AP Bio Unit One: Chemistry of Life
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab, concepts, models, etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Polar
Partial positive charge on one end, Partial negative charge on the other end.
Non-Polar
Molecules are equally charged
are polar molecules hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophilic (attract and dissolve in water well)
are non-polar molecules hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic (do NOT attract and dissolve water in well)
Cohesion
water sticks to water
Adhesion
water sticks to OTHER things
High specific heat
It takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of water
Evaporative cooling
water takes energy when it evaporates
Ice floats because..
it is LESS dense than LIQUID water
Universal solvent
WATER can dissolve many substances
Cohesion and adhesion help with what?
Capillary Action
Capillary action
Liquid climbing in narrow spaces without the need of external forces, like oxygen
Why is waters high specific heat so important?
It stabilizes temperature in cells and ecosystems
Why is evaporative cooling important?
helps to keep organisms cool when sweating or transpiring
Why is ice being less dense important?
keeps bodies of water (lakes, oceans, etc.) from freezing to the bottom, which helps life survive
Why is water being a universal solvent important?
Its essential for chemical reactions and nutrient transport
Water is the..
element of life
Water is Polar or Non-polar?
Polar (it has charged ends)
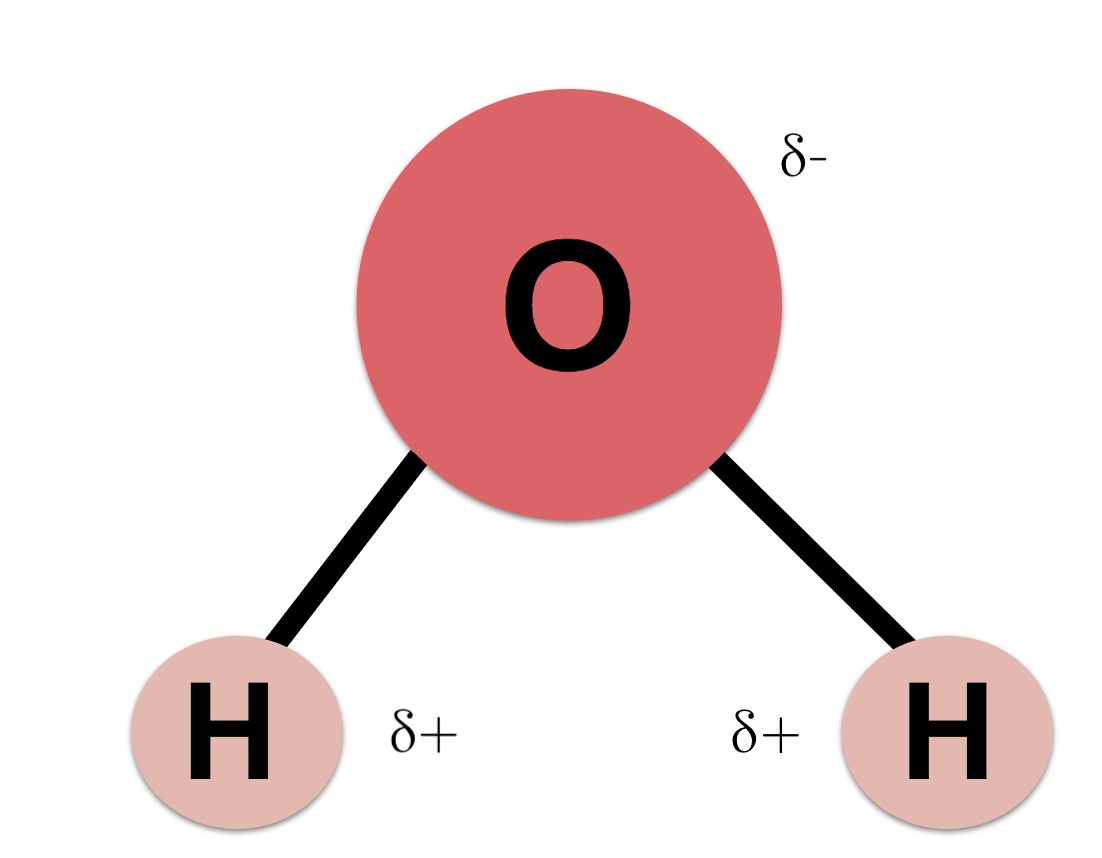
what causes surface tension in water?
Waters cohesive properties
what are the key elements of life?
