Chapter 3: Introduction to Cells and Their Structures
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the basic unit of structure and function in the body?
The cell.
How are cells measured?
In micrometers.
What does it mean when cells are described as differentiated?
They have developed specialized characteristics.
How do the size and shape of cells relate to their function?
Cells vary in size and shape; their structure and function are inter-related.
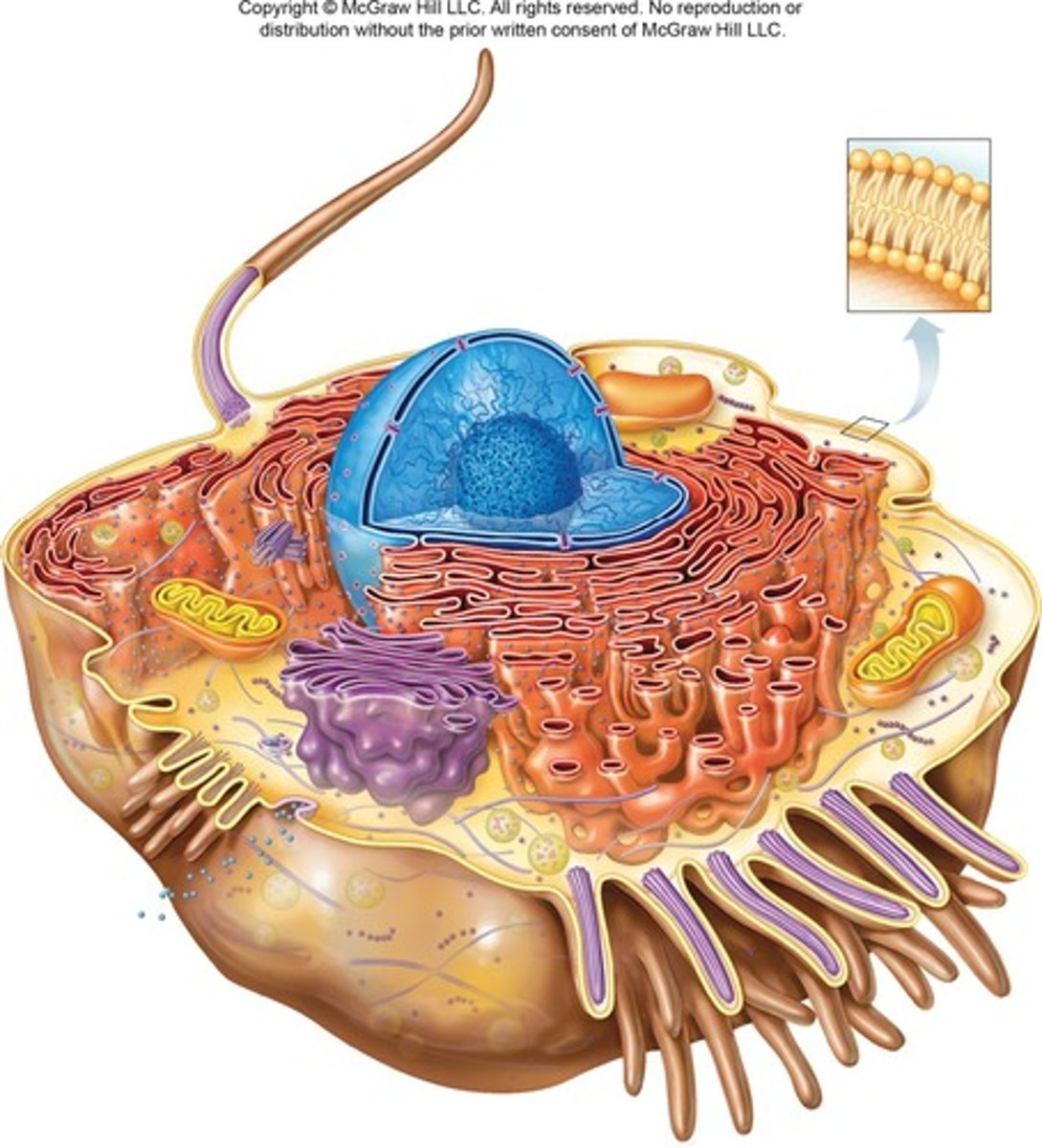
What are the three major parts of a cell?
Nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
It contains genetic material and directs the cell's activities.
What does the cytoplasm consist of?
Organelles suspended in a liquid called cytosol.
What is the role of the cell membrane?
It maintains the integrity of the cell and regulates entry and exit of substances.
