combined review mod 2
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
What is the definition of Digestion?
Process of transforming food into basic nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body
What are the three things digested food can be used for? CFP
Cellular growth, fight infections, provide energy to muscles and brain.
Cognition helps in digestion?
By giving thoughts about food, so that saliva can start flowing.
How does sound help digestion?
Possibly hearing the description of a meal
How can odor help digestion?
Smells can stimulate a hunger response.
How can appearance and taste help digestion?
Seeing the food can act as a stimulus, and taste begins as the food enters the mouth.
Two types of digestion are?
Mechanical, and chemical. Mechanical process involves chewing of mouth.
Peristalsis
Involuntary movement and contractions that help foods go down the tract.
What are enzymes?
Protein catalyst that speeds up reaction.
What is the GI tract?
long hollow tube consisting of several layers of tissue that begins with the mouth and ends at the anus.
Mucosa
(intestinal wall) is the inner-most layer, and it is made of absorptive cells and glands.
Circular and longitudinal muscles
comprise the outer layers, both of which function to mix and move food along the GI tract.
The three processes that can move nutrients from Gi tract to the blood/lymph system are?
Passive diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, active transport.
What is passive transport?
Moving of cells without energy.
What is facilitated diffusion?
It requires no energy like Passive transport, however requires a protein carrier.
Active transport and the main difference is?
Requires energy to move cells, and the key difference is nutrients move from low to high concentrations.
Differences between Passive transport and active transport
Passive: No energy required, from high to low concentration, includes osmosis and simpler diffusion that don’t require use of protein carrier, facilitated diffusion requires a protein carrier.
Active: ATP is required, from low to high concentration, processes that are more complex like endocytosis (movement of large molecules into a cell, some types require use of protein carriers.
What are the 6 parts of the GI tract from superior to inferior?"
Mouth, Esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum.
What organs produce and secrete stuff that help in digestion but are not a part of the Gi tract?
Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
What is the function of the mouth?
To alter the food particles to prepare them to be swallowed.
Saliva is?
a watery fluid containing (1) a lubricant (mucus) and (2) enzymes to prepare food for the next step in the GI tract.
Mucus
mixes with food, lubricating the particles and making it easier to swallow.
Enzymes released in the mouth have specific functions: There are two
Salivary amylase that breaks down starches
Lingual lipase breaks down fats
The tonge is responsible for taste. What are the 5 different types of taste for us?
1 – sweet
2 – salty
3 – sour
4 – bitter
5 – umami (a meaty flavor)
Esophagus
(the tube that connects the throat with the stomach): The role of the esophagus is to transport food to the stomach.
What is the flap called that prevents food from going into the windpipe?
Epiglottis
What is the sphincter muscle? How does it prevent backflow of food?
IT is a circular muscle, (think of sphi as sphere), that controls how much food will go down the food tract. It ends up closing so that food can not go back up.
What is the capacity of the stomach?
About four cups
What is the role of the stomach?
store, mix, dissolve, and continue the digestion of food.
What are the enzymes and acids in the stomach and what do they do?
Pepsin: Breaks down proteins
Gastric Lipase: Breaks down fats
Chyme: the resulting substance when food particles are mixed with stomach acids and enzymes. Chyme is a very watery mixture that slowly empties from the stomach into the small intestine. Processes can take 1-4 hours of moving stuff to small intestine.
Gastrin : hormone responsible for controlling the concentration of acid in the stomach
Intrinsic factor: is a vital glycoprotein produced in the stomach. In order for vitamin B-12 to be absorbed, intrinsic factor must be present
What is the spherical muscle that controls how much chyme goes into small intestine?
Pyloric Sphincter
Small Intestine
(approximately twenty feet long and connects the stomach to the large intestine): Where majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs.
What are the three main sections of the small intestine?
Duodenum: First portion and the widest portion.
Jejunum: The middle section:
Ileum: final section that connects small and large intestine.
