HOSA - Biotechnology: Microbiology & Cell Culture
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Model Systems
used by scientists to investigate something new in an organism or biological system they already know a lot about. Model systems are useful for gaining knowledge that can be applied to other systems.
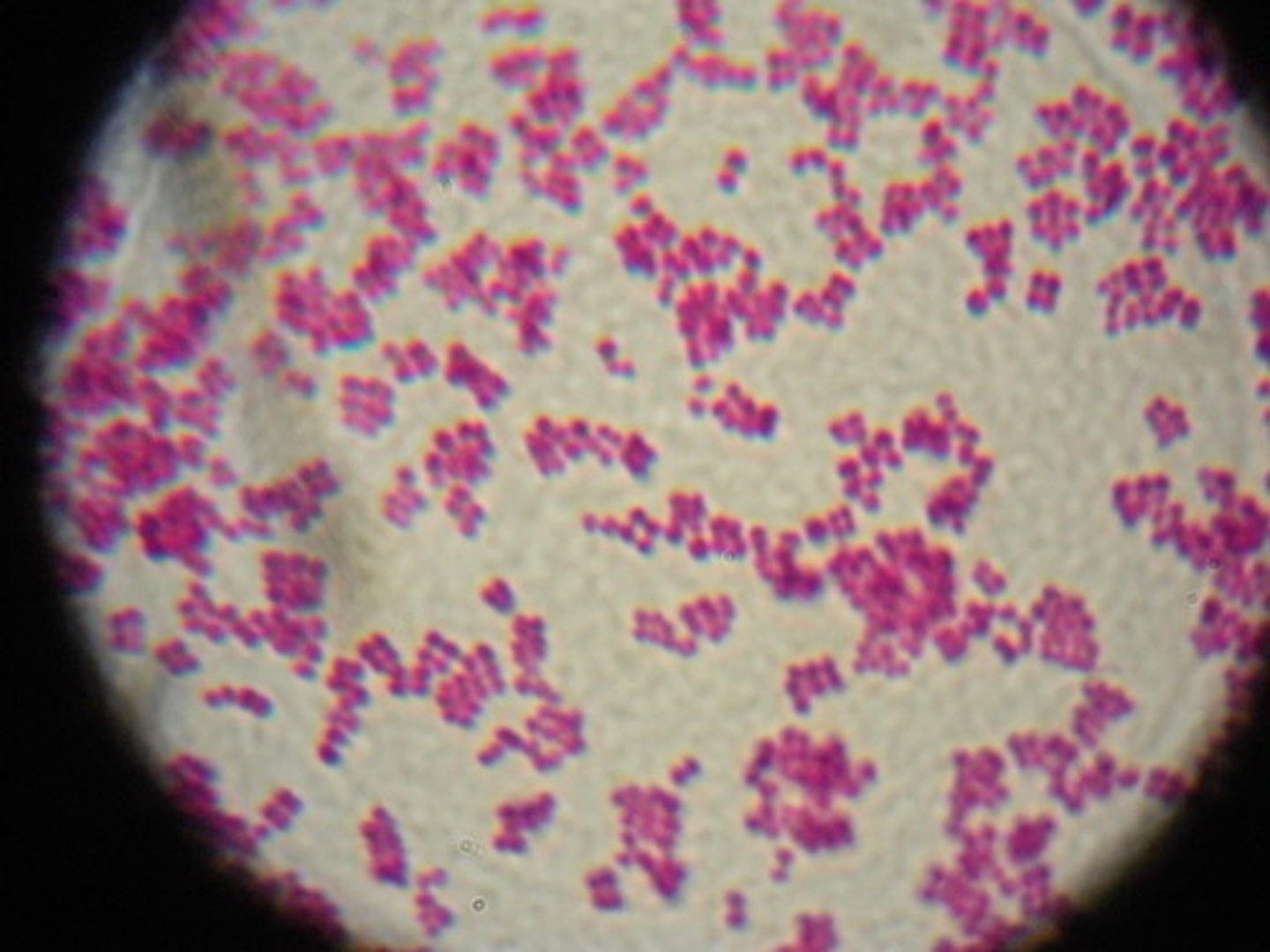
Coccus bacteria
Sphere shaped
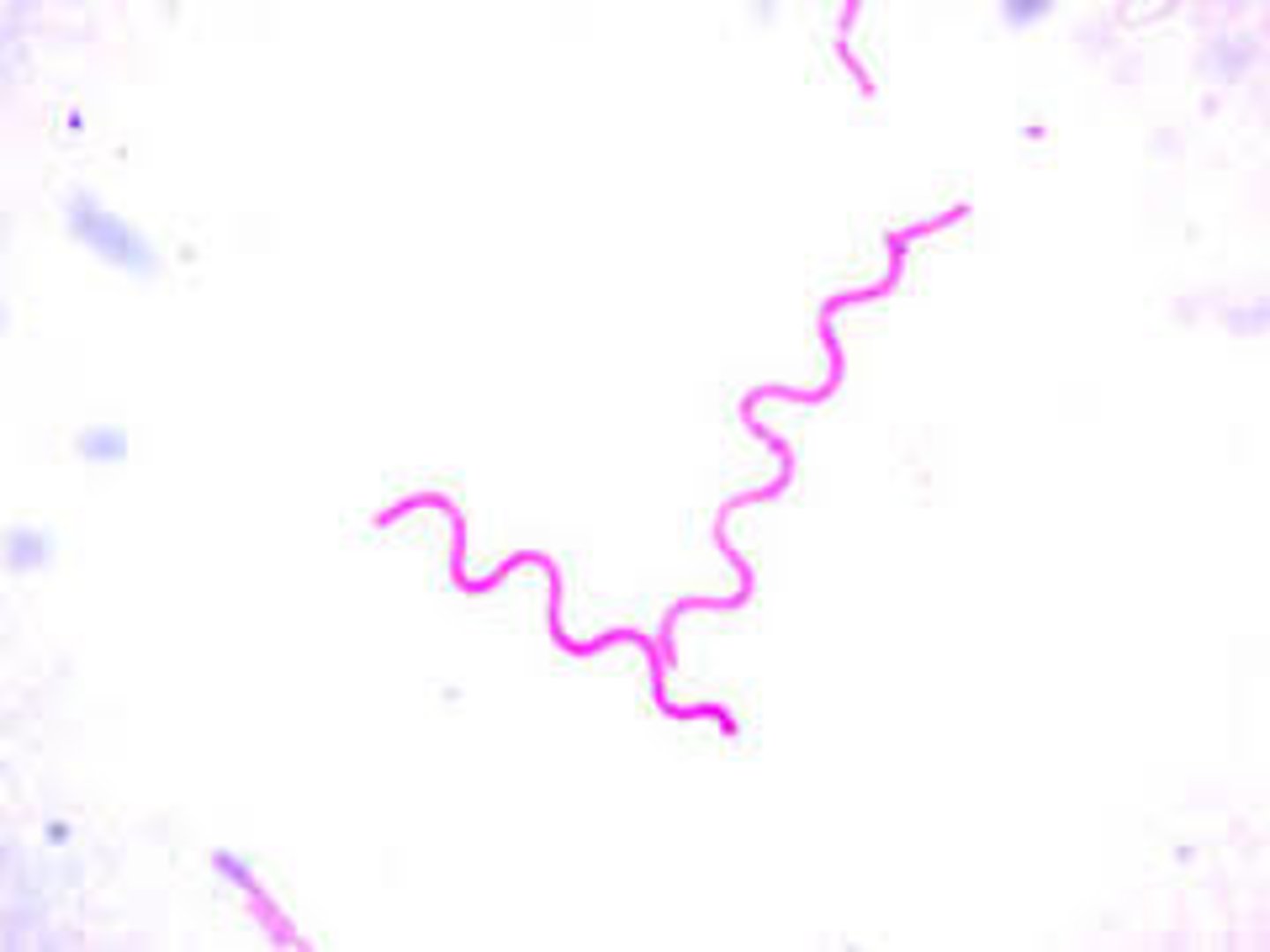
Spirilli bacteria
Spiral shaped
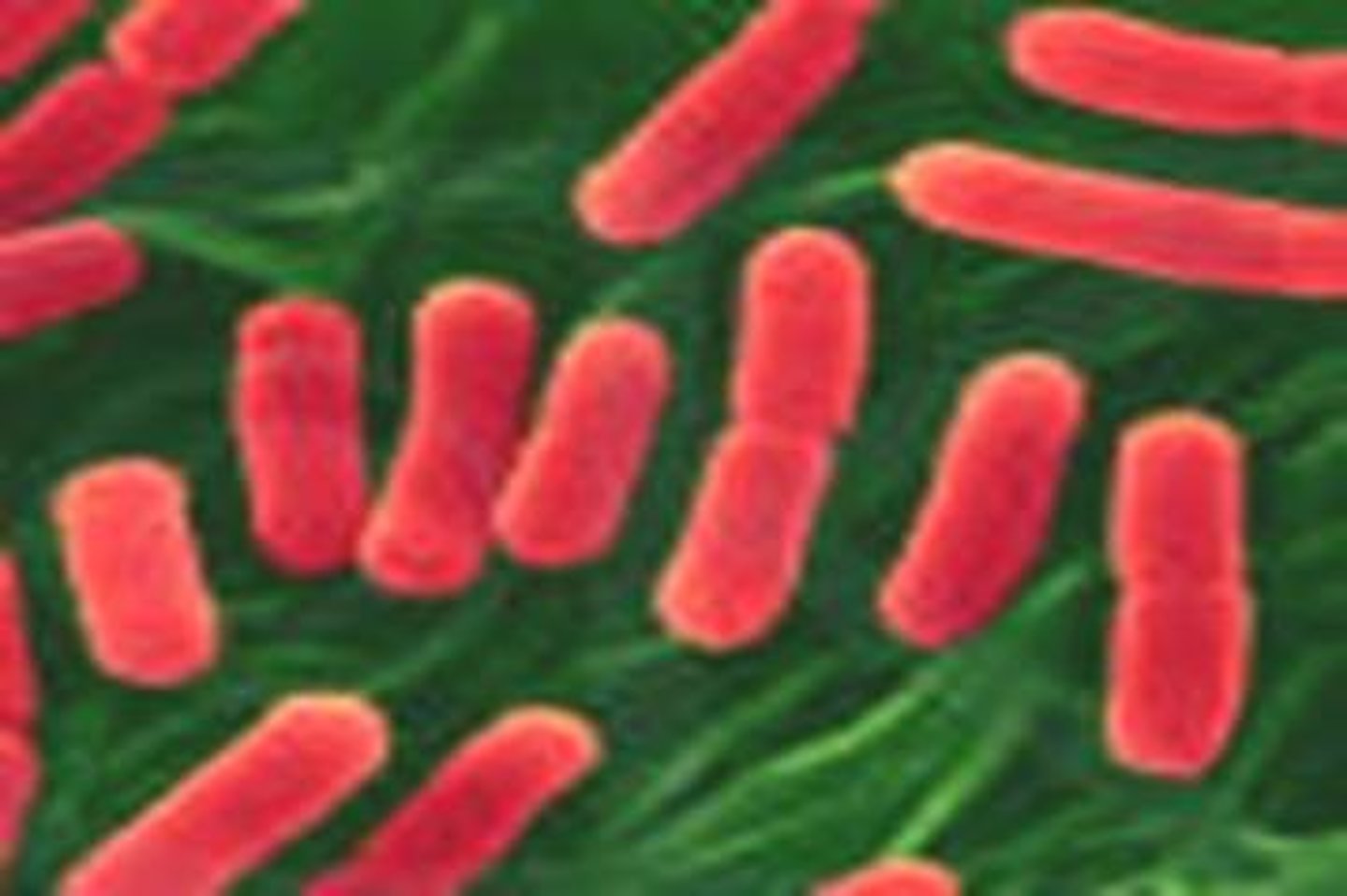
bacilli bacteria
oval/rod shaped
sodium chloride
required for growth of most bacteria
aseptic technique
method in cell culture that prevents the introduction of unwanted organisms into an environment
antibiotics
main line of defense against bacterial infections
MRSA
has developed resistance to most antibiotics and si extremely difficult to treat
peptidoglycan
bacteria's cell wall
Gram stain