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur. (CHNOPS)
what are macromolecules?
large biological molecules (often times a polymer made up of smaller monomers)
what are the 4 MAIN types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
what is a monomer?
single, simple molecules that function as building blocks to make polymers
what is carbons role?
backbone of ALL macromolecules / forms 4 bonds
what is hydrogens role?
part of water, organic molecules
what is nitrogens role?
found in proteins (aka amino acids) and nucleic acids
what is oxygens role?
in water, which is needed for cellular respiration
what is phosphorus' role?
in DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), and ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
what is sulfurs role?
found in some amino acids and proteins
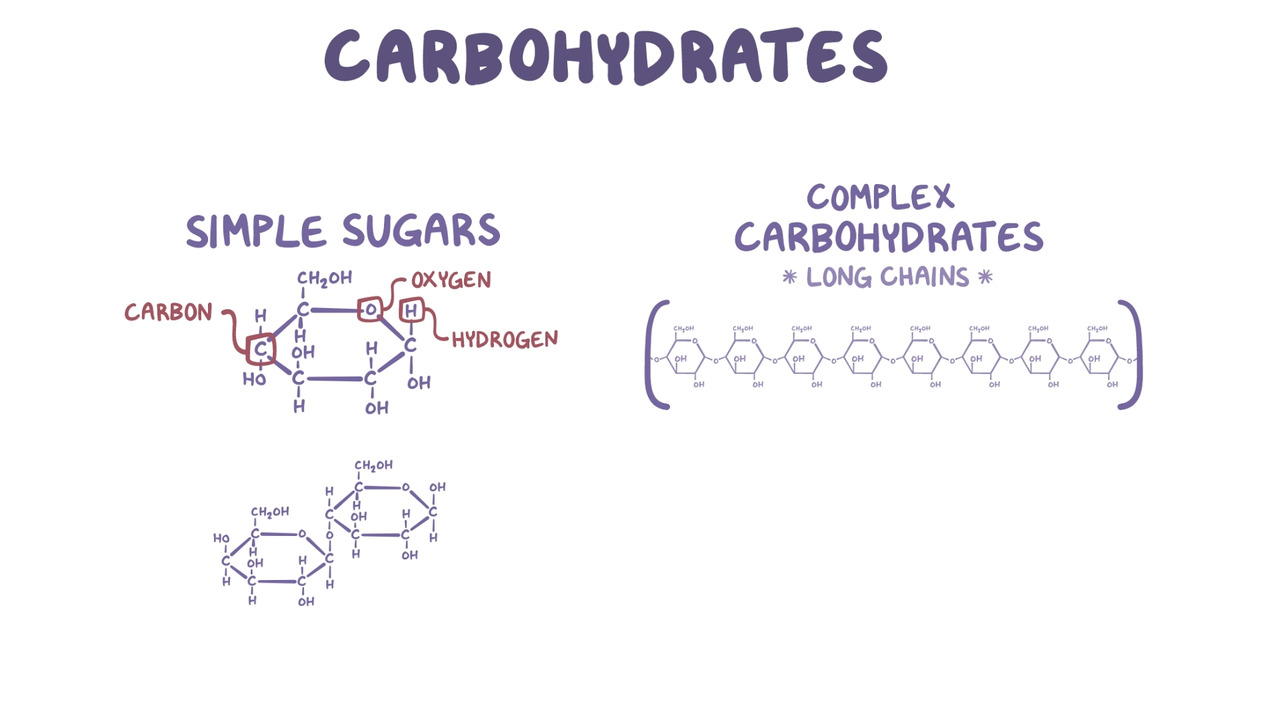
What key elements are found in carbohydrates?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)
what is the monomer in carbohydrates?
monosaccharides (aka simple sugar)(ex: glucose)
what is the function of carbohydrates?
quick energy and cell wall structure
what are the key elements in lipids?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)
what are the monomers in lipids?
fatty acids + glycerol
what is the function of a lipid?
long-term energy, insulation, and the structure and function of cell membranes
are lipids considered polymers?
no
which two macromolecules share the EXACT same key elements?
carbohydrates and lipids
what are the key elements in proteins?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur (CHONS)
what is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
what is the function of proteins?
enzymes, structure, and communication
which two elements in proteins are NOT found in carbohydrates or lipids?
nitrogen and sulfur
what key elements are found in nucleic acids?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHONP)
what are the monomers for nucleic acids?
nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytisine, guanine, and uracil)
what is the function of nucleic acids?
store and transmit genetic info in ALL living organisms (DNA/RNA)
what element is found in nucleic acids that is NOT found in proteins, lipids, or carbohydrates?
phosphorus
thymine is only found in..
