Anatomy Quiz 6 (Dara)
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
EDV
end diastolic volume
ventricle volume before contraction
130 mL
ESV
end systolic volume
ventricle volume after contraction
70 mL
SV meaning and formula
SV = EDV -ESV
blood pumped by one ventricle during contraction (one beat)
60% of EDV
CO meaning and formula
cardiac output
CO = HR * SV
volume pumped by LV in one minute
mL/min
Frank-Starling Principle
filling the heart with more blood leads to more blood out (more in, more out)
more muscle stretch corresponds to (more/less) blood coming in
more
SNS (dilates/constricts) bronchioles
dilates
SNS (dilates/constricts) peripheral vessels
contricts
singultus
hiccups
(upper/lower) respiratory system filters, warms, and humidifies air
upper
the larynx is in the (upper/lower) respiratory system
lower
first structure of the lower respiratory system
larynx
pharynx is part of the (upper/lower) respiratory system
upper
structures of the lower respiratory system (5)
larynx
trachea
bronchus
bronchioles
alveoli
voicebox
larynx
structure in which the epiglottis is located
larynx
chemical that allows the lung capillaries to regulate blood volume and BP
angiotensin II
the (right/left) lung is broader
broader because the heart is on the left
number of lobes in the right lung
3
number of lobes in the left lung
2
area between the right and left lung
mediastinum
the (right/left) lung is longer
left because the diaphragm on the right rises more to accommodate the liver
separation between lobes in the lung
fissures
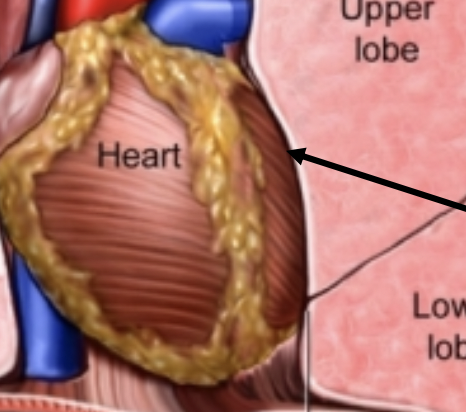
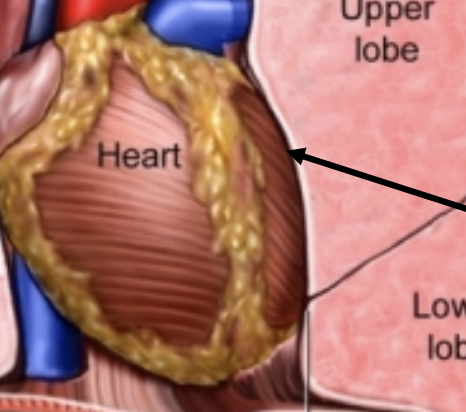
space in which the heart pushes the left lung
cardiac notch
segments of the pharynx
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
where the larynx and pharynx meet
laryngeal inlet
position of the epiglottis during swallowing
bends over the glottis to cover the larynx/ariway
epiglottis cartilage type
elastic
types of cartilage in the larynx
thyroid cartilage (hyaline)
cricoid cartilage (hyaline)
epiglottis (elastic)
hyaline cartilage is (more/less) flexible than elastic cartilage
less
what hyaline cartilage is made from
chondrocytes
synonym for Adam’s Apple
laryngeal prominence
location of laryngeal prominence/Adam’s Apple
thyroid cartilage of the larynx
composition of thyroid and cricoid cartilage
hyaline cartilage
cause of thyroid cartilage elongation during puberty
androgens
surgery to reduce size of the Adam’s Apple
chondrolaryngoplasty
functions of the larynx (3)
patent airway
switching mechanism to route food and air to appropriate destination
voice production
structure in which vocal cords are located
larynx
shape of glottis during normal breathing
triangular slit
voice comment controlled by vocal cord tension
pitch
windpipe
trachea
structure that close the glottis during swallowing
false vocal cords and epiglottis
property of sounds controlled by adjusting the force of air going across the vocal cords
loudness
epithelium type of the esophagus
stratified
trachealis muscle type and function
smooth
adjust diameter of trachea
adjust resistance to air flow
components of respiratory defense system (4)
nasal filtration
mucous
cilia (mucociliary escalator)
alveolar macrophages
mucociliary escalator function
sweep debris from mucus upwards towards the pharynx
epithelium type of the mucociliary escalator
pseudostratified columnar
the cycle of systole and diastole (does/doesn’t) need to occur in one chamber
does
least severe part of the heart to damage
atria because more filling is passive
CO is the blood pumped by the (right/left) ventricle
left
capnia
CO₂ content in the blood
cell type (does/doesn’t) change throughout the airway
does
zones that make up the respiratory tract
conducting zone and respiratory zone
bounds of the conducting zone
nasal cavity to terminal bronchioles
zone that makes up most of the respiratory tract
conducting
components of the respiratory zone
bronchioles and alveoli
gas exchange occurs in the (conducting/respiratory) zone
respiratory
dominant muscle type and shape in bronchioles
circular smooth muscle
as the bronchioles branch and get smaller, they have (more/less) cartilage
less
epithelium type in the respiratory tract
simple squamous epithelium
property of bronchioles that determines airflow resistance and distribution
diameter
bronchitis
inflammation of smooth muscle in the bronchioles
alveolar sac
≥ 2 alveoli that share an opening
alveoli cell type
simple squamous
things surrounding alveoli (2)
capillaries and elastic fibers
bronchi cell type
pseudostratified ciliated columnar