microbiological stain; gram-positive cell walls in bacteria take up the stain/gram-negative do not
mycoplasma
bacteria that have no cell wall
pili
hair-like projection on outside of bacteria; help w/ cell-cell contact & adhesion
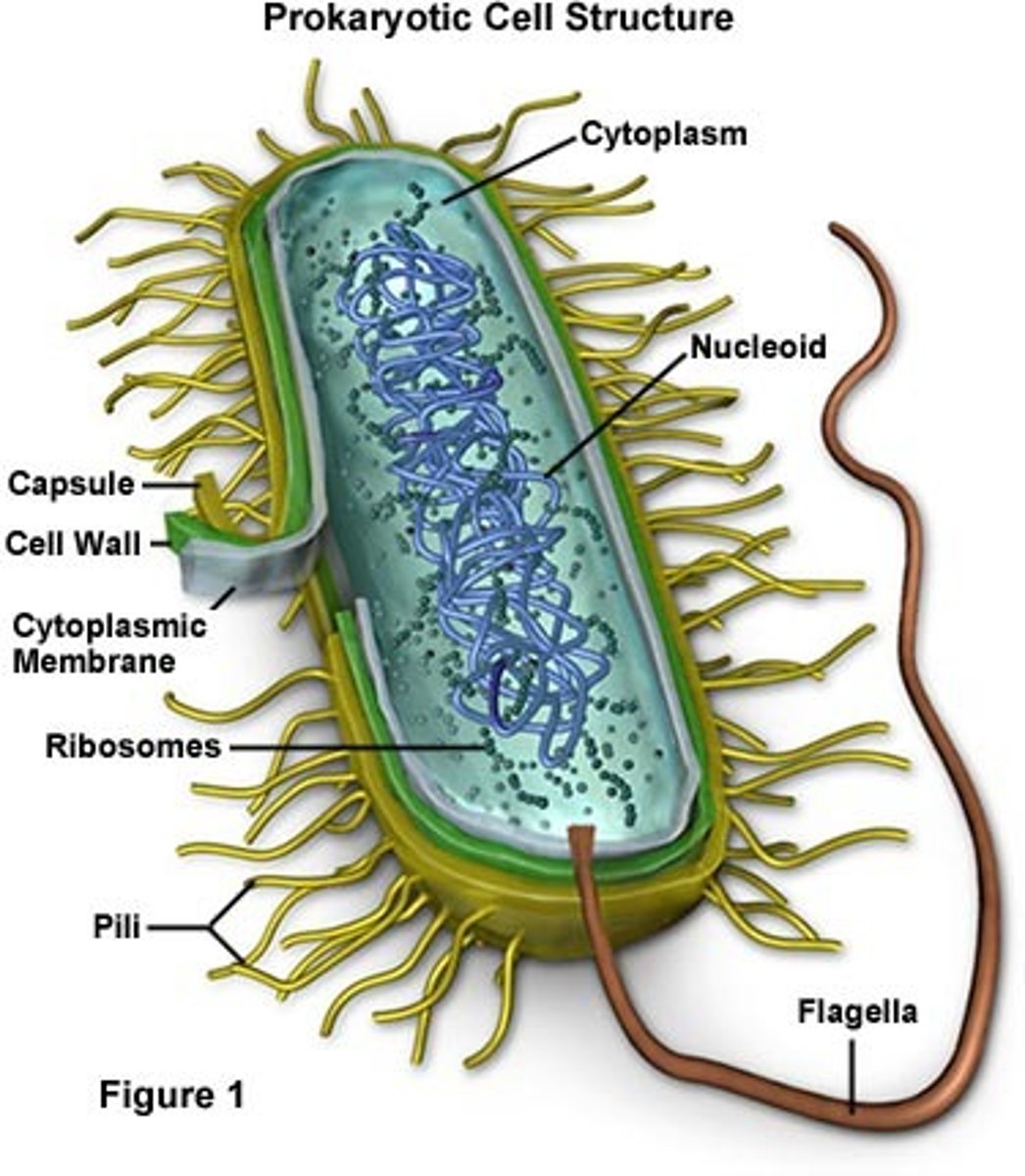
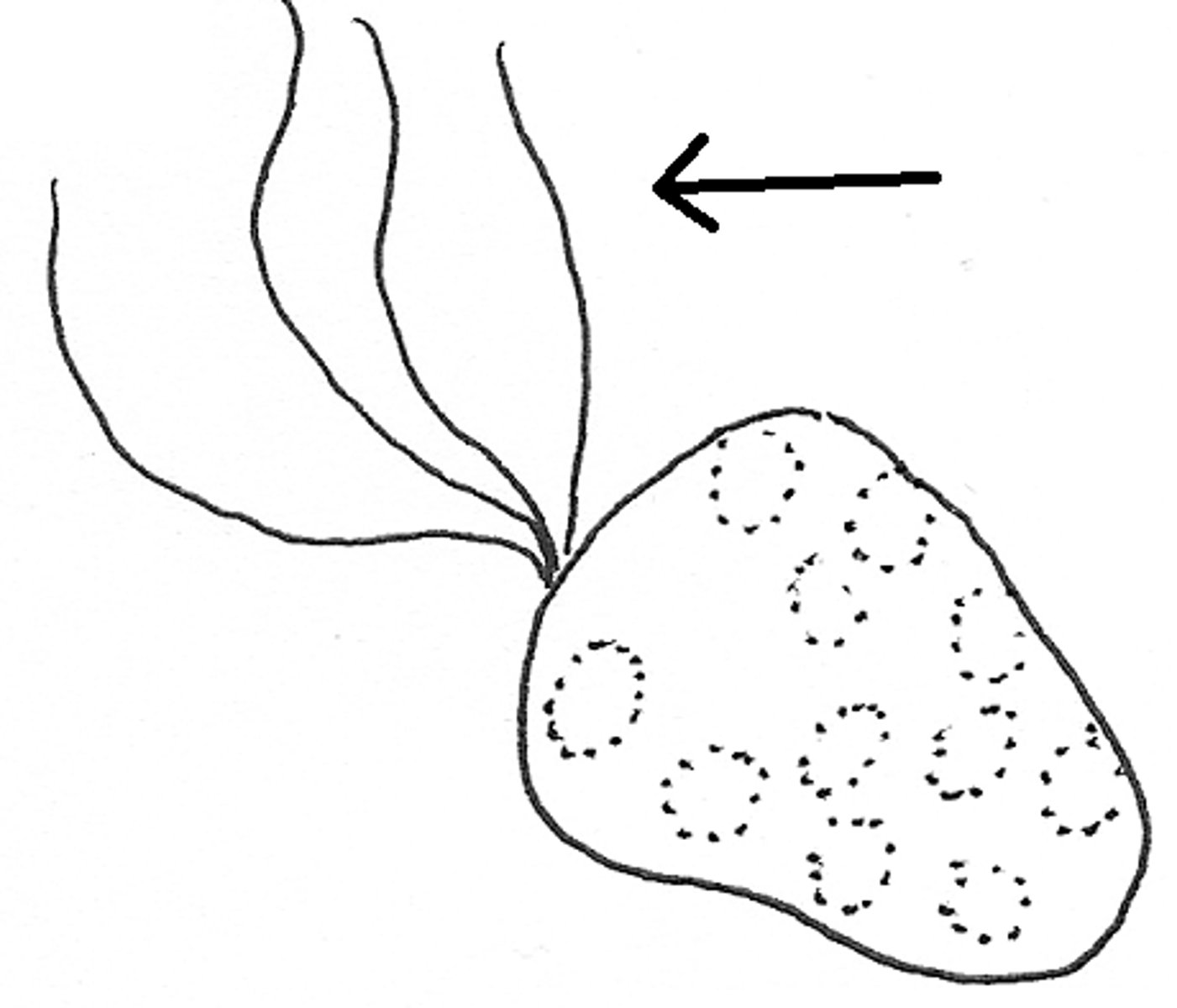
flagella
enable bacteria to move and swim in aquatic environments
aerobic bacteria
prefer high levels of oxygen for max growth rate (called obligate aerobes if NEED oxygen - called facultative aerobes if better but not required for them)
Anaerobic bacteria
prefer to grow in absence of oxygen (called obligate anaerobes if NEED absence for growth - called facultative anaerobes if just better for growth)
psychrophilic bacteria
grow best in cold conditions between -15 and 10 degrees C
mesophilic bacteria
grow best between 15 to 40 degrees C
thermophilic bacteria
grow best between 45 to 80 degrees C (source of Taq DNA polymerase - used in PCR)
