Skeletal System
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
epiphysis
ends of bone, forms a joint with another bone
diaphysis
shaft of the long bone (whole middle)
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage covering ends of the bone
periosteum
tough membrane covering over entire bone, source of bone-developing cells during growth or after fracture
medullary cavity
in middle of diaphysis, contains yellow bone marrow
endosteum
lining of the medullary cavity
red marrow
produces blood cells
yellow marrow
fat storage
axial skeleton
head,neck,trunk,vertebrae, ribs, and sternum
appendicular skeleton
limbs, bones connecting limbs
pectoral girdle
scapula and clavicle, upper limbs(arms)
hemopoiesis
blood cell formation, occurs in red bone marrow
compact bone
wall of diaphysis,solid,strong
spongy bone
(cancellous) epiphysis, red marrow
osseous
bone tissue
lacunae
tiny champers that osteocytes are enclosed in
Haversian Canal
run parallel to the bone
Volkmanns Canal
run perpendicular to the bone
lamellae
organized arrangement of collagen fibers into layers
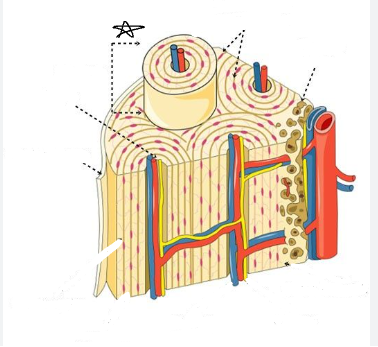
what is the star pointing to
osteon
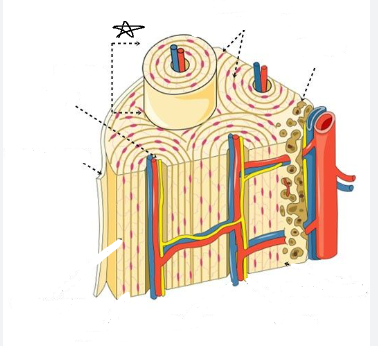
what is the star pointing to
lamellae
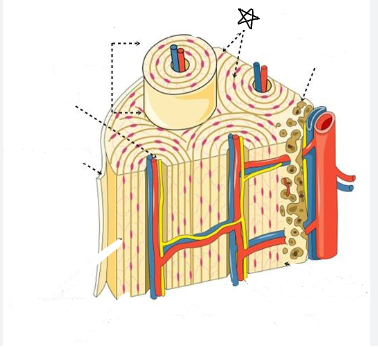
what is the star pointing to
spongy bone
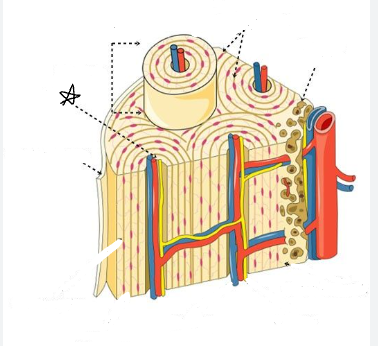
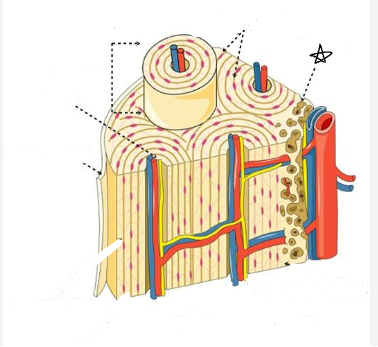
what is the star pointing to
bone cells
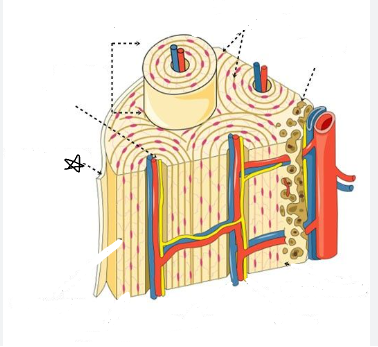
whats the star pointing to
periosteum
intramembranous bones
broad,flat bones of the skull
endochondral
all other bones
ossification
