Atomic Models: Contributions from Democritus to Bohr
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Democritus
Initial view of the atom (atomos): Indivisible, indestructible particles. Solid, homogenous, and had different sides.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
All elements are made up of atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same mass and properties. Atoms of different elements have different masses and properties. Atoms combine in simple ratios to make compounds. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or divided in chemical reactions.
Dalton's Model of the Atom
Solid, spherical particle.
J.J. Thomson
Particle found by J.J. Thomson: Electron.
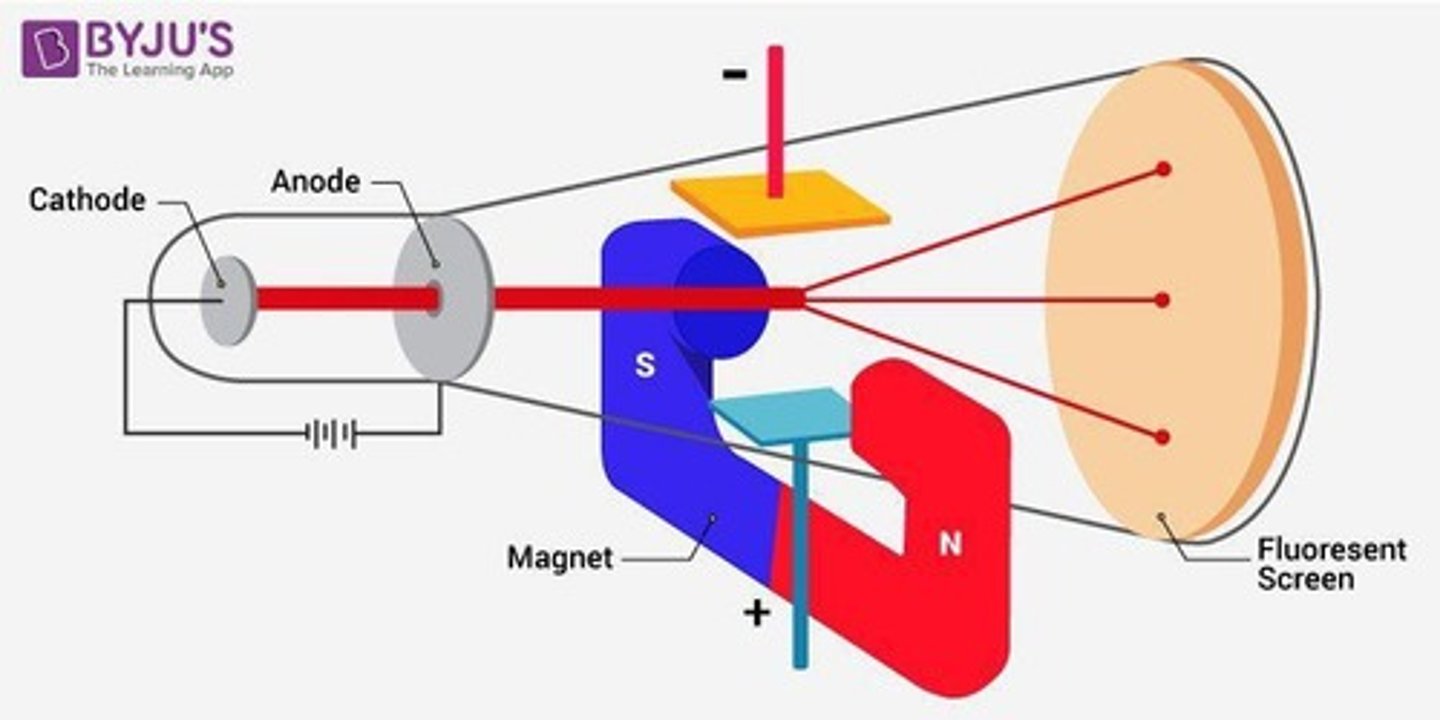
Thomson's Experiment
Used cathode ray tubes. He saw that cathode rays got deflected by electric/magnetic fields, which showed that there are negatively charged particles smaller than atoms.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
He focused a beam of positively charged alpha particles (two protons and two neutrons) at a thin sheet of gold foil.
