Chap 9: Kingdom Monera- Amoeba
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Amoeba
Consists of 1 cell, consumer/heterotroph, found in freshwater environments, shape is irregular and is determined by the cytoplasmic flow of the pseudopods
Movement of amoeba
Moves by means of pseudopods (false feet) caused by cytoplasmic flow, i.e. movement of the ectoplasm followed by the endoplasm, typically towards a food source.
Two parts of the cytoplasm
Ectoplasm (closest to membrane, and stiff/viscous), and Endoplasm (watery)
Use of pseudopods for feeding
Pseudopods move towards its food and engulfs it by means of phagocytosis. Prey is drawn into the endoplasm and stored in a small food vacuole. Any waste products are sent out to the endoplasm.
Storage of water in amoeba
Water is stored in a large contractile vacuole in the endoplasm. Water moves into this vacuole by means of osmosis, especially when solute concentration is high in the amoeba.
Osmoregulation in the amoeba
When full, the contractile vacuole moves to the edge of the amoeba (i.e. ectoplasm). The contractile vacuole will then burst and expel the water.
Osmoregulation brief definition
The balance/control of water and solute concentrations within an organism.
Why is osmoregulation necessary in amoeba
Lives in a water environment and has a higher concentration of solutes within its membrane.
Amoeba reproduction
Amoeba reproduces by means of “binary fission”, whereby the cell nucleus splits and the whole cell enlarges and divides.
Amoeboid disease
An intestinal/bowel illness caused by a microscopic parasite spread through human faeces. Contracted by drinking contaminated water. Can be asymptomatic, or can cause diarrhoea, nausea, and weight loss.
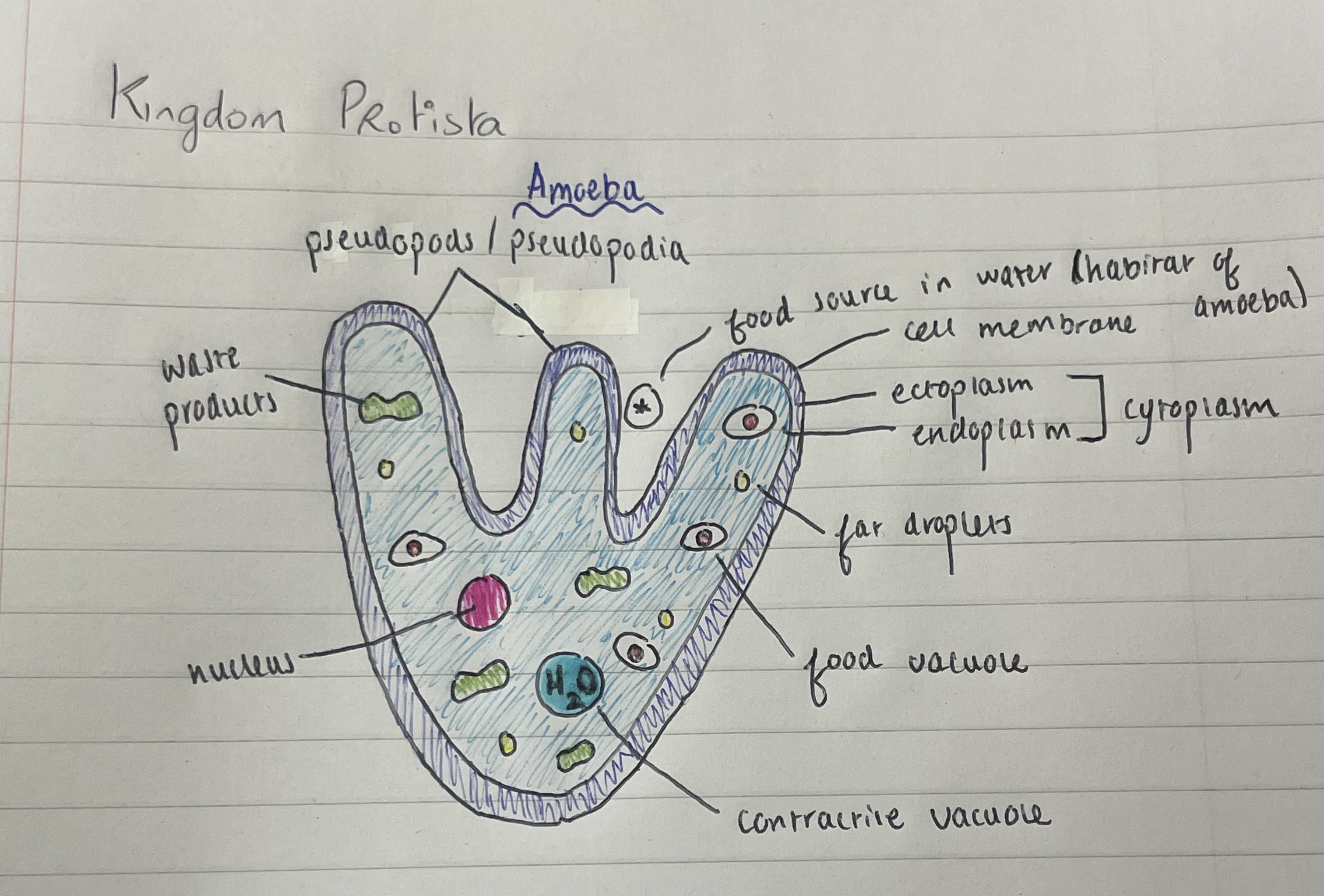
Diagram of Amoeba