process of cartilage gradually changing into bone tissue
osteoblasts
produce bone cells called osteocytes
osteoclasts
dissolve bone tissue, a process called resorption
synarthrotic joints
immovable joints, junctions called stutures
amphiarthrotic joint
slightly moveable joints, vertebrae
diarthrotic joints
freely movable joints, have a labricating fluid called synovial fluid
ball and socket
shoulder/hip
hinge
elbow/knee
pivot
lower arm
saddle
thumb
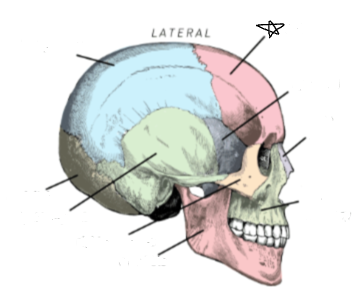
what skull bone is the star pointing to
frontal
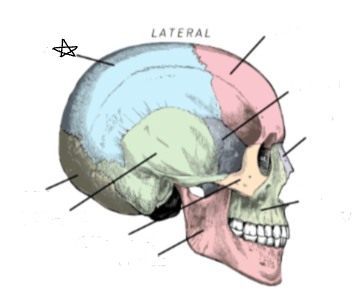
what skull bone is the star pointing to
parietal
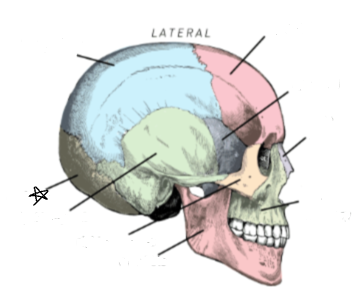
what skull bone is the star pointing to
occipital
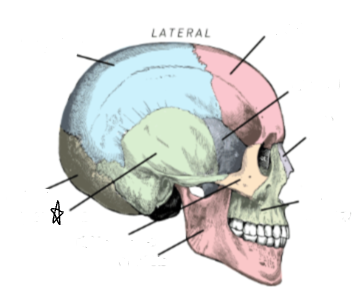
what skull bone is the star pointing to
temporal
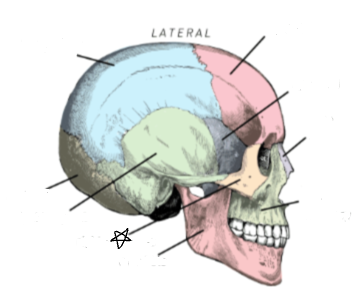
what skull bone is the star pointing to
zygomatic
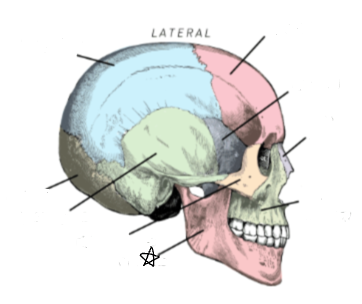
what skull bone is the star pointing to
mandible
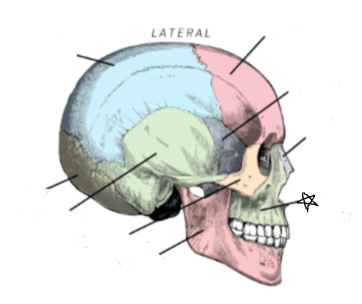
what skull bone is the star pointing to
maxilla
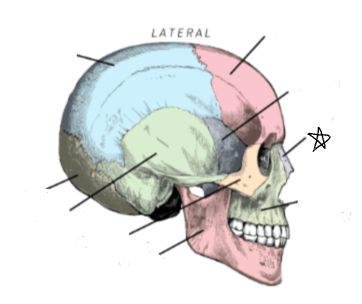
what skull bone is the star pointing to
nasal
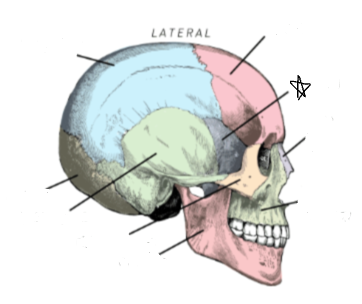
what skull bone is the star pointing to
sphenoid
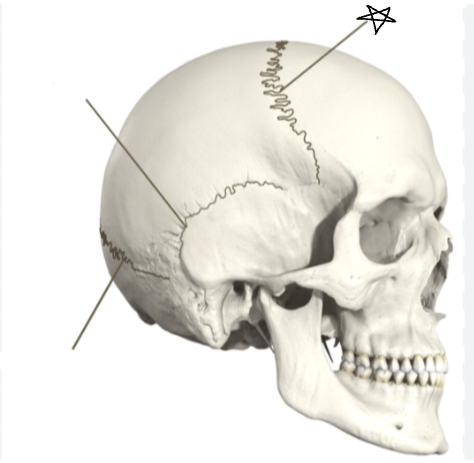
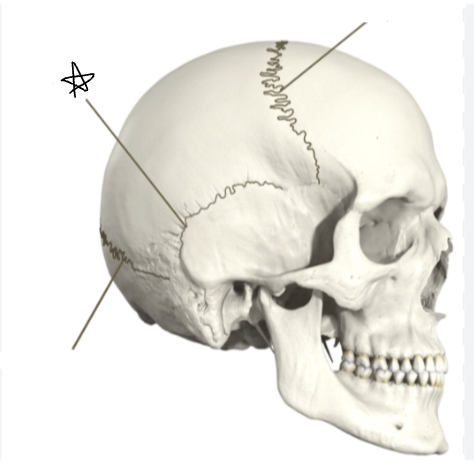
what suture is the star pointing to
coronal suture
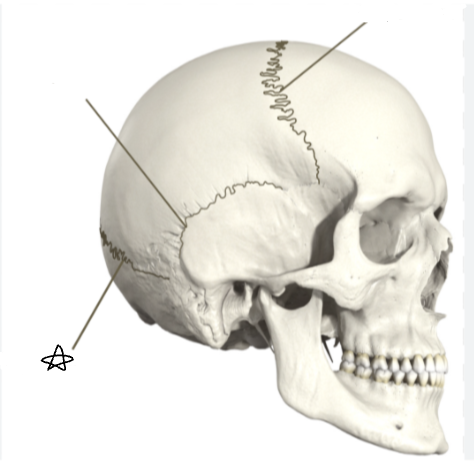
what suture is the star pointing to
squamous suture
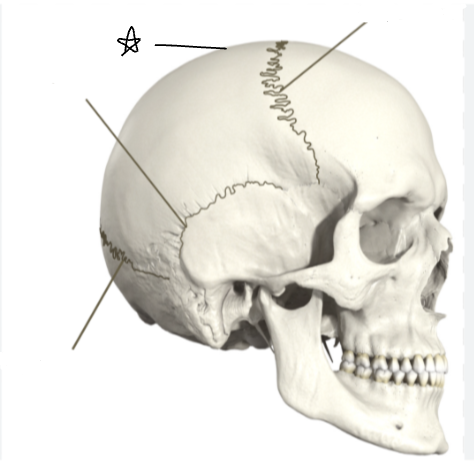
what suture is the star pointing to
lambdoidal
what suture is the star pointing to
sagittal (between parietal bones)
frontanels
