Ocular Anatomy
1/471
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
472 Terms
All of the following muscles DEPRESS the eyebrow EXCEPT:
What are the two glands found in the tarsal plate?
- Meibomian glands
- Gland of Wolfring
Where is the main lacrimal gland located?
fossa of frontal bone
Where are the accessory lacrimal glands located?
in the conjunctival stroma
Where are goblet cells located?
conjunctival epithelium
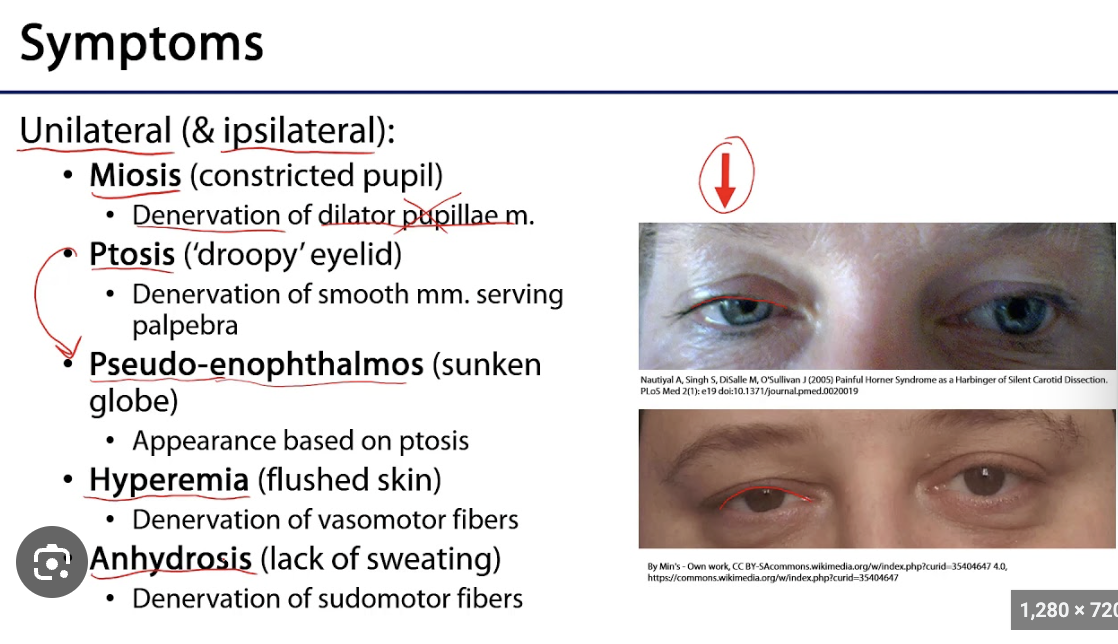
Horner's Syndrome
- Ptosis (from Muller's muscle, small, 2-3mm)
- Miosis
- Anhidrosis
--> Lack of sympathetic nervous system innervation
What muscle flares the nostrils?
--> Procerus
**Procerus = anything to do with nose
Major symptom of a nasolacrimal duct obstruction?
Unilateral epiphora
#1 cause of a nasolacrimal duct obstruction in a CHILD?
Valve of Hasner issue
#1 cause of a nasolacrimal duct obstruction in an ADULT?
Involutional stenosis (Age-related stenosis)
- Nasolacrimal duct narrows with age
- Next cause could be maxillary sinus infection (not as common)
Where does the lateral lymphatics drain?
preauricular lymph nodes
Where does the medial lymphatics drain?
submandibular lymph nodes
Major cause of Dacryocystitis? (infection of lacriminal sac)
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO)
Major cause of Dacryoadenitis? (infection of lacriminal gland)
Staphylococcus
Systemic disease that is the #1 cause of Dacryoadenitis?
Sarcoid (causes inflammation)
What cranial nerve carries parasympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland for lacrimination?
CN VII (vidian nerve-facial)
What muscle compensates for a ptosis?
Frontalis- tries to raise eye brow to open eye
What sinus surrounds the nasolacrimal duct?
Maxillary sinus
The muscle of Muller is derived from...
Levator
What bones make up the lateral wall of the orbit?
Greater wing of sphenoid bone + Zygomatic bone
"greater Z"
What bones make up the roof of the orbit?
Lesser wing of sphenoid bone + Frontal bone
"front less"
How many bones of the skull articulate to form the orbit?
