Macroeconomics Unit II: Circular Flow Diagram, GDP, Business Cycle
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Macroeconomics
branch of econ dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision making of an economy as a WHOLE
What is using interest rates, taxes, and govt. spending to regulate an economy’s growth and stability an example of?
Macroeconomics
t/f regional, national, AND global economies are included in macroeconomics
true
Circular flow diagram
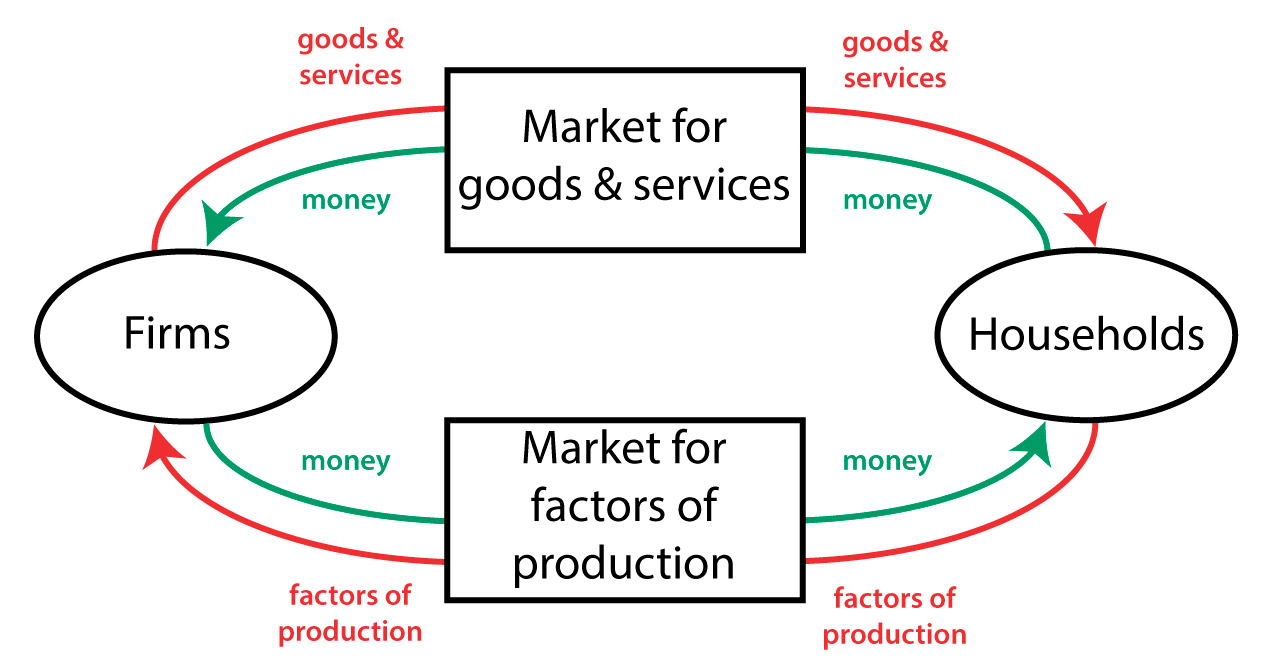
What are the two most important actors in the Circular Flow Model?
Households (buy products) and firms (create products)
what is the most basic model of how a large economy works?
the circular flow diagram
Macroeconomic indicators
measurements economists use to measure the health of a nation’s economy (ex. GDP)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country during one year
What is GDP considered a measure of?
“National income”
What does higher GDP typically mean?
Typically means the economy is doing well, but too high can mean inflation
What does a declining GDP mean?
Typically means the nation is in a recession and there are high unemployment rates (economy is at an inefficient point)
How is GDP Calculated?
Calculated by adding up the value of all FINAL products produced in ONE YEAR
expenditures approach to GDP (one of the methods/equations to calculate GDP)
Y = C + I + G + (X-M)
C = consumer spending (excluding spending on new housing)
I = Investments (the spending businesses do to produce goods/services)
G = Govt. spending (doesn’t include transfer payments)
X = Exports
M = Imports
Transfer Payments
A payment from govt. to household that is not in exchange for a product (ex: stimulus check)
not included in GDP
Net exports
(X-M)
Trade deficit
when imports are higher than exports
Trade surplus
when exports are higher than imports
Income approach to GDP (one of the methods of calculating GDP)
Involves adding up all of the income earned within the borders of a country in a given year; adds up wages, rents, interests, and profits
Income Approach to GDP formula
National Income = wages + rent + interest + profit
Value-added approach to GDP (one of the methods of calculating GDP)
involves adding up all of the value added at various stages of production
What IS included in GDP?
Consumer spending
All capital equipment bought by a firm (investment)
Exports - goods SOLD TO foreigners
What is NOT included in GDP?
Intermediate goods and services/input resources
Used goods
Financial assets (stocks, bonds, etc.)
Govt. transfers
Goods made (but not sold) before the year measured
Imports - goods BOUGHT FROM foreigners
These contribute to the other country’s GDP
Employed
includes those who worked as paid employees, own their own business, or worked as unpaid workers in a family member’s business (both full-time and part-time)
Unemployed
includes those who were not employed, unavailable to work, waiting to be recalled to a job they have been laid off from, and has tried to find employment in the previous four weeks
Not in the labor force
anyone who is 16 or under, uninstitutionalized, and does not fit in the first two categories
Uninstitutionalized means not official work (like getting paid to mow your neighbor’s lawn)
What is a Starbucks part-time employee?
Employed
What is a home-maker?
Not in the labor force because they are not actively looking for employment
What is someone who just got out of college and is now looking for work?
