Cells
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Last updated 6:57 PM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
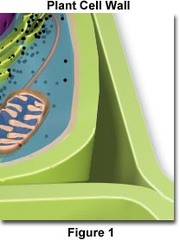
Cell wall
rigid supporting layer that surrounds the cells of plants & some other organisms
2
New cards
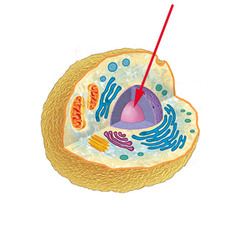
Nucleus
in cells, a large oval organelle that contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA and controls many of the cells activities - "control center"
3
New cards
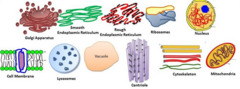
Organelle
a tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
4
New cards
Cytoplasm
the thick, jelly like fluid region of a cell that holds the organelles
5
New cards
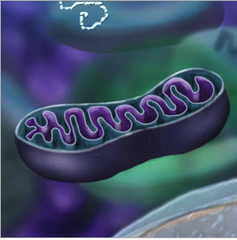
Mitochondria
rod shaped organelles that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions - the "powerhouse" of the cell
6
New cards
Vacuole
a sac like organelle that stores water, food & other materials
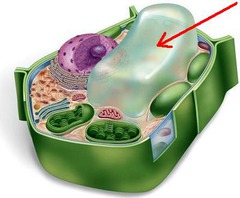
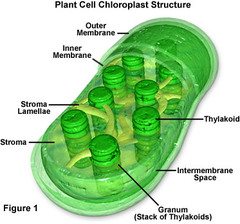
7
New cards
Chloroplast
an organelle in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and changes it to an energy form that cells can use in making food
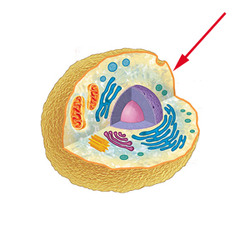
8
New cards
Cell Membrane
an organelle in both plant and animal cells that separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
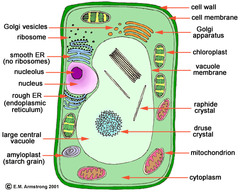
9
New cards
Plant cell
square shaped cell that contains cell wall and chloroplast and contains one large vacuole
10
New cards
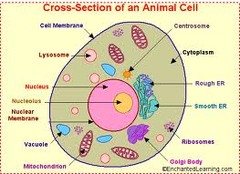
Animal cell
round shaped cell that contains a cell membrane, nucleus and small vacuoles
11
New cards
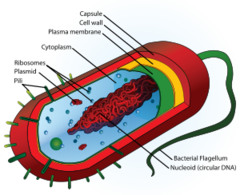
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
12
New cards
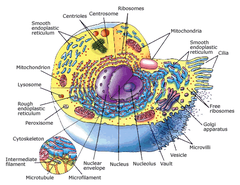
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
13
New cards
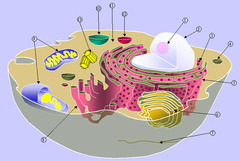
organelles
Structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell.
14
New cards
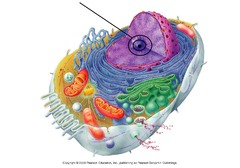
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
15
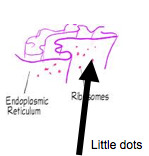
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
16
New cards
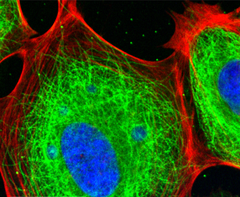
Cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement
17
New cards
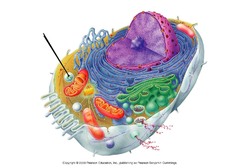
lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
18
New cards
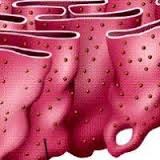
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
19
New cards
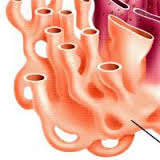
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
20
New cards
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell; internal distribution center.