7 bones
- Frontal
- Lacrimal
- Ethmoid
- Zygomatic
- Maxillary
- Palatine
- Sphenoid
3 things off the Lesser wing of sphenoid bone?
1) Levator (muscle of Muller)
2) Superior Oblique (EOM)
3) Optic nerve
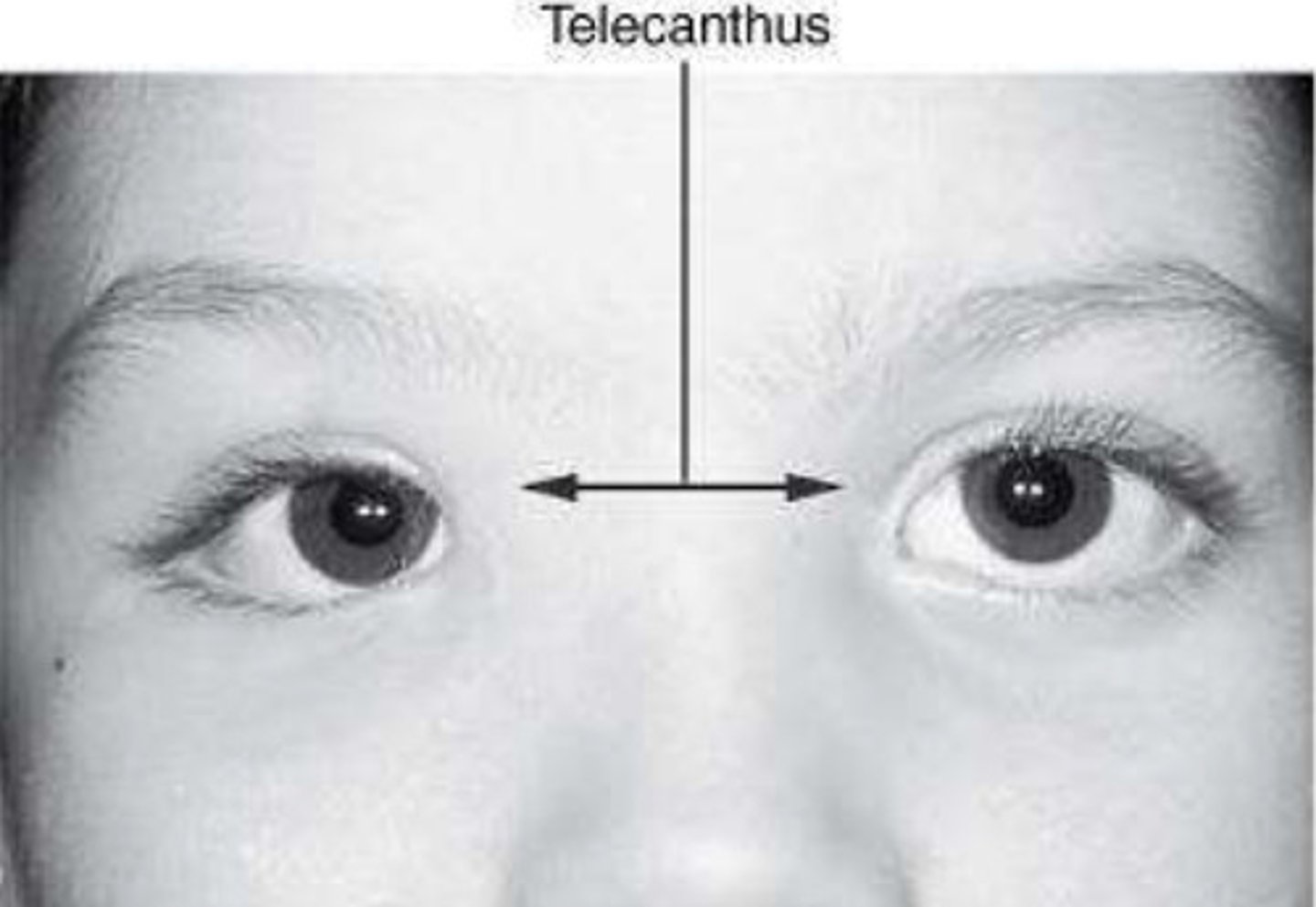
Telecanthus
Abnormally increased distance between the medial canthi of the eyelids
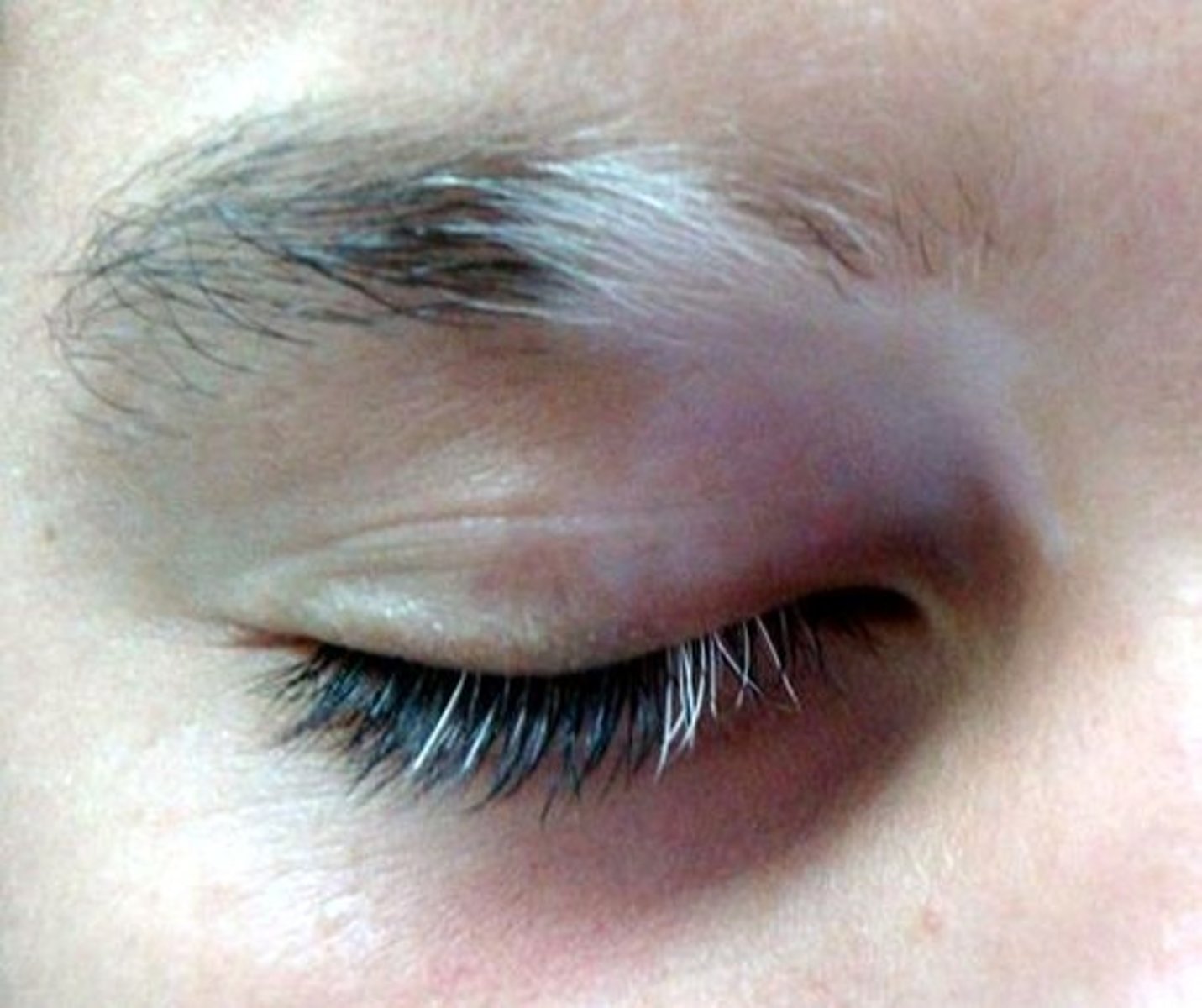
Poliosis
Whitening of eyelashes
Madarosis
Loss of eyelashes
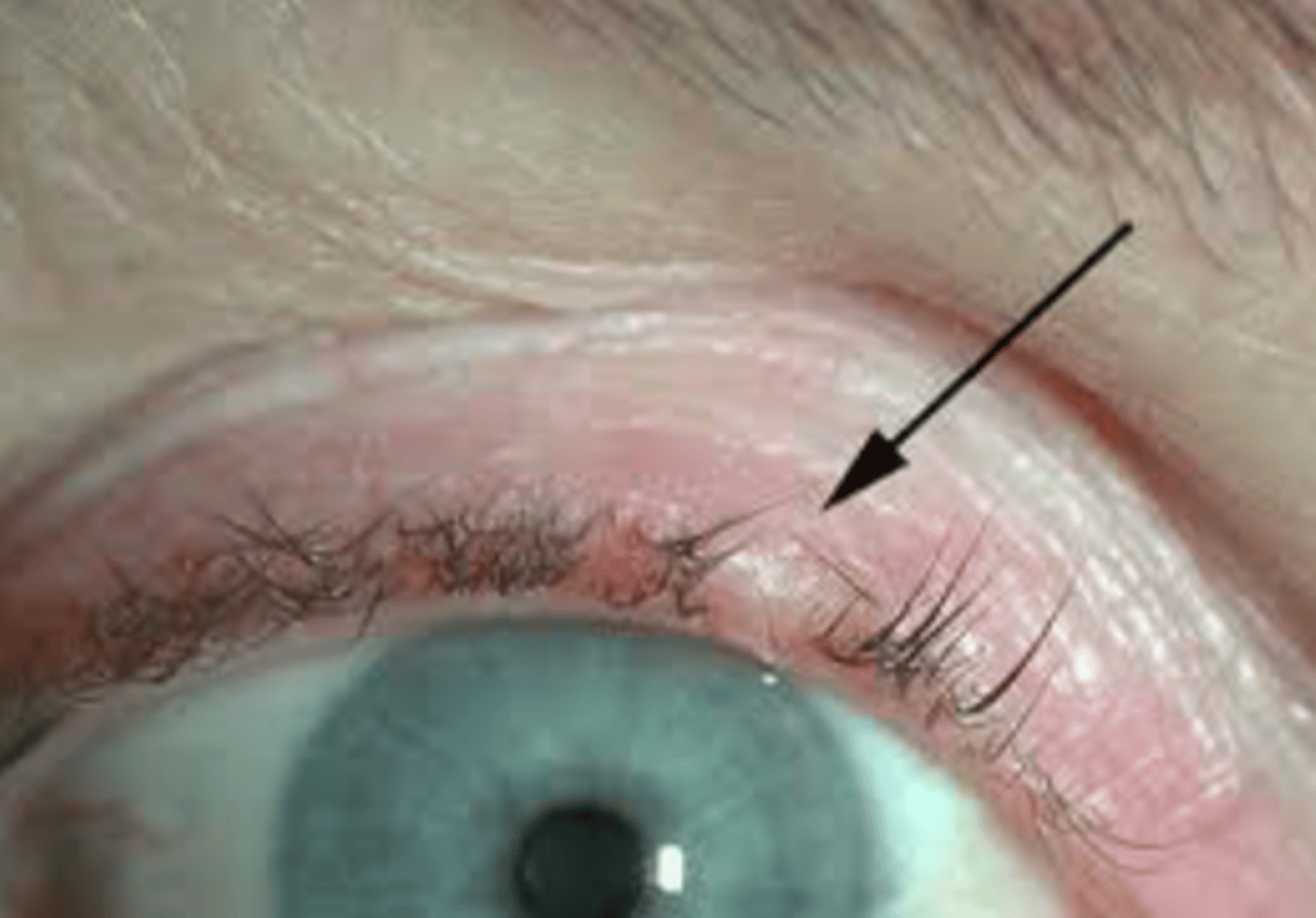
Trichiasis
Turning inward of eyelashes
- often secondary to ectropion
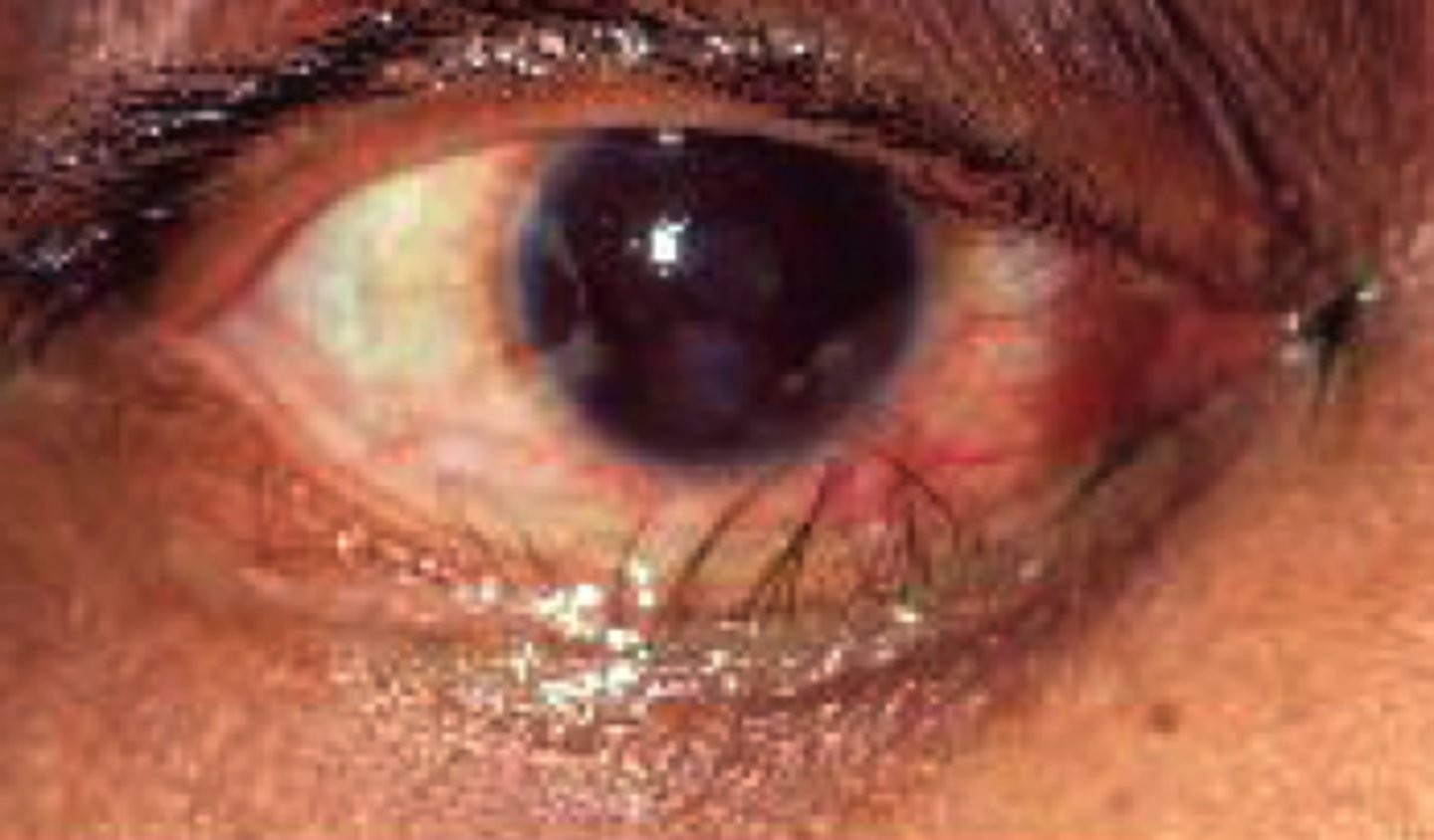