hyperthermophilic bacteria
thrive at temperates above 80 degrees C
halophiles
bacteria that live in extremely salty conditions
E. coli
mesophiles that live in human colon; nonpathogenic used in lab research for humans, pathogenic are responsible for food poisoning outbreaks
L. bulgaricus
one of species of bacteria used to make yogurt
lactobacilli bacteria
used in production of cheese, sauerkraut, pickles, kimchi, and animal feed
recombinant protein
protein that is artificially produced in genetically engineered organism - used for therapeutic drugs, agriculture, and food production
Insulin
recombinant protein used to treat diabetes
Bovine somatotropin (BST)
cow growth hormone that stimulates cows to produce more milk
Recombinant bovine somatotropin (rBST)
made by expressing cow somatotropin in bacteria
agar
gelling agent used for growth of bacteria on solid media
solid media
referred to as agar
petri plates
dish used to isolate individual colonies of bacteria, provide large surface area

slants
agar is poured in a tube, allowing it to set at an angle & thus provides large surface area for bacteria growth; Used to culture bacteria for short period of time, not isolation

Bacteria grown on petri plates/slants
stored for 1-2 wks at 4 degrees C
stab cultures
tubes of solid agar with bacteria stabbed into the media, used for storage up to 1 yr

lysogeny broth (LB)
most generic form of solid media - nutrient agar made from peptone & beef extract
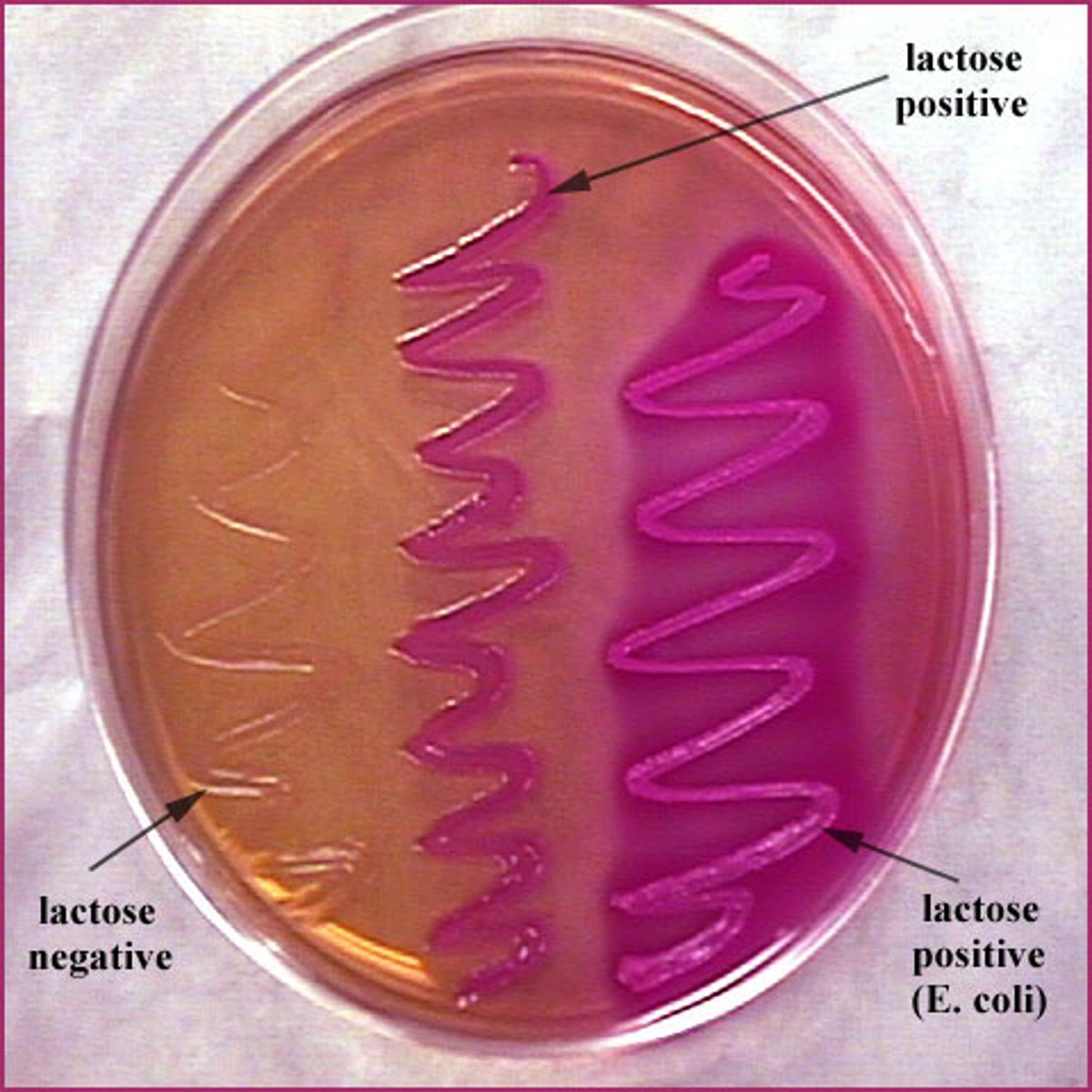
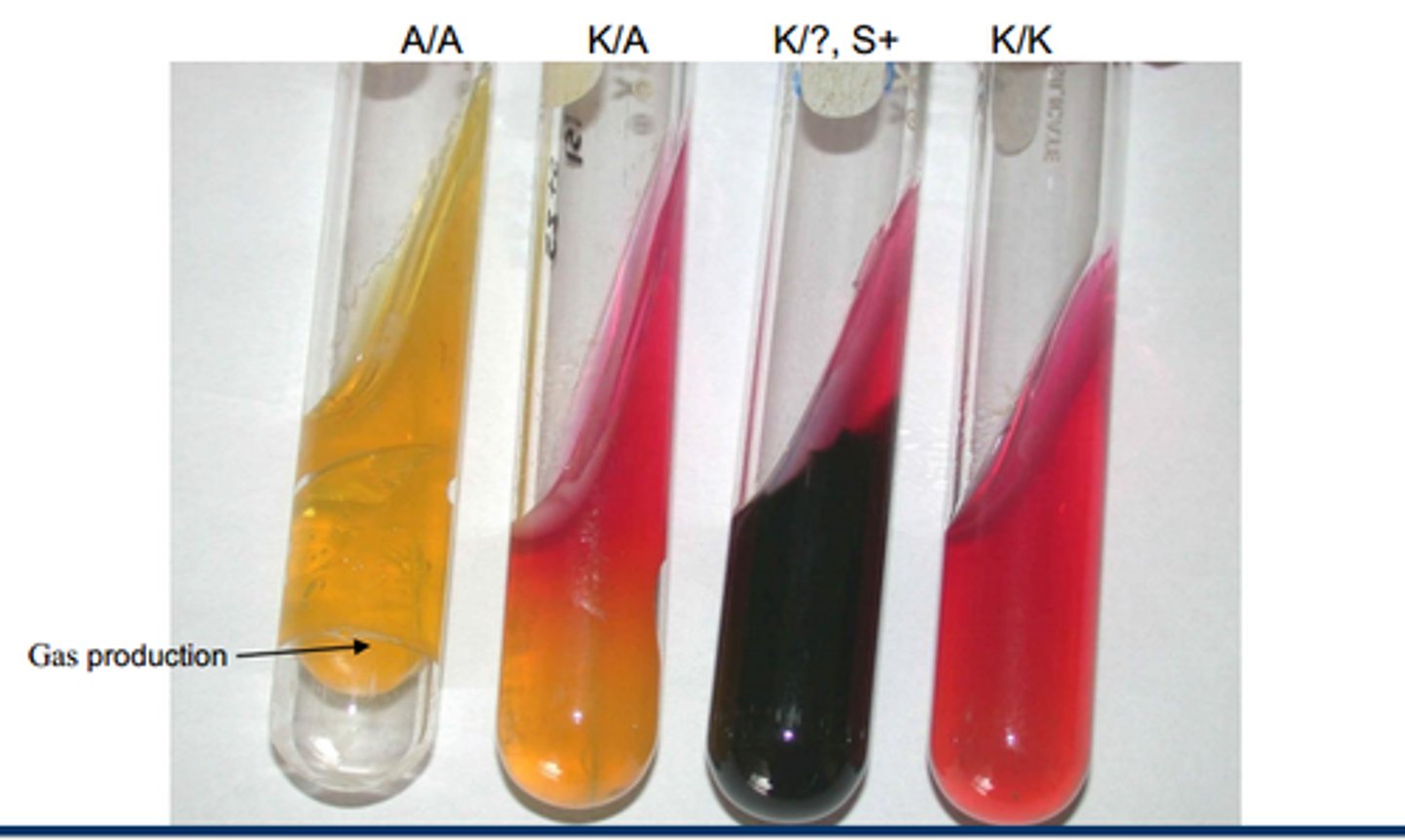
Differential media
formulated with chromogenic (colored) substrates to distinguish between diff types of bacteria
Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test