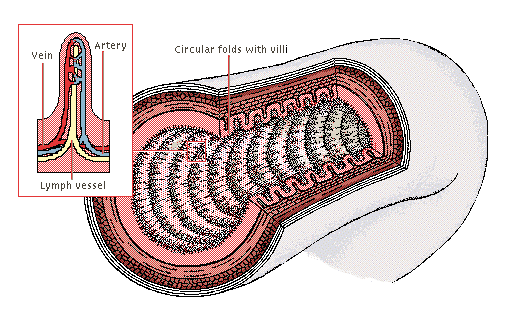
What are villi and what is their function?
They are like small hair that cover the inner lining of the small intestine. They trap food, and allow for absorption.
What does the liver do?
It secretes Bile, which helps break down fats into smaller pieces. Bile enters to the first part of the small intestine to break down fats.
Where is bile stored?
Gallbladder
What do the pancreas do?
Release pancreatic juices (bicarbonate, water, enzymes), that breaks down fats, proteins, and carbs. Also releases glucagon and insulin.
Which juice helps neutralize chyme (acidic)?
Bicarbonate in the pancreatic juice.
Large intestine and its functions
Water and minerals like salt, potassium and chloride can be absorbed here. Feces are produced here.
What are the 4 parts of the large intestine.
Ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid.
Probiotics
are foods that contain these bacteria. Fermented milk and yogurt are examples of probiotics that can be marketed to improve your gut health and digestion.
Prebiotics
refers to substances that stimulate bacterial growth in the large intestine.
Two important bacteria necessary for the health are?
Bifidobacterial and lactobacilli
ileocecal sphincter
connects the small intestines to the large intestines. Much like the pyloric sphincter (see above), the role of the ileocecal sphincter is to prevent the contents of the large intestine from reentering the small intestine
What is heartburn?
also known as acid reflux, occurs when the stomach acid comes up the esophagus. It is important to remember that the stomach is lined with mucus to protect it from the acids, but the esophagus is not.
Is the esophagus lined with mucus like the stomach?
No, so it can get damaged easily.
What are some symptoms of heartburn
Nausea, coughing, vomiting, gagging, or hoarseness.
GERD (gastro esophagal reflux disease) and its cause?
The cause of GERD or heart burn is that the esophagal sphincter becomes weak, and it can’t contract anymore. That means that it can not prevent the acid from going back up into the esophagus anymore, and thus the esophagus gets burnt by acid.
What are some remedies, and foods for GERD?
You should eat foods that are low in fat, chew food well, avoid overeating, avoid coffee, tea, alcohol, and spices. You should wait 2 hours after a meal to lie down or should sleep with head elevated. Smoking is also bad if you have GERD.
Constipation is?
when stools (feces) are hard, dry, and infrequent, and it is a result of slow movement through the large intestine.
What are some bad foods and good foods for constipation?
Iron and calcium rich foods can cause constipation, so it is better if you eat foods that are high in fiber.
What is diarrhea?
The opposite of constipation… described as loose, watery , and frequent stools.
What can cause diarrheaa?
Infections or a disease, antibiotics (can destroy healthy bacteria that are in the colon).
Remedies for diarrhea are?
Fluid consumption should be increased to prevent dehydration. Tea, broth, toast, and low fiber foods should be consumed.
What is usually lost due to diarrhea?
Excess water, sodium, and potassium can be lost due to severe diarrhea.
What is diverticulosis?
It occurs as we age so it is natural. It is simply where food pouches start to form in the colon, and food can get stuck in them. It does not really affect most people.
What is diverticulitis? There is a difference.
Compared to diverticulosis, where that is a normal aging process and so is this, this is where food gets stuck in the pouches and can cause inflammation, and infection.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms and remedies?
It is not that well known. Symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea, and/or constipation. Certain foods aggravate the symptoms, including gas producing foods (such as beans), milk products, alcohol, caffeine, and fat. Therapy includes frequent small meals, low fat meals, high fiber intake, probiotics, and avoiding foods that trigger symptoms.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is more common in males or females?
FEmales
Ulcers or peptic ulcers
Sore that can occur in the stomach., small intestine, or lower esophagus.
What can cause ulcers?
Bacteria such as (H. Pylori), and possibly even medications. Smoking, stress, and genetics.