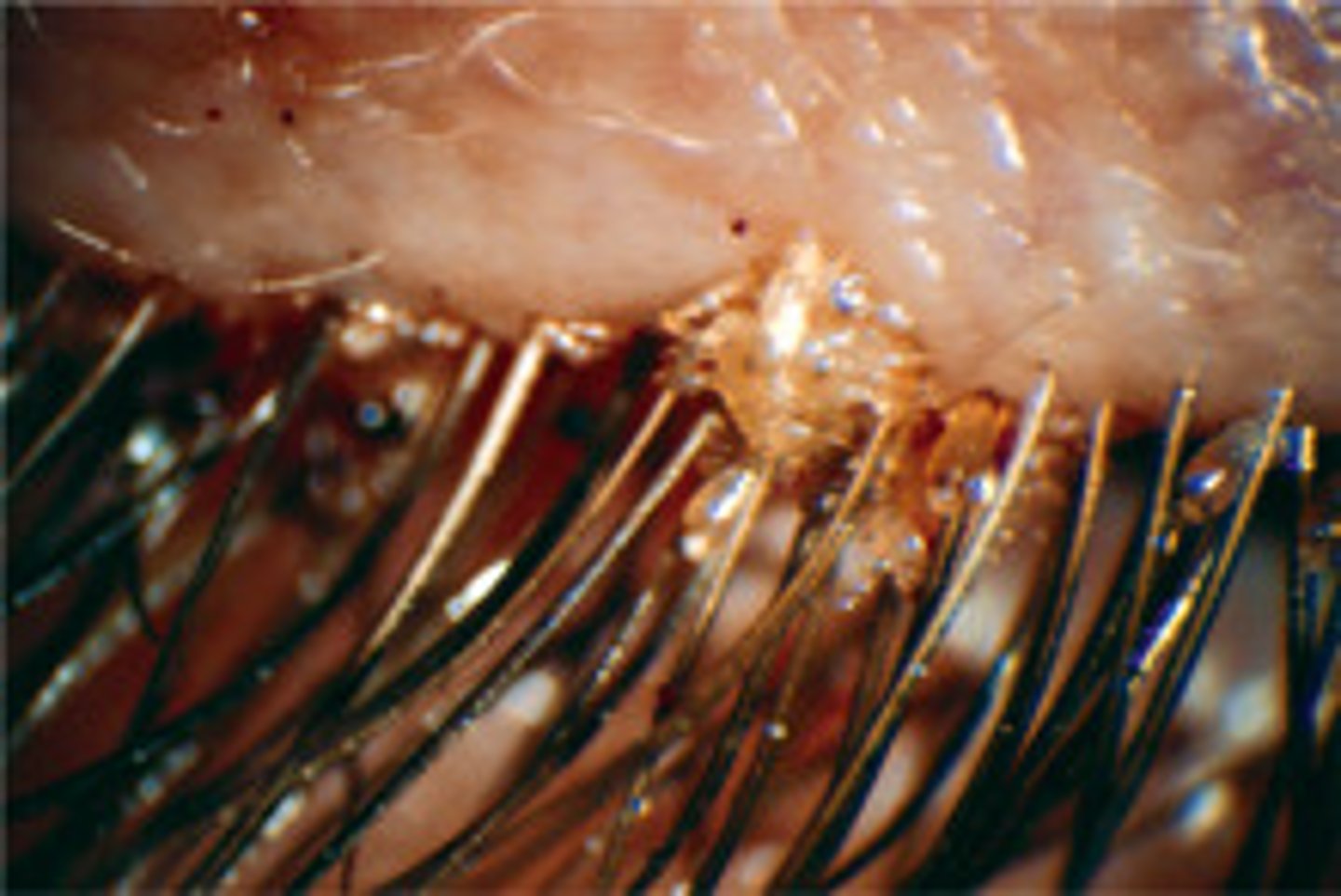
Phthiriasis palpebrarum
Infection of eyelashes caused by Phthirus pubis
What is the thinnest skin layer in the body?
The skin layer of eyelid
- Contains: fine hairs, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, NO fats
Subcutaneous areolar layer
Thin layer of loose connective tissue that lies between the outer skin the underlying orbicularis
- Upper lid subcutaneous areolar layer: contains levator
Submuscular Areolar Layer
Thin layer of loose connective tissue that lies between the orbicularis and orbital septum
