arm circles
Supination
lateral rotation of hand so palm faces forward
(ask soup)
Pronation
medial rotation of the hand so palm faces down
(pros)
Protraction
movement in ANTERIOR direction
eg) bringing shoulders forward
opp: retraction
Retraction
movement in POSTERIOR direction
eg) bringing shoulders back
opp: protraction
Dorsiflexion
movement that DECREASES angle between ankle & foot
Plantar Flexion
movement that INCREASES angle between ankle & foot
(plant)