Unemployed
What is a retiree?
Not in the labor force
Labor Force Equation
Employed + Unemployed
Unemployment Rate Equation
(Unemployed/Labor Force) x 100%
Labor Force Participation Rate Equation
[(Employed + Unemployed)/adult population] x 100%
OR: (Labor force/adult population) x 100%
Limits of UR as a Macroeconomic Indicator
discouraged workers are considered not in the labor force —> not counted in UR
Someone who is not working to their skill level is considered employed —> not counted in UR
Someone who is working part-time but wants to work full time is considered employed —> not counted in UR
Discouraged workers
individuals who are not working, but want a job, but gave up; considered not in the labor force
Frictional Unemployement
unemployment from people entering or reentering the labor force
due to job search
the govt. should NOT try to eliminate thise
structural unemployment
unemployment due to changes in structure (ex. technology, wage)
cyclical unemployment
due to downturns/economic contractions in the business cycle
What unemployment is it when someone goes from being not in the labor force to being unemployed?
frictional
what type of unemployment is caused by minimum wage, union wage (workers threatening strike for higher wages), or efficiency wage above wage equilibrium?
structural
What type of unemployment is indicated by RGDP declining?
cyclical
What does unemployment insurance do to unemployment?
Increases FRICTIONAL unemployment
What is the main form of unemployment?
Structural Unemployment
on the test if you don’t know the type of unemployment, its most likely to be structural
What type of unemployment does the govt. try to combat?
cyclical
What type of unemployment was high after the Great Depression?
cyclical
Natural Rate of Unemployment
an estimated number when no cyclical unemployment
The goal - used by policy makers as a guide for where to move the economy
What is the Natural Rate of Unemployment also called?
“Full Employment”
Equation for the NRU
NRU = Structural Unemployment Rate + Frictional Unemployment Rate
T/F the government’s goal is to get the Natural Rate of Unemployment to 0%
F; it can never (and should never) be 0%
Purchasing power
how much you can buy with one unit of currency
Inflation
the rise in the GENERAL PRICE LEVEL in the economy
NOT for a specific good or service
What does inflation do to the purchasing power of the dollar?
reduces; you can’t buy as much with each unit of currency as before
Inflation rate (IR)
the percent change in the general price level from the year before
Deflation
When the IR is NEGATIVE
What does deflation do to the purchasing power of the dollar?
increases; you can buy more with each unit of currency as the year before
T/F the IR is a YEARLY measure
True
Disinflation
Prices are still rising, but not as fast as the rate they were before
Hyperinflation
super high rates of inflation
What is hyperinflation caused by?
Printing too much money —> demand increases —> prices hyperinflate
What effect does hyperinflation have on the economy?
It erodes people’s savings severely —> people lose faith in economy
Nominal value
any value stated in current dollars — does NOT take into account changes in general price level
Real Value
a value adjusted to take account changes in the general price level/purchasing power of the dollar
What is the Business Cycle driven by?
Demand
How can inflation/deflation/disinflation be seen on the Business Cycle Model?
Business cycle in Contractions (below potential RGDP) means disinflation or deflation
Business cycle in Peaks (above potential RGDP) means inflation
What are the three costs of inflation?
Shoe leather costs
Menu Costs
Unit of Account costs
Shoe Leather Costs
people make more transactions to avoid holding cash due to inflation
associated with very high rates of inflation
Menu Costs
the cost of changing prices sustained by a firm due to inflation
Unit of Account Costs
Money becomes a less reliable unit of measurement
What are some important Price Indexes?
CPI
PPI
Aggregate Price Level
The general price level in the economy
can be used to calculate the inflation rate
Price Index
a tool used to track aggregate Price Level and Inflation
measures the prices of a given market basket of goods in a given year
the value is normalized so that it is equal to 100 in the selected base year
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The most important Price index
What does CPI let us calculate and what are the equations?
inflation rate = [(second CPI - first CPI)/first CPI] x 100
Real Average Wage = (Nominal wage in a year/CPI in a year) x 100
Real GDP = (GDP of a year/CPI of the same year) x 100%
“Market Basket”
a hypothetical set of goods and services purchased by a consumer
used to create a price index to measure changes in aggregate price level
What takes up most of the CPI in America and why?
Housing — b/c it is a necessity and takes up a lot of the avg. consumer’s income
Producer Price Index (PPI)
a price index that contains the prices of goods and services produced by producers
contains mostly raw materials
Does CPI or PPI respond quicker to inflationary pressure?
PPI; can be used as an early warning sign for upcoming inflation
GDP Deflator
for a given year, is 100 times the ratio of nominal GDP to Real GDP in that year
Equation for GDP Deflator
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP) x 100
What does it mean if GDP Deflator is over or under 100?
Over —> there has been inflation since base year
Under —> there has been deflation since the base year
Limits of using a price index
substitution — people may substitute goods over the years (goods that are in a consumer’s market basket today would not be in the market basket in the past)
introduction of new goods — new goods created would not have been part of the market basket in the past
Unmeasured quality changes — goods in the market may have increased/decreased in quality over the years, but that’s not reflected in the index
What is the relationship between inflation and lending?
Borrowers prefer inflation
Lenders prefer deflation
Real Interest Rate Formula
Real r = Nominal r - inflation rate
r = interest rate
Underemployment
when a worker is working less than full-time, or not up to their skill level
What is the relationship between CPI and Inflation?
CPI measures inflation; a higher CPI typically means inflation b/c consumer prices are rising and a lower CPI typically means the opposite
Potential Output
the level of RGDP associated with reaching unemployment