DNA
uracil is only found in..
RNA
what does adenine pair with?
thymine (in DNA) and uracil (in RNA)
what does guanine ALWAYS pair with?
cytosine
what does cytosine ALWAYS pair with?
guanine
without the key elements, what happens?
cells cannot grow, reproduce, or maintain structure
what PROCESS is needed to build macromolecules?
dehydration synthesis
what happens during dehydration synthesis?
two monomers join to form a polymer
what is removed during dehydration synthesis?
water
why is dehydration synthesis important?
it’s how carbs, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids are made
what is required during dehydration synthesis?
enzymes and energy (ATP) in the cells
what happens during hydrolysis?
polymer is BROKEN into monomers by adding water to break the bond
why is hydrolysis important?
used in digestion and recycling molecules / releases energy and building blocks for cell
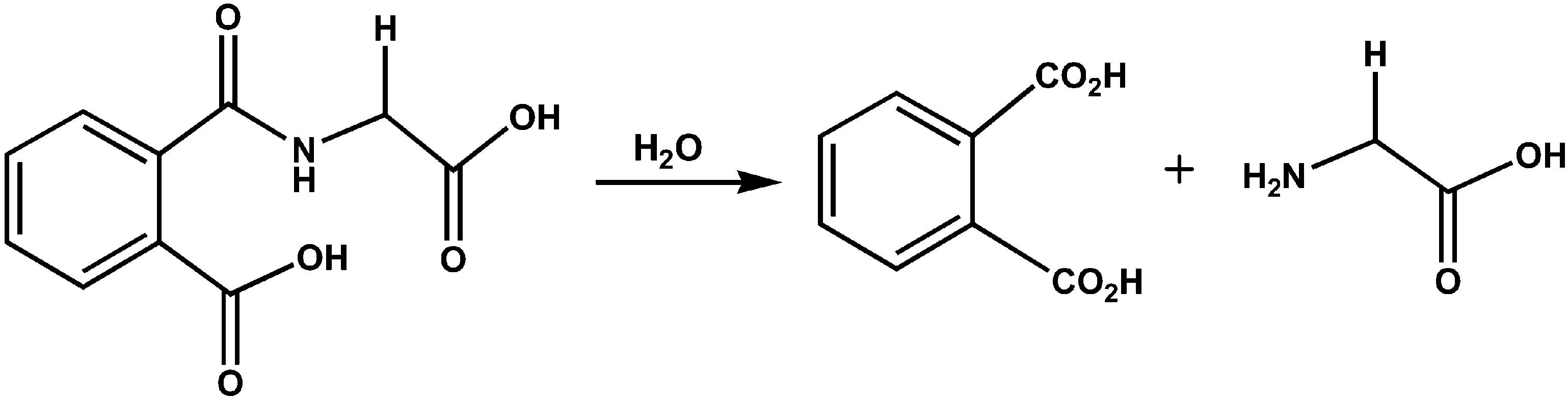
what model does this represent?
hydrolysis (water is being ADDED)
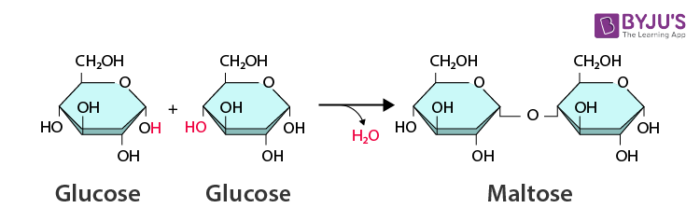
what model does this represent?
dehydration synthesis (water is being REMOVED)
what is the basic ratio in carbohydrates?
1:2:1 (like C6 H12 O6)
what are disaccharides?
TWO monosaccharides joined together by DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS
what is an example of a disaccharide?
sucrose, because it’s made by combining GLUCOSE with FRUCTOSE
long chains of monosaccharides are called…
polysaccharides
what are the four main polysaccharides?
