14) Transport Processes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
examples of point sources
leaky storage tanks
accidental spills
waste lagoons, landfills, dumps
septic systems
mine tailings
graveyards
injectionwells
examples of nonpoint sources
land applied manure/sewage/sludge
fertilizers and pesticides
air pollution fallout
urban runoff
military firing ranges
examples of linearly distributed sources
pipeline leakage
saltwater intrusion
road salt
losing streams
canal leakage
types and examples of contaminant types
chemical: inorganic, organic, metals, radionuclides
biological: bacteria, viruses
miscible/dissolved: cations and anions, organics
immiscible fluids: gasoline, chlorinated solvents
what are teh three key transport mechanisms
advection: transport due to bulk groundwater flow
diffusion: molecular transport due to solute concentration gradients (no water movement)
mechanical dispersion: spreading of solute mass due to groundwater velocity variations at the pore scale
details on advection
amount of solute transferred depends on
concentration in water and amount of water flowing
flux measurement (volume through cross-sectional area over time) mass per area per time
solutes move along with groundwater flow
advective mass flux = Ja = q C = ne v C
details on molecular diffusion
solutes move through stationary fluid due to random brownian motion
solutes move from high concentration to low concentration
spreads solutes in all directions but no water movement
how is diffusion affected in porous media?
value of diffusion coefficient is smaller than Dd because of tortuous flow paths that molecules have to travel
some molecules have longer path to follow, so diffusion coeff is smaller
true or false: tortuousity is always less than 1
true, it’s less than what it would be in free water (1)
what is mechanical dispersion
tendency for solutes to spread out from the path it would be expected to follow
multiple velocities in porous media causes spreading of solute in space
advective process that results from velocity variation
what is dispersion caused by?
some pores are larger than others, allowing fluid flowing through larger pores to move faster
some fluid particles will travel along longer flow paths in soil than others to go the same linear distance
as fluid moves through pores, it will more faster in the centre of the pores than along the edges (friction)
true or false: solute transport cannot occur with no advective water movement
false: solute transport can still happen (very slowly) even with no advective groundwater movement
what form of transport becomes dominant in very low hydraulic conductivity media
diffusion
longitudinal dispersion vs transverse dispersion
longitudinal: spreading parallel to the direction of groundwater flow
transverse: spreading in the direction perpendicular to groundwater flow, smaller than longitudinal, can be different horizontally than vertically
what are scale effects of dispersion
dispersion increases with scale until asymptote is reached
decrease in concentrations due to pore-scale mechanical dispersion and macro-scale heterogeneitywh
at is hydrodynamic dispersion
molecular diffusion and mechanical dispersion together
JH, subscript i refers to direction in which mass flux is being calculated (longitudinal or transverse)
under low flow velocities __ dominantes, and under high flow velocities __ dominantes
low flow = diffusion (D*) dominates
high flow = dispersion (av) dominates
what situations would you expect to see more dispersion? less?
more dispersion = high K materials like gravel and sand
less dispersion = low K materials like clay
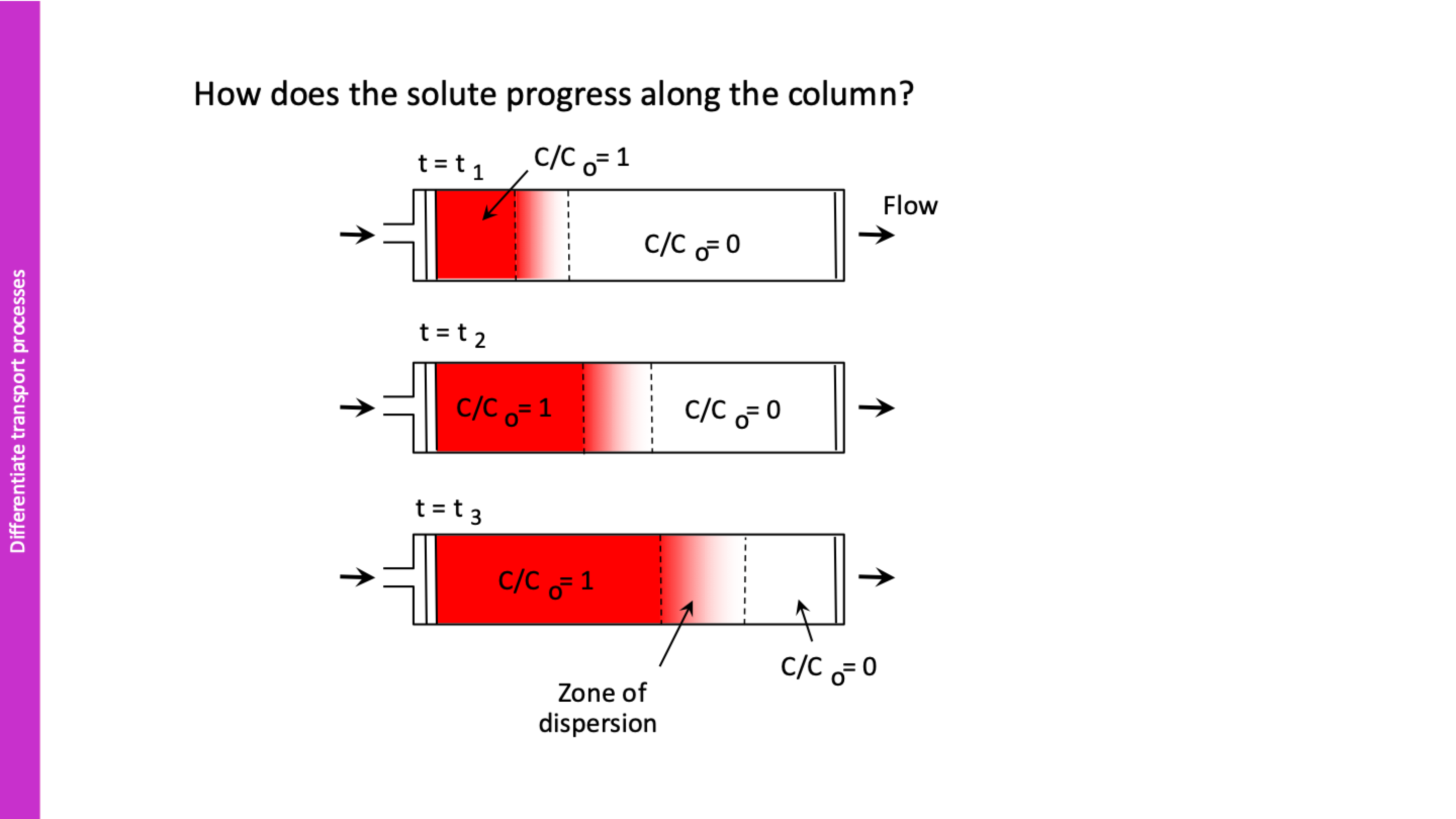
explain this
shows how tracer progresses, the lines show zone of dispersion where 0<C/C0<1
important details about solute transport processes
advection moves the contaminants at the bulk average groundwater velocity
hydrodynamic dispersion spreads contaminants in all directions
spreading is greatest in parallel to flow (longitudinal)
dispersion is due to variations in flow velocity
transport is a transient process occurring within a steady groundwater flow system
what is the advection dispersion equation