large bronchiole cell type
columnar
ciliated
simple

small bronchiole cell type
cuboidal
ciliated
simple

terminal bronchiole cell type
cuboidal
non-ciliated
simple

the distance between the blood and the alveolar air is (large/small)
small (allows for rapid diffusion)
number of bronchi
3 (primary, secondary, tertiary)
alveoli cell types
Type I (squamous epithelial; gas diffusion)
Type II (surfactant)
Type (I/II) alveoli cells are more abundant
Type I
cells that secrete surfactant
Type II alveolar cells
composition of surfactant
proteins and phospholipids
function of surfactant
reduce surface tension
prevent lung collapse after exhalation
alveoli (are/aren’t) vascularized
are (surrounded by capillaries)
LaPlace surface tension law
P = (2•tension) ÷ radius
when a fetus starts producing surfactant, and when it has sufficient surfactant
production starts at 24 weeks
fetus has enough surfactant at 34 weeks
the alveoli (do/don’t) have a basement membrane
do (basement membrane binds to the capillaries)
the alveoli (do/don’t) have resident macrophages
do
name of resident macrophages in the alveoli
dust cells
RDS name and cause
respiratory distress syndrome
difficulty breathing caused by alveolar collapse
long compliance
how easily the lungs expand
factors affecting lung compliance (3)
lung connective tissue
surfactant levels
thoracic cage mobility
healthy lungs have (high/low) compliance
high
lungs with (high/low) compliance easier to fill and to empty
high
lungs with high compliance are (hard/easy) to fill and empty
easy
lungs with low compliance are (hard/easy) to fill and empty
hard
(high/low) compliance lungs require more muscular energy
low
reason why premature babies have low lung compliance
inadequate surfactant levels
reason why emphysema leads to low lung compliance
destruction of connective tissue
reason why arthritis and skeletal disorders lead to low lung compliance
impairment of articulations
alveoli (do/don’t) require effort to inflate
do (LaPlace’s surface tension law)
a higher pressure indicates that the alveolus has a (smaller/larger) radius
smaller radius
the effect of surfactant is larger in (small/large) alveoli
small
result of surfactant
pressure in all alveoli is equal regardless of size
surfactant (increases/decreases) surface tension
decreases
bronchopulmonary segments (are/aren’t) discrete
are (each can be removed without compromising the other segments)