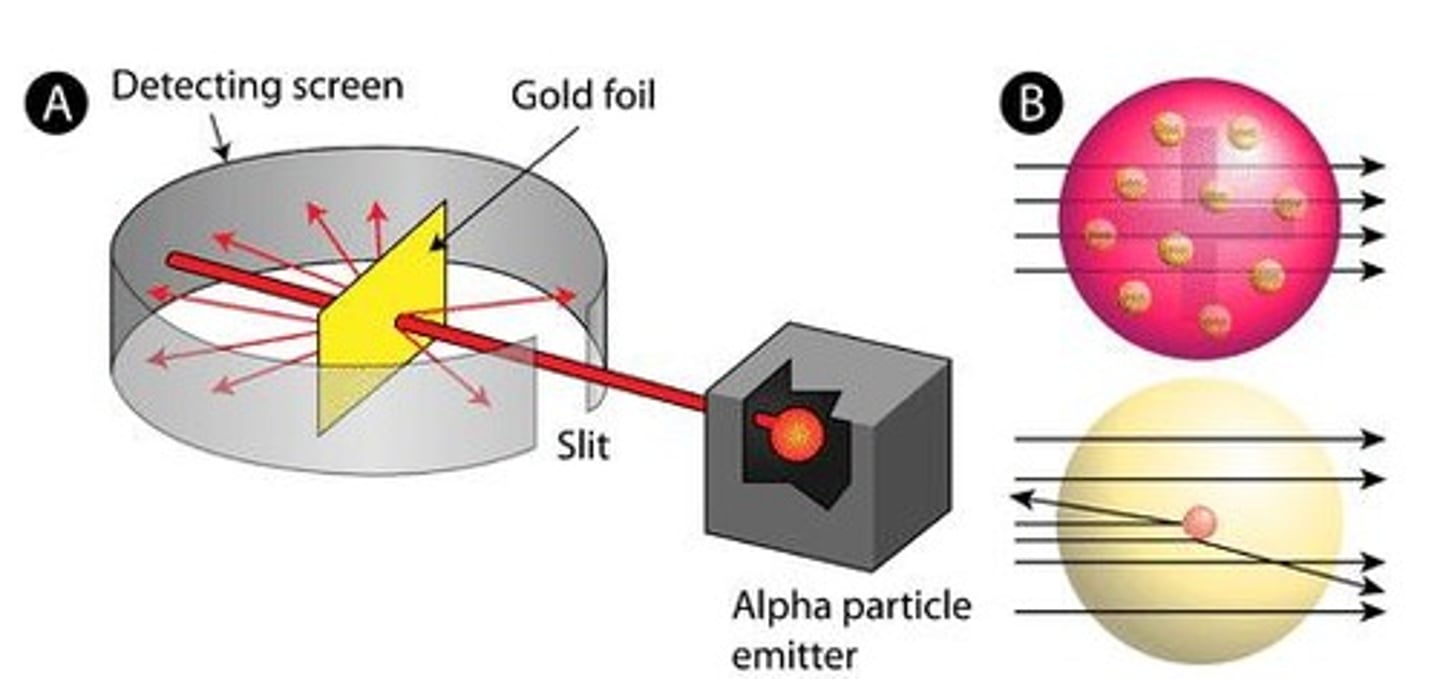
Rutherford's Development
The Atom has a small, dense, positive nucleus at its center, which is orbited by electrons. The atom is mostly space.
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment
He suspended tiny charged oil drops between 2 metal plates and then measured electric fields to find the charge of 1 electron.
