12-14: Light Dependent Reactions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
Last updated 7:14 PM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1
New cards
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
* takes in carbon dioxide and water
* takes out carbohydrates and oxygen
* takes in carbon dioxide and water
* takes out carbohydrates and oxygen
2
New cards
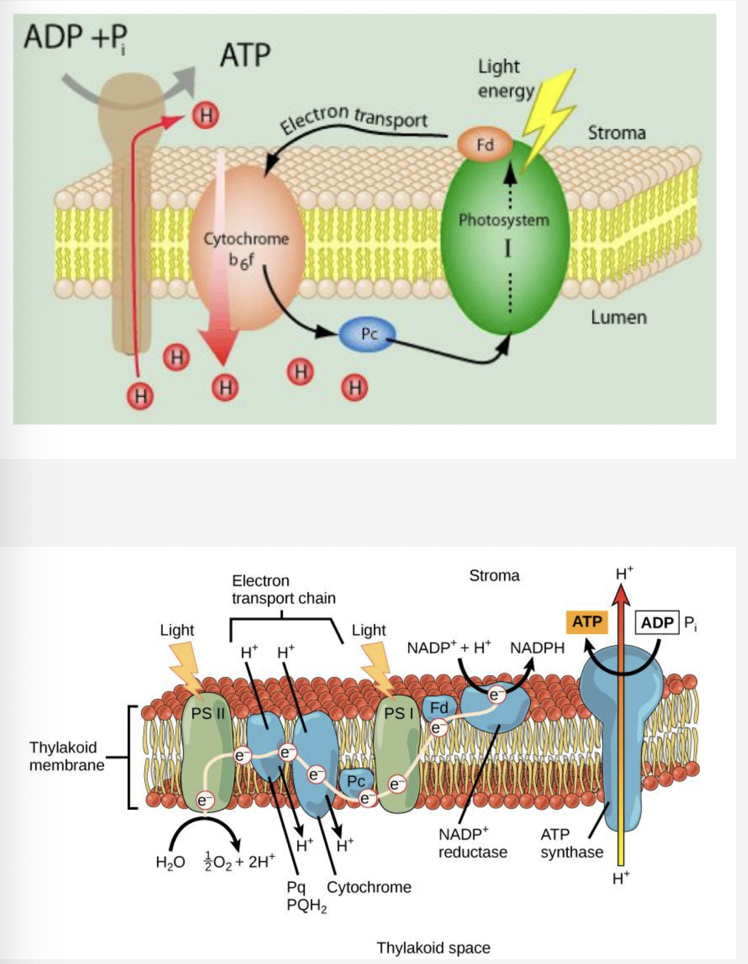
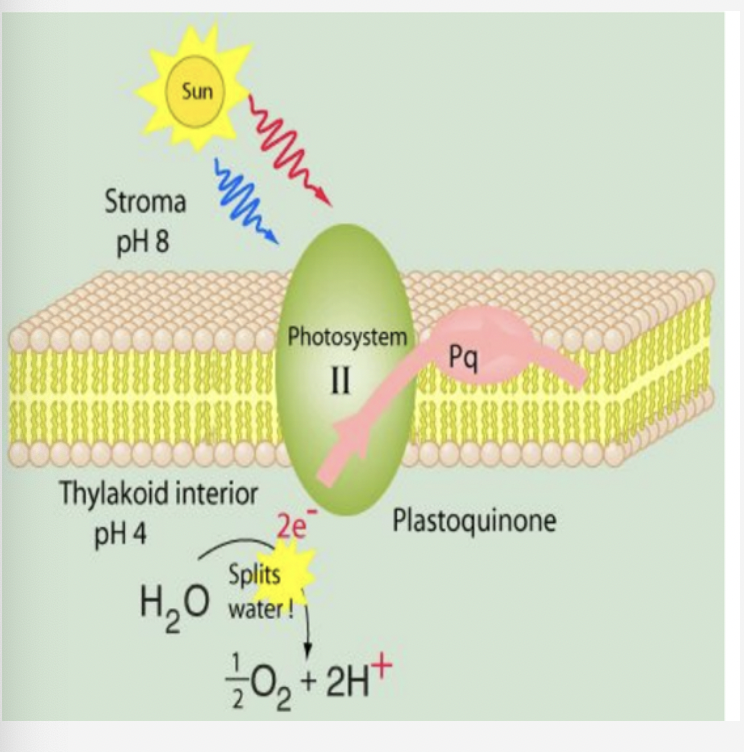
photosystem 2 & photoexcitation
* light dependent rxns
* light antenna complex absorbs a photon and transfers it to p680 chlorophyll molecule → excites an electron
* p680 loses an electron bc it gets positively charged and gets it back from water splitting
* each water molecule donates 2 electrons so that the process happens twice to produce oxygen
* acceptor molecules taking p680’s electron passes it to a molecule of PQ
* light antenna complex absorbs a photon and transfers it to p680 chlorophyll molecule → excites an electron
* p680 loses an electron bc it gets positively charged and gets it back from water splitting
* each water molecule donates 2 electrons so that the process happens twice to produce oxygen
* acceptor molecules taking p680’s electron passes it to a molecule of PQ
3
New cards
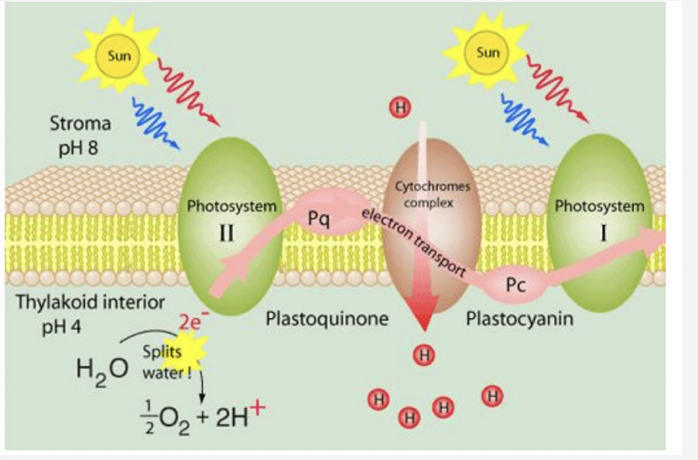
electron transport shuttles
* PQ accepts electron from PS 2 and protons from the stroma
* the electron then travels through the thylakoid membrane → donates electron to cytochrome complex