- Upper lid submuscular areolar layer: contains levator and palpebral potion of main lacrimal gland
Orbicularis layer
Contains the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi, one of the muscles of facial expression innerved by CN VII
Orbital septum
Dense irregular connective tissue that serves as a barrier to the orbit in the upper and lower eyelids
- Orbital septum prevents fat from falling down onto the lid margins and keeps infections localized to the anterior portion of the eyelid away from the orbit
- Does NOT protect the lacrimal sac from infection
Periorbita = loosely covers the orbital bones. Projects anteriorly to become orbital septum and posteriorly to fuse with the dura of the optic nerve
Orbital septum continuous with periorbita and periosteum of the skull. Attaches medially to the posterior lacrimal crest.
Superior orbital septum serves as insertion site for the levator
What EOM inserts the closest to the limbus?
Medial rectus (clockwise)
What EOM inserts the furthest from the limbus?
Superior rectus
What VF defect does a pituitary gland tumor cause?
Bilateral hemianopsia
What are the 3 holes of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone?
1) foramen ovale (V3)
2) foramen spinosum (middle meningeal artery)
3) foramen rotundum (V2)
What nerve passes through the foramen rotundum?
V2 (maxillary division)
What nerve passes through the foramen ovale?
V3 (mandibular division)
What nerve passes through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
Posterior muscular system
Consists of the superior levator palpebrae muscle and the superior (i.e. Muller's muscle) and inferior tarsal muscles
superior palpebral levator muscle
origin? does what? innervation?