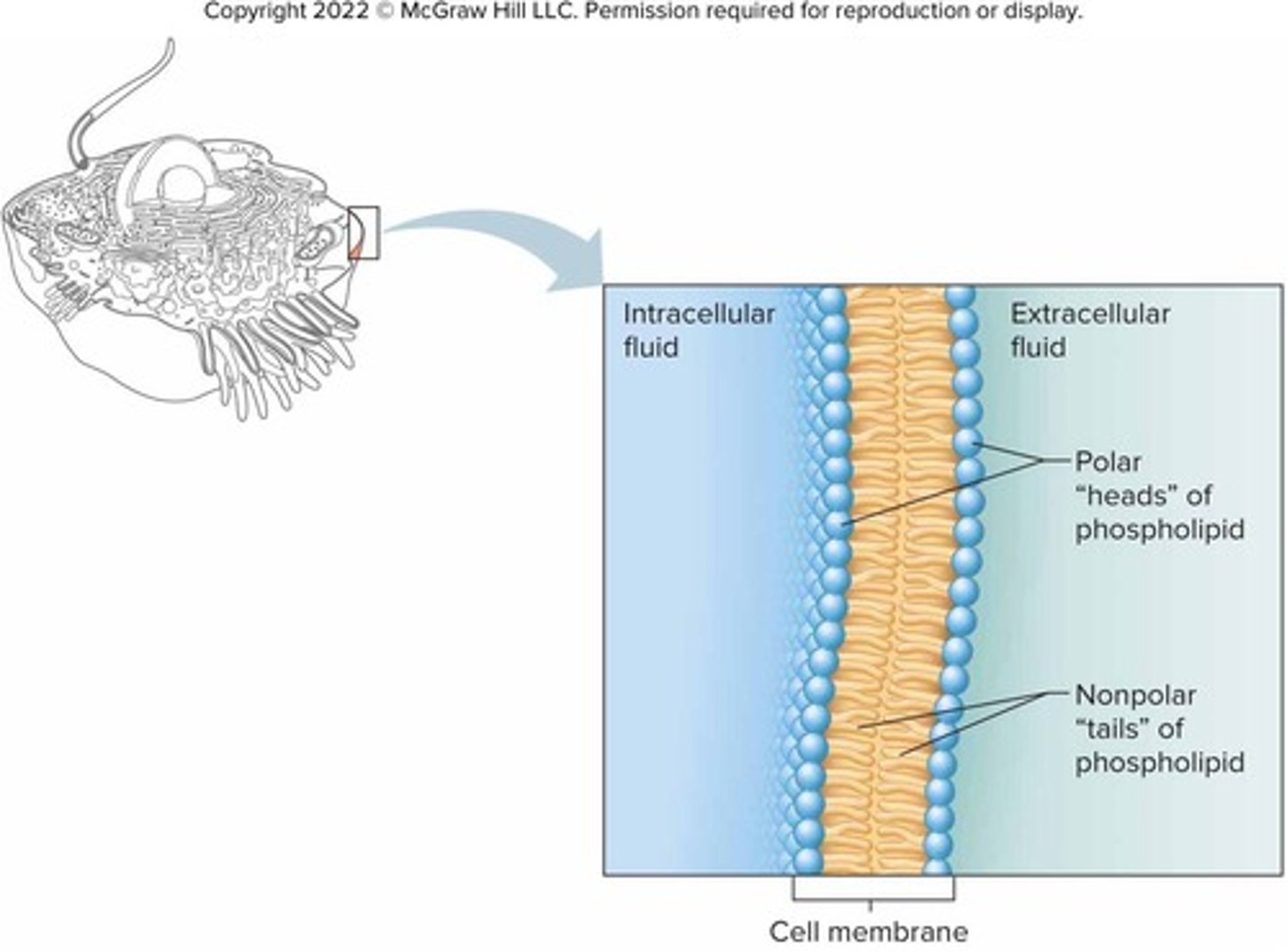
What is the cell membrane primarily composed of?
Lipids and proteins, with some carbohydrates.
What is the structure of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
Water-soluble heads form the surfaces, while water-insoluble tails form the interior.
What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
It stabilizes the membrane and helps keep it impermeable to water-soluble substances.