used to determine effect of various antibiotics on bacteria covering the surface of the agar. the larger zone of inhibition, the greater the antibacterial effect of compound tested
Liquid media (broth)
used to produce large quantities of bacteria suspended in liquid; often formulated w/ same ingredients as solid media but no agar
Liquid cultures
cannot be used for isolation of individual colonies
Terrific Broth
extends growth phase of recombinant E. coli & increases plasmid/protein yield
In solid media,
antibiotics are used to select for resistant bacteria
inoculation loop
platinum or nichrome wire with small loop at end

inoculation needle
straight wire

bunsen burner
used to heat sterilize inoculation loops & mouths of glass bottles, culture tubes, or culture flasks; maintain upward air current to reduce airborne contamination

spreaders
spread bacteria evenly over petri plates
incubators
maintain constant temp; some have shaking platform that allows liquid cultures to be shaken during incubation - oxygenates aerobic culture
fermenters/bioreactors
allow large scale growth of bacteria under controlled conditions
biological safety cabinet (BSC)
must be used whenever doing tests on human disease causing cells; limits chance of aerosol contaminating worker
colony
single bacterium that has multiplied on solid medium into millions of clones of itself; round visible dot on solid medium
serial dilution
diluting a culture several times by the same dilution factor
know all conversions! study from book
example:
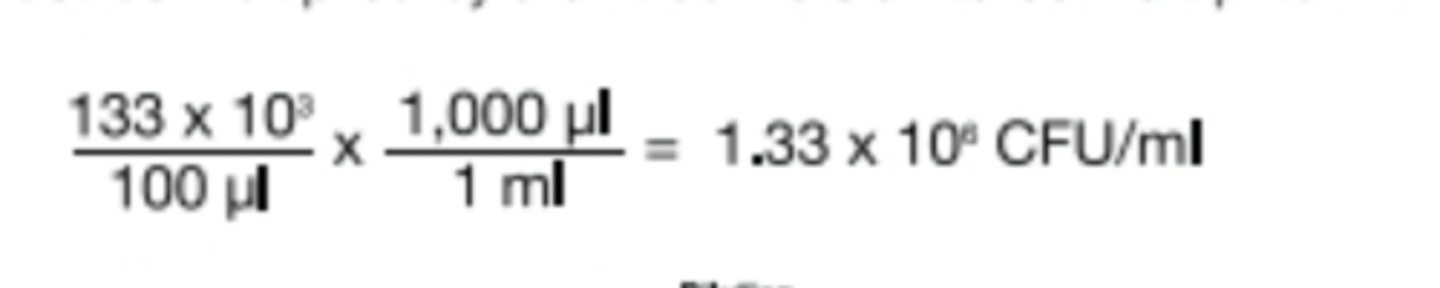
optical density (OD)
measures how cloudy a culture is; shows cell concentration
assays
procedures carried out to test or measure activity of a drug or biomolecule in an organism or sample; quantify cells, molecules, antibodies, etc
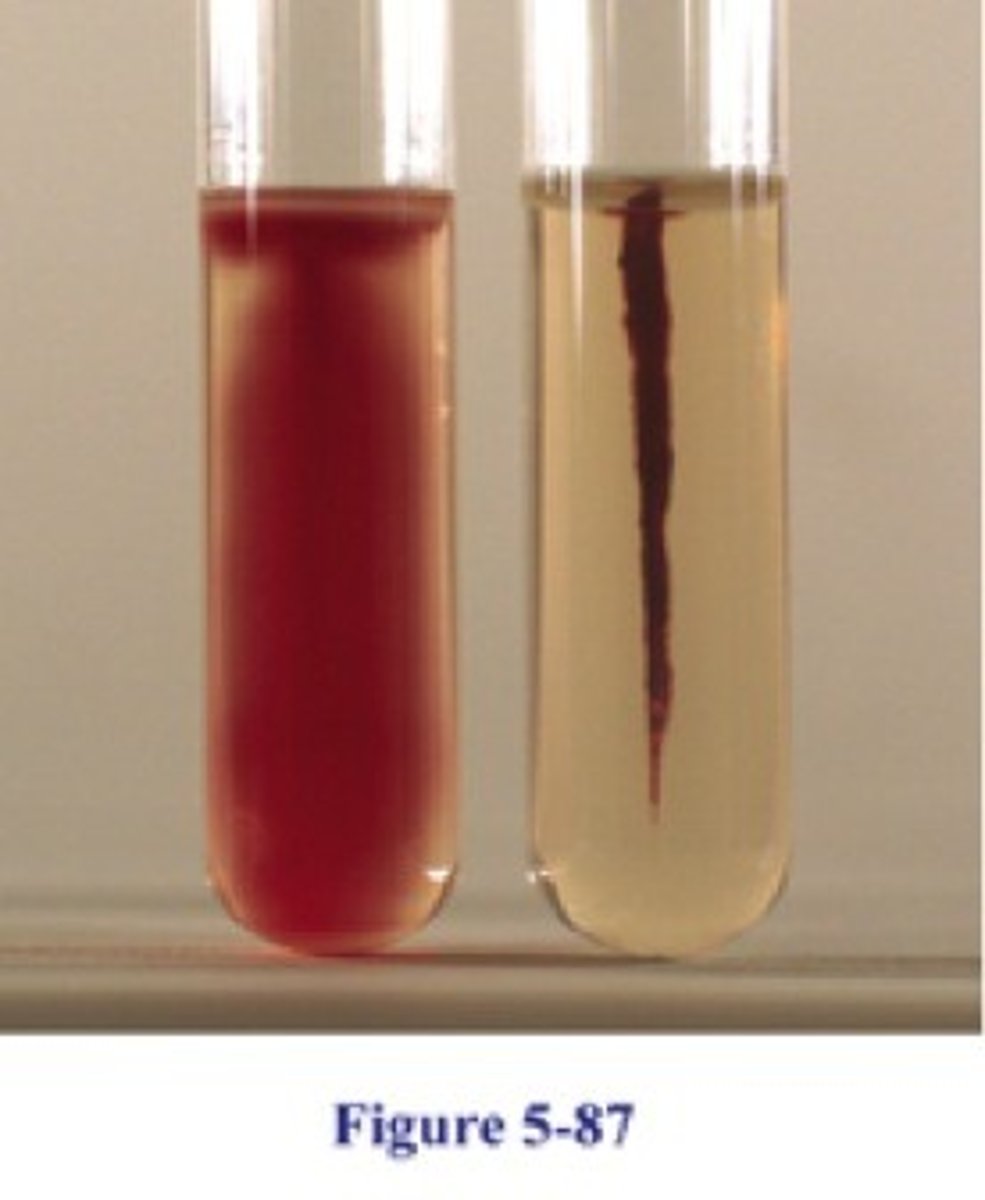
Gram stain pt. 2