- Originates from the lesser wing of the sphenoid at the orbital apex
- Main retractor of the upper eyelid
- Innervated by CN III
- Whitnall's ligament = superior transverse ligament on the zygomatic bone, serves as a fulcrum that changes the course of the muscle from anterior-posterior to superior-inferior
Eyelid furrows
Superior palpebral furrow = formed by the insertion of the levator aponeurosis into the skin of the upper lid
Inferior palpebral furrow = formed by the indirect attachment of the inferior rectus muscle into the skin of the lower eyelid
--> Eyelid furrows separate the tarsal and orbital potions of the eyelid
Tarsal plate
Dense irregular connective tissue that provide rigidity to the eyelids. Composed of horizontal and vertical collagen fibrils that surround the meibomian glands
Palpebral conjunctiva
Inner lining of the eyelids that contains 2 layers:
1) Epithelial layer
- Stratified outer protective layer that extends into the fornices and onto the bulbar conjunctiva
- Contains goblet cells that produce the mucin layer of the tear film
2) Stroma
- Loose vascularized CT composed of a superficial lymphoid layer and a deep fibrous layer
- Superficial lymphoid layer = very immunologically active layer, contains IgA, macrophages, mast calls, PNMs, eosinophils
- Deep fibrous layer = connects the conjunctiva to the underlying internal structures, contains the accessory lacrimal glands, nerves, BVs of the eyelids
Where are goblet cells?
- Caruncle
- Inferior nasal fornices
- Temporal bulbar conjunctiva
**none in the limbus
Iris sphincter vs. Iris dilator
Iris sphincter:
- Located in pupillary zone in iris stroma
- M3 receptors
Iris dilator:
- pupillary + ciliary zone
- alpha-1 receptors
- Located in anterior epithelium
Which layer of the eyelid contains goblet cells?
Palpebral conjunctiva (immunologically active, also has IgA antibodies)
What is another name for the ethmoid bone in the medial wall of the orbit?
Lacrimal papyracea
Which orbital wall does not utilize the sphenoid bone?
Floor
Obliques are main depressors/elevators...
51-55 deg ADducted (towards nose)
Rectii are main depressors/elevators...
23 deg ABducted (towards ears)
EOM attachments
- Obliques always attach BEHIND equator
- Rectii always attach IN FRONT of equator
What EOM has a different anatomical and physiological origin?
superior oblique
- Anatomical origin: lesser wing of sphenoid bone, CTR
- Physiological origin: trochlea
Which EOM would not be affected with a tumor located on the Annulus of Zinn?
Inferior oblique
What are the 2 types of sinuses within the cranium?
- Paranasal sinus (filled with air)
- Cavernous sinus (filled with venous blood)
3 branches of the Aortic arch?
"ABCS"
1) Brachiocephalic artery (right side)
- Breaks into ICA
2) Common carotid artery (left side)
3) Subclavian artery (left side)
Brachiocephalic artery
- Breaks into the 2 Vertebral arteries and the Internal carotid artery (ICA)
- ICA breaks into 4 branches
What are the branches of the Internal carotid artery (ICA)?
"OPAM" - 4 branches
1) Ophthalmic artery (7 branches, "CL MS LSE")
2) Posterior communicating artery (PCA)
3) Anterior cerebral artery
4) Middle cerebral artery
Ophthalmic artery
Branch off the ICA that goes directly to the eye
"CL MS LSE" - 7 branches
1) Central retinal artery (CRA)
2) Lacrimal artery
3) Muscular artery
4) Short posterior ciliary arteries (SPCAs)
5) Long posterior ciliary arteries (LPCAs)
6) Supraorbital artery
7) Ethmoidal artery
Circle of Willis
Junction between ICA and PCA
Includes:
- All branches of ICA ("OPAM")
- Pontine arteries
- Vertebral artery and branches
What arteries form the Circle of Willis?
- Posterior cerebral arteries
- Posterior and anterior communicating arteries
- Anterior cerebral arteries
- Basilar artery forms the BASE of the circle of willis
What arteries supply the choroid?
SPCAs and LPCAs
SPCAs = posterior choroid
LPCAs = anterior choroid
What supplies the inner retina (ILM to OPL)?
