pubhlth 206a- week 7: using DAGS for causal & effect in observational studies
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
some lessons
association is not causation, though causation produced association
statistics alone cannot differentiate cause from effect
subject matter knowledge is essential for valid causal inference
confounder
associated with the outcome (or in some definitions, a risk factor for the outcome)
associated with exposure
not on the causal pathway between exposure & outcome
how to detect possible selection bias: convential methods
study sample notably diff from the target population w/ respect to factors that are relevant to study questions
individuals who are more susceptible more likely to drop out
of a study (or more likely to participate)exposed cases more (or less) likely to be selected than
unexposed casesexposed controls more (or less) likely to be selected than
unexposed controlsbased on subject matter knowledge
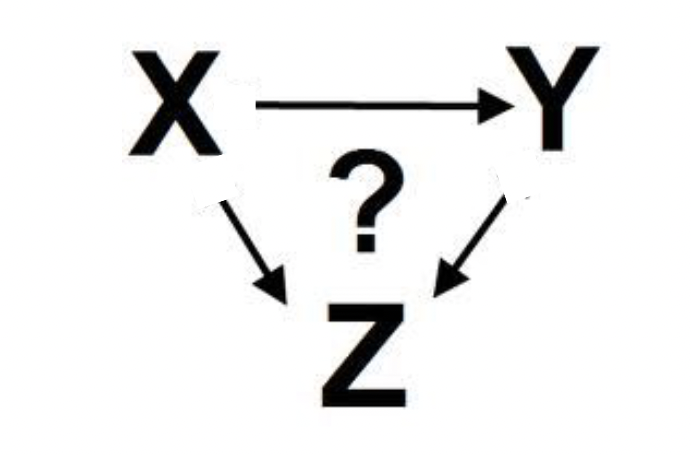
directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) visual
graphs
diagrams representing an assumed system of causal connections b/w variables
directed
arrows represent causal direction b/w variables
ex: A —> B means that changing A would cause change in the expected value of B
acyclic
cycles are not permitted b/c a variable can’t cause itself
ex: a0 —> b1 —> a2 —> b3
NOT a dag
ex: a ←→ b
DAGs benefits
make assumptions explicit
identify potential biases& covariates to measure
avoid introducing biases during sampling or analysis
determine how to correct for selection biases
characterize mediation & direct vs indirect effects
in order ot identify a causal effect of e on y
all non-directed (backdoor) paths leading from E (exposure) to Y (outcome) must be BLOCKED
paths are connections between variables on a DAG, through any
number of arrows going in either directiondirected paths from E to Y are connections going only forward from E towards Y
a path is blocked shen it contains
a noncollider that is conditioned on a collider
*conditioning on a collider
reverse causality
e —> y or y —> e