Passive Transport and Active transport
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
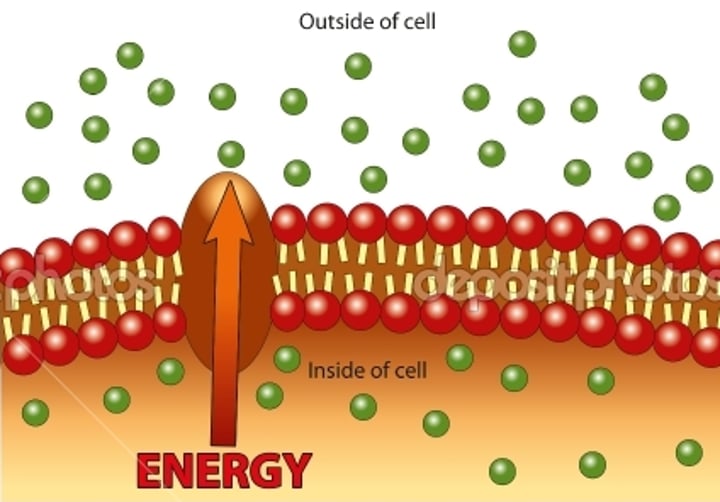
Active transport
moving molecules across a membrane into an already crowded space, which requires ATP (energy): Low concentration to high concentration
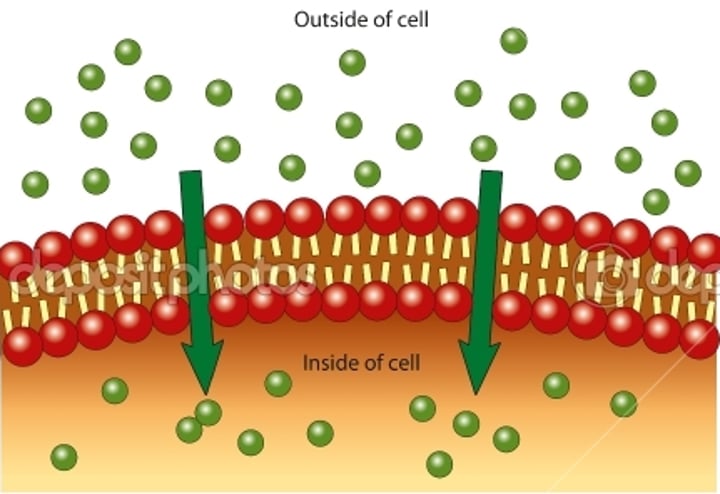
Passive Transport
diffusion (spreading out) across a membrane and occurs naturally (no energy necessary), high concentration to low concentration
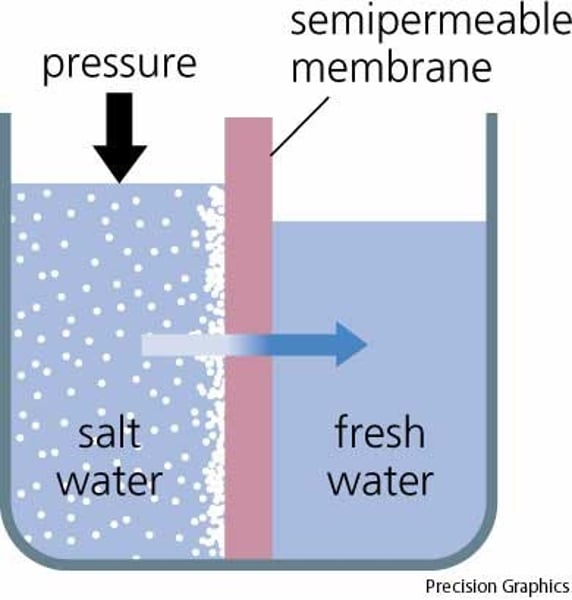
Osmosis
a special type of passive transport: it is diffusion of WATER across a membrane
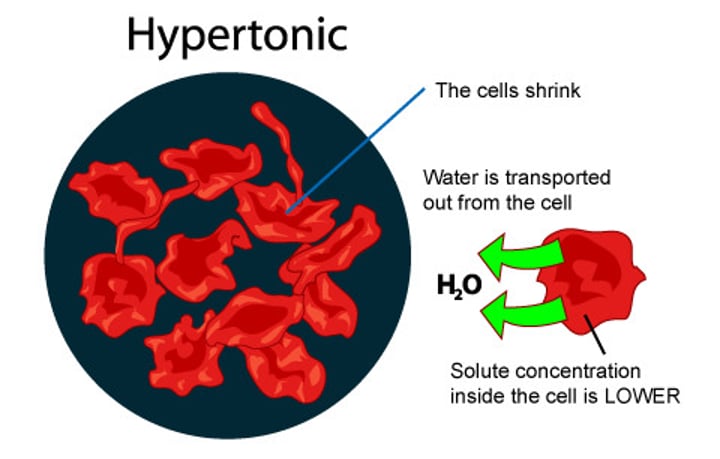
Hypertonic solution
HIGHER solute concentration outside of cell= "sucks" water out of the cell = cell has negative change in mass
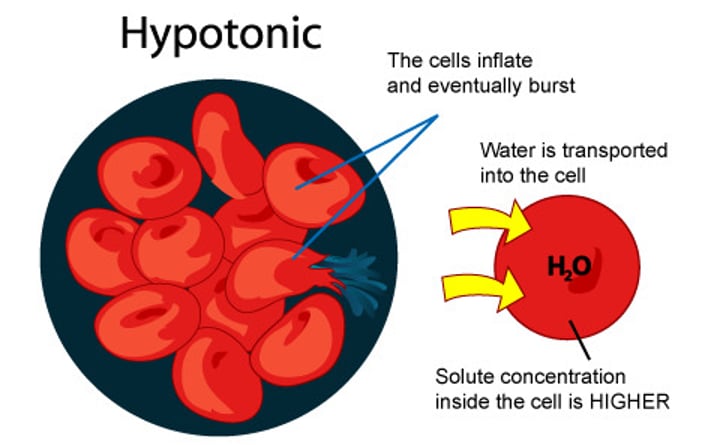
Hypotonic solution
LOWER solute concentration outside of cell= "blows" water into the cell = cell has positive change in mass
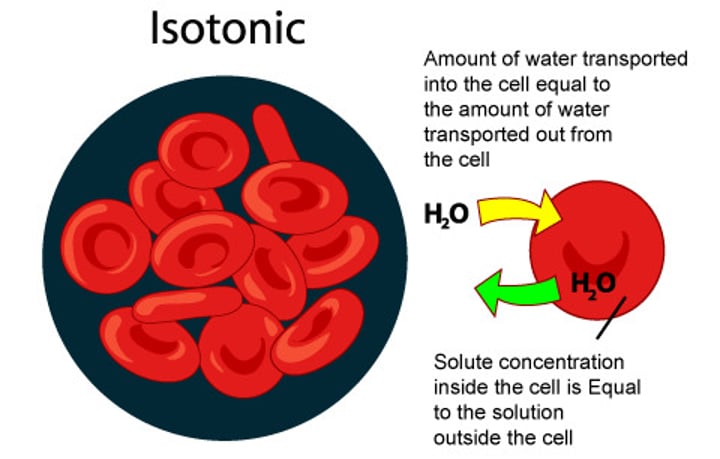
Isotonic solution
SAME solute concentration
Homeostasis
keeping conditions within the cell stable and consistent even when the external environment is changing
Equilibrium
Balance. When there is the same concentration inside and outside the cell. The molecules continue to move but they move equally into and out of the cell
semipermeable membrane
if the membrane is permeable, that means the substance can pass through the membrane, if its semi-permeable that means its selective on what it allows to pass through.
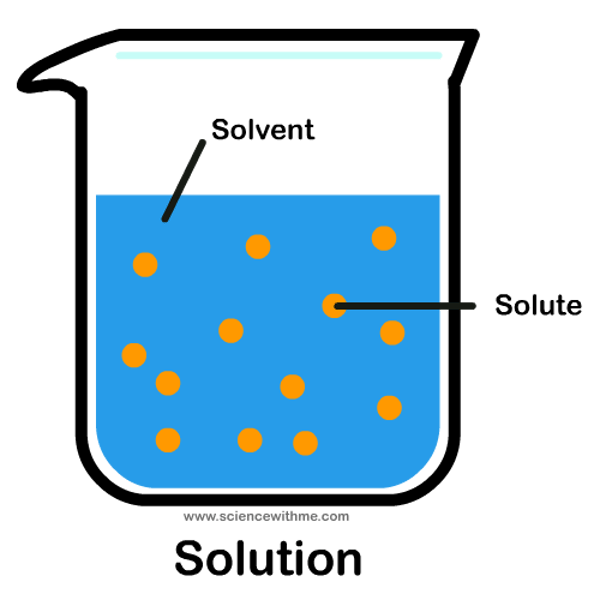
Solute
the minor component in a solution, dissolved in the solvent.
active transport
What type of transport moves substances from low concentration to high concentration?
active transport