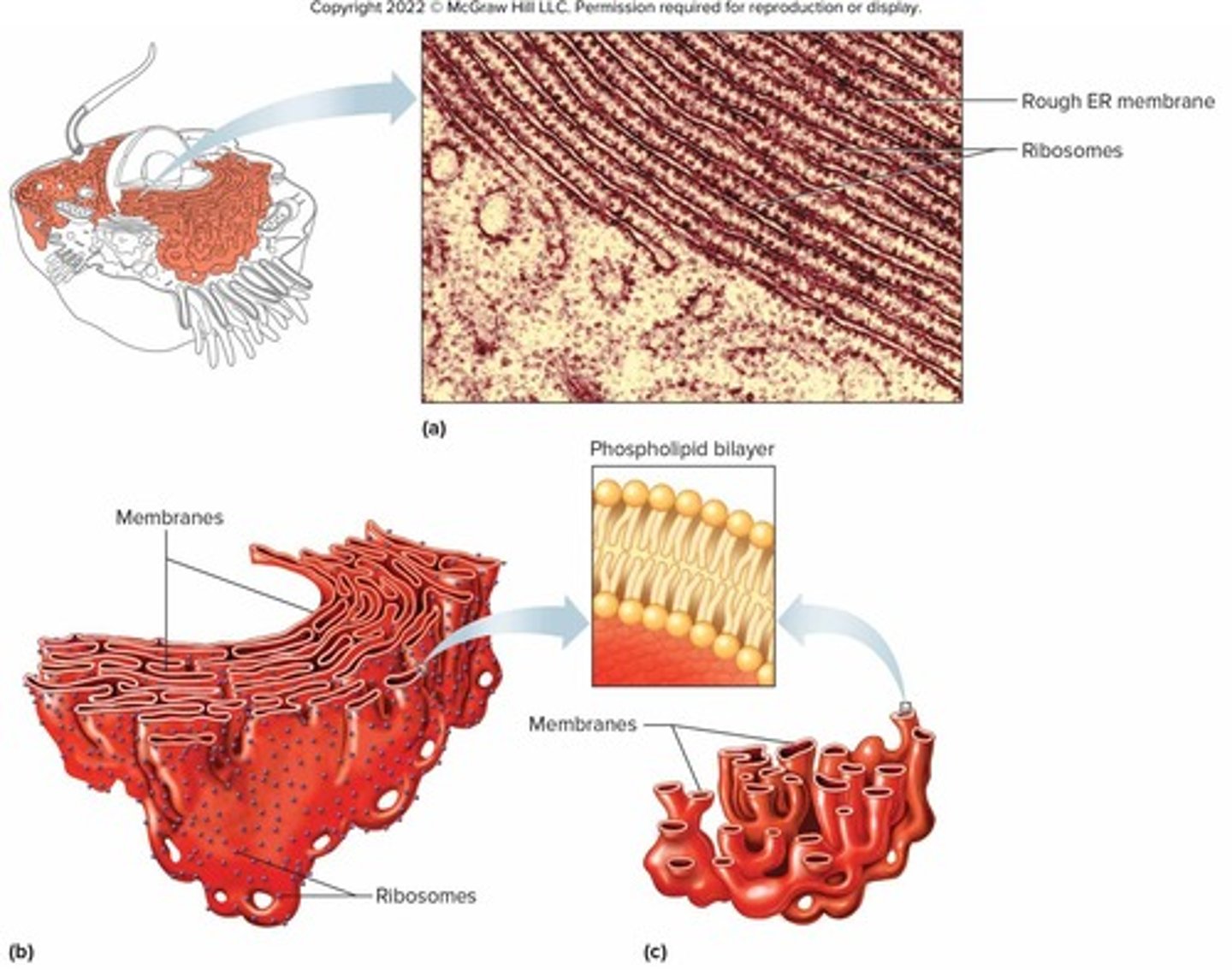
What are ribosomes composed of and what is their function?
They are composed of protein and RNA and provide structural support and enzyme activity for protein synthesis.
What distinguishes rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) from smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)?