solute mass flux in - solute mass flux out ± loss/gain of solute mass = net rate of change of solute mass within the element
what are the assumptions in the 2D advection dispersion equation
saturated porous medium
groundwater velocity is uniform and steady
flow is aligned with x-direction
dilute solution (no density effects)
what is the ogata-banks solution
assume v is known and steady
can solve for C at any point, x, along the column at any time t
solution reduces to the 1-D form of the diffusion equation when v=0
numerator: x-vt, how far are you along x relative to advective front vt
denominator: how much longitundinal dispersion is there about the centre of mass
what do variables mean in ogata-banks solution
C = concentration at location x and time t
C0 = boundary concentration at x=0
v = pore water velocity in +x direction (darcy/porosity)
DL = longitudinal dispersion coefficient
Erfc = complementary error function
what happens in ogata banks solution for the graphs>
more dispersion = flatter and longer
more advective flow = more vertical
what is assumed for 1D advection dispersion equation?
only moving water through pores of porous medium
uniform velocity and dispersion coefficient
what does ogatabanks solution mean
solute follows normal distribution about center of mass at x=vt
solute mass is conserved
plume spreading must cause peak concentrations to decline
peak concentration occurs at center of mass where x=vt and y=0
what things cause plume growth
advection
molecular diffusion
mechanical dispersion
what things limit plume growth
chemical:
sorption
precipitaiton/dissolution
volatilization
reactions
abiotic degradation
biological: degradation
what is adsorption
process where solute molecules attach to the surface of solid particles in a porous medium
clays are strong adsorbers because they have high surface area, platy structure, and electrical charge at surface
what is electrical conductivity
material’s ability to conduct/transport an electric charge which is directly related to concentration of ions in water
high EC = high salinity
specific conductivity is EC corrected to to 25°C
what is an isotherm
relationship between concentration of solute in aqueous solution to mass sorbed on solid surface
what is G in equations
source or sink for solute mass
during sorption, mass is lost from dissolved phase onto mineral surfaces, so we use sink term
G is adsorption term representing the rate of mass sorbed to solids per unit volume porous medium per unit time
what is retardation factor? what happens if its zero
measure of mean velocity of reactive contaminant relative to mean velocity of non-reactive contaminant
slows the advection of contaminant and reduces dispersion of contaminant
there is no slowing down of the plume
what are assumptions of Kd model
linear sorption isotherm
equilibrium
fast, reversible reaction
isothermal conditions
may not be valid for all concentrations, if other chemicals are present, different pH
what are effects of sorption on plumes
sorption may not be reversible
contaminants undergoing sorption will travel more slowly than non-reactive contaminants in a plume (retardation)
strong sorption can cause a contaminant to be immobile over a relevant time scale, such as many decades or centuries
each contaminant has its own particular sorption affinity, and will move at its own rate
how might ADE apply in landfill leachate
continuous space
ogata-banks equation for 1D best suited if source is large, otherwise need 2D or 3D solution
consider retardation
how might ADE apply in nuclear waste disposal
can use ogata-banks with v=0 (no flow)
slow diffussion
how might ADE apply in chemical spill
2-S slug input solution
consider retardation factor
most concentrated value in centre of plume
true or false: the greater the groundwater flow velocity, the greater the hydrodynamic dispersion
true
both equations (transverse and longitudinal) have velocity in them
hydrodynamic = mechanical dispersion + diffusion
true or false: dispersion, sorption, and diffusion are three transport processes that cause growth of groundwater contaminant plumes
false, sorption slows down, dispersion and diffusion do cause growth