What is a drug that can cause Ulcers and what does it do?
Nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAID) which destroy the innner mucus lining.
Symptoms of ulcers include?
Burning sensation in the stomach following meals or at night, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite.
What are carbohydrates?
Large macromolecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen molecules.
How much energy do carbs provide?
4 kcal/ gram
In what form are carbs found in the blood?
In the form of blood glucose, or what is called glycogen, which is storage form of glucose.
How does glycogen help in preserving normal blood glucose levels.
When blood sugar becomes low, glycogen is converted to glucose to raise the blood glucose levels.
Monosaccharides
are simple sugars
Three types of monosaccharides?
glucose, fructose, and galactose.
What is fructose?
It is fruit sugar, and is the sweetest tasting one.
What is glucose?
Blood sugar
Galactose
This is usually attached to glucose, and is found in milk.
Disaccharides
(di means two) are two monosaccharide units joined together.
Examples if disacharides?
Sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What are the differences between sucorse, lactose, and maltose, and what are they found in?
Similarity is that they all contain glucose.
Sucrose = glucose + fructose: It is very sweet and is found in table sugar, honey, and maple syrup.
Lactose = glucose + galactose: known as the milk sugar
Maltose = glucose + glucose: It is rarely found in food. Maltose is used in the liquor industry to convert sugar to alcohol.
Complex carbs
Often referred to as polysaccharides, complex CHO are made up of many glucose units joined together. Examples include starch, glycogen, and fiber.
Difference between fiber and starch.
Fiber can’t be digested.
Starch can be found in?
sources include vegetables, beans, breads, pasta, and rice.
Three types of fibers
Insoluble, soluble, functional
Insoluble fibers (non fermentable)
Does not dissolve in water
Not broken down by intestinal bacteria
increases stool mass
speeds passage through the large intestine
Soluble (viscous) fiber
Dissolves in water
Broken down by intestinal bacteria
Slows glucose absorption and can lower cholesterol
Provides satiety to a meal
Functional fiber
Fiber that is added to a product
Promotes intestinal health
Are foods that are high in starch usually also high in fiber as well? True or false?
True
What other organs besides mouth with salivary amylase breaks down complex carbs to simpler ones?
The pancreas releases pancreatic amylase to break down the polysaccharides into mono and disaccharides. The wall of the small intestine also has specialized enzymes that break down the disaccharides to monosaccharides:
Maltase does what?
digests maltose and the results are two glucose units.
what does the suffix -ase mean?
Usually means an enzyme that speeds the process of breakdown.
Sucrase does?
digests sucrose and yields glucose and fructose.
Lactase does?
digests lactose to produce glucose and galactose.
lactose intolerance?
Lactase is not produced enough. so lactose can not be broken down properly. People can only tolerate cheese yogurt, and very small amount of milk.
Monosaccharides are absorbed actively or passively, or facilitated?
active absorption, so they require energy and a carrier protein.
Two types of enzymes important for digestion?
Amylase, disaccharidases.
Name the three enzymes that break down disaccharides into monosaccharides
The wall of the small intestine also has specialized enzymes that break down the disaccharides to monosaccharides:
Maltese digests maltose and thre results are two glucose units.
Sucrase digests sucrose and yields glucose and fructose.
Lactase digests lactose to produce glucose and galactose.
If inadequate amounts of carbhohydrates are consumed, the body will instead begin to convert protein derived from muscle into glucose for fuel. This process is known as _________.
gluconeogenesis
What can the brain and CND use when glucose is absent for energy?
They can use ketones.
Three functions of carbs:
Provide fuel, preserve proteins, prevent ketosis.
Protein sparing:
Preserve proteins
What is ketosis?
When body turns fat into energy instead of glucose for energy.
What percentage of diet should be carbs?
45-65% of total cal intake.
Normal blood sugar levels?
70-100 mg/dl
insulin is produced where and its function?
produced by the pancreas and then released into the blood.
When insulin is released, lived takes glucose from blood and stores as glycogen. Muscles, and fat tissues, and other cells start to absorb glucose in their cells as well, bringing down sugar levels.