RER contains ribosomes and conducts protein synthesis, while SER does not have ribosomes and conducts lipid synthesis.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
It refines, packages, and delivers proteins made on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
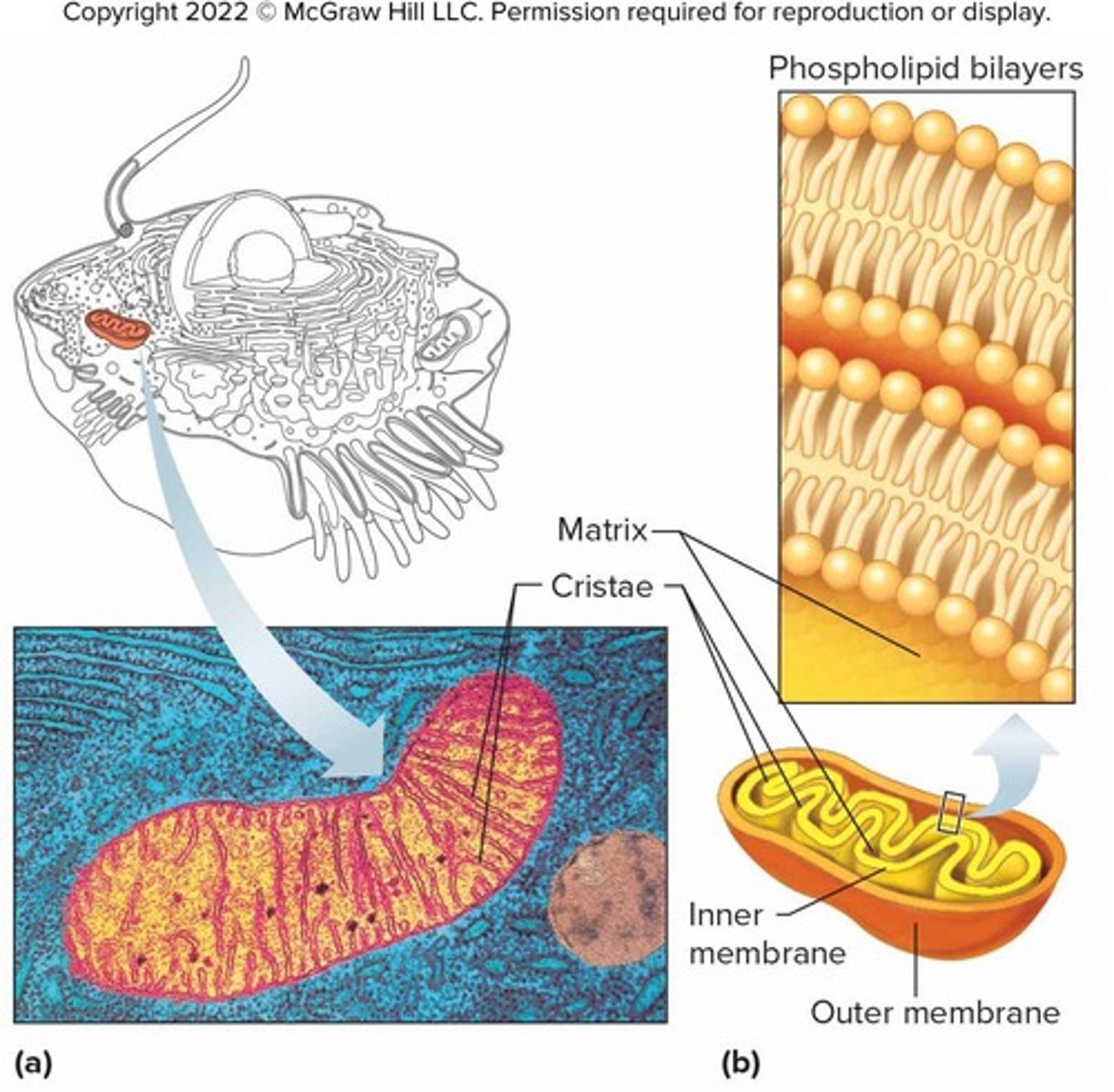
What are mitochondria known as and what is their primary function?
They are known as the 'powerhouse of the cell' and house chemical reactions that extract energy from nutrients.