Central retinal artery
SPCAs vs. LPCAs
SPCAs:
- Supplies posterior choroid
- Supplies the optic disc (Circle of Zinn)
LPCAs:
- Supplies anterior choroid
- Supplies MACI = major arterial circle of iris
Layers of the Retina
1) ILM
2) NFL
3) GCL
4) IPL
5) INL
6) OPL
7) ONL
8) ELM
9) PhR layer
10) RPE
Inner Retina (which layers)
ILM to OPL
Outer Retina (which layers)
OPL to RPE
SPCAs supplies...
- Posterior choroid
- Circle of Zinn (optic disc)
LPCAs supplies...
- Anterior choroid
- MACI = major arterial circle of iris
MACI
MACI = major arterial circle of iris
- Fenestrated
- Has non-pigmented ciliary epithelium (NPCE) and Beta-2 receptors
- Beta-2 receptor allows Na+ and Bicarbonate to pass in
Made up by:
- Anterior ciliary arteries (ACA)
- Long posterior ciliary arteries (LPCA)
Circle of Zinn
Supplies the optic disc
#1 way to produce aqueous humor?
Active transport
Cavernous sinus blood supply that runs through
Blood supply:
- SOV = superior ophthalmic vein
- IOV = superior ophthalmic vein
- Cavernous sinus drains into the sigmoid sinus
- Sigmoid sinus becomes the internal jugular vein
- Superficial cortical veins
Eye --> vortex veins --> --SOV and IOV--> Cav. sinus --> Sigmoid sinus --becomes--> Internal jugular vein --> Heart
Signs of trauma to the cavernous sinus?
- Pulsatile proptosis
- Chemosis of conjunctiva
Ex: carotid cavernous fistula (CCF)
What cranial nerves pass through the cavernous sinus?
CN 3, 4, V1, V2, 6 + Internal Carotid Artery
O TOM CAT
Oculomotor nerve (CN III), Trochlear nerve (CN IV), Ophthalmic nerve (CN V1), Maxillary nerve (CN V2), and Abducens nerve (CN VI)
What nerves go through the common tendinous ring?
"NOA"
Nasociliary nerve (V1)
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Foramens and openings in the orbits

What CN innervates what EOM? 4, 6, 3
SO4
LR6
3
What EOMs are innervated by the superior division of CN III?
- Superior rectus
- LPS
What EOMs are innervated by the inferior division of CN III?
- Inferior rectus
- Medial rectus
- Inferior oblique
Pathway of CN III
→ Brainstem
→ cavernous sinus
→ superior orbital fissure
→ Over/Under/Through common tendinous ring
Superior orbital fissure (SOF)
hole between the greater and lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
What foramen is located inside the common tendinous ring (CTR)?
optic foramen
- part of lesser wing of sphenoid
- where optic nerve comes through
Where do the oblique muscles attach?
BEHIND equator
Where do the rectii muscles attach?
in FRONT of the equator
What nerves travel through the superior orbital fissure?
CN 3, 4, 6, V1
(not V2)
What bones make up the floor of the orbit?
"My Pal gets his Z's on the floor"
Maxillary (majority)
Palatine
Zygomatic
What nerve runs below the eye along the floor of the obit that provides sensory innervation below eye?
V2 (inferior rectus)
Tolosa-Hunt syndrome
Inflammation of the SOF and/or cavernous sinus that often affects CN III, IV, V, VI
Signs: painful external ophthalmoplegia, diplopia
What is the main refracting element of the eye?
air/tear film interface
(contributes 44D to the refractive power of cornea)
What is the only miotic layer in the corneal epithelium?
basal layer
Fuchs' Dystrophy
- Corneal endothelium problem, endothelium makes too much Descemet and Descemet's membrane is very thick
Hemidesmosomes
- Connects basal cells of corneal epithelium to basal lamina of basement membrane
- Connects reticular lamina of basement membrane to Bowman's layer
**Hemi always connects something to basement membrane!
What 3 risk factors increase the risk of RCEs?
1) Poor hemidesmosomes attachments
2) Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy
3) Age-related thickening of the BM
What is the water content of the corneal stroma?
78% (detergescence)
What type of collagen is found in the corneal stroma?
Type 1 collagen
What type of collagen is found in Bowman's layer of the cornea?
Type 1 collagen
What type of collagen is found in the Decesmet's membrane of cornea?
Type 4 collagen
What part of the body has type 1 collagen?
"Bones, Bowmans, sclera, stroma"