bakit ang pogi ni James REID? Systematics GBIO2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Characterisation
The organisms to be studied is described for all its morphological and other characteristics
Identification
It is the finding of correct name and place of an organism in a system of classification. It is done with the help of keys. This is carried out by determining similarities with already known organisms
Nomenclature
It is the science of providing distinct and proper names to organisms so that they can be easily recognized and differentiated from others.
Classification
It is the placing of an organism or a group of organisms in categories according to a particular system which is based on certain easily observable but fundamental characters and in conformity with a nomenclature system. A hierarchy is maintained for these categories.
Types of Classification
Binomial Nomenclature
two part name (genus, species)
Hierarchal Classification
Seven (8) Taxonomic Categories
Systematics
Study of the evolution of biological diversity
Levels of taxonomic classification
is also called Linnean hierarchy or taxonomical hierarchy. It is the classification of organism in a definite sequence of categories in a definite sequence of categories from domain to species or from species to domain. There are eight categories:
Eight Categories of Taxonomic Classification
Domain - Eukarya
Kingdom - Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Canidae
Genus - Vulpes
Species - Vulpes vulpes
Shortcut for the EIGHT CATEGORIES
DKPCOFGS or Dear King Philip Came Over for Good Spaghetti
Archaea
one-celled organisms with membranes composed of branched hydrocarbon chains
Bacteria
one celled organisms that have a substance called peptidoglycan that form their cell wall
Eukarya
one or multi-celled organisms with their genetic material organized in a nucleus
Kingdoms
are levels which are broken down from the domains. There are six [answer] which include Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, and Protista
PHYLUM
is the next level in the classification system and is used to group living organisms together based on some common features; “chordates,” and it refers to all animals with a spinal column. As humans, we are also part of the chordate [answer] . Like the Kingdom Plantae, [answer] is broken down into divisions:
CLASS
The class level is another way to group together organisms that are alike, but it becomes even more specific than phylum. There are more than 100 [answer]; includes the Mammalia, Aves, Reptilia in animals or Magnoliopsida (dicots), and Liliopsioda (monocots) in plants.
ORDER
An [ANSWER] is a major subdivision of an organism's class. It is just another way to break down the class of plants and animals. Some [ANSWER] include carnivores, primates, rodents for animals and fagales, and pinales (pines) for plants.
FAMILY
The next level in the classification of living organisms is categorized much like the group of people that we call [answer]. We are all different, but we share enough similarities that we belong in the same [answer]; the same applies to all living things.
GENUS
The [answer] is the first part of a living thing’s scientific name, also known as binomial nomenclature. Let’s look at lions and tigers, for example, the scientific name for a lion is Panthera leo, and the tiger is Panthera tigris; Panthera is the [answer].
SPECIES
The [answer] is the final and most specific level of the classification system. The best way to describe a [answer] is a group of organisms that are best suited for breeding healthy offspring, which can also continue to reproduce.
Examples of Linnaean Taxonomic Classification

Examples of Linnaean Taxonomic Classification

PHYLOGENY
the evolutionary history of lineages
is to group species into larger categories that reflect lines of evolutionary descent, rather than overall similarities and differences.
Phylogenetic Tree
A scientific diagram that biologists use to represent the phylogeny (evolutionary history of a species) of organisms.
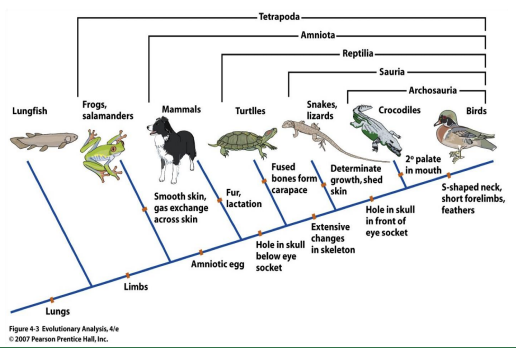
CLADE
a group of species that includes a single common ancestor and all descendants of that ancestor – living and extinct
CLADOGRAM
a diagram that shows clades and how they are linked by shared traits
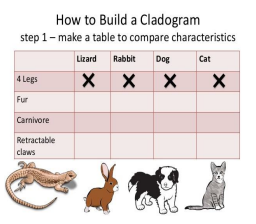
CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS
It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships.
“Dichotomous
means divided into two parts
Dichotomous Key
A method of identification whereby groups of organisms are divided into two categories repeatedly based on their characteristics
Typically, a [answer] for identifying a particular type of object consists of a specific series of questions. When one question is answered, the key directs the user as to what question to ask next
[answer] always give two distinct choices in each step, often they are opposites. Black/white; good/evil; pointed/rounded