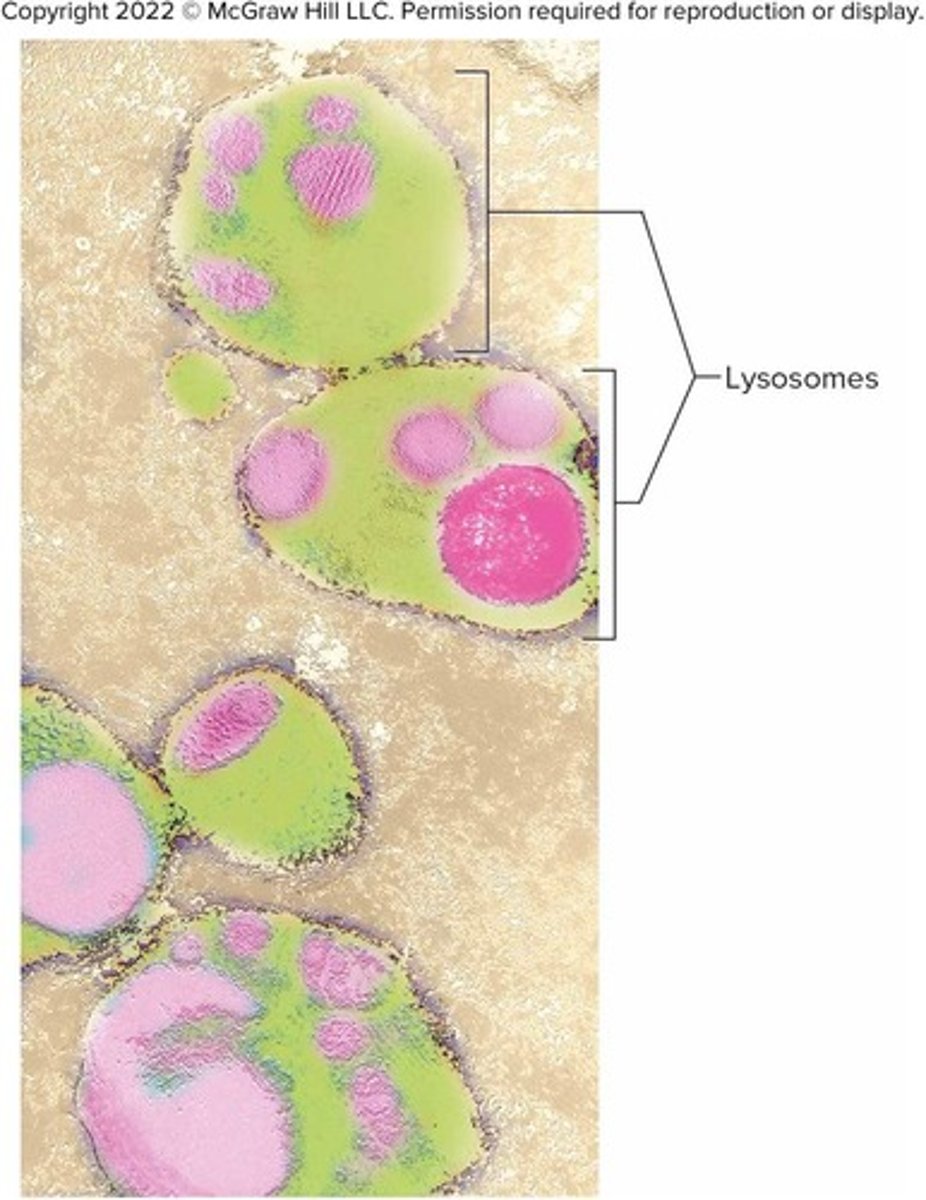
What do lysosomes contain and what is their role?
They contain enzymes that digest proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, bacteria, debris, and worn-out cell parts.
What is the function of peroxisomes?
They contain enzymes that digest lipids, alcohol, and hydrogen peroxide.
What is the cytoskeleton and what does it consist of?
It is a supporting framework of protein rods and tubules in the cytoplasm.
What are microfilaments and their function?