* simultaneously it releases the proton into the lumen → increases the proton complex
* cytochrome complex passes the electron to another shuttle molecule PC which carries it PS 1
* the electron then travels through the thylakoid membrane → donates electron to cytochrome complex
* simultaneously it releases the proton into the lumen → increases the proton complex
* cytochrome complex passes the electron to another shuttle molecule PC which carries it PS 1
4
New cards
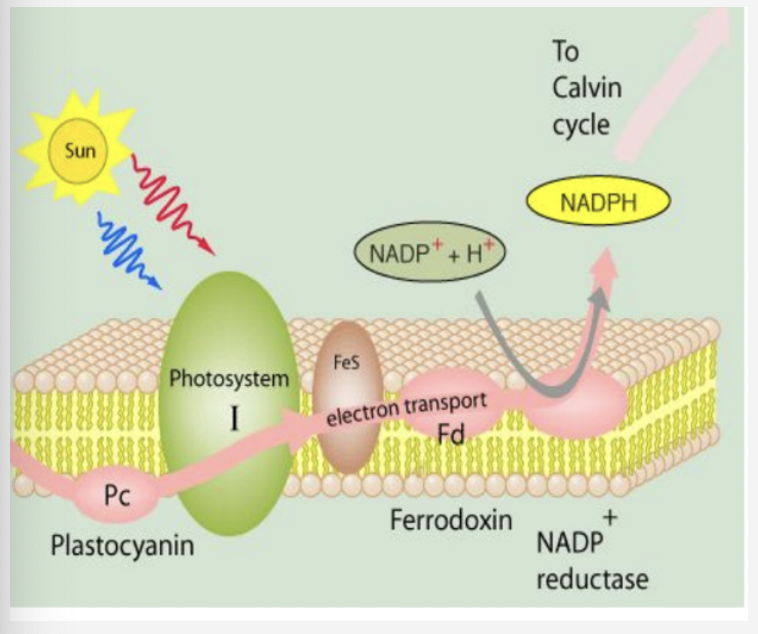
photosystem 1 and photo excitation
* electron gets re-excited
* photon strikes PS 1 and electron is excited and transferred to another acceptor
* p700 is left with a positive charge
* electron transferred from PS 2 is delivered by PQ to neutralize P700 (electron comes from water)
* photon strikes PS 1 and electron is excited and transferred to another acceptor
* p700 is left with a positive charge
* electron transferred from PS 2 is delivered by PQ to neutralize P700 (electron comes from water)
5
New cards
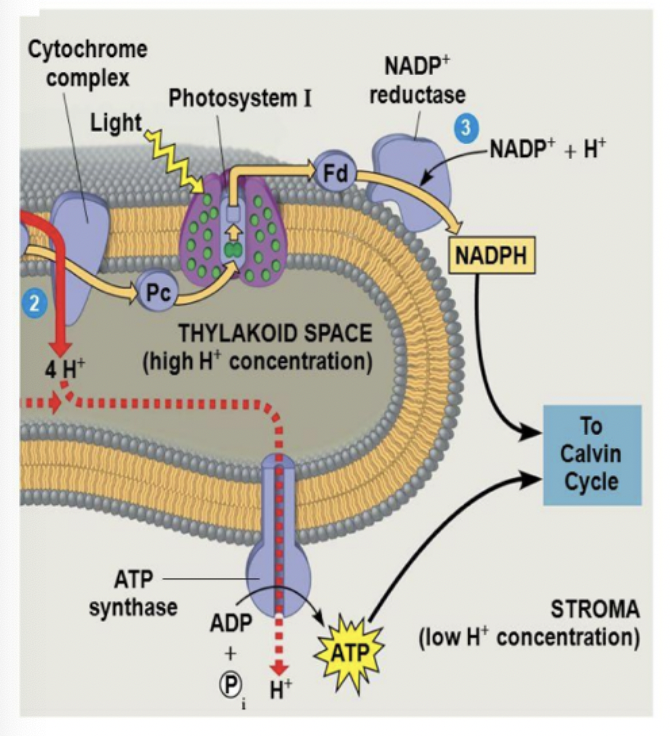
ferredoxin and NADPH
* electron from PS 1 is transferred to ferredoxin
* oxidation of ferredoxin transfers the electron to NADP+ and makes NADP
* a second ferredoxin (or the same one twice) adds another electron along w protons from the stroma to make NADPH
* all of this happens with an enzyme called NADP+ reductase
* oxidation of ferredoxin transfers the electron to NADP+ and makes NADP