21
New cards
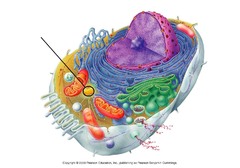
centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
22
New cards
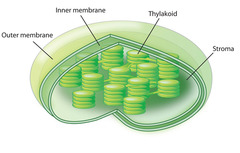
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
23
New cards
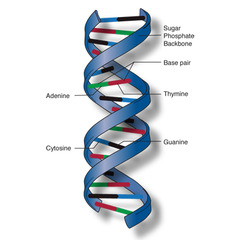
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
24
New cards
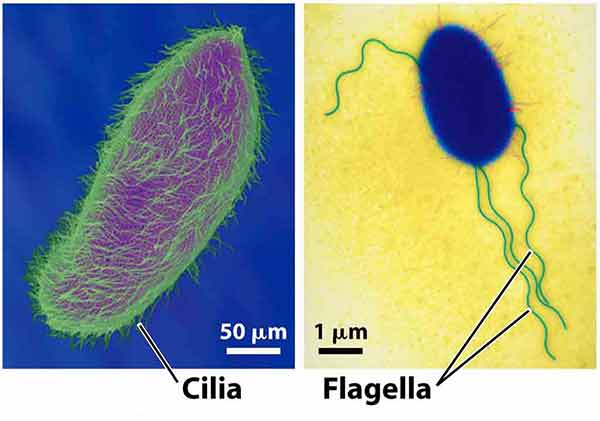
Cilia/Flagella
Cilia are short, hair like appendages extending from the surface of a living cell. Flagella are long, threadlike appendages on the surface of a living cell
25
New cards
What are the 3 parts of the cell theory?
-All living things are composed of cells.
-Cells are the basic units of structure and function for living things.
-All cells come from pre-existing cells. Also, organisms grow by “adding on more cells” NOT by increasing the size of their cells.
-Cells are the basic units of structure and function for living things.
-All cells come from pre-existing cells. Also, organisms grow by “adding on more cells” NOT by increasing the size of their cells.
26
New cards
Differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes have a nucleus,endoplasmic reticulum, and a mitochondria while prokaryotes only have a cell membrane, cell wall, free floating DNA and ribosomes and no nucleus.
27
New cards
Examples of prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
28
New cards
Examples of Eukaryotes
plants and animals
29
New cards
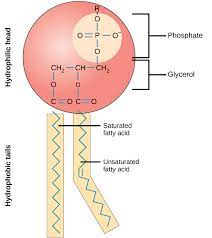
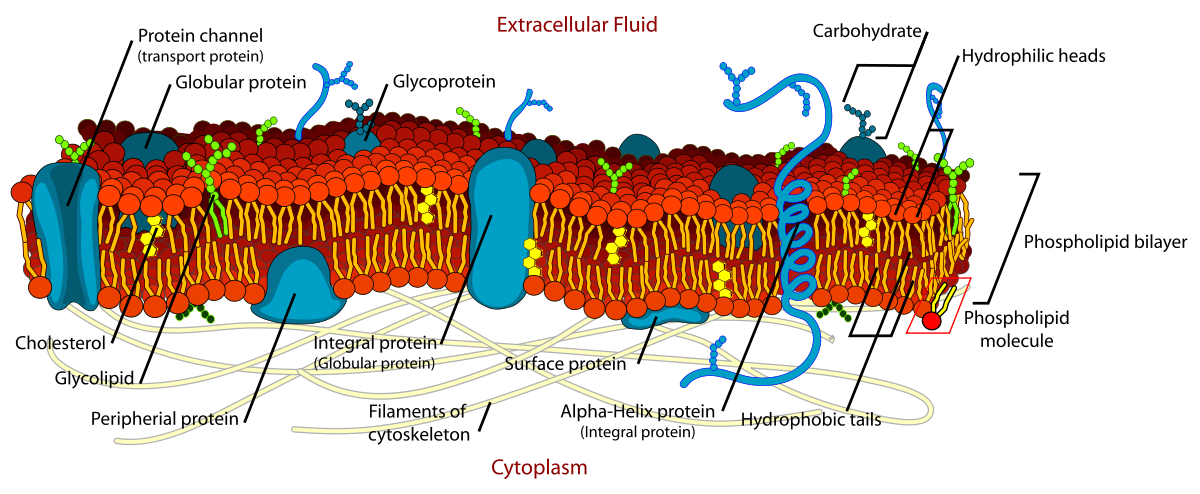
phospholipids
Lipid that goes across the cell membrane. Fatty acid tail is hydrophobic and head is hydrophilic. They form a bilayer with the hydrophobic parts pointing away from the water.
30
New cards
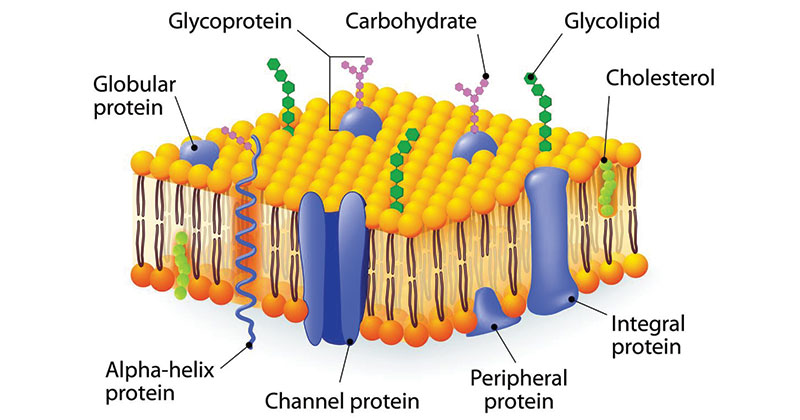
carbohydrate chains
keeps membrane fluid; keeps hydrophobic tails from sticking together.