soft spots of an infants skull
foramen magnum
large opening through bottom of skull, where the spinal cord enters the skull
cervical vertabrae
first 7 (C1-C7)
thoracic vertabrae
T1-T12
lumbar vertabrae
L1-L5
order of vertebrae
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
how many ribs are there
12 pairs
true ribs
first seven pairs, attached direct to sternum
false ribs
last 5 pairs after true, attached to 7th true rib
floating ribs
last two pairs
pectoral girdle
shoulder, clavicles, scapulas
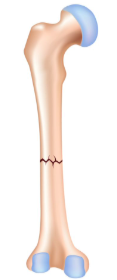
what kind of broken bone is this
closed

what kind of broken bone is this
open/compound
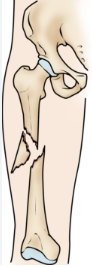
what kind of broken bone is this
multiple
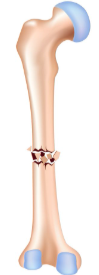
what kind of broken bone is this
comminuted
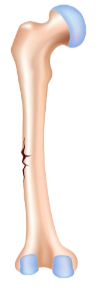
what kind of broken bone is this
greenstick
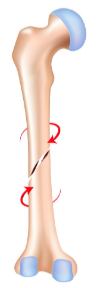
what kind of broken bone is this
spiral
weakest skull bone
temporal
which skill bone looks like a butterfly wing
sphenoid
what does the hyoid do
anchors tongue
how do you number phalanges
1-5 starting at thumb or big toe
what are the three sections of a phalange
proximal
middle
distal
where do you find red marrow
spongy bone
thumb and big toe don’t have a…
middle section
what bone looks like a hammer?
femur
tibia has a
flat top and is bigger
fibula
skinny leg bone
how many areas does a pelvis have
3
3 sections of the pelvis
illium (top part, flat)
pubic region
ischium (bottom, under holes)
foot
tarsals, metarsals
scientific term for heel
calcaneous
coccyx
tailbone
spongy bone is also called
calcaneous