THE MULTI-STORE MEMORY MODEL
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
who developed the multi-store memory model
attkinson and shiffrin in 1968
what does the MSMM describe
how information flows through the memory system by processing
how many memory stores does it suggest exist
3
what are the 3 stores called
the sensory register or SR
the short term memory store or STM
the long term memory store or LTM
describe the MSMM
environmental stimuli enters the sensory register from the surroundings
it goes into one of multiple registers depending on what sense it was picked up by
if attention is paid it moves to the short term sensory register
if its rehearsed it will stay in the STM longer
if its encoded it moves to the LTM
if none of these happen it leaves the STM and is forgotten
if it moves to the LTM it will stay here
it can be brought back into the STM by retrieval
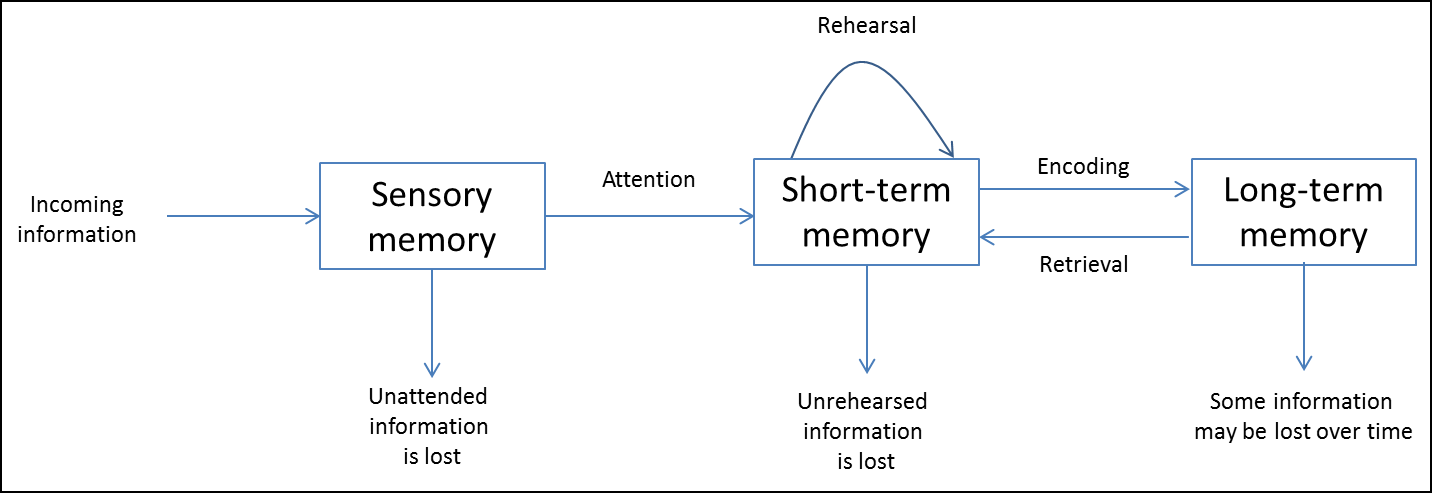
what happens in the sensory register
all stimuli from the environment moves to the SR
how many stores are there in the sensory register
there is one for each sense so the different types of information are processed separately
how is information coded in each store
information in each store is coded in a modality-specific way
what does modality-specific mean
it means all of the information is encoded separately but exactly how it is so a memory of a whole object or situation can be made
what is the duration of the sensory register
it is very small and lasts about half a second
what is the capacity of the sensory register
the capcity of the register is very high as there are millions of cells that can take in many pieces of information
how does information move from the sensory register to the short term memory store
information moves to the STM if attention is paid to it
how is information in the STM coded
information is encoded acoustically
what does it mean if information is encoded acoustically
it means information is coded in terms of how it sounds
what is the duration for information in the STM without being rehearsed
about 18 seconds
what is the capacity of the STM like
it has a limited capacity of 7 ± 2
what is maintenance rehearsal
it occurs when we repeat information to ourselves over and over again
it will stay in the STM for as long as we rehearse it
what happens to information in the STM if it is rehearsed for long enough
it moves into the LTM to be encoded long term
what is the duration of the LTM like
the duration of the LTM is potentially unlimited
how is information coded in the LTM store
information is coded semantically
what is the capacity of the LTM
the capacity is thought to be potentially unlimited
what type of information is stored in the LTM
it holds information that has been rehearsed for a prolonged period of time
what process is used to transfer LTM information back to the STM
the process is called retrieval
how do studies support the idea that the STM and LTM are separate stores
the MSMM supports other studies showing the STM + LTM to be separate stores
for example baddeley found we tend to mix up words that sound similar when using our STM and words that have similar meanings when using our LTM
other studies by jacobs, miller and peterson+peterson also give further support as they show the two stores code different amounts of information, in different, ways for different periods of time
these studies clearly show the STM and LTM are separate stores as the MSMM claims
what evidence is their for more than one STM store
studies such as the one done by shillin and warrington on one of their clients KF who had amnesia
they found his memory for digits read to him was very poor but when he read the digits himself his recall was much better
further studies on KF and others showed their could be another STM store for non verbal sounds
this suggests the MSMM is wrong in suggesting the STM is one store that processes all types of information
why does the MSMM not fully explain how long term storage happens
prolonged rehearsal is not needed to transfer information into the LTM
according to the MSMM the amount of rehearsal is suggested to be the most important in transferring information into the LTM
but craik and watkins found the type of rehearsal is more important than the amount and that elaborative rehearsal is needed for long term storage
this occurs when you link to information to existing knowledge or think about what it means
this means that information can be transferred to the LTM without prolonged rehearsal
this suggests the MSMM doesnt fully explain how long term storage is achieved