Thread-like structures made of actin that provide cellular movement, such as muscle contraction.
What are microtubules and their role in the cell?
Larger tubes of tubulin that maintain cell shape and make up cilia, flagella, and centrioles.
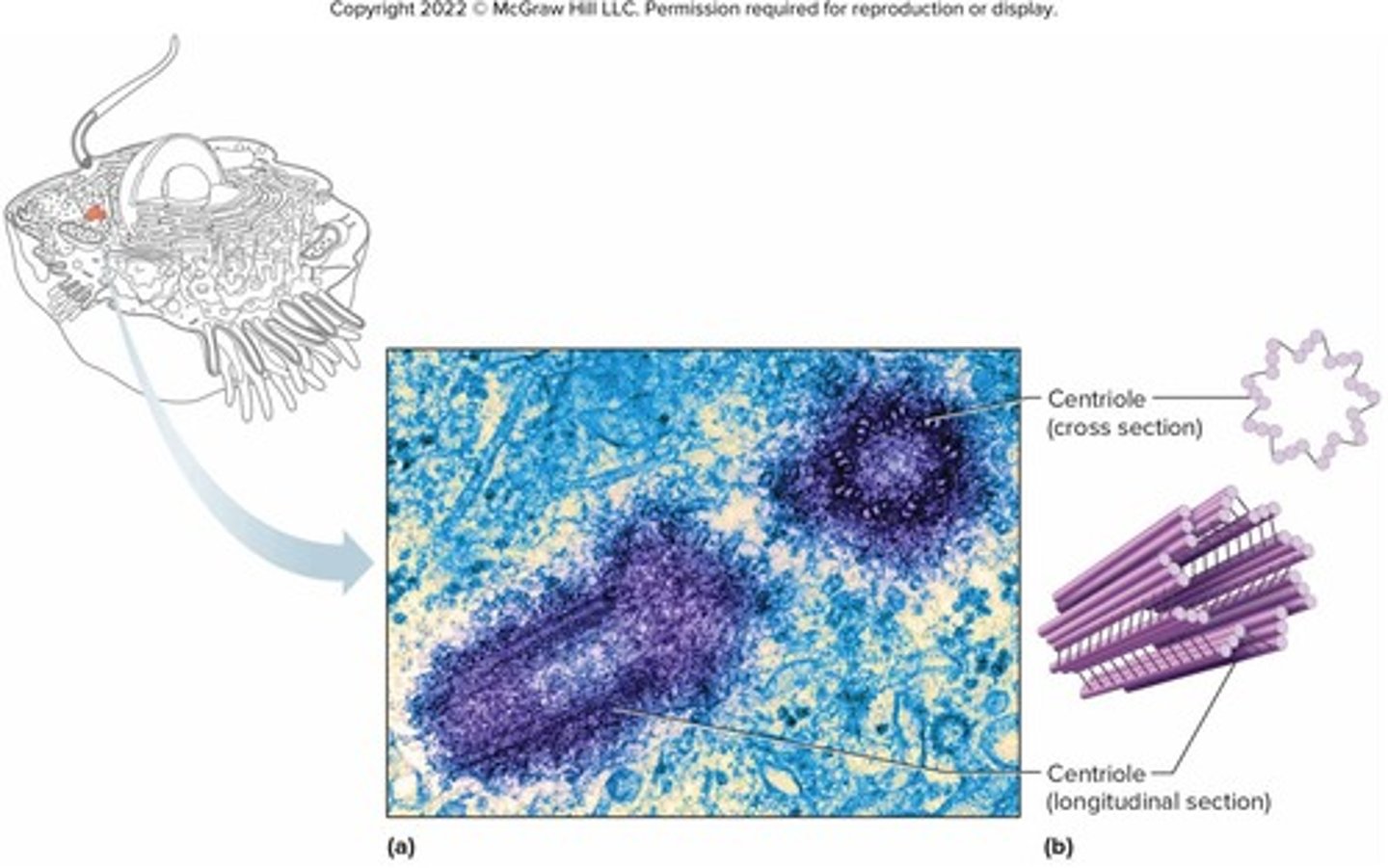
What is the function of centrioles in the centrosome?
They produce spindle fibers during cell division, distributing chromosomes to forming daughter cells.
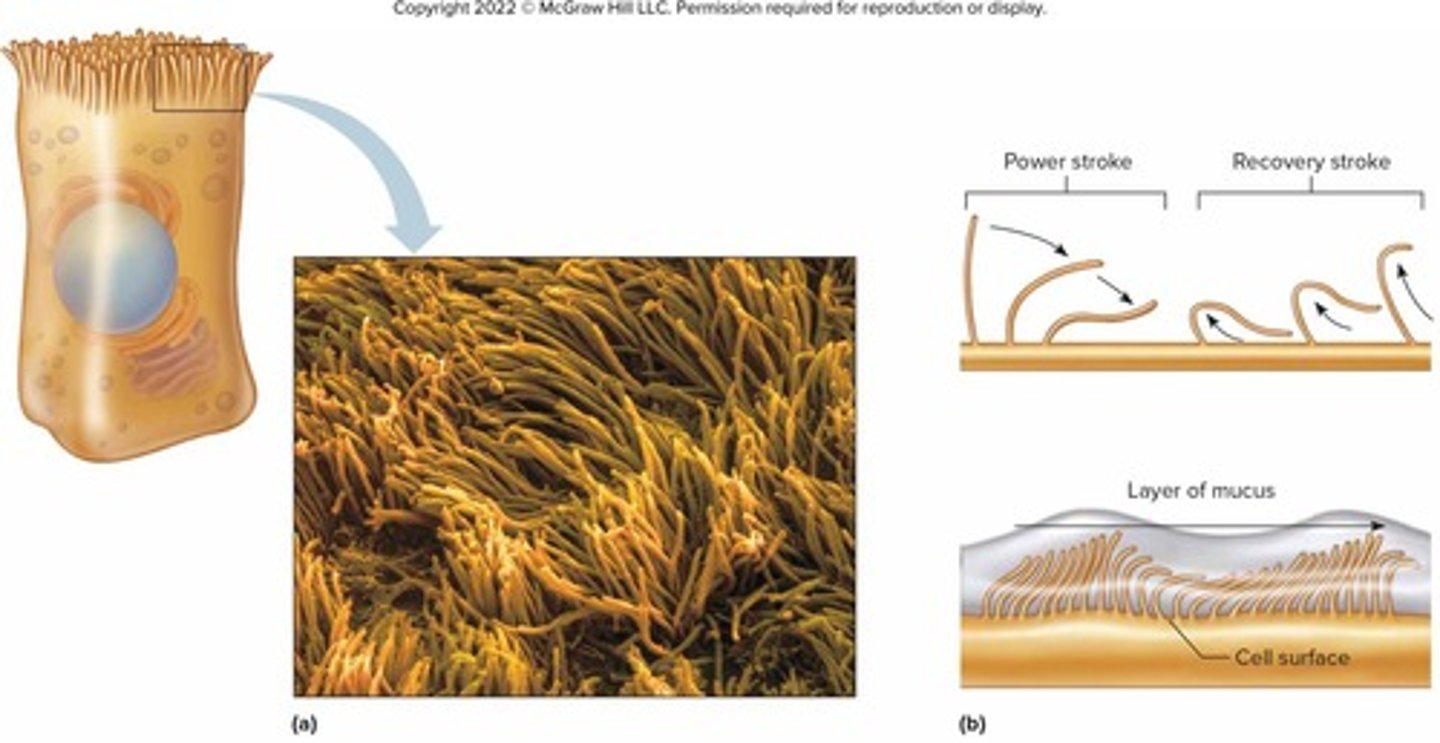
What are cilia and what is their function?