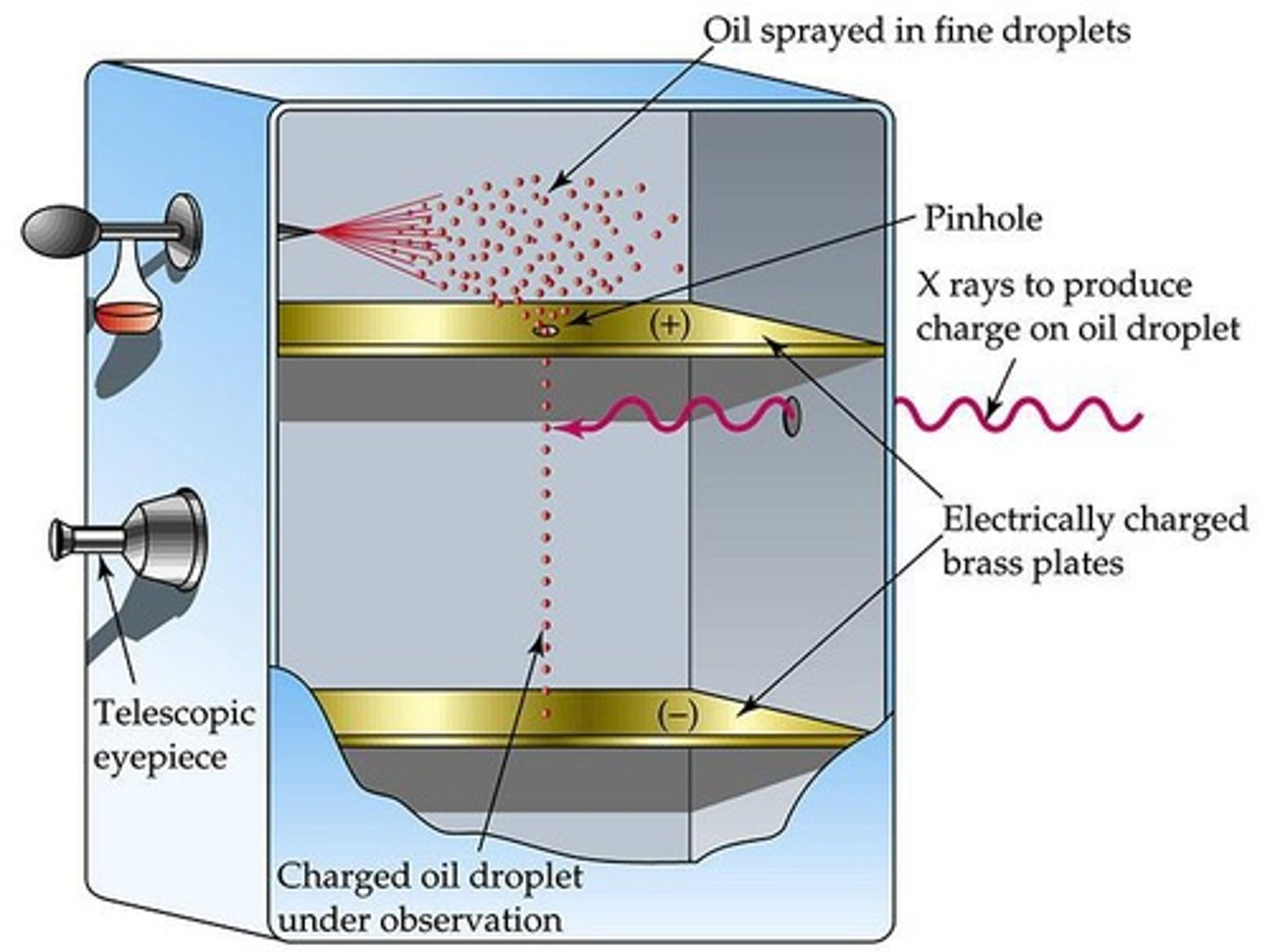
Millikan's Development
Found the specific charge of an electron (1.602 × 10-19 coulombs).
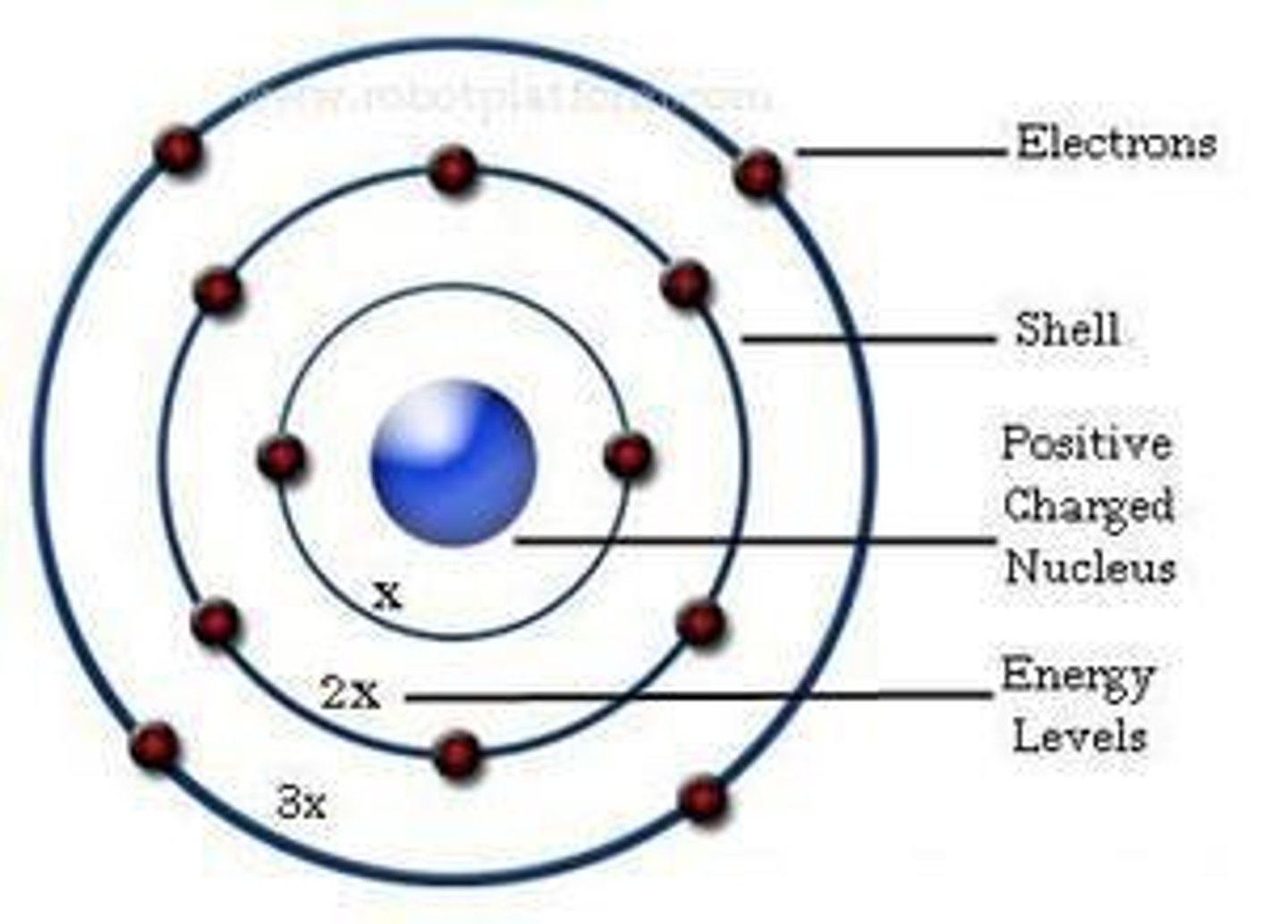
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Electrons can orbit the nucleus in shells, can jump between shells, and release specific amounts of energy (quanta). Rutherford's model didn't think about this.