31
New cards
protein channels
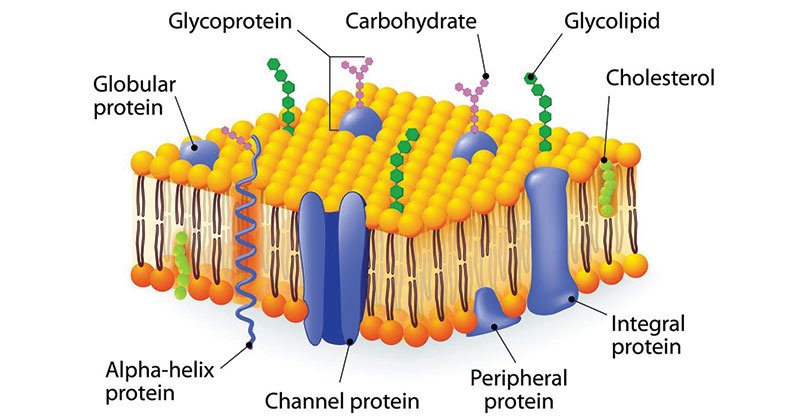
transport and attachment
32
New cards
cholesterol
at high temperatures, cholesterol acts to stabilize the cell membrane and increase its melting point; while at low temperatures, it inserts into phospholipids and prevents them from interfering with each other to avoid aggregation or just maintain fluidity.
33
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
The arrangement of molecules that make up a cell membrane. Proteins "float" scattered in the phospholipids.
34
New cards
Selective Permeability
Allows only certain substances to cross. No polar or charged particles can cross phospholipid bilayer
35
New cards
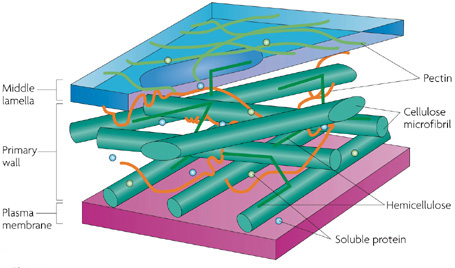
Structure and Function of Cell Wall
This surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress. It also allows cells to develop turgor pressure, which is the pressure of the cell contents against it.
36
New cards
Simple Diffusion
moving directly across the membrane
37
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water, passive transport and moving from high water concentration to low water concatenation and moving to higher solute concentration.
38
New cards
equilibrium
molecules continue to move across membrane with no NET change in concentration. Can be used to show the difference between osmosis and simple diffusion.
39
New cards
gradient
a difference in concentration between slides of a membrane.
40
New cards
Hypotonic
having fewer solutes (more water)
41
New cards
Hypertonic
having more solutes (less water)
42
New cards
isotonic
having equal solutes
43
New cards
Unicellular organism
an organism that consists of a single cell. Examples of this are bacteria or paramecium.
44
New cards
Multicellular Organism
an organism that consists of many cells. Examples of this are animals and humans
45
New cards
Explain the purpose of cell specialization in multicellular organisms and how this can help the organism to survive.
this allows organisms to have special cells that can work together to do a certain job. For examples nerve cells send and receive impulses which help organisms maintain homeostasis . Examples include nerve cells, RBC's, skin cells
46
New cards
Differentiate the four levels of organization in multicellular organisms.
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism itself.
47
New cards
What happens in an animal and plant cell when it is hypertonic and hypotonic?
In an animal cell if the cell is placed in distilled water or hypotonic solution the cells swell and burst. When the substance in an animal cell is hypertonic the cell shrivels and shrinks. In a plant cell when a hypotonic substance goes through the cell then the cell stiffens and generally retains shape. When a hypertonic substance goes into a plant cell, the cell body shrinks and pulls away from the cell wall.
48
New cards
plasmolyzed
is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution
49
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
moving through a transport protein (door)
50
New cards
Active transport
movement of materials across a membrane that requires energy.Uses ATP energy
51
New cards
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across the cell membrane that does not require energy.
52
New cards
Exocytosis
movement out of the cell
53
New cards
endocytosis
movement into the cell
54
New cards
Phagocytosis
Solid particles (cell eating)
55
New cards
Pinocytosis
liquid particles (cell drinking)