Motile extensions of the cell membrane that propel mucus in the respiratory tract and move eggs toward the uterus.
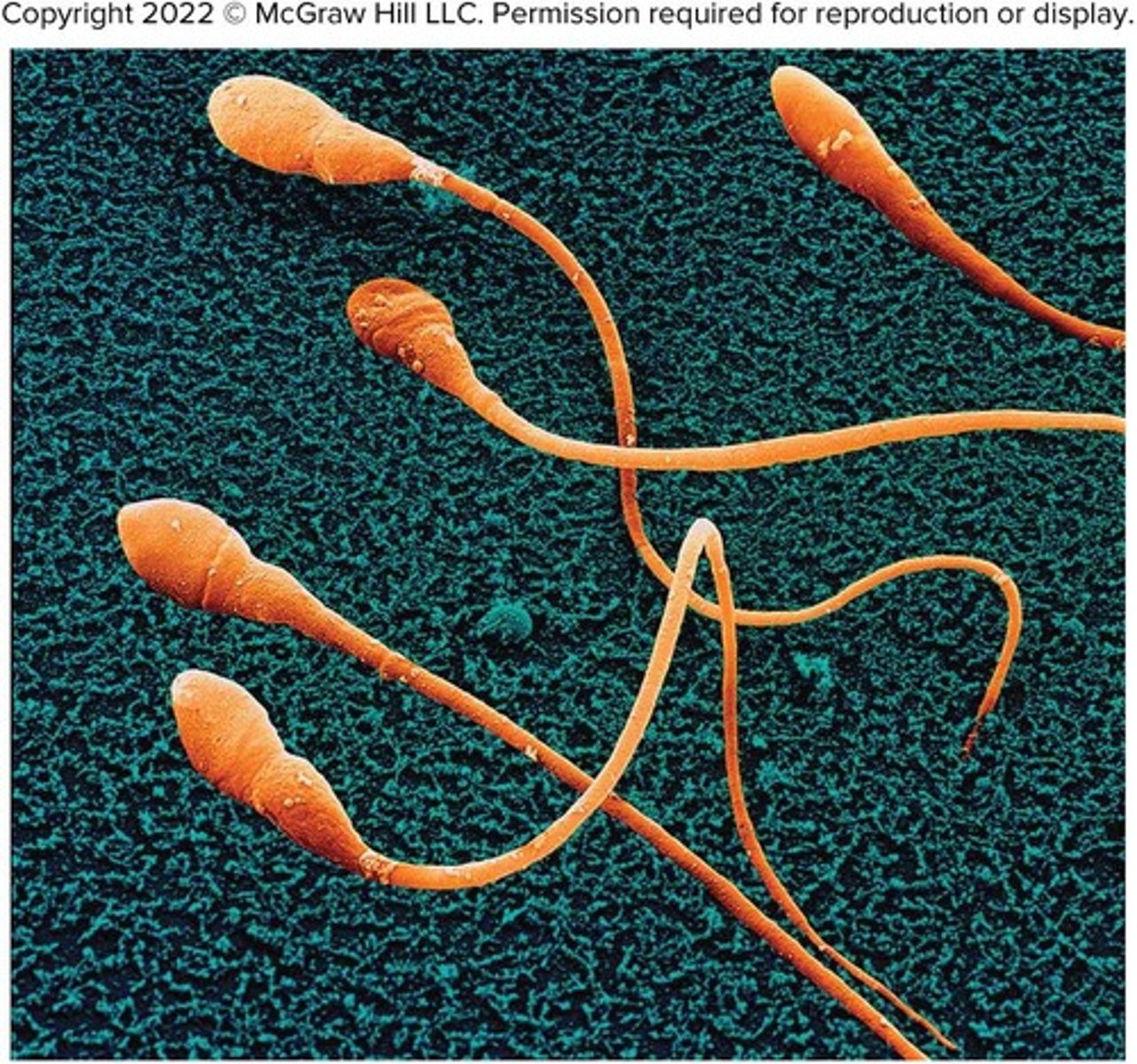
What distinguishes flagella from cilia?