what type of transport moves molecules against their concentration?
passive transport
What type of transport would most likely move small molecules, monomer units and uncharged particles?
passive transport
What type of transport moves substances without the use of energy?
active transport
what type of transport requires ATP?
passive
what type of transport would osmosis be?
passive
what type of transport (passive, active or both) moves molecules from high concentration to low concentration?
passive
What type of transport would facilitated diffusion be?
active. There already is a lot of Na+ inside the cell so it would take energy to bring more inside the cell.
if inside a cell has a large concentration of Na+, what type of transport would be needed to bring more Na+ into the cell?
active transport
Which type of transport would be used to move charged or large molecules?
passive transport (simple diffusion)
If there is a large concentration of glucose outside the cell, and the glucose moves into the cell, what kind of transport is this?
passive (osmosis).. If the cell has a lot of solute inside of it that means it has low concentration of water. Therefore the water will move from where there is more water (outside the cell) to where there is less water (inside the cell)
A cell has a large concentration of solute inside of it. Water moves from outside the cell to inside the cell. What kind of transport is this?
passive transport (facilitated diffusion)
There is more molecule A inside the cell than outside. Molecule A tries to diffuse through the cell membrane but it is not able to get through. As a result it uses a protein channel and then is able to move across the cell membrane to the outside of the cell. What kind of transport is this?