Protons
Charge: +1 (positive). Location: Nucleus. Mass: abt 1 atomic mass unit (amu). Importance: Determines atomic # and what the element is.
Electrons
Charge: -1 (negative). Location: orbiting the nucleus in shells. Mass: abt 1/1836 amu, very small compared to protons and neutrons. Importance: chemical properties and reactivity of atom, driving force of chemical bonds.
Neutrons
Charge: 0. Location: Nucleus. Mass: abt 1 amu. Importance: Contributes to atomic mass and stabilizes nucleus by preventing repelling of protons.
Atomic Number
Gives # of protons, which also defines an element.
Isotope
The same element with a different number of neutrons, which causes a different atomic mass.
Relative Atomic Mass
The mass of a single isotope compared to the mass of a carbon-12 atom (12 amu). Relative atomic mass is normally close to the atomic mass (protons + neutrons).
Average Atomic Mass
The average between all the isotopes (naturally occurring) of a certain element. Calculation: (Mass of Isotope 1 × % Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 × % Abundance of Isotope 2) + ... (where % abundance is expressed as a decimal).
Hydrogen
Symbol: H, Atomic Number: 1, Mass Number: 1, Atomic Mass: 1.008.
Helium
Symbol: He, Atomic Number: 2, Mass Number: 4, Atomic Mass: 4.003.
Lithium
Symbol: Li, Atomic Number: 3, Mass Number: 7, Atomic Mass: 6.941.
Beryllium
Symbol: Be, Atomic Number: 4, Mass Number: 9, Atomic Mass: 9.012.
Boron
Symbol: B, Atomic Number: 5, Mass Number: 11, Atomic Mass: 10.81.
Carbon
Symbol: C, Atomic Number: 6, Mass Number: 12, Atomic Mass: 12.011.
Nitrogen
Symbol: N, Atomic Number: 7, Mass Number: 14, Atomic Mass: 14.007.
Oxygen
Symbol: O, Atomic Number: 8, Mass Number: 16, Atomic Mass: 15.999.
Fluorine
Symbol: F, Atomic Number: 9, Mass Number: 19, Atomic Mass: 18.998.
Neon
Symbol: Ne, Atomic Number: 10, Mass Number: 20, Atomic Mass: 20.180.
Sodium
Symbol: Na, Atomic Number: 11, Mass Number: 23, Atomic Mass: 22.990.
Magnesium
Symbol: Mg, Atomic Number: 12, Mass Number: 24, Atomic Mass: 24.305.
Aluminum
Symbol: Al, Atomic Number: 13, Mass Number: 27, Atomic Mass: 26.982.
Silicon
Symbol: Si, Atomic Number: 14, Mass Number: 28, Atomic Mass: 28.085.
Phosphorus
Symbol: P, Atomic Number: 15, Mass Number: 31, Atomic Mass: 30.974.
Sulfur
Symbol: S, Atomic Number: 16, Mass Number: 32, Atomic Mass: 32.06.
Chlorine
Symbol: Cl, Atomic Number: 17, Mass Number: 35, Atomic Mass: 35.45.
Argon
Symbol: Ar, Atomic Number: 18, Mass Number: 40, Atomic Mass: 39.488.
Potassium
Symbol: K, Atomic Number: 19, Mass Number: 39, Atomic Mass: 39.098.
Calcium
Symbol: Ca, Atomic Number: 20, Mass Number: 40, Atomic Mass: 40.078.