Flagella are longer than cilia and cause the entire cell to move; the tail of a sperm cell is the only flagellum in a human cell.
What is the nuclear envelope?
A double-layered membrane surrounding the nucleus that separates nucleoplasm from cytoplasm.
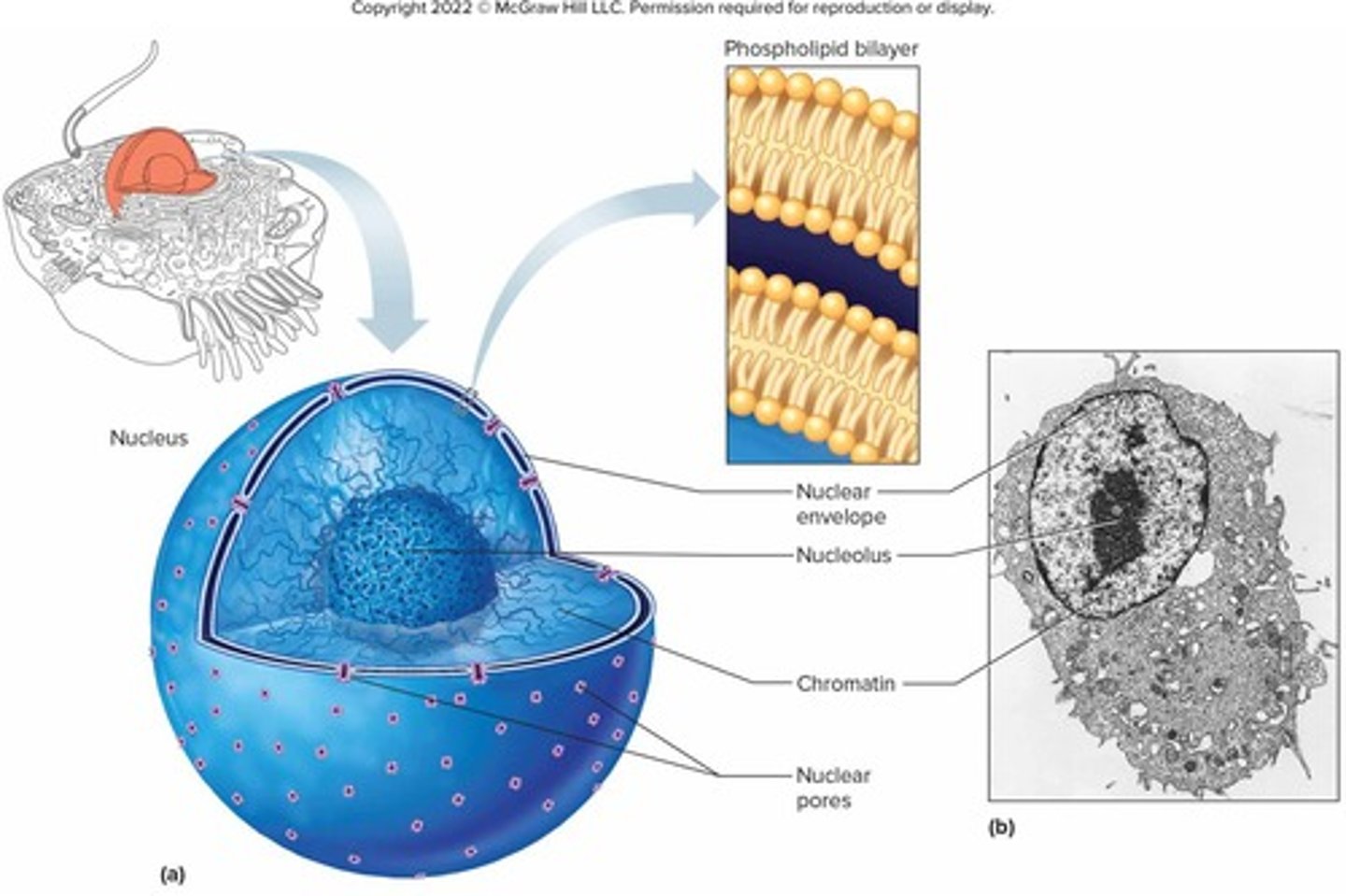
What is the function of the nucleolus?
It is the site of ribosome production.
What is chromatin and its role in the cell?
It consists of the cell's chromosomes, containing DNA wound around proteins, and stores information for protein synthesis.