* a second ferredoxin (or the same one twice) adds another electron along w protons from the stroma to make NADPH
* all of this happens with an enzyme called NADP+ reductase
6
New cards
proton gradient
* activity increases proton concentration in thylakoid lumen & decreased it in the stroma
* splitting of water
* PQ & cytochrome complex transport protons from stroma to lumen
* NADPH production removes protons form the stroma
\
This proton gradient can be used for chemiosmosis
\
* splitting of water
* PQ & cytochrome complex transport protons from stroma to lumen
* NADPH production removes protons form the stroma
\
This proton gradient can be used for chemiosmosis
\
7
New cards
ATP synthase
* produced by phosphorylation - light energy, no oxidation occurred to produce the proton gradient
8
New cards
electron energy
* the boost in energy provided by the photons in sunlight gradually decreases as the electrons move through ETCs of PS 1 and 2
9
New cards
cyclic electron transport
* PS 1 works independently of PS 2 if the electron on ferredoxin is transferred to PQ rather than NADP+ reductase
* this continuously pumps protons into the lumen → produces more ATP
* more ATP is needed more than NADPH in the Calvin cycle which makes this process very useful
* 9 ATP and 6 NADPH are needed to make 1 G3P (half of a glucose)
* this continuously pumps protons into the lumen → produces more ATP
* more ATP is needed more than NADPH in the Calvin cycle which makes this process very useful
* 9 ATP and 6 NADPH are needed to make 1 G3P (half of a glucose)