Cellulose, chitin, starch, and glycogen
where is cellulose found?
in the cell walls of plants
where is chitin found?
it is found in fungi and insect exoskeletons (think of the sound cockroaches make when you step on them)
where is starch found?
in plants
where is glycogen found?
in animals (includes humans)
what is the function of cellulose in plants?
provides structural support to the cell walls
what is the function of chitin?
provides structural support in fungi and arthropods (insect)
what is the function of starch?
energy storage in PLANTS
what is the function of glycogen?
energy storage in ANIMALS
all carbohydrates are formed via..
dehydration synthesis
all carbohydrates are broken down via..
hydrolysis
how do monosaccharides bond?
through covalent bonds (glycosidic bonds) using dehydration synthesis
what is the function of a monosaccharide?
quick energy
what is the function of a disaccharide?
transport form of sugar in plants
what is the function of a polysaccharide?
stores energy or structural support
why are lipids NOT considered “true” polymers?
they do not have repeating monomers like carbs / proteins
are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophobic because they have NONPOLAR bonds
what are the major types of lipids?
Fats (triglycerides), phospholipids, steroids, and waxes
what is the structure of a Fat (triglycerides)?
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
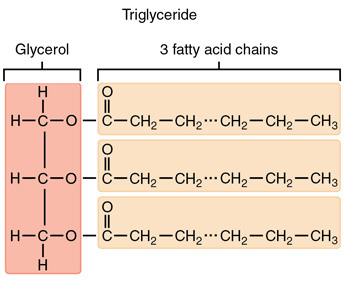
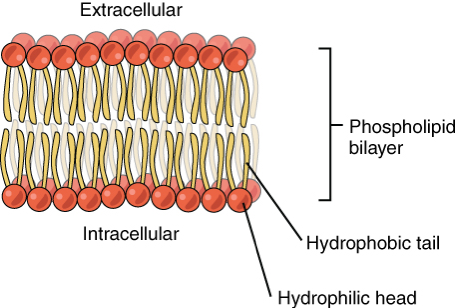
what is the structure of a phospholipid?
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group
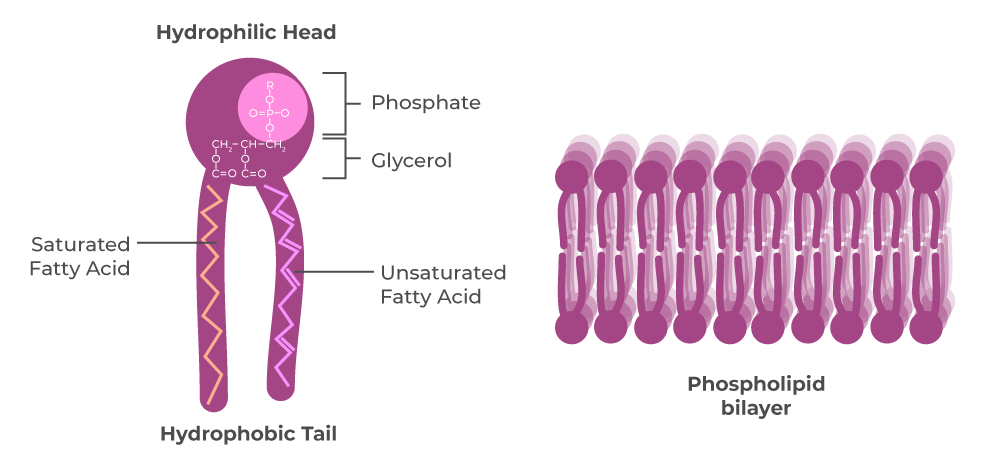
what is the structure of a steroid?