identify unknown bacteria; determine cell wall composition
Bacteria either gram-positive or gram-negative
Gram-positive: thick cell wall; Gram-negative: thin cell wall
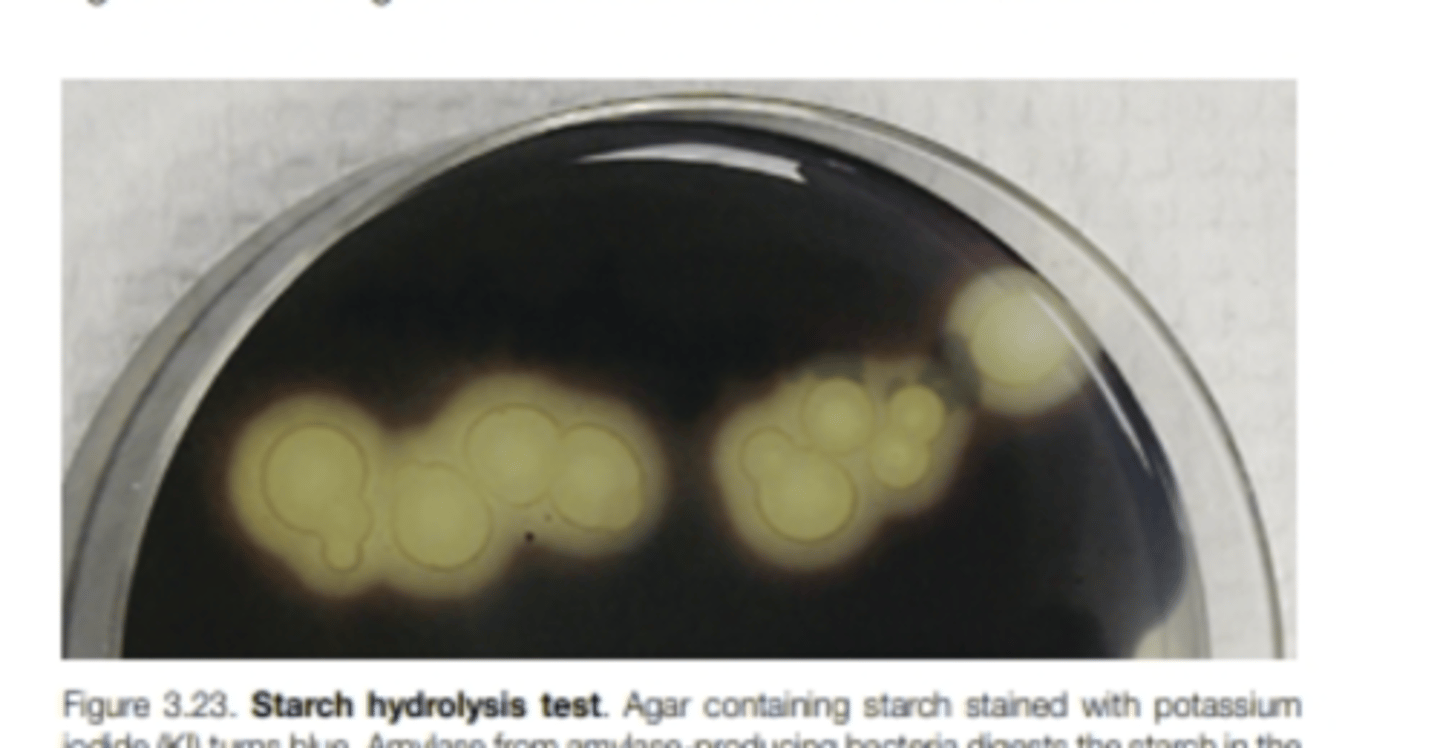
Starch hydrolosis test
determines if bacteria produces amylase
Eukaryotes
third domain of life; animals, plants, fungi, yeast, and protists; have nucleus and membrane bound organelles
plasma membrane
regulates what materials enter and leave the cell
phospholipids
create hydrophobic zone that prevent water loss; selective bilayer
fungi kingdom
yeasts, molds, and mushrooms; have cell wall made of chitin
yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs)
extra artificially manufactured chromosomes in yeast to express recombinant eukaryotic genes
Protists
eukaryotes; photosynthetic primary producers Ex. algae
yeast cells
used in baking and brewing
recombinant proteins
made in eukaryotic cells
posttranslational modification
includes glycosylation, a process where carbohydrate molecules are attached to newly synthesized protein
yeast/other fungi cell line (ex. Aspergillus)
cheapest/easiest euk cell to culture for protein production
mammalian cell line
ideal system for protein production; expensive/difficult to culture
antibodies
recombinant proteins produced used as therapeutic drugs
stem cells
can differentiate into new cell types (brain,blood, muscle) depending on molecular signals they are given; replace damaged tissue w brand new tissue
Embryonic stem cells
derived from inner cell mass of developing embryo and are pluripotent (can differentiate into most types of tissue but cannot recreate an entire organism)
induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)
allows cells to be removed from patient, and then differentiated into type of cell required to treat patient's disease