4 fused carbon rings (no fatty acids)
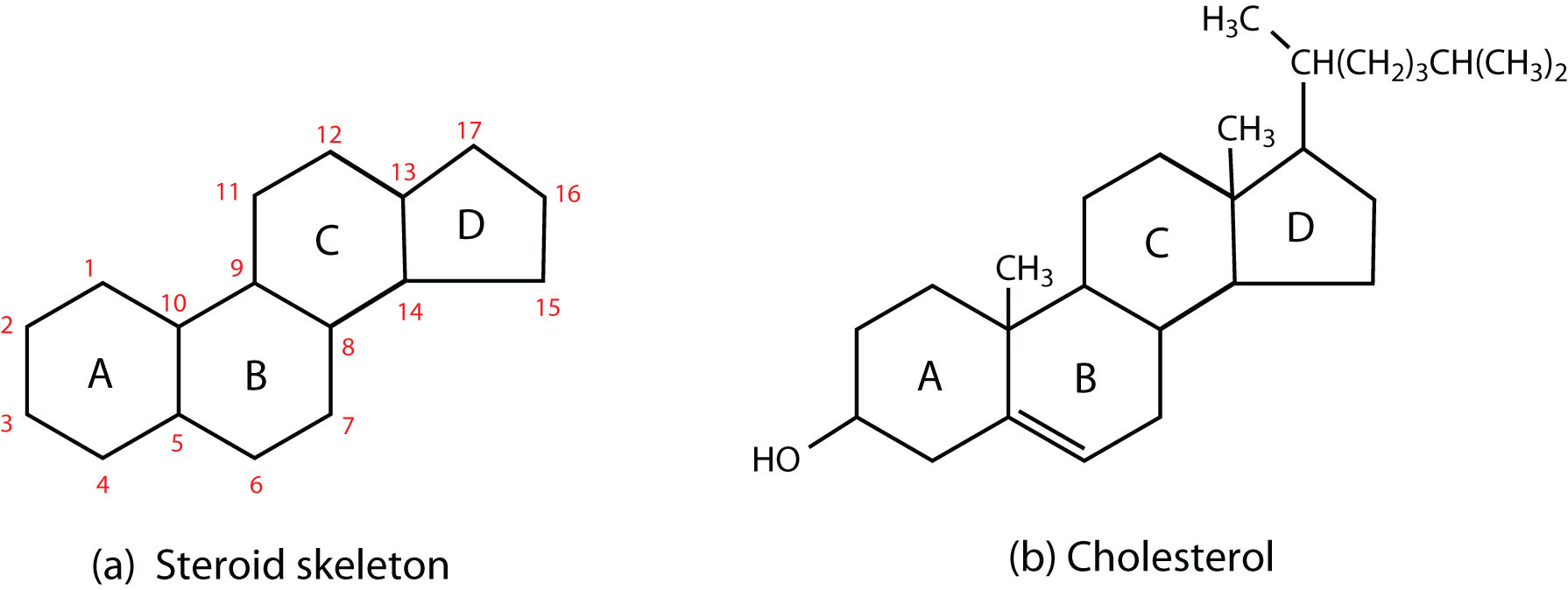
what are the structure of waxes?
long chains of alcohol + fatty acids
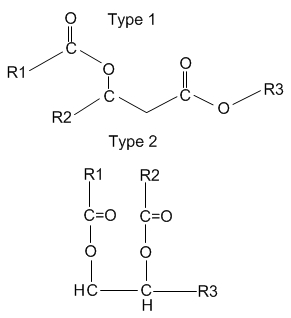
what is the function of fats?
long term energy storage and insulation
what is the function of phospholipids?
they make up cell membranes
what is the main function of steroids?
hormones (like testosterone or estrogen, etc.) and cholesterol in membranes
what is the function of waxes?
waterproofing in plants AND animals
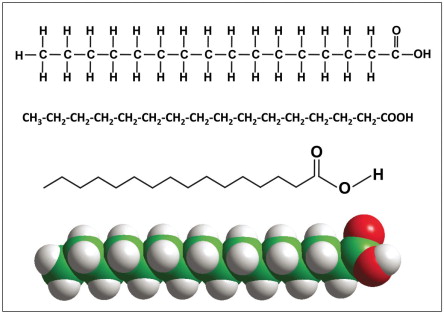
what are the two types of fatty acids?
saturated and unsaturated fats
which fatty acid has NO double carbon bonds?
saturated fats (notice how the structure is STRAIGHT)
which fatty acids have one or more DOUBLE carbon bonds?
unsaturated fats (notice how they BEND/ are KINKED)
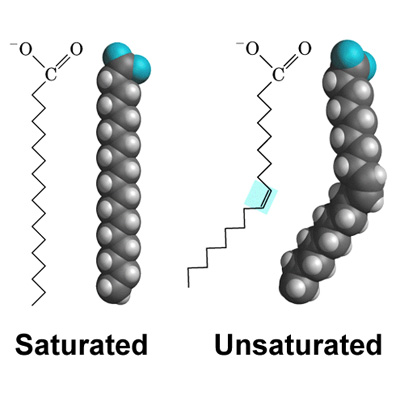
saturated fats stay in what state at room temp?
solid state (ex: butter)
unsaturated fats stay in what state at room temp?
liquid state (ex: olive oil)
what are the main functions of lipids?
energy storage, insulation/protection, cell structure, and signaling
what are the two different unsaturated fatty acids?
monounsaturated (MUFA) & polyunsaturated (PUFA)
what bond is in MUFA’s?
ONE double bond (ex: olive oil)
what bond is in PUFA’s?
TWO+ double bonds (ex: omega-3 and omega-6)
what are two ESSENTIAL fatty acids that come from our diet?
linoleic acid (omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3)